Each of us at least once in our lives noticed the feeling of a lump in the throat and experienced difficulty in swallowing. When this disorder becomes permanent, it significantly impairs quality of life. Swallowing disorders, or dysphagia, can develop for a number of reasons. Most often, this problem is faced by elderly people with weak tone of the muscles of the oropharynx. There are several methods for treating dysphagia, the choice of which is determined by the etiology and severity of the disorder.
Causes of dysphagia
Dysphagia can be caused by a variety of diseases and conditions: stroke, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), tumors and diabetes. In some cases, swallowing problems occur due to improperly fitted dentures or severe tooth decay. In addition, the disorder may occur as a side effect of treatment, for example during chemotherapy.
Rehabilitation after a stroke at home
Independent work of a person who has suffered a stroke and the participation of relatives and friends are necessary components of recovery. The home program includes the following activities:
- Reorganization of the patient’s life taking into account the defect. On the one hand, everyday tasks should be accessible, on the other hand, there needs to be motivation to get up once again and do something independently, to develop independence. It is necessary to observe the principle of the “golden mean”.
- Perform exercises prescribed by specialists at home. Depending on the patient’s condition, they can be done independently or with the support of relatives.
- Gradual increase in load in accordance with the level of restoration of cognitive functions.
- Emotional and psychological support from family. This includes both supporting the self-esteem and positive attitude of a person who has suffered a stroke, and reducing the influence of stress factors.
- Social and professional rehabilitation - imply a return to the usual circle of friends and activities; it is possible to change official employment to easier options.
- A speech therapist-aphasiologist comes to your home and conducts the necessary classes and performs speech therapy massage.
- You can purchase a Forbrain device to practice on your own.
Home rehabilitation does not imply the complete exclusion of specialists from the patient’s life. In accordance with the schedule, it is necessary to come for scheduled examinations, take medications, attend additional rehabilitation classes (physical therapy, physiotherapy, massages, Tomatis therapy, classes with Forbrain, etc.).
Swallowing phases
Choosing the most effective treatment plan for dysphagia depends largely on the cause of the problem and the stage at which swallowing difficulties occur. It is customary to distinguish three phases of swallowing:
- oral (oral) phase: entry of food into the oral cavity, chewing it, formation of a food bolus;
- pharyngeal (pharyngeal) phase: pushing the food bolus first into the middle and then into the lower part of the pharynx, which is accompanied by closure of the trachea, preventing aspiration of food into the respiratory tract;
- esophageal (esopharyngeal) phase: movement of the food bolus from the esophagus into the stomach.
Difficulty swallowing and lump in throat
Impaired swallowing is a sign of severe structural changes in the body, when a lump in the throat indicates stress or inflammatory diseases of the oropharynx. Specialists from the ENT Center clinic in Moscow will conduct an examination and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Impaired swallowing (dysphagia) and a lump in the throat can signal serious illnesses that require immediate treatment, or they can be a sign of simple fatigue. The specialists of our ENT Center clinic in Moscow will help you determine the cause and cope with the discomfort.
Causes and their symptoms
In infants, swallowing disorders most often have a congenital nature. Provoking factors include cerebral palsy, esophageal stenosis, gastroesophageal reflux disease, and congenital facial defects. In the latter cases, treatment is carried out surgically; in others, the use of special mixtures or tube feeding is required.
It is also necessary to differentiate between true dysphagia and pseudodysphagia. The first is accompanied by a violation of the act of swallowing, when the second only causes a sensation of a lump in the throat, making it difficult for food to move through the esophagus.
True dysphagia
True dysphagia is associated with the following reasons:
- Catarrhal processes in the esophagus, oropharynx. Inflammation causes dysphagia, hyperthermia, deterioration of general condition, a feeling of suffocation and a lump in the throat.
- Thyromegaly is associated with the growth of the thyroid gland, which compresses the esophagus, impairing swallowing function.
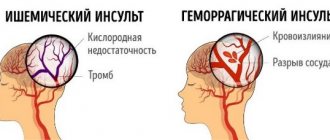
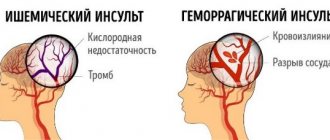
- A stroke is accompanied by difficulty swallowing, drooling, coughing, weakening of the muscles of the face and body, impaired coordination of movements, and speech function.
- Parkinson's disease. Swallowing disorders are associated with degerant processes in the central nervous system, which leads to damage and weakening of the muscles of the oropharynx, tremors of the limbs, and impaired vestibular function.
- Multiple sclerosis. The problem can be recognized by tremors of the limbs, muscle weakness, disturbances in chewing, swallowing and speech activity.
- Achalasia is associated with insufficient reflex weakening of the lower esophageal sphincter. The pathology is characterized by food dysphagia, regurgitation of undigested food, chest discomfort, flatulence, heaviness in the stomach, nausea and vomiting.
- Benign and malignant tumors of the neck, mediastinum, head. As the tumors grow, they can put pressure on the blood vessels, trachea and esophagus, disrupting the swallowing process and causing weight loss, chest pain, and suffocation.
Pseudodysphagia
Most often, swallowing dysfunction is functional. A person feels a lump in the throat, but there are no structural changes in the body. The cause may be stress or emotional overstrain (psychosomatics). However, most often organic causes of discomfort are caused by infectious and inflammatory diseases of the oropharynx (tonsillitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis, peritonsillar abscess), which are accompanied by a lump and sore throat, increased body temperature, and general malaise. Diagnostics
Frequent disruption of the act of swallowing, the feeling of a lump in the throat should not be ignored, as it can lead to (choking while eating and food entering the respiratory tract - aspiration) inhalation of food. Aspiration provokes acute and chronic pathologies of the lungs, including suffocation with a fatal outcome.
To determine the cause of discomfort, you need to contact several specialists - a therapist, ENT specialist, gastroenterologist, neurologist, psychotherapist. Only a comprehensive examination will determine the true cause.
To obtain a clinical picture, the doctor collects anamnesis and prescribes:
- general clinical and biochemical blood test, blood test for thyroid hormones;
- radiography (MRI or CT as indicated) of the head, chest, throat, videofluroscopy;
- esophageal manometry, gastroscopy;
- Dopplerography of head and neck vessels;
- electromyographic study.
Treatment
Treatment of lump in the throat syndrome and dysphagia is complex and depends on the cause. Patients are prescribed:
- antiphlogistic, antibacterial, antiviral therapy in the presence of catarrhal processes in the ENT organs and gastrointestinal tract;
- antidepressants, antipsychotics, tranquilizers for the relief of neurotic disorders;
- hypnosis, cognitive behavioral therapy, individual and group rehabilitation for mental health disorders;
- reflexology, physiotherapy;
- breathing exercises, physical therapy.
In the presence of obstructive processes or tumors, surgery is prescribed to remove them, and in case of inoperable esophageal cancer, stenting is prescribed.
How to feed a patient
If the act of swallowing is impaired, but the reflex is preserved, it is important to maintain the ability to feed independently. The patient is recommended soft, semi-liquid and liquid meals, which are taken under the supervision of medical personnel or people caring for him. It is important to eat at regular intervals and reduce your portion size. Foods that irritate the mucous membrane should be excluded from the diet.
If swallowing function is not restored within three days, the patient is fed through a nasogastric tube.
The ENT Center offers a wide range of services, which allows not only to determine the cause of dysphagia and lump in the throat, but also to provide the necessary treatment within the walls of our clinic. To do this, we employ specialists of various profiles - otolaryngologists, endocrinologists, psychologists. You can get acquainted with our doctors and make an appointment with them on the clinic’s website.
Dysphagia Treatment Methods
Treatment of dysphagia is often based on the use of compensatory and rehabilitative approaches. Compensatory techniques do not fundamentally solve the problem, but they can compensate for the weakness of the muscles that support the act of swallowing, and thereby reduce the symptoms of the disorder. This strategy involves changing the consistency of food to make it easier to swallow and performing positional treatment maneuvers (such as rolling or tilting the head) to help push food down the esophagus.
The rehabilitation method of treatment is aimed at changing the physiology of swallowing and restoring swallowing function, thereby achieving improvement in the long term. Treatments may include exercises to build strength in the muscles of the head, mouth, larynx and esophagus, as well as teaching swallowing techniques to block the airway. Currently, as part of rehabilitation treatment, various swallowing maneuvers are used - for example, “sip over the glottis”, when the patient inhales, holds his breath and then takes a swallow.
How is diagnosis carried out and methods of working with swallowing problems after a stroke selected?
Dysphagia is diagnosed using several methods. Video fluoroscopy, fiberoptic endoscopy, ultrasound, manometry, and finger method are used. The main task of these methods is to determine at what phase of swallowing the patient has problems. Only by determining this can you solve the nutrition problem, take safety measures and work on the process of restoring the functions of all organs involved in the process. In a situation where the swallowing process is impaired after a stroke, a decision may be made to insert a probe for the first time.
This decision is made on the basis of certified screening tests that help determine whether this patient can be fed through a tube or not, since this may pose a risk of aspiration. The probe and tracheotomy tube are placed temporarily. No more than a month. Because the probe, no matter what “friendly” plastic it is made of for the human body, as a result of constant contact can form bedsores in the nasopharynx, esophagus, and cause damage to the mucous membrane. And constant irritation of the mucous membrane leads to the separation of protective secretions, which can interfere with the process of classes with a speech therapist.
The probe is placed for safety reasons and allows you to solve the power issue. If swallowing is restored, the probe is removed and the person begins to swallow on his own. Then the speech therapist, together with the nutritionist, determines exactly how to feed such a patient - use mixtures, specially crushed food, thickeners (since water is sometimes more difficult to swallow than, for example, puree).
But if swallowing has not been restored within a month, a gastrostomy tube is placed. It has a larger diameter than the probe, which allows, unlike a probe, to freely feed the patient not only with special mixtures, but also with coarser food. It is important that it is possible to clean it.
Sometimes a gastrostomy tube is placed to make swallowing exercises easier. Because doing this with a probe is much more difficult. Therefore, a gastrostomy tube can last a lifetime or as long as needed to restore the swallowing process.
Therapeutic and surgical treatment
Rehabilitation therapy is a fairly effective method of treating dysphagia. However, in cases where the disorder is caused by a chronic condition such as GERD, or is associated with a particular shape and size of the esophagus, medical treatment or even surgery may be required. Conservative treatment includes taking antacids or other medications to control the symptoms of GERD. If the cause of swallowing problems is a decrease in the level of salivation or thickening of saliva, the patient may be prescribed special medications.
If the difficulty in swallowing is caused by the diameter of the esophagus being too small or its muscle tissue being too dense, the defect is usually corrected surgically, for example, by performing laparoscopic cardiomyotomy. During the operation, the surgeon cuts the muscles of the lower esophageal sphincter to allow food to pass more freely from the esophagus into the stomach.
Treatment
Stroke with impaired swallowing in patients is a fairly common occurrence in modern medical practice. As a rule, the swallowing reflex begins to recover approximately 2 or 3 weeks after the attack. The period of complete recovery, as doctors note, is individual for each patient. Some minor disturbances may remain for a very long time.
When feeding patients with swallowing disorders, certain rules should be followed. In this case, patients should regularly perform exercises, the purpose of which is to improve swallowing function and its complete restoration.
Before carrying out any therapeutic actions, it is necessary to adequately assess the patient’s capabilities. First, it is necessary to determine whether the patient can lift and hold his head. The patient should then be asked to cough and swallow saliva. After this, the patient can be given a spoonful of water. In cases where water flows freely from the mouth and the patient does not attempt to swallow it, you should continue feeding the patient through a special tube and wait a little while trying again.
Dental care and dysphagia
Sometimes the development of dysphagia can be associated with dental problems. Missing teeth, their poor condition, or poorly chosen dentures cause insufficient chewing of food. Although oral hygiene alone will not cure dysphagia, taking good care of your teeth and gums is important to preventing and reducing swallowing problems. Brushing your teeth with a fluoride toothpaste at least twice a day will help prevent the development of caries, plaque and tartar.
Often, a whole team of medical specialists is involved in the treatment of dysphagia: dentist, speech therapist, therapist and ENT surgeon. Together, they develop the optimal treatment strategy to eliminate or alleviate any manifestations of swallowing dysfunction.
What happens after a stroke?
Cerebral hemorrhage has a wide range of negative consequences, the severity and characteristics of which are mainly determined by the location and breadth of the lesion. The most common violations include:
- Deformation or complete loss of speech (aphasia). These include disorders of oral speech (motor form of aphasia), disorder of understanding of directed speech (sensory aphasia), disorders of reading and writing, and counting (acalculia).
- Problems with vision and hearing (cortical blindness and deafness when the primary visual or auditory cortex of the brain is affected).
- Agnosia is a disturbance in the process of perceiving information in one or another analyzer (for example, the holistic visual perception of objects may be impaired despite the fact that the visual organs and the primary cerebral cortex are intact).
- Disorders of orientation in space.
- Psycho-emotional disorders caused by physiological disorders. They manifest themselves as sudden mood swings and increased fatigue. The collision of the individual with reality requires adaptation to a new state, during which the person experiences anger from the inability to perform banal everyday actions, dissatisfaction with himself, a change in social role and professional activity.
- Movement disorders - manifest as paralysis (usually on one side of the body or certain muscles) and problems with the swallowing reflex (dysphagia). In the absence of adequate therapy, long-term recovery and even stabilization of the current condition is possible. In case of damage to the motor muscles and areas of the cerebral cortex, the development of another motor disorder is likely - apraxia, in which the program of action itself is destroyed while the physical ability to move is preserved. The brain “doesn’t know” how to carry out the most basic movement: pour sugar into a cup, comb your hair, and so on.
- Cognitive impairment, including impairment of memory, attention, voluntary thinking processes, as well as decreased intellectual capabilities.
Depending on the individual picture of the disease, disturbances may appear in all areas or only in one of them. Restoring the usual level of development of all these functions is possible with timely provision of medical care and high-quality rehabilitation.
Prevention of contractures
A side effect of a stroke is loss of mobility. Against the background of this functional disorder, contractures occur—limited mobility of the upper and lower extremities. Limitation of mobility leads to the fact that the patient cannot move, work with his arms and legs. This joint disease is easier to prevent than to treat later. Preventive measures:
- Correct body position - in bed, the patient should lie in a position close to normal physiological. To reduce muscle tone, you need to use rollers, pillows, and other means. Orthoses help keep your limbs in the correct position. To prevent your hand from clenching into a fist, it is convenient to use a massage ball, dumbbell, etc.
- Therapeutic gymnastics - exercises should affect all joints. Start gymnastics by warming up the muscles. For maximum effect, you can use a special gel. Therapeutic gymnastics lasts 20–30 minutes, includes 5–10 repetitions. A set of exercises must be practiced from the first days of the disease. This will avoid joint contracture and guarantee a better result.
Caring for a patient who has suffered a stroke requires great patience and perseverance from the caregiver.
Remember, high-quality home care, compliance with doctor’s orders, and emotional support are the conditions for the patient’s rapid recovery. In contact with
Rehabilitation after a stroke of a bedridden patient
The peculiarities of rehabilitation of a bedridden patient at home are that the main burden falls on relatives or a specially trained nurse who needs to:
- perform motor and speech exercises together with the patient;
- ensure hygiene, prevention of bedsores and everyday life;
- carry out massage at the minimum required level;
- monitor the intake of medications prescribed by your doctor.
It is also worth noting that all additional rehabilitation methods that are carried out in our center are also available at home. Specialists conducting classes can travel to your home for individual sessions.
If your relative or loved one has a stroke, it is necessary to begin rehabilitation as soon as possible. Our speech therapists-aphasiologists can come to the hospital for early rehabilitation. Call tel. and the administrator will answer all questions and help you select an aphasiologist.