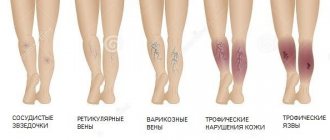
Varicose veins Signs, symptoms, causes. When to see a doctor, what questions to ask. Signs, symptoms, causes. When to see a doctor, what questions to ask. Examinations, tests and procedures for diagnosing varicose veins. Treatment of varicose veins. Vein care and prevention.
Veins are blood vessels that carry blood to the heart. Varicose veins occur most often on the legs and thighs. Thickened, twisted, or dilated sections of the vein are called varicose veins. As a rule, it is inherited and becomes more noticeable as a person ages.
Causes of varicose veins
There are many theories about why varicose veins occur, but the consensus is that defective/damaged valves in the veins are the cause. The valves prevent blood from flowing back inside the vein. They keep blood in the vein, which moves towards the heart. It is not clear what causes the valves to operate less efficiently. Some experts believe that the problem is hereditary. Some people may be born with abnormal vein walls.
Varicose veins can be aggravated by many factors:
- Pregnancy
- Prolonged standing
- Overweight
- Tension: Chronic constipation, urinary retention, chronic cough or any other condition that forces a person to strain for a long period of time causes an increase in the forces transmitted to the veins of the legs. These mechanisms also contribute to the formation of hemorrhoids, which are varicose veins located in the rectal and anal areas.
- Previous surgery or leg injury: These conditions interfere with normal blood flow through the channels.
- Age: In general, most older people experience some degree of varicose veins.
Advantages of minimally invasive methods for treating varicose veins:
When comparing minimally invasive methods for treating varicose veins (EVLO and RFA of veins), one can note their significant advantages over traditional surgical ones:
- no anesthesia or hospitalization required
- high treatment efficiency (up to 98%)
- the surrounding tissues are not damaged: no scars or bruises
- The operation lasts only about an hour
- no pain syndrome
- quick rehabilitation period
Our clinic is equipped with modern equipment for accurate, quick diagnosis and effective treatment of varicose veins. All equipment is reliably imported. Disposable consumables, including catheters, guarantee complete safety of treatment.
At the ABIA Clinic you will receive qualified diagnostics and assistance in the treatment of varicose veins. We work every day, without days off. Come!
When to see a doctor about varicose veins
If a person has varicose veins and has any of these symptoms and signs, they should see a doctor.
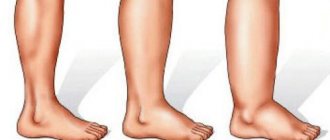
Inflammation, discoloration or ulceration of the skin or swelling of the calf or leg are more common with problems involving the deeper veins, especially a blood clot. Unexplained pain or swelling in the leg, in particular, suggests a blood clot. Varicose veins by themselves usually do not cause leg swelling.
Varicose veins themselves are relatively harmless, but can cause minor problems from time to time. If the skin covering the vein is thin or irritated, minor trauma from a blow or even shaving can cause bleeding. In this case, raising the leg and applying pressure for a few minutes should be enough to stop the bleeding. If, at any time, the patient feels chest pain or has trouble breathing, this may indicate the presence of a blood clot in the blood vessels of the heart or lungs.
Having varicose veins does not necessarily mean that a person will eventually develop a blood clot or that the blood clot somehow caused them. However, in rare cases, a clot increases pressure in the veins, blocking blood flow. This increased pressure will cause blood to flow back through weakened valves, creating varicose veins.
Are phlebologists and vascular surgeons the same thing?
It is immediately worth noting that a vascular surgeon and a phlebologist are different specialists. They deal with similar diseases, but with different specifics of the disease and treatment methods. Therefore, in some cases, patients with vascular diseases are sent to a phlebologist, in some situations to an angiologist, and in rare cases directly to a vascular surgeon. To understand the difference in these medical specialties, you need to understand that phlebology is part of vascular surgery, the most difficult when the patient urgently needs to take care of his health.
A surgeon in this area has a specific “area of responsibility” - these are all the veins, vessels, arteries that require surgical intervention. In all other cases, no matter what the nature of the pathology, even if it is an acquired disease, the vessels are treated therapeutically. If surgical intervention is unavoidable, the patient is sent straight to a vascular surgeon.
But still, phlebologist and vascular surgeon, what is the difference? To do this, let's take a closer look at the specifics of each of them.
Examinations, tests and procedures for diagnosing varicose veins
Diagnosing varicose veins is relatively easy. They are easily recognized simply by their characteristic appearance upon physical examination. The healthcare provider will likely perform a thorough medical history and examination, looking not only at the extent of the patient's varicose veins, but also at potential risk factors.
Any of several simple tourniquet tests can be done to determine the points of reflux.
Another useful device to help localize the extent of the problem is Doppler ultrasound. This test can rule out the presence of clots in deeper veins.
Magnetic resonance venography is another test performed when the duplex scan test is unclear. This test can even look for blood clots in the deep veins.
Blood tests (laboratory) are not helpful in diagnosing varicose veins.
Follow-up care after a diagnosis of varicose veins is usually only necessary if a person is considering surgery or sclerotherapy. Otherwise, contact a healthcare professional only if symptoms become severe or worsen.
Caring for varicose veins at home
- Raise your legs as high as possible. If possible, take half-hour breaks throughout the day to rest. It is very important to raise your legs above heart level to get the maximum effect, and do this for about half an hour each time.
- Wear compression stockings.
- If you are overweight, try to lose weight. Eat a high-fiber, low-fat, low-salt diet.
- Avoid alcohol.
- Contact your doctor if you have health problems such as chronic constipation, urinary retention, or chronic cough.
- Avoid wearing tight clothing such as belts or belts.
- Don't cross your legs when sitting.
- Walking more is good exercise and can help the muscles push blood out of the deeper venous system.
Risk factors for varicose veins of the lower extremities:
Phlebologists identify the main group of risk factors that lead to varicose veins of the lower extremities. Among them are:
- long-term static loads (long periods of standing, standing work, sitting work with legs bent at the knees)
- flat feet
- weight lifting, physical activity
- presence of the disease in relatives
- several pregnancies
- taking hormonal (contraceptive) drugs
- obesity (excess body weight)
- wearing uncomfortable shoes (high heels)
Under the influence of these factors and without appropriate treatment, varicose veins progress.
Treatment of varicose veins
Sclerotherapy involves injecting a chemical into a vein, which occludes it and causes scarring. Sclerotherapy is not entirely successful in relieving symptoms and preventing more varicose veins from forming. Complications associated with sclerotherapy include allergic reactions to the chemical used, burning or stinging at various injection sites, inflammation, skin ulcers, and permanent skin discoloration. Wearing compression stockings is usually recommended after sclerotherapy. Doctors who perform this procedure must have special training and experience to avoid complications.
Lasers are used as treatment for veins, but are often used in the treatment of smaller veins, medically called telangiectasia (local over-dilation of small vessels). These veins are small, measuring only up to 1 millimeter in diameter, and are dilated capillaries. Using lasers to treat these small vessels may cause changes in skin color or texture. Often multiple treatments are required. This technique is less useful in treating large varicose veins.
If a person has superficial thrombophlebitis, the doctor usually recommends warm compresses and pain medications. Additional treatment depends on whether the doctor thinks the patient may have an infection.
Surgical intervention for varicose veins
Several surgical procedures are available to relieve varicose veins, but not everyone with varicose veins is a candidate for surgery.
If the patient is pregnant or has recently become pregnant, it is advisable to wait at least 6 weeks after giving birth before considering this option because many varicose veins will disappear after pregnancy.
If the veins are only bothering the patient for cosmetic reasons and the patient is not concerned about pain or inflammation, then surgery may not be the best option.
Most surgical interventions are performed on an outpatient basis. The operation involves either ligating the vein (tying) or removing or retracting (pulling back) the smaller branches. There are risks and benefits to any surgery. These should be discussed with your doctor. Recurrence of varicose veins does occur and may be due to incompetent vein puncher or failure to ligate a vein in the groin.
Avulsion requires many tiny incisions and removal of varicose veins that have been outlined in the skin.
Vein stripping requires a recovery period of 5-10 days before returning to your regular routine. For just vein ligation, a few days off is more than enough. There is the possibility of permanent numbness from damage to the nerves in the skin (for this reason, only the vein up to the knee is usually exposed, and not the vein below the knee). The numbness is only mild and does not cause any future problems.
Endovenous laser therapy is a Lazarus method of destroying a vein. The procedure is usually performed in a doctor's office and takes about 30-45 minutes. A small laser is passed into the vein with guidance from an ultrasound machine. The laser is fired in several places, and the entire procedure is performed with some local anesthesia. Recovery is quick and involves minimal pain. The procedure is relatively new and, with the exception of some mild bruising and a feeling of numbness, no other effects were observed in the short term.
Radiofrequency ablation: Ablation is a similar technique to endovascular laser therapy, but it uses heat to destroy the vein. The probe is placed into the vein under ultrasound and, once in position, the vein is heated along its entire length. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia and takes about 30 minutes. Short-term results are excellent with radiofrequency ablation.
Ligation: Previously, this was a surgical treatment for varicose veins until the advent of the new treatments described above. It usually involved making an incision in the groin and tying off the saphenous vein where it enters the femoral vein. The procedure can be performed under local anesthesia.
The sooner a person begins the lifestyle changes described in the home self-care discussed earlier, the better the chances of preventing the formation of new varicose veins.
Prevention of varicose veins
A person cannot change their genes, but they can keep their weight under control, exercise, eat healthy foods high in fiber, and wear loose, comfortable clothes whenever possible. If a person is genetically predisposed to developing varicose veins, they may appear despite best efforts.
TED (thromboembolism - deterrent) stockings are the best non-surgical treatment for varicose veins. They prevent skin destruction and exacerbation of varicose veins. Most people have less swelling in their legs and less fatigue at the end of the day when using TED stockings.
Diagnosis of the disease
Modern methods of treating varicose veins on the legs allow you to achieve excellent results. But, as with any other disease, the correct diagnosis and timely treatment of varicose veins play an important role.
The CELT clinic has everything necessary to conduct a full diagnosis and make a correct diagnosis. We employ experienced phlebologists, candidates and doctors of medical sciences, and we have installed modern diagnostic equipment.
The main diagnostic methods include:
- conducting duplex scanning of the veins of the legs, which allows you to accurately determine the condition of the veins and, in accordance with it, select a treatment method;
- examination by a phlebologist surgeon who thoroughly knows the anatomy and physiology of veins and is able to identify concomitant diseases that may affect the development of pathological processes in the veins;
- Carrying out an X-ray examination of the veins after the introduction of a contrast agent into them - venography.
It is worth noting that varicose veins are dangerous due to their complications in the form of diseases such as pulmonary embolism, thrombophlebitis and thrombosis, which often lead to disability and death.