Normal indicators and their deviations
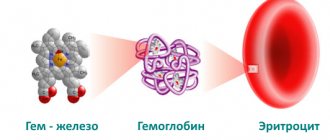
Hemoglobin is a protein whose purpose is to transport oxygen into cells from the lungs and carbon dioxide back into the lungs. Iron molecules in hemoglobin help maintain the functioning of red blood cells. When abnormal abnormalities occur in the body, hemoglobin will increase to deliver more oxygen to the cells.
Protein levels will vary between men and women, and the figure will also depend on the person's age. A slight deviation from the indicators does not mean that pathological disorders are present in the body.
A deviation of 20 units or more is considered a high hemoglobin level.
There is also the so-called glycated hemoglobin - this is an indicator that allows you to diagnose diabetes mellitus at any stage of the disease. This type of protein is present in the blood of healthy people, but in patients with diabetes its norm is significantly exceeded. If the protein levels are slightly elevated, it makes sense to retake the analysis and then compare the results.
Deterioration of blood circulation in the vessels of the brain in most cases is associated with the deposition of cholesterol plaques on their walls. Over time, pathology leads to strokes and heart attacks; timely cleaning, which is also carried out using traditional medicine, helps to significantly reduce the risk of their development. Read more in the article: “Cleansing blood vessels with folk remedies at home.”
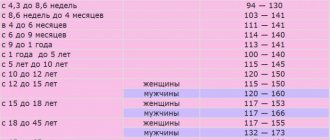
Table of hemoglobin norms in blood (in g/l):
| Age category (years) | Women | Men |
| 12-15 | 115-150 | 120-160 |
| 15-18 | 117-153 | 117-166 |
| 18-45 | 117-155 | 132-173 |
| 45-65 | 117-160 | 131-172 |
| Over 65 | 117-161 | 126-174 |
With a high concentration of iron-containing protein in the blood, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) decreases, which indicates disturbances in the body.
With an excessive and constant increase in iron-containing protein in the blood, the number of red blood cells in the body also begins to increase - this leads to thickening of the blood, which can cause serious complications: thrombosis, heart attack, pulmonary thromboembolism, stroke, etc. Such consequences appear due to a sharp increase in the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin, which can occur due to temporary changes or due to dangerous pathologies developing in the body.
Blood test for hemoglobin at MedArt
The laboratory of the MedArt medical center is equipped with an automatic hematology analyzer DxH 500 Beckman Coulter, manufactured in the USA. This equipment is characterized by increased accuracy when conducting research. The medical staff of our center is highly qualified and well prepared for their work. The result of a general blood test will be 100% reliable and will not raise any doubts in you.
With us, you can take a general (clinical) blood test without spending a lot of time and effort on getting a referral, and then finding out the test results. We guarantee fast and high-quality hematological diagnostics. You can get results within a day, and in emergency situations, according to indications, within 1 hour.
A comfortable and calm environment will help you relax, in this case the test results will not be distorted due to stress or nervousness.
Reasons for increasing protein
An increase in hemoglobin levels can be caused by two main reasons:
- exposure to external factors and lifestyle;
- pathological deviations.
Lifestyle
In the first case, the metabolism in the body is not disturbed, the number of red blood cells does not increase, but for some reason the body needs oxygen more, so the hemoglobin level automatically increases. This situation is temporary, and the body will return to normal as soon as the cause of the lack of oxygen is eliminated. This group of temporary factors that contribute to an increase in hemoglobin includes:
- living in mountainous areas: for people living in high mountainous areas, high hemoglobin in the blood is the norm;
- features of the profession: climbers and pilots (lack of oxygen in the blood is a consequence of high altitude), bodybuilders (taking anabolic steroids and steroids and excessive physical activity cause oxygen starvation);
- excessive nicotine consumption: smoking increases blood viscosity, increasing iron levels in the blood;
- non-compliance with the drinking regime: if the body lacks fluid, the amount of protein in the blood automatically increases;
- unhealthy diet: predominance of protein foods in the diet.
Pathological deviations
The second group of reasons causing an increase in protein includes pathological disorders in the body. With such disorders, the body's metabolism is disrupted and red blood cells are reduced. To compensate for the lack of red blood cells, the body begins to increase the production of hemoglobin. The pathological group includes:
- kidney dysfunction;
- hormonal disorders;
- pulmonary fibrosis;
- congenital heart defects;
- intestinal obstruction;
- diabetes;
- cancer;
- vascular and heart diseases;
- poisoning;
- liver pathologies;
- stress;
- dehydration;
- pernicious or hemolytic anemia;
- bone marrow dysfunction;
- hereditary hemoglobinemia.
Hemoglobin levels may increase in response to an increase in platelets in the blood. The number of these blood cells increases with serious disturbances in the functioning of the body and a number of dangerous diseases.
Advertising:
The general causes of increased protein are the same for all sexes and ages, but some factors in the development of the disorder are unique to certain categories of patients.
Many diseases and pathological changes in various organs occur with acute pain syndrome. To combat such symptoms, special anti-inflammatory drugs classified as non-steroidal drugs (NSAIDs) have been developed. Read more in the article: “new generation NSAIDs.”
Among women
Previously, it was believed that women did not face the problem of high hemoglobin levels. But doctors have refuted this opinion and found that an increase in iron-containing protein in women is most often caused by:
- pneumonia;
- infectious infections;
- asthma;
- malignant neoplasms;
- mental and emotional overload.
Sometimes an increase in hemoglobin-containing proteins is associated with a woman’s lifestyle or is a consequence of taking certain medications.
During pregnancy, increased hemoglobin in women, the causes and consequences of which are unpredictable, is considered a dangerous condition. With this disorder, pregnant women may experience disturbances in the functioning of the liver or kidneys, and may cause developmental abnormalities in the unborn child. In this case, doctors recommend that the pregnant woman follow a certain diet and take a course of vitamins to maintain normal hemoglobin levels.
In men
The stronger sex is more often susceptible to excess iron-containing protein in the blood. This is due to the fact that men are more prone to bad habits, and they often eat unhealthy “cholesterol” foods. Also, men are more often diagnosed with heart and vascular diseases, which contribute to an increase in hemoglobin levels in the blood.
Among men, more often there are representatives of professions in which disorders are associated with the implementation of their activities: miners, pilots, submariners, climbers, bodybuilders. In order to avoid the development of the disorder, doctors recommend that the stronger sex adhere to a healthy lifestyle.
In children
During intrauterine development, the fetus cannot breathe through the lungs on its own, but takes in air from the mother’s blood. The pregnant woman and the baby may not have enough oxygen between them, which is why the fetus's body begins to adapt to low oxygen levels by increasing protein levels.
In a newborn, according to recent studies, intrauterine hypoxia with placental insufficiency is often the cause of high hemoglobin. Over time, with the development and growth of the baby, the situation stabilizes, and by the age of two, the protein concentration returns to normal. If this does not happen, then the baby may have serious health problems: heart defects, blood diseases, neoplasms.
In adolescence, the reasons for elevated protein levels are the same as in adults. But more often in adolescents, the pathological condition is caused by pulmonary fibrosis, dehydration, intestinal obstruction, and blood diseases. Parents of boys involved in sports should pay attention to the use of anabolic steroids by teenagers, which increase the level of transport protein in the blood.
Advertising:
Preparing for analysis
Hemoglobin testing is included in a general (clinical) blood test, for which blood is taken either from a vein or from a finger. Moreover, in children, the preferred option is to collect capillary blood. Next, the material is loaded into the analyzer to count the number of cells and evaluate the characteristics of red blood cells, leukocytes (including drawing up a leukocyte plan) and platelets. Of course, manual counting is considered the most accurate method of research, but since this process is very long and labor-intensive, it is now practically not used, only in cases where maximum accuracy of analysis is required.
Preparing for a general analysis involves standard steps to prevent distortion of the results:
- The test must be taken in the morning and on an empty stomach; the last meal should be light and not large, at least 8 hours before blood sampling;
- A few days before the test, it is not recommended to eat fatty and fried foods, as they negatively affect the body and cause increased production of leukocytes;
- It is strictly not recommended to drink alcohol two days before the test;
- Before donating blood, physical and emotional stress is contraindicated; the test must be taken in a calm and rested state;
- You should not smoke an hour before blood sampling;
- The fact that you are taking any medications deserves special attention; you must consult with your doctor about the possible suspension of taking the medications, or drink them immediately after drawing blood, but not before.
If it is urgently necessary to take a general blood test (unforeseen hospitalization), then blood sampling is done without any preparation. There are also no restrictions on regular drinking water.
Signs of high hemoglobin
Typically, elevated levels of iron-containing protein are detected during blood donation, but there are a number of external signs that may indicate such a disorder:
- drowsiness or insomnia;
- joint pain;
- fatigue and lethargy;
- redness or paleness of the skin;
- increased thrombus formation;
- decreased or lack of appetite;
- increased blood pressure;
- decreased hearing or visual acuity;
- dizziness and headaches;
- heavy sweating;
- bone pain;
- painful numbness or burning of the extremities;
- problems with concentration and memory;
- slight increase in temperature;
- frequent digestive disorders;
- itchy skin.
All these are nonspecific symptoms that do not necessarily indicate an excess of hemoglobin. Only blood tests can accurately determine the deviation.
Indications for prescribing a test for hemoglobin levels
A general blood test is carried out on a regular basis by every person who monitors their health to monitor the condition of the body and prematurely identify hidden diseases that have not yet begun to manifest themselves. It is important to start their timely treatment. Typically, such an analysis is performed once a year; much more often, for preventive purposes, blood is donated by pregnant women to prevent oxygen starvation of the fetus (hypoxia) and a sharp deterioration in the well-being of the expectant mother.
As a basic study, blood sampling for a general analysis is carried out during hospitalization and before surgery to determine the condition of the body and prevent any complications. It is equally important to carry out analysis during treatment to monitor the effectiveness of the chosen drug strategy.
Also, the reason for referral for analysis for a more detailed study of hemoglobin levels are the patient’s complaints: increased drowsiness, fatigue, lack of strength, pale skin. All this can indicate not only a low level of protein, but also the presence of a serious disease: various types of anemia, diseases of the hematopoietic system, and even the presence of cancerous tumors.
- Blood test for leukocytes, leukocyte norms, preparation for analysis
- RDW in a blood test, what is it, norms, preparation for the test
Reducing high hemoglobin
A slight increase in hemoglobin usually does not require medical intervention, but if there is a significant deviation from the norm, treatment must be prescribed. You can reduce the production of iron-containing protein only by eliminating the main cause of its increase. Increased hemoglobin in men, the causes of which are physiological in nature, is brought back to normal by changing lifestyle, adjusting nutrition and fluid intake. The same recommendations apply to adolescents, children and women.
If a blood test shows not only an increase in protein, but also an increase in leukocytes, this indicates that there are pathological disorders in the body.
If your hemoglobin is elevated, doctors may recommend a ferritin test.
This is a water-soluble protein complex responsible for the production of iron in the body. If the ferritin level greatly exceeds the norm, then this condition can be dangerous for a person. Excess iron leads to the aggravation of all diseases and causes premature aging of the body.
Advertising:
If an increase in protein concentration is accompanied by pathological disorders, then it is necessary to treat the underlying disease. To reduce hemoglobin levels, complex measures are used, which may include:
- following a special diet;
- drug therapy;
- hirudotherapy;
- blood transfusion;
- traditional methods of treatment.
The choice of treatment method is determined individually in each individual case and depends on the causative factors that caused the pathological disorder in the body.
Drug therapy
There are no drugs specifically designed to increase hemoglobin. The action of the medications is aimed at thinning the blood and improving its clotting. The following medications may be prescribed:
- Chime
. Reduces enzyme activity, promotes blood flow to tissues, and helps dilate blood vessels. Allowed for use by pregnant women and children. Disadvantage: lowers blood pressure, increases stomach acidity. - Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid)
. Prevents blood clots, thins the blood, and has a positive effect on the functioning of the heart and blood vessels. Used only as part of complex therapy. Disadvantage: negative effect on the gastrointestinal mucosa. - Trental
. Improves blood flow and microcirculation, reduces blood viscosity, dilates blood vessels, and normalizes heart function. Disadvantage: long-term use may cause blurred vision, brittle hair and nails, and decreased appetite. - Cardiomagnyl
. It has a general strengthening effect, improves blood flow to tissues, strengthens vascular walls, reduces blood density and iron levels. Contains aspirin.
When using medications during treatment, the level of red blood cells should be kept under control - for this, blood tests are taken regularly. Taking medications is the main component of therapy. But sometimes, to improve performance, you can do without drug treatment by simply changing your diet.
Diet
A properly formulated diet will help not only normalize the level of iron-containing protein in the blood, but also prevent its further increase and stabilize normal levels. The menu should include products that improve blood composition, with a large amount of useful vitamins and microelements. Allowed dishes based on:
- green vegetables and fruits;
- sauerkraut;
- lean fish and seafood;
- greenery;
- chicken breast;
- legumes;
- fermented milk products;
- chicken eggs.
Dishes included in the menu should not contain cholesterol, so you should avoid fried, fatty, smoked and preservatives. Also, the diet should not contain foods high in folic acid (vitamin B9) and iron. The following are limited or completely excluded from the menu:
Advertising:
- liver and meat;
- eggs and milk;
- sausages and smoked meats;
- beets, radishes, fruits and berries of red and yellow-orange color;
- rolled oats and buckwheat porridge;
- mushrooms and nuts;
- baked goods and sweets, sweet drinks;
- chocolate, cocoa products.
It is recommended to carry out weekly fasting days based on fresh juices, purified water, and herbal decoctions.
Traditional methods
If the disorder is not associated with serious diseases of the internal organs, then traditional medicine methods can be used to normalize hemoglobin. The main condition for home treatment is a balanced drinking regime - you need to drink as much fluid as possible to thin the blood. Other folk remedies include:
- taking a decoction of birch leaves;
- daily consumption of herbal tea made from mistletoe, dandelion roots, horsetail, shepherd's purse;
- inclusion in the diet of salads from woodlice, fireweed, and sati plants (to improve the taste, you can add white chicken meat to them);
- using mumiyo (the tablets are taken in a course for 10 days - one tablet in the morning on an empty stomach).
When using folk remedies, one should not forget about following a diet and it is necessary to periodically take blood tests to monitor the level of protein in the blood.
Other healing methods
Leeches have long been used to reduce blood viscosity and improve its quality. Hirudotherapy helps to “drain” excess blood and thereby increase hemoglobin concentrations.
This procedure cannot be carried out independently; for this you should contact specialized clinics.
Donation helps keep hemoglobin levels normal.
If no methods have been able to improve the patient’s condition, the doctor may prescribe erythrocytophoresis. Its essence lies in a blood transfusion, during which the blood is processed: red blood cells are removed, after which the plasma is returned to the patient. This measure is resorted to only as a last resort, and doctors do not recommend resorting to the procedure at the beginning of treatment for elevated hemoglobin.
Diagnostic procedures for elevated hemoglobin
As with any other disease, early diagnosis is important for elevated hemoglobin.
The sooner you can find out the cause of this pathological deviation, whether it is an independent symptom or a manifestation of a more serious disease.
Diagnosis consists of a general blood test.
If the doctor doesn’t like the tests, he will send you for additional examinations.
After the diagnosis is made, the doctor prescribes a plan of treatment procedures, medication, and proper nutrition.
Dangerous consequences
Advertising:
An increase in hemoglobin levels is associated with an increase in blood viscosity. That is, either the protein concentration increased and the blood became thicker, or the blood thickened and its saturation with hemoglobin structures increased. Such phenomena can cause a number of negative consequences for the body.
Why high hemoglobin is dangerous:
- high saturation of blood protein bodies increases the likelihood of them sticking together - thrombus formation occurs;
- Thick blood moves slowly through the vessels, which leads to the deposition of cholesterol and other harmful substances on the walls of blood vessels - plaques and blockage of blood vessels appear;
- excessively viscous blood requires effort to pump it - the load on the heart and blood vessels increases;
- the low speed of blood movement impairs gas exchange and nutrition throughout the body, blood circulation in the brain is disrupted;
- A high level of hemoglobin that persists for a long time leads to delays and disturbances in the development of children.
An increase in iron-containing protein can cause congestion, strokes, heart attacks, thrombosis, and ischemia. Most of these conditions are fatal, so it is better to prevent their occurrence by promptly starting treatment for high hemoglobin levels.
[media=
https://youtu.be/hmkIHa8swHM
]
Age norms of hemoglobin
Normal hemoglobin levels vary depending on the age and gender of the patient. For men, this figure is slightly lower than for women. They are characterized by the following norms.
| Age | Norm, g/l |
| 3 months | 114 |
| 6 months | 117 |
| 1 year | 116 |
| 3 years | 118 |
| Teens and mature men | 135-160 |
Since the functions of hemoglobin are to transport oxygen, its level is very important for the proper functioning of the body. For female patients, the table looks like this.
| Age | Norm, g/l |
| 3 months | 115 |
| 6 months | 119 |
| 1 year | 118 |
| 3 years | 120 |
| Teens and mature women | 120-140 |
If normal values increase by 10 or more units, it is necessary to prescribe therapeutic therapy and a diet that allows you to restore balance in the blood composition. Neglecting your own health can cause the development of many complications and pathologies that could have been avoided with timely diagnosis and treatment.
A little about the main functions of blood
The main function of red blood cells is to transport oxygen to the cells of the whole body.
All the tasks that the body sets for the blood are carried out thanks to the coordinated work of its following components:
- plasma – the liquid non-cellular part of blood;
- erythrocytes, platelets, represented by various elements leukocytes - cell mass (or suspended formed elements of blood);
- ions of various micro- and macroelements, enzymes, hormones and other substances entering the blood.
All of the above components perform the following functions:
- transport substances necessary for life (hormones, enzymes, nutrients and “fuel” elements) and remove “waste” materials accumulated in the blood (carbon dioxide, etc.);
- regulate the flow of water and electrolytes into the tissue;
- ensure the functioning of the immune system when pathogenic objects (microorganisms, own mutated cells) enter the blood.
A parameter such as blood thickness is determined by the balance between the liquid (plasma) and cellular (formed elements) part of the blood. It is this property that allows it to penetrate the smallest vessels and capillaries. This ensures the necessary delivery of blood to all tissues of the body.
Anemia (or anemia) is accompanied by a decrease in those blood parameters that relate to red blood cells. It is these red cells that carry oxygen, and if their production is disrupted, hypoxia of the tissues of all body systems develops.
What are the signs that indicate that the blood is thick?
Headache and dizziness may be manifestations of blood thickening.
When the blood thickens, the following changes in well-being are felt:
- aching headaches;
- dizziness with loss of coordination of movement;
- muscle weakness;
- decreased tolerance to stress;
- noise in ears;
- fainting conditions;
- dry skin;
- paresthesia in the legs and arms: crawling, tingling, burning, numbness;
- blue discoloration (cyanosis) of the mucous membranes of the mouth, eyes and areas of the skin;
- increased sensitivity to low temperatures;
- drowsiness;
- frequent yawning;
- heaviness and pain in the legs;
- anxiety;
- depression;
- sleep disorders;
- absent-mindedness;
- slow bleeding after cuts;
- constipation and flatulence (sometimes).
When the blood is thick, women tend to have repeated miscarriages. In addition, blood tests often reveal elevated hemoglobin levels. Patients with blood hyperviscosity syndrome often exhibit one of the following syndromes:
- chronic fatigue,
- irritable bowel,
- candidiasis.