Extrasystole is called untimely depolarization and contraction of the heart or its individual chambers. This is the most frequently recorded type of arrhythmia. Extrasystoles can be found in 60-70% of people. But what is the situation with the draft and are they recruited into the army with extrasystole? A note from a cardiologist about the presence of extrasystole does not yet indicate the presence of significant disruptions in the functionality of the body. Rhythm disturbances can occur even in completely healthy people; for this reason, suitability for service is determined according to certain conditions.
Are they recruited into the army with ventricular extrasystole?
With ventricular extrasystole (one of the types of cardiac arrhythmia), untimely contractions of the ventricles of the heart occur - in other words, such contractions are called extrasystoles. This phenomenon does not always indicate certain diseases; extrasystole in some cases can also occur in absolutely healthy people.
Experts from the draft commission do not consider ventricular extrasystole as a disease. For this reason, all young men with a similar diagnostic conclusion are drafted into the army. Doctors claim that vegetative-vascular dystonia and neurosis are an unqualified diagnosis of other diseases with such symptoms, for example: diseases of the nervous system and psyche, possible heart disease, hypertension, improper functioning of the vascular system.
For this reason, doctors from the military commissariat sign up and take the young man to serve, believing that a healthy diet in the army, regular stay in the fresh air, daily routine and physical activity will cure those suffering from ventricular extrasystole.
What are the patient's actions?
To avoid consequences, you need to start contacting your medical unit immediately, and also have a copied copy of your medical record with you for the doctor. Then the health worker will monitor the patient’s condition. As an option, he will be provided with some medication options aimed at restoring blood pressure and preventing migraine attacks, panic attacks, tachycardia, and neuroses.
Thus, relieving the crisis with supportive therapy will have a beneficial effect on the patient. However, under conditions of military service in the army, cure is unlikely to be possible. If the symptoms listed above continue to occur, the physician should be notified of the condition. Ultimately, the employee is required to pay a commission from management.
Do they take into the army with cardiac extrasystole?
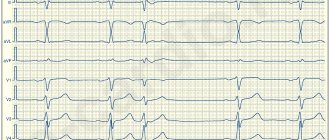
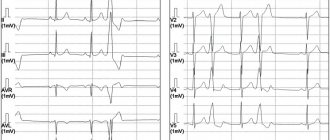
It is believed that this is the most common type of arrhythmia. Extrasystole has the characteristic of increasing the automaticity of individual zones of the myocardium (premature contractions of the heart). It is provoked by an excitation impulse that appears in the focus of heterotropic automatism. There are certain types of extrasystoles depending on the response of the atria. Before answering the question about the suitability of a conscript with extrasystole, you should understand the method of examination for such a disease. The classification is presented below.
According to the Schedule of Diseases, the classification according to Laun and Wolf is used:
- Degree 1 – monomorphic extraordinary contractions are recorded (no more than 30 per hour of observation);
- Degree 2 – contractions occur more frequently, from one focus (more than 30 per hour);
- Degree 3 – polytopic extrasystole;
- Degree 4 – divided from the ECG rhythm pattern;
- Degree 5 – the most dangerous type “R on T” in a prognostic sense is registered, which means that the extrasystole “climbed” onto the previous normal contraction and can lead to rhythm disturbances.
In addition, a “zero” degree is allocated for people who do not have extrasystole.
The intensity of symptom expression will be personal. Typical signs of extrasystole:
- Feeling of heart sinking;
- Interruptions in rhythm;
- Strong tremors in the chest.
In addition, hot flashes, shortness of breath, weakness, feelings of anxiety and discomfort may occur. If the disease occurs in an intense form, then the internal organs will feel a lack of oxygen, especially the coronary, cerebral and renal circulation is reduced. Extrasystole can cause dizziness, angina attacks and fainting.
According to the Schedule of Diseases, Article 42, those young men who have a classification of the degree of ventricular extrasystole according to the Laun-Wolff gradation of 3-4 are exempt from service with the assignment of category “D”. This diagnostic conclusion can only be made by a cardiologist after a thorough examination of the heart’s activity. Persons with severe symptoms of extrasystole will not be hired for service due to sudden complications or cardiac arrest.
Diseases and secondary arrhythmia
It should be noted that often arrhythmia is a sign of developing dangerous diseases that can cause release from service. Such pathologies may be:
- diseases of a rheumatic nature;
- disruption of the heart (including acute heart failure);
- heart disease;
- mitral valve prolapse;
- chronic myocardial pathologies;
- endocrine and hormonal disruptions.
In this case, the conscript should undergo a full examination and identify the cause of the arrhythmia. The diagnostic results must be documented and presented during the medical examination at the military registration and enlistment office.
Fitness category with extrasystole
The fitness category is determined by the Schedule of Diseases. A conscript whose complaints are determined by the state of ventricular extrasystole by the commission may not be allowed to serve. However, for this purpose, it is required at the time of passing the medical commission to have in hand the appropriate documentation that will prove this diagnosis.
With problems of this type, according to the Schedule of Diseases and Article 42 of the army, a conscript will be released with fitness category “D”.
How does the military medical commission make a decision on the fitness of a conscript?
Cardiologists distinguish 2 types of extrasystole: functional and organic. Often young people have type 1 disorder. In this case, arrhythmia is caused by stress, emotional and physical stress, and drinking alcohol, coffee or energy drinks. The pathology of heart contractions, as a rule, does not pose a danger to young men and in most situations does not require therapy: as soon as the condition that provoked the syndrome is eliminated, the heart rhythm will return to normal. Organic type disorders appear with significant cardiovascular diseases: myocardial infarction, ischemic disease, cardiac muscle dystrophy. As a rule, this type of disease is typical for the population over 40-60 years of age.
The second criterion that determines the relationship between extrasystoles and service is whether the extrasystoles are amenable to therapy. They will accept service if the disorder can be easily eliminated with the help of medications or goes away on its own. In order to be released from the army, one must also prove that the violation is of a persistent nature.
Another factor on which the future of a conscript citizen depends is the classification of the violation. The decision on suitability is made after comparing the specialist with the Lown-Wolf characteristics, which were given above in the article.
Supraventricular arrhythmia
Any disturbances in the regulation of cardiac activity affect the functioning of the entire body. Thus, dangerous functional heart diseases include arrhythmia, which occurs due to changes in the rhythm of myocardial contractions. Supraventricular arrhythmia occurs in patients of any age and is often asymptomatic. To prevent complications of this pathology, drug and surgical treatment may be required.
What is supraventricular arrhythmia?
Arrhythmia is any disturbance in the natural rhythm of heart contractions. As a rule, we are talking about a rapid, inconsistent or slow rhythm of contractions. Further classification of the disease depends on the location of the pathological rhythm and the form of its course. In case of supraventricular arrhythmia, the lesion is located in the upper parts of the heart, the atria.
The heart is the only muscular organ in the body capable of continuous heavy work. A thick layer of heart muscle, called the myocardium, contracts rhythmically to transport blood from the organ's internal chambers to every cell in the body through blood vessels. Strict regulation of myocardial activity not only ensures the preservation of muscle structures, but also maintains the constancy of hemodynamics.
The heart has short periods of activity and rest. During the period of activity, the muscles contract and push blood into the vessels or adjacent chambers. A rest period is necessary for passive filling of the organ section with blood. If the heart muscle contracted without interruption, the cells would not receive the required amount of blood, and the vessels would remain empty. That is why external and internal regulatory factors maintain a constant speed, frequency and sequence of contractions. With arrhythmia, this mechanism is disrupted, causing the heart to work ineffectively.
Thus, supraventricular arrhythmias, the classification of which can be quite arbitrary, cause any disorders of cardiac activity within the atria.
8
24/7
Forms of pathology
Pathological supraventricular arrhythmias alter cardiac activity in various ways. The modern classification includes the following forms of the disease:
- Atrial fibrillation. The pathology is characterized by a sharp violation of the sequence and frequency of contractions of the myocardium of the upper parts of the heart. The efficiency of the pumping function is quite low, which is why blood cannot be completely transported to the lower part of the organ and arteries. This is the most common form of the disease, which has been diagnosed at least once in 85% of people over 65 years of age.
- Premature atrial contraction (extrasystole). After a single contraction of the myocardium, a period of rest, diastole, normally begins. With extrasystole, an additional impulse occurs in the muscle tissue of the organ, provoking a rhythm disturbance. This is a benign form of arrhythmia that rarely causes dangerous complications in patients.
- Supraventricular tachycardia is an increase in the frequency of contractions of the atrial myocardium. Normally, the heart contracts from 60 to 100 times per minute, but with tachycardia the frequency often ranges from 100 to 240 beats. This form can occur in childhood and adolescence. With tachycardia, blood pressure decreases and the efficiency of blood supply to tissues decreases.
- Atrial flutter. The instability of myocardial contractions in this case is less dangerous than with fibrillation, however, one form of arrhythmia can gradually transform into another. The heart rate may increase to 200 or more beats per minute. The pathology usually occurs in elderly patients with primary cardiovascular diseases.
- Sinus supraventricular arrhythmia is a disorder of heart activity that occurs due to improper functioning of the pacemaker. The main function of the sinus node is to generate an electrical impulse in a certain rhythm. This impulse spreads from the sinus node to other parts of the organ’s myocardium along the conduction pathways and causes successive contractions. Sinus node syndrome is characterized by impulses that occur too frequently or too rarely.
Most of the listed disorders are dangerous not only because of the resulting lack of blood supply to the organs. Supraventricular arrhythmia changes the pattern of blood flow and provokes the formation of blood clots. This is why stroke is a common complication of the disease.
Causes
Supraventricular arrhythmia occurs against the background of damage to the sinus node and the conduction pathways of the upper heart. This disease can be caused by congenital and acquired organ defects.
Main causes and risk factors:
- Damage to the myocardium and pathways due to ischemia and infarction.
- Atherosclerosis and impaired tone of the coronary arteries, as a result of which the heart receives insufficient blood supply.
- Congenital heart defects.
- Damage to the heart valves and blood vessels.
- Congestive heart failure.
- Thyroid gland dysfunction.
- Infectious or toxic damage to the heart muscle.
- Complications of surgery.
- Consumption of alcohol, caffeine and drugs.
- Side effects of medications.
- Obesity, smoking and sedentary lifestyle.
- High blood pressure.
- Lung diseases.
Doctors are not always able to determine the exact cause of the disease. Supraventricular arrhythmia of unknown etiology is often diagnosed in adolescents and is predominantly asymptomatic. In rare attacks, the arrhythmia itself, supraventricular extrasystole and other forms of cardiac dysfunction do not significantly affect the patient’s quality of life.
Symptoms
Supraventricular arrhythmia does not differ in the constancy of its symptomatic and clinical picture. Depending on the form and frequency of attacks of the disease, the patient may only occasionally experience mild discomfort or constantly suffer from acute disturbances in the blood supply to the organs. Thus, paroxysmal supraventricular arrhythmia and fibrillation have the most pronounced symptoms, while extrasystole is usually characterized by a mild course.
8
24/7
Possible symptoms and signs:
- Sharp chest pain and palpitations.
- Breathing problems.
- Weakness and dizziness.
- Impaired consciousness, fainting.
- Sweating.
- Muscle weakness.
- Anxiety and stress.
If complications arise against the background of arrhythmia, the symptoms become more intense. With congestive heart failure, patients may experience swelling of the extremities.
Diagnostics
If symptoms appear that indicate an irregular heartbeat, you should consult a physician or cardiologist. The doctor may suspect the disease even at the stage of clarifying complaints and studying the anamnesis, since arrhythmia is a characteristic complication of many primary diseases of the cardiovascular system. Further diagnostic tactics include instrumental studies and laboratory tests.
Diagnostic methods:
- Electrocardiography is the study and recording of the electrical activity of the heart using special sensors. The results of the study make it possible to identify any heart rhythm disturbances that arise during the process of obtaining a cardiogram. However, the method is ineffective for diagnosing hidden arrhythmia.
- A Holter study is a recording of a cardiogram for 24 hours or longer using a portable device placed on the patient’s body. The advantage of the method is that the patient is engaged in normal activities, and the device records any violations. Doctors do not need to analyze the complete cardiogram record, since the patient notes the time of occurrence of attacks of the disease. This is the optimal way to diagnose hidden arrhythmia.
- Echocardiography is a visual examination of the heart based on ultrasound. During diagnosis, the doctor sees the image of the heart on the monitor and evaluates its performance. The method allows you to detect the root cause of arrhythmia. Sometimes it is necessary to place a probe in the esophagus for a more accurate diagnosis.
- Bicycle ergometry is a study of the electrical activity of the heart (ECG) during physical activity. There are often cases when supraventricular arrhythmia manifests itself only against the background of increased muscle load. Thus, this method is also aimed at diagnosing the latent form of the disease.
- Angiography is a visual examination of the heart vessels to detect the cause of arrhythmia. The doctor injects a contrast agent into a vein and obtains an image of the heart's vessels using a scan. In this way, disturbances in the blood supply to the heart muscle are detected.
- Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are modern methods of organ imaging necessary for detecting small and large lesions. In cardiology it is also used to diagnose the cause of arrhythmia.
- Blood analysis. A test for enzymes and hormones can detect myocardial infarction or thyroid pathology.
The use of several examination methods increases the accuracy of diagnosis and the effectiveness of subsequent treatment.
Treatment and prevention
Chronic supraventricular arrhythmias, extrasystoles and other forms of cardiac arrhythmia may require medical and surgical treatment. The main goal is to stop attacks, permanently restore natural myocardial activity and prevent complications.
The main medicinal purpose is the group of antiarrhythmic drugs. These drugs are used during an attack for symptomatic treatment and on an ongoing basis. To prevent stroke, anticoagulants are prescribed to prevent the formation of blood clots. Glycosides and beta blockers that regulate heart activity are also used for treatment.
Surgical methods can be aimed at installing an artificial pacemaker or removing the source of arrhythmia in the myocardium. If the pacemaker normalizes the heart during an attack, then radical surgery can help completely get rid of the problem. Radiofrequency catheter ablation is the most effective and minimally invasive method of surgical treatment.
We should not forget that supraventricular arrhythmia, the treatment of which can be long and ineffective, can be prevented. If the patient already has primary heart disease, it is necessary to undergo regular examinations. Therapeutic diets, moderate exercise and giving up bad habits reduce the risk of arrhythmia. It is important to consult a doctor as soon as possible with suspicious symptoms and determine treatment and preventive tactics.
8
24/7
How to increase extrasystoles?
For those who are trying to avoid the army with such a disease and are wondering how to increase extrasystoles, it is worth keeping in mind that it is not always possible to increase them. But the following methods can help:
- Physical activity (before the examination it is good to run, jump, stress your body).
- Stressful situations.
- Emotional and physical stress.
- Drinking alcohol (not the best option, since you won’t be able to come to the medical examination drunk).
- Coffee or energy drinks.
Reviews
Dear readers, you can leave your feedback on whether they will serve in the army with extrasystole in the comments, your opinion will be useful to other users of the site!
Yaroslav:
They take it with such a disease. Medical commission specialists do not even consider this disorder to be a disease. Well, naturally, if there are already serious pathologies, but they are mainly found in old people.
Andrey:
I was diagnosed with such a disorder, but they accepted me into the army anyway, since my stage was mild. The doctors explained it to me, but I didn’t really understand it. I wasn't going to quit the army.