Pathologies of the cardiovascular system are accompanied by pulse disturbances in 85-90% of cases. Spontaneous deviations in cardiac activity occur in 100% of situations, which indicates the absolute prevalence of dysfunctions of this kind.
The most obvious option for the patient himself is tachycardia (increased heart rate).
There are two types of this pathological condition:
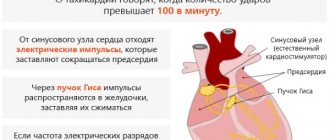
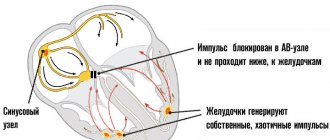
- Sinus form. It is represented by a disruption of the normal generation of an electrical impulse by the natural pacemaker (sinus node), located in the right atrium.
- Paroxysmal. It is determined by the formation of new, abnormal foci of activity. It occurs somewhat less frequently, flows more severely and is generally considered more life-threatening.
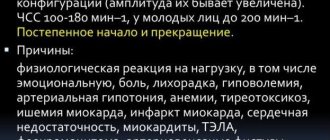
A pulse of 120 heart beats per minute is characteristic only of the sinus type; for the second, figures of 140 and higher are pathognomonic. This type of deviation does not pose any danger.
Does this mean that you can sit with your hands folded? No, definitely. On the one hand, over time, the acceleration of cardiac activity can progress, turning into something else: extrasystole, or ventricular fibrillation.
On the other hand, a pulse of 120-125 is almost always secondary and caused by other diseases. It is not known what we are talking about, therefore, fatal complications are quite likely.
What do these indicators mean?
Usually nothing specific. It is possible to state a fact: heart rate acceleration. The pathological process is almost never primary.
It may be due to the onset of the disease or natural factors. If some third-party diagnosis is to blame, there are plenty of options. Not always cardiac abnormalities. Neurogenic processes and gland dysfunction are possible.
You need to figure it out together with your doctor. You should start with a cardiologist, then involve other specialists as necessary.
Sinus tachycardia, for which typical values are 100-130 maximum, is relatively difficult to tolerate, but the danger to life in the early stages is minimal.
In some cases, it is impossible to determine the cause of the condition even after a thorough examination. Then they talk about the idiopathic form of the increase in the indicator.
Causes of elevated heart rate at rest
Development factors can be both cardiac and non-cardiac.
Problems with the muscle organ
- Arterial hypertension. Both symptomatic, caused, for example, by renal pathologies, and the disease itself, dysregulation of blood vessels and other varieties.
The essence is the same. The patient's blood pressure is steadily rising. Up to what numbers depends on a lot of factors. Including gender, age, condition of blood supply structures, duration of the process. Stages 2-3 lead to a stable increase in the pulse rate.
Recovery appears extremely difficult. Over time, the patient ceases to feel the negative effects of blood pressure at peak levels. The symptoms fade and the person gets used to the abnormal condition.
At the same time, a pulse of 120 beats per minute is not directly related to blood pressure. We are talking about indirect factors. The same etiological moment causes an increase in two vital indicators.
- Myocarditis. Inflammation of the muscle layer of the heart. It is she who is responsible for the functional state of the organ. It occurs relatively rarely, as a complication of third-party pathologies, such as rheumatism. Then we are talking about an autoimmune form or infectious conditions, respectively, we talk about viral, bacterial, fungal types.
Tachycardia accompanies the patient constantly, does not recede for a second, even at night. A resting pulse of 120 or more is a hallmark of myocarditis.
Recovery is carried out urgently in a hospital. Duration from several days to a week. Antibacterial therapy is used, and suppressors may be prescribed.
- Pericarditis. Or inflammation of the pericardial sac. There is a danger due to the likelihood of complications. Which ones? Tamponade as the main threat. This is compression of the muscular organ itself by accumulated effusion.
Urgent surgical intervention is required. Medication is indicated in the early stages, if there are no consequences yet.
- Heart defects. Congenital and acquired. They are found relatively rarely, especially if the state of health does not cause subjective concern. Many processes proceed gradually, for years, without pronounced symptoms from the body. Sometimes the diagnosis is made based on the results of the autopsy.
Tachycardia is a relatively rare occurrence in patients with anatomical defects. Recovery is possible, but at the right time. If you are late there will be nothing to help.
The main treatment is surgical. Contraction frequency is adjusted medically, after the fact, as a secondary measure.
- Atherosclerosis. Conditionally it can be classified as a cardiac pathology. In this case, the coronary arteries and aorta are affected.
Damage to the vessels supplying the myocardium can lead to a heart attack or an acute attack of angina with a heart rate of 120-140 beats per minute. Both options are dangerous. Accompanied by a persistent acceleration of the rhythm.
Another option results in left ventricular dilatation, aortic valve stenosis and decreased overall hemodynamics. Tachycardia occurs regularly, but does not last constantly.
Extracardiac pathologies
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Gives pronounced disturbances in pulmonary activity. First, the right ventricle suffers, then the entire muscular organ.
Bronchial asthma gives the same symptoms. Especially at the advanced stage of the condition. Recovery requires a lot of ingenuity, since the drugs themselves can provoke an increase in heart rate. This is true for glucocorticoids and bronchodilators, as well as other medications.
The difficulties are obvious, given the duration of therapy - a lifetime, it is necessary to select the optimal regimen. Relatively safe.
- Anemia. Usually iron deficiency. As a result of an insufficient amount of the element in the body, hemoglobin deficiency occurs. Stable anemia and tissue hypoxia occur.
The condition is relatively easy to treat. On the one hand, the root cause is eliminated. This includes constant minor bleeding or nutritional deficiency.
On the other hand, the infusion of iron supplements in a adjusted dosage is indicated. Which one you need to look at based on the severity of the condition.
- Hyperthyroidism. Or a disruption of the normal production of thyroid hormones. Recovery under the supervision of a specialized specialist. The causes of the condition are multiple: tumors, inflammation of an infectious or autoimmune nature, and other issues are possible.
Hormone replacement therapy is required. The duration is relatively short. In case of functional impairment, treatment is limited to this. There is no point in doing anything yet.
Tachycardia resolves on its own after removal of excess thyroid-specific substances.
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases. From colds, ARVI to tuberculosis and other dangerous conditions. A heartbeat of 120 beats per minute is the result of intoxication with waste products of the bacterial flora and excessive stimulation of the heart itself.
The main method for eliminating the pathological condition is to carry out specialized measures to evacuate harmful substances from the bloodstream.
It is most effective to take action in a hospital. If the disease is mild, the deviation goes away on its own.
- Cachexia. It is caused by nutritional disorders for objective reasons (inability to take care of oneself at home, inadequacy), or subjective factors. For example, with a complex known as dysmorphophobia - dissatisfaction with one’s own body. Both options are dangerous.
The first can potentially be stopped by the introduction of nutrient solutions. The second requires long-term work with a psychotherapist. Depletion leads to a stable utilization of one's own resources.
First, fat comes into play, then muscle. The body doesn't last long. The heart begins to fail, it lacks nutrition.
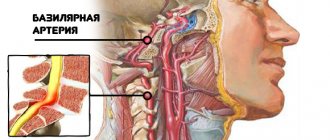
- Disorders of the nervous regulation of the cardiovascular system. Development options are different. From osteochondrosis and intervertebral hernias, to vertebrobasilar incompetence, tumors of cerebral structures and other issues.
Typically, sinus tachycardia with a pulse of 120-128 in a calm state lasts relatively short time. The episode lasts for about half an hour. Rarely more.
Subjective factors
A heart rate of 125-127 beats per minute develops as a result of cardiac and non-cardiac causes. But sometimes the factors are subjective, the patient is able to correct them himself.
- Smoking. Secondary atherosclerosis occurs. It is caused by vasoconstriction as a result of prolonged consumption of nicotine. Pathological changes begin almost from the first cigarette. For some, progression occurs rapidly, for others it takes much longer, over the course of years. Alcohol habit. Alcohol has no beneficial effect on a person's life. Consuming ethanol is a destructive habit. All myths about benefits are nothing more than lies and misconceptions.
- Obesity. Body weight does not play a primary role. Overweight patients suffer from lipid metabolism disorders. The metabolic factor cannot be completely corrected. It is partly due to unfavorable genetics. Therefore, it is necessary to reconsider your diet. Pills alone won't help matters.
- Constant consumption of coffee and tea, energy drinks. These are psychoactive, although to a minimal extent, products. They tone blood vessels and cause stable stenosis (narrowing) of blood supply structures. They also do not provide any benefits to the body.
- Constant use of diuretics. Young women are guilty of this habit. This is extremely dangerous. Indeed, with the release of excess fluid, a kilogram or two is eliminated. But diuretics are not harmless drugs. In the short term they are planting buds. Recovery is almost impossible. It will only get worse. The only solution will be transplantation. The likelihood of successful treatment is slim.
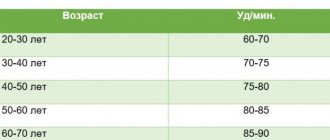
- Age. The older the patient, the higher the risk of developing stable tachycardia against the background of banal wear and tear of cardiac structures. It is necessary to treat the underlying disease that led to pathological changes.
The reasons are considered in the system and eliminated gradually. In the absence of evidence for organic phenomena, they speak of an idiopathic or natural form.
In the end, an acceleration of the pulse to 120 beats or even more is possible due to stress, emotional, and physical stress. All known factors are taken into account.
Tachycardia - what are the symptoms?
A symptom of the development of tachycardia is an increased pulse, and as follows from the definition, an acceleration of the heart rate above 100-125 beats per minute. Patients describe their condition differently - “the heart is pounding like a hammer”, it wants to “jump out of the chest”, “the heart is beating unevenly”.
Strong and frequent heart beats may be accompanied by symptoms such as:
- dizziness,
- scotoma, darkness before the eyes,
- feeling of weakness,
- dyspnea,
- loss of consciousness.
If your heart is galloping like a driven horse while you are calm, you need to see a doctor and conduct additional diagnostic tests that will help you decide on further treatment. Tachycardia, due to many factors that can cause it, requires, first of all, treatment as an effect, which means eliminating the cause that causes it.
What can you do at home?
Not much. It is not clear what condition we are talking about. You need to carefully understand and then act. The main rule is to call an ambulance if tachycardia lasts more than 20 minutes.
Before the doctors arrive, the algorithm is as follows:
- Measure blood pressure, heart rate.
- Take a tablet of Anaprilin or half, if the heart rate is below 120, motherwort, valerian. You can drink 10-30 drops of Corvalol.
- Open a vent or window to ensure adequate ventilation.
- Relax, calm down. At the moment of tachycardia, panic and fear may develop. You need to pull yourself together.
- Sit down, lower all limbs.
- Breathe normally, there is no need to control the process.
Attention:
Taking other drugs is strictly prohibited. You cannot sit in the bath, douse yourself with water, wash your face, eat, or exercise. When the doctors arrive, explain the situation briefly and to the point.
Low blood pressure and high pulse - what does this mean?
Pulse is the frequency with which the ventricles of the heart contract per unit time. Blood pressure is a term used to refer to the volume of blood that moves through the heart during one beat.
When volume, that is, blood pressure, falls, the heart can compensate for this change by speeding up the heart rate, which is observed as an increased heart rate.
Unfortunately, this is not always so simple and only affects healthy people. In the case of patients, for example, with atherosclerosis of arterial vessels, hypertension, anemia and many other diseases, the relationship between pulse and blood pressure is disrupted.
When is urgent medical attention needed?
If the accelerated pulse does not go away within 10-30 minutes, you should contact a specialist. In addition to an increase in heart rate, other symptoms occur.
Which manifestations should cause concern in the patient:
- Chest pain. Usually pressing, burning. Low to medium intensity. Lasts from 2 to 30 minutes. If more, there is a risk of heart attack.
- Dyspnea. In a state of complete rest. It occurs as a result of gas exchange disturbances. Dysfunction of pulmonary structures is possible.
- Paleness of the skin.
- Cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle.
- Arrhythmias. Flow parallel to the acceleration of contraction frequency. This is fibrillation, extrasystole. Subjectively, they feel like missing beats, freezing in the chest.
- Cold sweat. Hyperhidrosis.
- Headache. Cephalgia.
- Vertigo. To the point that a person cannot navigate in space and is forced to take a lying position.
- Noise in ears.
- Fainting, syncope. May occur several times in one day. Poor prognostic sign.
- Feeling of fear, panic. Or complete indifference to everything happening around. Both options are dangerous and require correction.
Symptoms require qualified assessment by physicians. Better in stationary conditions. Without special techniques, superficial conclusions can be drawn.
Therapeutic measures
An increase in heart rate to 120 or higher requires immediate correction. There are both medicinal and traditional methods of treating heart palpitations. Let's talk about them further.
First aid
If discomfort occurs and heart rate increases, therapists advise taking the following actions:
- measure pulse;
- take a sitting position;
- take a deep breath and exhale;
- drink a glass of water;
- wash your face with cold water;
- take another deep breath until you calm down completely;
- measure the beat frequency again.
If the indicators return to normal, then everything is in order; no further measures can be taken. What to do if nothing has changed or the decrease in heart rate is insignificant? You should take tincture of valerian or motherwort, Corvalol drops, or dissolve a Valocordin tablet, depending on what is in the medicine cabinet.
Drug treatment
If an increase in heart rate occurs frequently, then you should carry a package of Valocordin or Valerian Extract in tablets with you. This is the fastest way to normalize your condition while being in a public place and without resorting to serious medications. If elevated levels persist for a long time, the following medications should be taken:
Lidocaine.- Ethmozin.
- Difenin.
- Propaphenone.
- Pindolol.
- Timolol.
- Ibutilide.
Taking any medications should only be prescribed by a doctor after a detailed examination and based on the tests taken.
Buying and taking medications on your own is strictly prohibited, since an incorrectly calculated dosage or incompatibility of drug components can lead to a deterioration in well-being and negative consequences for a person.
Folk remedies
A short-term increase in heart rate can be stopped using the following home methods:
- A well-known folk remedy for lowering heart rate is honey. If you suck one teaspoon of honey a day, your heart rate will gradually return to normal.
- Currants have a similar effect. Blackcurrant decoction can reduce heart rate.
- You can resort to herbal decoctions. It is best to use chamomile, motherwort, valerian, and Chinese lemongrass. You can also make alcoholic tinctures from these herbs and take them diluted with water. To prepare a decoction, you need to pour boiling water (two glasses) over a spoonful of the herb and leave it in a water bath for 15 minutes; for a tincture, add a glass of alcohol to a spoonful of herbs and leave it for a week.
Tests needed to identify the root cause
Under the supervision of a cardiologist. The approximate list of events is quite wide:
- Oral questioning of the patient and collection of anamnesis. Aimed at objectifying symptoms and identifying the clinical picture.
- Next, measure blood pressure and heart rate. Statement of the fact of deviation from the norm.
- 24-hour Holter monitoring. Registration of the same indicators for 24 hours. Makes it possible to assess the situation in dynamics, in natural conditions for the patient.
- Electrocardiography. Shows the functional state of the cardiovascular system. Can be prescribed after exercise (bicycle ergometry).
- Echocardiography. Ultrasound technique for tissue visualization. All defects become clearly visible.
If necessary, cardiac tomography and coronography are indicated. It is possible to prescribe vascular Doppler ultrasound (USDG).
A cardiologist does not always cope alone. When the origin of the pathological process is complex, third-party doctors are involved. It is possible to convene a whole council, based on the complexity of the case.
What treatment will be required
It is carried out using medicinal methods. Surgical methods of therapy are relatively rarely used. An approximate scheme for the use of drugs:
- Cardiac glycosides. To correct myocardial contractility. Digoxin or lily of the valley tincture. In extremely limited quantities, minimal dosages.
- Beta blockers. Metoprolol or Carvedilol according to indications.
- Antiarrhythmic. Also in small courses, only if there are significant deviations from the norm. Amiodarone as the main name.
- Antihypertensive. Used against the background of a current stable increase in blood pressure.
- Sedatives and tranquilizers. In the acute period to bring the emotional and mental state back to normal.
Surgical treatment is carried out if there are indications: heart defects, advanced atherosclerosis and others. Prosthetics, vasodilation by stenting, and elimination of cholesterol plaques are indicated.
It is possible to install a pacemaker and cauterize foci of pathological activity with radio waves (ablation).
Changing your lifestyle involves giving up smoking, alcohol, and adjusting your diet (treatment table No. 10 and its variations). Minimizing physical activity. Salt no more than 7 grams.
The use of traditional methods of treatment is a very controversial decision. With unproven effectiveness, they carry high risks. Even with pharmaceutical activity, precise dosage selection is required. Dangerous complications are possible.
Causes and consequences of rapid heartbeat
The heartbeat of a healthy person may increase, but also quickly return to normal. If we are talking about pathology, then the reasons for the increase in heart rate are the following:
- presence of bleeding;
- large blood loss;
- improper functioning of the adrenal glands, in which a large amount of a hormone that regulates the irritability of the nervous system is released into the blood;
- low hemoglobin content in the blood;
- hyperthermia;
- intoxication due to poisoning with narcotic or alcoholic substances;
- dehydration;
- infection and inflammatory processes;
- emphysema, when the tissues become less extensible.
Constantly rapid heartbeat can have serious consequences. If the problem is not detected in time, the brain, heart, kidneys and adrenal glands, blood vessels and eyes may suffer.
This condition causes memory impairment and is fraught with Alzheimer's disease, heart attack, stroke and death.