Tachycardia is an increase in the number of heart contractions of more than 90 beats at a certain point in time (usually calculated per minute). The development of acceleration of cardiac activity is caused by irritation of a special area of the organ: the third reflexogenic zone.
Rapid heartbeat, especially pronounced with high blood pressure, is rare, despite the apparent obviousness of the process.
The thing is that regulating heart rate and increasing blood pressure are two independent elements that have little connection with each other. They have different mechanisms.
Why does the pulse increase when blood pressure is high?
As already mentioned, there is no direct connection between the development of tachycardia and blood pressure levels. We are talking about an indirect process. How does it develop?
As a result of irritation of the special reflexogenic center of the heart, the organ is given a signal about the need for more active pumping of hematological fluid.
At the same time, blood pressure levels increase gradually and adequately to the nature of the work performed (physical activity, in other words).
Corticosteroids, special hormonal substances produced by the adrenal cortex, are responsible for the increase in tonometer readings in this case. These include cortisol and adrenaline, as well as norepinephrine.
At the end of the work, there is a gradual decrease in vascular tone and a weakening of tachycardia. With full and balanced physical activity, pulse rates and blood pressure levels decrease even in the most avid hypertensive patients.
If the process does not stabilize, you need to look for causes in diseases of the cardiovascular system and other pathologies.
Moreover, if tachycardia reaches 180-185 beats per minute or more, the pressure should drop, this is natural.
Otherwise, most likely, something is wrong with the neuro-reflex regulation. Rapid heartbeat and high blood pressure require a comprehensive, competent assessment.
What indicators are considered high?
The pulse is the main indicator of heart function; if it is constantly elevated, it is important to undergo a full diagnosis and establish the cause of this condition. There are certain age standards:
| Age | Pulse readings |
| in children from 2 to 10 years old | ≥130 |
| in teenagers | ≥100 |
| in patients aged 16-30 years | ≥80 |
| in middle aged people | ≥75 |
| in elderly people and pregnant women | ≥90 |
Blood pressure standards are calculated based on static data and are conditional:
| Age | Norm | Hypertension | ||
| Systolic (upper pressure) mm Hg. Art. | Diastolic (lower pressure) mm Hg. Art. | Systolic mmHg Art. | Diastolic mmHg Art. | |
| 12 | 120 | 75 | > 125 | > 80 |
| 16 | 125 | 80 | > 135 | > 85 |
| 18 | 130 | 85 | > 140 | > 90 |
| 20 | 116 | 72 | >123 | > 76 |
| 20-30 | 120 | 75 | >129 | >81 |
| 30-40 | 127 | 80 | >129 | >82 |
| 40-50 | 135 | 83 | >137 | >84 |
| 50-70 | 142 | 80 | >159. | >85 |
| in pregnant women | 100 | 70 | >140 | >90 |
An increase in blood pressure and pulse after physical or psychological stress is considered normal. Pathology is indicated by a regular increase in indicators for no apparent reason.
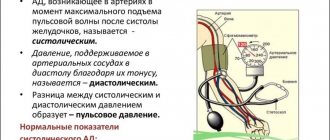
Blood pressure in the vessels is proportional to the load on the heart muscle.
Causes physiological and pathological
Since there is no direct connection between tachycardia and the development of high blood pressure, the factors for the development of rapid heartbeat will be the same.
Among the probable causes of the condition:
- Significant increase in body temperature. In this case, the cause of the sharp increase in blood pressure and pulse are toxins that are actively produced by the bacterial flora. The effects are observed on both cerebral structures and the heart. Hence, both processes are combined, which are often mistaken for sides of the same coin. But that's not true. We're talking about a pathological coincidence.
- Emotional overload. Accompanied by the release of large amounts of cortisol, adrenaline and norepinephrine. The result is a significant increase in blood pressure and, in part, an acceleration of cardiac activity.
- Neurotic disorders. Associated with hormonal instability on the part of the adrenal glands. Substances characteristic of stress are produced: the same corticosteroids. What this entails is already clear.
- Intense physical activity. Climbing stairs, running, lifting weights, etc. All this is mechanical work that requires better tissue nutrition. In such a situation, both processes described are physiological in nature. Everything returns to normal after a little rest.
- A high pulse with high blood pressure is possible due to dehydration. The blood thickens, the amount of fluid circulating in the body decreases. To provide the body with the optimal amount of nutrients and oxygen, the heart is forced to work more actively, sometimes to the point of wear and tear.
- Violation of the patient's hormonal levels. The first effect is hyperthyroidism, that is, a high concentration of thyroid hormones in the bloodstream.
The substances produce a toxic effect and stimulate special centers of the heart and brain responsible for regulating vascular tone and heart rate.
The second possible option is excessive production of cortisol as a result of the development of oncological processes (pheochromocytoma, adenoma, adrenal cancer) or neoplasia in the adenohypophysis (so-called pituitary adenomas).
The mechanism of these pathologies is different, but the result is identical.
- The use of substances that have a tonic effect. Tea, coffee, alcohol, psychoactive components. They provoke not only tachycardia, but also an increase in tonometer readings.
- Anemia of various etiologies. Including iron deficiency and other forms of the disease.
- Use of drugs with hypertensive properties: Citramon, Atropine, Corticosteroids. Moreover, it is uncontrolled and in the wrong dosages. No one can say in advance how this might end.
- Unfavorable climatic conditions. If a particular person lacks an adaptive mechanism.
- Large volumes of blood loss (for example, with a stomach ulcer). Causes disruption of local and generalized hemodynamics. The heart has to work more actively in order to provide all tissues and organs with the necessary substances with a smaller volume of circulating blood.
- Myocardial infarction. Acute circulatory disorders in the structures of the heart. Potentially lethal.
- Congestive heart failure.
- Hypertension, with hypertensive crisis of the first type (sympatho-adrenal crisis).
- Heart defects.
- Inflammatory pathologies of the organ: myocarditis, endocarditis.
All causes of high blood pressure and high pulse should be “swept aside” gradually. The diagnosis is made based on the information obtained by exclusion.
What does this mean?
Due to frequent heart contractions, the blood supply to internal organs is disrupted. This condition is especially dangerous for people prone to hypertension:
- alcohol abusers;
- obese;
- with iron deficiency;
- with anemia;
- with abnormalities of the heart or blood vessels;
- with chronic cardiovascular diseases;
- constantly exposed to physical activity;
- leading a sedentary lifestyle;
- with diabetes mellitus and endocrine pathologies.
The risk group includes older people due to the natural thinning of blood vessels, and women during pregnancy due to an increase in the amount of circulating blood. Adolescents with elevated levels of hormones that cause vasoconstriction and impair blood circulation are also at risk.
How dangerous is this condition and is it a threat at all?
Yes, an increase in heart rate along with blood pressure poses an immediate danger not only to health, but also to life. What are the main consequences of increased cardiac activity?
- Thromboembolism may form due to the destruction of red blood cells and activation of the blood clotting process. This is extremely dangerous. A blood clot can block an artery and be fatal.
- With a long-term pathological process, especially if tachycardia is a frequent companion of the patient, the immune system is suppressed. This happens due to disruption of metabolic processes at the general level.
- Development of coronary heart disease. The main factor in the development of the problem is hypoxia of myocardial tissue. The next step is a heart attack.
- Injury as a result of unexpected fainting. Impaired consciousness or syncope may develop unexpectedly in a dangerous environment.
- The long course of the pathology leads to cardiogenic shock with a sharp drop in blood pressure. The result is the death of the patient.
- Finally, sudden cardiac arrest and death are possible.
You shouldn't joke with tachycardia. You need to see a doctor.
Causes of rapid heartbeat with high blood pressure
Most of us don’t think about the causes of the disease, but about what to drink to make the unpleasant symptoms go away. If the chosen drug produces results, the patient will continue to ignore going to the doctor for a long time. This kind of attitude towards your body is unacceptable.
If you often experience high blood pressure and feel a rapid heartbeat, do not wait until the situation becomes critical.
Often the cause of changes in pressure and pulse are pathologies of the heart and large vessels, such as:
- ischemic disease;
- atherosclerosis;
- thrombosis.
Thyroid disease may affect heart rate. This is due to the fact that the hormones it produces regulate the intensity of the basal metabolism and can lead to severe tachycardia or arrhythmias.
Infectious diseases accompanied by intoxication can cause tachycardia. The use of certain medications, as well as the lack of certain vitamins and microelements, change the pulse rate, increase blood pressure.
What to do to reduce high heart rate against the background of significant blood pressure?
Self-administration of medications to lower heart rate is not recommended. It is not known what consequences this will entail.
A heart rate of 90-120 beats per minute is acceptable; anything higher requires calling an ambulance. Especially if an attack of tachycardia lasts more than 2 hours in a row.
In general, tachycardia lasting more than 2 minutes is considered pathological.
- Before doctors arrive, you must avoid any physical activity. From mechanical activity, the pressure will increase even more, the pulse will accelerate, this is already a threatening condition.
- Take a sitting position. Relax and don't be nervous. Place a soft cushion of blankets or a pillow under your back.
The main thing is not to lie down, otherwise blood circulation will be uneven. On the one hand, this will cause an even greater acceleration of the heart rate, on the other hand, breathing will be impaired, and the risk of pulmonary edema will increase. It can all end in the death of the patient.
- Apply vagal techniques: press on the eyeballs with little force for 10-15 seconds, then break for 30 seconds. and continue this way for 5 minutes.
Breathe steadily and slowly, holding your breath as you exhale. (5 seconds for each element of the cycle), repeat for 10 minutes. This will not only lower your heart rate, but also your blood pressure.
- You can take one sedative tablet based on herbal ingredients: motherwort or valerian, most importantly not in alcohol form. You can do both at once. Valocordin or Corvalol will also help.
- If the heart rate is 100 beats or higher, take a beta blocker tablet (Anaprilin 50 mg or Carvedilol). Strictly one, do not exceed the dosage.
You should not take pills to lower your heart rate like Bravadin. They will provoke a worsening of the condition.
If after 20 minutes the heart rate and pressure have not decreased, you need to call an ambulance. There is no point in hesitating or hesitating, health and maybe even life are at stake.
Upon arrival of the team, the issue of assistance on the spot or hospitalization is decided. If you refuse to go to the hospital, it is recommended to consult a cardiologist as soon as possible.
Dangerous symptoms requiring immediate medical attention
Unfortunately, the symptoms are not always obvious. Some people, especially those who are accustomed to their condition, do not feel their heartbeat. Such conditions are detected only on a cardiogram.
The warning signs are:
- Palpitations. Feeling like your heart is going to jump out of your chest. Often the process is accompanied by visual impairment, including transient blindness, darkening, and the formation of scotomas (areas of loss of visual fields).
- Headache of a stabbing nature.
- Dizziness.
- Chest pressure, pain. They are given to the arms, back, epigastric region (where the stomach is located).
- Heaviness in the legs, weakness, drowsiness, disturbances in general condition.
- Fainting and syncope. Loss of consciousness. Repeated processes of this kind are especially dangerous.
- Shortness of breath, inability to breathe normally. Feeling of lack of air.
- Numbness of the limbs and fingers.
If there is at least one manifestation, you should urgently seek medical help. It is not known what process we are talking about. Need diagnostics.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis of the causes of high blood pressure against the background of tachycardia is the prerogative of a cardiologist. If necessary, consultations with other specialists are carried out. Endocrinologist and neurologist.
The list of studies is standard:
- Questioning the patient for complaints. Objectification of symptoms, in other words.
- Life history examination. Etiological factors are established.
- Electrocardiography. There is an invasive electrocardiographic test that is used in extreme cases.
- Holter monitoring using a portable pressure measuring device.
- The monitor is worn for 24 hours, then the nature of cardiac activity is assessed.
- Tilt table test. In Russia and the CIS countries it is almost never carried out due to risks.
- Study of venous blood for hormones: thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pituitary gland.
- Encephalography. It is not very informative, but allows you to exclude pathologies from cerebral structures.
- General and biochemical blood test.
Comprehensive diagnostics allows you to quickly determine the cause of the problem.
Symptoms
To make a diagnosis, the doctor will refer the patient to undergo laboratory tests of blood and urine. You will also need instrumental examination methods, such as MRI, CT, Dopplerography, ECG, ultrasound of internal organs and the thyroid gland. Based on the results obtained, an individual treatment regimen will be selected.
You can recognize hypertension and increased heart rate by listening to your feelings. The patient often exhibits symptoms such as:
loss of consciousness;- dizziness;
- darkness, spots in the eyes;
- heartache;
- dyspnea;
- dull pain in the back of the head;
- tremor, convulsions;
- swelling;
- facial hyperemia.
The sooner the disease is identified, the easier it is to cure it. If hypertension is detected at a late stage, then it is impossible to do without lifelong use of medications or even surgical intervention.
Treatment
A difficult and complex task. Sometimes pills alone are not enough. Therapy is aimed at restoring heart function and eliminating the root cause of the condition.
Among the methods:
- Administration of special medications. Calcium channel blockers and beta blockers. They should be taken systematically at high heart rates. There are emergency medications, but they cannot be used without the knowledge of a doctor.
- Surgical techniques: endovascular ablation, installation of a pacemaker (pacemaker), etc. All surgical techniques are carried out as planned, excluding emergency cases. You need to discuss the pros and cons with your doctor and clarify any unclear points.
All methods are determined by the doctor based on their initial parameters and the data obtained.
It is important to change your lifestyle: minimal physical activity, only therapeutic exercises, lack of stress, normalization of the diet, vitamin supplementation, quitting smoking cigarettes and electronic devices, drinking alcohol (full), normalizing the drinking regime (up to 2 liters a day or a little less).
Therapeutic measures are varied and will require efforts not only on the part of the specialist, but also on the part of the patient himself.