Description of the drug
The main active ingredient is meldonium. Produced in Latvia, Poland, Lithuania and Slovakia.
Presented in pharmacy chains in two forms:
- A transparent solution for injection, 1 ml of which contains 100 mg of the main substance.
- Gelatin capsules with 250 or 500 mg of meldonium dihydrate. Contents: white powder with a slight odor and sweetish taste.
The solution is sold in ampoules of 5 ml, a cardboard box contains 10 ampoules and instructions for use.
Meldonium is a synthetic drug with an effect similar to the precursor substance hydroxytrimethylaminobutyric acid, related to B vitamins.
The substance is able to improve metabolic processes and provide cells with energy.
Meldonium:
- Increases performance.
- Reduces the manifestations of mental, physical and mental stress.
- Increases the strength of heart contractions.
- Reduces the frequency of angina attacks.
- Increases the body's endurance during physical activity.
The medicine should be stored in a dry place at temperatures up to 25°C for no more than 4 years.
We tell you what chronic fatigue syndrome is and how to get rid of it
Constant weakness and drowsiness, problems with attentiveness, bad mood—is this a familiar situation? Of course, such a broken state can occur after a hard week of work. But if the weekend comes and you still can’t recover, this problem needs to be solved - it won’t go away on its own.
Together with the manufacturer Grindeks and the product Mildronate ® 250, we will understand what asthenia is, or, as it is also called, chronic fatigue, and whether it is possible to get rid of it.
What is asthenia?
Asthenia is not a disease in the usual sense, but a condition that says that something is wrong with the body. It is accompanied by constant fatigue, loss of strength, loss of attentiveness and concentration. A person with asthenia becomes irritable and lethargic, and stops getting enough sleep.
Sometimes the manifestations of asthenia are similar to the onset of the flu - the temperature may rise, photophobia and sensitivity to sharp sounds may occur, and appetite may decrease. But unlike a viral infection, symptoms last longer, and bed rest does not help recovery.
With asthenia, a person cannot recover from exercise, loses concentration and is often irritated.
Asthenia or fatigue: how to distinguish
Often the body is able to recover from stress and fatigue within a few days. For example, if a person has had a hard week at work, it is enough to get enough sleep over the weekend to be fresh and energetic on Monday.
But if stress and tension become faithful companions, then in two days the body simply does not have time to rest. Fatigue accumulates and as a result, even a week may not be enough to recover.
Asthenia, unlike overwork, is not a consequence of physical or mental stress and does not disappear after rest.
With asthenia, it is not enough to just sleep. As a result, the person becomes irritable and absent-minded
Causes of asthenia
- Irregular work schedule. For example, a person should work from 9 to 18, but in fact he arrives at work at 8 and leaves at 21, and sometimes even works on weekends.
- High load. Those at risk are those who combine a lot of things: work and study, raising children, gym, entertainment and self-development. In such a busy schedule, a person simply has no time to rest.
- Constant stress at work. For example, if a person goes to work as if he were going to war, and there are rush jobs or an angry boss waiting for him. All this affects the psychological state and leads to asthenia.
- No vacation. A person may feel that without him everything at work will be lost, so it is better to go on vacation only for a week and once a year. But the body will not be able to recover from a year’s stress in such a short time.
- Malnutrition. We need to find energy for life. But if, instead of a full lunch, we snack on chocolate and coffee, the body simply has nowhere to get strength.
Of course, if you live in a mode of constant work and stress for a week or even a month, you may not feel that anything is wrong with your body. But if fatigue accumulates and a person does not have the resources to recover, then burnout begins and asthenia appears.
Sometimes it occurs along with some disease. For example, a person has been poisoned by something, the body has devoted all its efforts to recovery, but there are not enough resources for recovery.
Unfortunately, people rarely turn to doctors at the first signs of asthenia. It seems that this is all banal fatigue or just laziness. But asthenia can and should be treated
I have asthenia. What to do about it?
Of course, you should not self-medicate. Only a specialist can find out what is happening to you. To determine whether you have asthenia, you need to go to the doctor and get tested.
To recover, you need to remove all the causes of asthenia - start eating right, resting more, doing things not related to work and family.
And in order to support the body, you can start taking vitamins or special medications, such as Mildronate ®250, which supports:
- Cardiovascular system. With stress and fatigue, the heart begins to work to the limit and a lack of oxygen occurs. Thanks to meldonium in the composition, Mildronate ®250 helps deliver oxygen to cells, reduces the risk of damage to the cell membranes of the heart and has a tonic effect
- Nervous system. Mildronate ®250 stimulates the central nervous system and increases motor activity and physical endurance.
Mildronate ®250 is suitable for those who:
- Leads an active lifestyle and wants to recover quickly after training.
- Works in an office and experiences stress or constant fatigue.
- People who want to find time for everything - from work to family and entertainment.
During physical and mental overload, Mildronate® quickly restores energy reserves and increases the body's resistance to stress.
Why take Mildronate?
The drug is used only in the treatment of adults. Regardless of the dosage form, the indications for prescribing Mildronate are:
- Heart diseases caused by impaired coronary circulation (in complex therapy).
- Chronic heart failure and cardialgia.
- Reduced performance.
- Pathologies of peripheral arteries.
- The recovery period after surgery to restore the body.
- Encephalopathy.
- Stroke.
- Bronchial asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
- II and III stages of alcoholism.
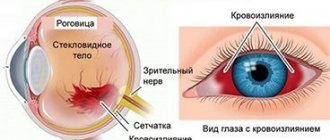
- Violations of the integrity of the vessels supplying blood to the tissues of the eye.
The use of Mildronate slows down the formation of necrotic areas and shortens the rehabilitation period after acute damage to cardiac muscle tissue.
During active training, meldonium restores the balance of oxygen in cells, prevents the accumulation of toxins, and helps restore energy reserves.
The drug is successfully used in sports in healthy people because:
- Increases adaptability to physical activity.
- Improves muscle nutrition, including the heart, and accelerates their recovery.
- Reduces fatigue.
- Increases the effect of sports.
Mildronate is not suitable for gaining muscle mass, but is used to prevent overwork.
Contraindications and side effects
It is prohibited to use Mildronate for:
- Individual intolerance to meldonium or any of the auxiliary components.
- Increased intracranial pressure, caused, among other things, by a tumor and impaired venous outflow.
Undesirable effects from taking the drug may appear in the form of:
- Allergic manifestations - itching, rashes, redness or swelling.
- Rapid heartbeat.
- Reactions from the digestive system - nausea, vomiting, heartburn, belching.
- Excessive stimulation of the nervous system.
In general, Mildronate is a low-toxic drug that does not cause life-threatening conditions. However, Mildronate is not used in pediatrics. Also, the drug is not prescribed during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Instructions for use of Mildronate
The solution is administered undiluted intravenously according to indications; the capsules are used orally as a whole without crushing.
Mildronate injections
Prescribed for progressive angina, vascular pathologies of the fundus, cerebral circulatory disorders, myocardial infarction. In case of a heart attack, it is administered once a day in a volume of 500-1000 mg. Further treatment is carried out with capsules.
For vascular pathologies of the fundus of the eye, the solution is administered behind the eyeball or under its outer shell, 0.5 ml for 10 days.
To persons with acute circulatory disorders in the brain, Mildronate is administered intravenously once a day at a dose of 500 mg. The duration of the course of treatment is 10 days. Then the patient is transferred to capsules at a dosage of 500-1000 mg per day in one or two doses.
Mildronate capsules
Prescribed to patients suffering from diseases of the cardiovascular system as additional therapy at a dose of 500-1000 mg. It can be taken once or divided into two doses. Duration of therapy is 4-6 weeks. You can repeat courses as prescribed by your doctor 2-3 times a year.
For cardialgia, take one tablet of Mildronate 500 mg once a day.
For pathologies of peripheral arteries, the medicine is taken twice a day, 500 mg.
Athletes and people experiencing increased intellectual and physical stress can take 1000 mg in two doses for 10-14 days. After 14-21 days the course can be repeated.
For persons suffering from chronic alcoholism, Mildronate is prescribed 500 mg four times a day for 7-10 days.
The maximum dose of the drug is 2000 mg. It is recommended to take before lunch due to its stimulating effect.
Mildronate solution for intravenous injection 100 mg/ml 5 ml ampoules No. 10
INSTRUCTIONS FOR MEDICAL ADMINISTRATION
1. NAME OF THE MEDICINE
Trade name: MILDRONATE solution for injection 0.5 g/5 ml International nonproprietary name: Meldonium (.Meldonium)
2. GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS Description
Colorless transparent liquid.
3. COMPOSITION OF THE MEDICINE
1 ampoule (5 ml) contains 0.5 g of meldonium. Excipient: water for injection.
4. FORM OF RELEASE
Injection.
5. MEDICINE CLASSIFICATION CODE
Other drugs for the treatment of heart disease. ATX code: C01EB
6. PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES Pharmacodynamics
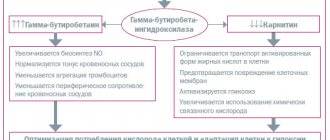
Meldonium is a precursor to carnitine, a structural analogue of gamma butyrobetaine (GBB), in which one carbon atom is replaced by a nitrogen atom. Meldonium, by reversibly inhibiting gamma butyrobetaine hydroxylase, reduces the biosynthesis of carnitine and prevents the transport of long-chain fatty acids through cell membranes, thus preventing the accumulation of strong detergents in cells - activated forms of non-oxidized fatty acids, preventing damage to cell membranes. When the concentration of carnitine decreases under ischemic conditions, β-oxidation of fatty acids is delayed and oxygen consumption in cells is optimized, glucose oxidation is stimulated and ATP transport from sites of biosynthesis (mitochondria) to sites of consumption (cytosol) is resumed. Essentially, the cells are supplied with nutrients and oxygen, and the use of these substances is optimized. In turn, with an increase in the biosynthesis of the carnitine precursor, i.e. GBB, NO synthetase is activated, resulting in improved rheological properties of the blood and a decrease in peripheral vascular resistance. When the concentration of meldonium decreases, the biosynthesis of carnitine increases again and the amount of fatty acids in the cells increases. It is believed that due to the effectiveness of meldonium, the tolerance of cellular load increases (with a change in the amount of fatty acids). Effect on the heart and circulatory system
In animal studies, it was found that meldium is positive for the contractile activity of the myocardium, it has a protective effect (including in relation to alcohol and catecholamines), it helps to disrupt the heart rhythm, and reduces the area of myocardial infarction. Coronary heart disease (stable angina pectoris) Analysis of clinical data from the course of use of meldonium in the treatment of stable angina pectoris in combination with other antianginal drugs showed that the drug reduces the frequency and intensity of angina attacks, as well as the amount of glyceryl trinitrate used. The drug has an antiarrhythmic effect in patients with coronary heart disease (CAD) and with ventricular extrasystoles; a lesser effect is observed in patients with supraventricular extrasystoles. The drug has the ability to reduce oxygen consumption at rest, which is considered an effective criterion for antianginal therapy of CAD. Meldonium has a beneficial effect on atherosclerotic processes in the coronary and peripheral vessels, reducing total serum cholesterol levels and the atherogenic index. Chronic Heart Failure Clinical studies have examined the role of meldonium in the treatment of chronic heart failure due to coronary artery disease and have noted its ability to increase exercise tolerance and work output in patients with heart failure. The effectiveness of meldonium in the case of heart failure 1-111 NYHA functional class has been tested. It has been established that the use of meldonium in combination with other traditional drugs for the treatment of heart failure improves myocardial inotropic function and increases exercise tolerance, improves the quality of life of patients without causing severe side effects. However, it has been noted that meldonium may cause slight hypotension. Effect on the central nervous system In animal experiments, meldonium has been shown to have an antihypoxic effect and an effect on cerebral circulation. The drug optimizes the redistribution of cerebral circulation volume in favor of ischemic foci and increases the strength of neurons under hypoxic conditions. The drug has a stimulating effect on the central nervous system: it increases motor activity and physical endurance, stimulates behavioral reactions, and also {_) exhibits an anti-stress effect (stimulation of the sympathoadrenal system, accumulation of catecholamines in the brain and adrenal glands, protection against changes in internal organs caused by stress) . Efficacy in neurological diseases The effect of meldonium on the rehabilitation process in patients with neurological disorders (after diseases of the blood vessels of the brain, brain surgery, trauma, tick-borne encephalitis) has been studied. The results of testing the therapeutic activity of meldonium indicate its dose-dependent positive effect on physical endurance and restoration of functional independence during the recovery period. When analyzing changes in individual and total intellectual functions after using the drug, a positive effect on the recovery process of intellectual functions during the recovery period was established. It has been established that meldonium improves the convalescent quality of life (mainly due to the renewal of the physical function of the body), and the drug eliminates mental disorders. ^tshshas^
Meldonium is characterized by a positive effect on the regression of the funcodal system and reduces disorders in patients with neurological deficits.
recovery. The general neurological condition of patients improves (reduction of damage to brain nerves and pathology of reflexes, regression of paresis, improvement of coordination of movements and autonomic functions). Pharmacokinetics Pharmacokinetic studies were conducted in healthy volunteers using a single dose of 25, 50, 100, 200, 400, 800 or 1500 mg of meldonium. It has been established that the maximum concentration of meldonium in blood plasma (Cmax) and the area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) increase in proportion to the dose applied. The time to reach maximum concentration (Tmax) was 1-2 hours and the half-life of elimination (t/z) was 4 hours. Excretion of the drug in urine increases with doses up to 400 mg; When using doses greater than 400 mg, excretion remains virtually unchanged. The pharmacokinetics of meldonium is affected by the presence of food in the stomach, i.e. food delays the absorption of meldonium after a single dose of 400 mg. With repeated use of meldonium at a dose of 400-800 mg per day (twice a day for 7 days or once a day for eight days), the equilibrium concentration of the drug in plasma is achieved 72-96 hours after the first dose. Metabolism studies in experimental animals have shown that meldonium is metabolized primarily in the liver. 7. INDICATIONS FOR USE Mildronate is used as part of combination therapy in the following cases: - cardiovascular diseases: stable angina pectoris, chronic heart failure (NYHA IIII functional class), cardiomyopathy, functional disorders of the cardiovascular system; - acute and chronic cerebrovascular accidents; - reduced performance, physical and psycho-emotional overload; - recovery period after cerebrovascular accidents, head injuries and encephalitis. 8. METHOD OF APPLICATION AND DOSAGE Method of application: intravenous injection. Adults are prescribed 0.5-1.0 g per day, using the entire dose at once or dividing it by 2 times. The maximum daily dose is 1.0 g. Due to the possible development of an stimulating effect, it is recommended to use it in the first half of the day. There are no special recommendations for use in elderly patients. For elderly patients with impaired liver and/or kidney function, lower doses are required. Patients with impaired liver and/or kidney function require lower doses. Use in children is contraindicated due to the lack of data on effectiveness and safety. The duration of treatment is 4-6 weeks. If you miss another dose of the drug, take it immediately. Do not take a double dose to replace a missed dose. Continue taking as recommended by your doctor.
9. SIDE EFFECTS
In the following, the listed side effects are classified according to organ system groups; when indicating the frequency of occurrence, the following classification is used: very often (>1/10), often (>1/100, <1/10), less often (>1/1000, <1/100), rarely (>1/10,000 , <1/1000), very rare (<1/10,000), including isolated cases. Blood and lymphatic system disorders Eosinophilia*. Immune system disorders Common: allergic reactions. Cardiac disorders In some cases: tachycardia. Disorders of the circulatory system In some cases: low blood pressure. Nervous system disorders Common: headache, agitation*. General disorders General weakness*. * Insufficient number of observations to determine frequency of occurrence. If the listed adverse reactions occur, as well as if an adverse reaction not mentioned in the instructions occurs, you should consult a doctor.
10. CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Hypersensitivity to meldonium. — Renal and liver failure (there is insufficient data on the safety of use). — Pregnancy, lactation period. — Children under 18 years of age. I. OVERDOSE No cases of overdose with mildronate have been reported. The drug is low-toxic and does not cause threatening side effects. Symptoms: in case of low blood pressure, headaches, dizziness, tachycardia, and general weakness are possible. Treatment is symptomatic. In case of severe overdose, it is necessary to monitor liver and kidney functions. 12. PRECAUTIONS Patients with a history of chronic liver and kidney diseases should be careful when using the drug (monitoring liver and kidney function). Pregnancy and breastfeeding To determine the effect of meldonium on pregnancy, embryo/fetal development, childbirth and postpartum development, animal studies are not sufficient. The potential risk to humans is unknown, so this drug should not be used during pregnancy. It is not known whether the drug is excreted into mother's milk. If necessary, breastfeeding should be stopped.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and maintain moving machinery. A study of the effect on the ability to drive vehicles and maintain moving machinery has not been conducted. Many years of experience in the treatment of acute myocardial infarction and unstable angina in cardiology departments show that mildronate is not a first-line drug for acute coronary syndrome.
13. INTERACTION WITH OTHER MEDICINES
Mildronate can be used in conjunction with long-acting nitrates and other antianginal agents (stable exercise angina), cardiac glycosides and diuretics (heart failure). Mildronate can also be combined with anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents, antiarrhythmic drugs and other drugs that improve microcirculation. It must be borne in mind that mildronate may enhance the effect of glyceryl trinitrate, nifedipine, beta blockers, other antihypertensive drugs and peripheral vasodilators.
14. CONDITIONS AND STORAGE DURATION
Store at a temperature no higher than 25 C. Do not freeze! Keep out of the reach of children. Shelf life - 4 years. Do not use after the expiration date stated on the package.
15. HOLIDAY CONDITIONS
On prescription.
16. PACKAGING
5 ml in a clear glass ampoule with a line or break point. 5 ampoules in a cell package made of polyvinyl chloride film. 2 cell packs with instructions for use in a cardboard pack.
17. INFORMATION ABOUT THE MANUFACTURER (APPLICANT) Registration Certificate Holder
JSC Grindeks. St. Krustpils, 53, Riga, LV-1057, Latvia Phone: +371 67083205 Fax: +371 67083505 Email Manufacturer(s) HBM Pharma s.r.o. St. Sklabinska 30, Martin 036 80, Slovakia Date of text correction: March 2013