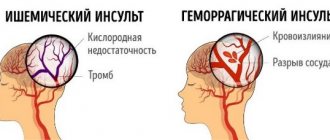
Temperature during a stroke is an indicator of cerebral hemorrhage, hemorrhagic stroke. With an ischemic stroke, the temperature in most cases is slightly lowered; with a hemorrhagic stroke, the temperature rises. An increase in body temperature is a protective reaction, which is the response of the body's immune system to various infections and injuries. With a hemorrhagic stroke, damage to blood vessels occurs, bleeding into the brain tissue occurs - the body reacts with an increase in temperature. The larger the area of brain damage, the higher the temperature.
Upon admission to the neurological department of the Yusupov Hospital, the patient receives qualified care. A neurologist examines the patient, prescribes tests and treatment. As the temperature rises, metabolic processes in brain cells intensify, and poor circulation causes oxygen starvation - both of these processes cause extensive brain damage. Timely medical care reduces the risk of developing severe complications. After a stroke, it is difficult to deal with high fever - antipyretics can aggravate the condition of a patient with a hemorrhagic stroke, and in the case of an ischemic stroke cause hemorrhagic transformation. Hemorrhagic transformation is the saturation of the brain area with blood, which enters beyond the vessels into the focus of cerebral infarction. Fever and extensive brain damage often lead to the onset of coma in the patient.
Temperature after stroke: causes and treatment
Temperature during a stroke is a very important indicator of the patient’s condition. It is most often used to determine the degree of brain damage in a patient. Temperature readings up to 38 degrees are considered to be the maximum permissible. Stroke studies have shown that the majority of stroke patients had a normal mean temperature upon admission to the clinic. In patients with extensive strokes, the temperature began to rise after a few hours (4-6) to 40 degrees. In patients with moderate strokes, the temperature rose to 40 degrees 12 hours after the stroke. A mild stroke most often occurs without fever or with a slight rise in temperature.
Ear congestion
Fungus
Allergy
20838 04 February
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Ear congestion: causes, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Congestion in the ear or ears occurs as a result of a violation of sound perception and is characterized by various sensations, which may include deafness, a feeling of squeezing and heaviness, and the sound of one’s own voice being too strong. Ear congestion, regardless of the causes of its occurrence, is difficult for the patient to tolerate and, as a rule, requires the help of a specialist.
Types of ear congestion
Blockage in one or both ears may be accompanied by pain, tingling, noise or ringing in the ears, and dizziness. In some cases, congestion disappears after swallowing.
A dangerous symptom is ear congestion accompanied by fever, headache, discharge from the ear (purulent or bloody), and foreign body sensation.
Ear congestion does not always indicate a pathological process.
This condition can be caused by water getting into the ear, pressure changes
during air travel or diving to depth.
Sometimes too strong and incorrect blowing of the
nose from two nasal passages at the same time leads to a blocked ear (ears), which is associated with an increase in pressure in the middle chamber of the ear due to a sharp intake of air from the Eustachian tube.
Taking certain medications
(antibiotics, psychotropic substances) has a toxic effect on the ear, causing the development of congestion and hearing loss.
Diseases that can cause ear congestion.
Earwax
blocking the ear canal. Attempting to remove earwax yourself using improvised objects significantly increases the likelihood of pushing the plug deeper into the ear and sticking to the eardrum (this increases the risk of injury to the eardrum, which leads to complete or partial hearing loss). In these cases, the condition of congestion in the ears is accompanied by excruciating pain, noise, dizziness and nausea.
Mycotic, or fungal, infection of the external auditory canal
. Infection with fungi can be complicated by narrowing or blockage of the ear canal with a feeling of fullness in the ears. The spread of fungi in the ear is aggravated by hearing aids, in-ear headphones, and inflammatory diseases of the ear. The main signs of the disease are itching, ear congestion and resulting hearing loss, and increased sound of one’s own voice in the affected ear.
Damage to the external auditory canal and middle ear structures
may be accompanied by hearing loss and congestion. Bleeding and the formation of a blood clot that blocks the ear canal lead to deterioration in sound transmission. In addition, injury to the eardrum is possible during cleaning of the ear canal, a sudden change in pressure, or a strong blow to the outer ear. In this case, sharp pain occurs, which is replaced by congestion, ringing, noise and hearing loss.
Acute inflammatory diseases
accompanied by swelling and sometimes the formation of purulent contents.
They can lead to ear congestion and hearing loss. In particular, with otitis media of the middle ear (tympanitis),
the tympanic cavity and auditory tube are involved in the inflammatory process. Swelling, which narrows the lumen of the auditory tube, and suppuration of the soft tissues cause ear congestion and hearing impairment. As a rule, the infection enters this sterile cavity from the Eustachian tube, which is directly connected to the nasopharynx.
In children of the first and second year of life, acute otitis may occur when breast milk or formula enters the nasopharynx during regurgitation.
In older children, otitis media and congestion can be caused by
inflammation of the adenoids
, the lymphoid tissue responsible for the local immunity of the nasopharynx and closing the openings of the auditory tubes in the nasopharynx. The anatomical proximity of the adenoids and the auditory tube ensures the rapid transition of infection from the nasopharynx to the ears. In addition, enlarged adenoids can block the openings of the auditory tube, which causes a feeling of stuffiness.
Allergic reactions
can also lead to acute inflammation and swelling of the middle ear.
Otitis externa
characterized by inflammation of the external auditory canal. Congestion in the ear in this case occurs due to swelling of the tissues of the ear canal.
If the disease is caused by a foreign body entering the ear canal
, then swelling and congestion are complemented by a picture of severe irritation. The patient complains of severe itching, pain, a feeling of fullness, and heat in the ear area. The pain intensifies with chewing movements.
For furunculosis
In the external auditory canal, the picture of the disease is aggravated by a closed space where the inflammatory process develops. Increasing pain in the ear is complemented by its irradiation to the corresponding half of the head. The patient cannot lie on the painful side. Due to severe swelling of the tissues of the external auditory canal, sound transmission into the affected ear is disrupted, and a feeling of stuffiness occurs.
Among the anatomical and postoperative defects
that cause ear congestion include deviated nasal septum, narrowing of the nasal passage due to hypoplasia of the nasal wings, and stenosis of the external nasal valve.
Impaired nasal breathing leads to frequent runny nose, infection of the nasal sinuses and, as a consequence, to the transition of the inflammatory process to the auditory tube.
Ear congestion in these cases appears on the side of the narrow nasal passage. The same consequences occur after operations in the nose area.
Sensorineural hearing loss
occurs due to damage to any part of the auditory nerve. Most often, this is an irreversible phenomenon, the symptoms of which include imbalance, dizziness, nausea, fullness and noise in the ear, and poor perception of low sounds. The causes of sensorineural hearing loss can be previous infectious and vascular diseases, tumor processes, injuries, and toxic effects of various substances.
Meniere's disease
is a non-purulent disease of the inner ear, which is accompanied by congestion. An increase in the volume of lymph in the labyrinth of the ear leads to increased pressure and attacks of progressive deafness, tinnitus, and sudden dizziness. In most cases, one ear is affected first. The disease begins either with attacks of dizziness or with deterioration of hearing, which is completely restored between attacks. However, after a few years, hearing loss becomes irreversible.
Myofascial pain syndrome, temporomandibular joint diseases
. Patients with myofascial pain syndrome, which is associated with disruption of the masticatory muscles and limited mobility of the lower jaw, may also complain of ear congestion. In addition, the disease is accompanied by headaches and facial pain, difficulty opening the mouth, and clicking in the temporomandibular joint.
The root cause of the syndrome is spasm of the masticatory muscles.
A similar clinical picture is also given by diseases of the joint itself caused by malocclusion. Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels, increased blood pressure
. Congestion in the ears due to damage or narrowing of blood vessels is explained by a deterioration in the blood supply to all tissues, as well as impaired circulation in the area of the inner and middle ear.
Vasomotor rhinitis, or runny nose during pregnancy
occurs under the influence of hormonal changes and is characterized by impaired vascular tone and the release of mucous secretion. With allergic rhinitis, the clinical picture of the disease is almost the same, but the provoking factor is not hormones, but a specific allergen. Swelling of the mucous membrane and narrowing of the nasal passages lead to obstruction of the auditory tube and cause ear congestion.
Tumors in the area of the auditory canal, auditory tube and inner ear
– the most serious cause of ear congestion. Among them should be called cholesteatoma - a tumor-like formation that consists of epidermal cells impregnated with cholesterol. Cholesteatoma is characterized by slow but steady growth. Forming in the middle ear, it can spread to the outer and inner ear, causing congestion and a feeling of heaviness in the ear, purulent discharge, swelling and redness of the auricle.
Which doctors should I contact if I have ear congestion?
If ear congestion occurs, you should contact an otolaryngologist. In the future, you may need to consult a neurologist, cardiologist, or allergist.
Diagnosis and examinations for ear congestion
To diagnose the disease that caused ear congestion, a careful questioning of the patient, examination of the outer ear and ear canal to the eardrum, and an audiometric examination are necessary. The infectious nature of the disease is determined on the basis of the clinical picture, otoscopy data and culture of the discharge.
Complications after a stroke
After a stroke, fever often occurs due to the following complications:
- the damage occurred over a large area of the brain;
- swelling of brain tissue has developed;
- during a stroke, the thermoregulation center in the brain was damaged;
- complication after a stroke – pneumonia;
- an allergic reaction to medications developed.
In cases where the cause of the increase in temperature is its central genesis, doctors perform craniocerebral hypothermia. The brain is cooled through the outer covering of the head using special equipment. This method increases the brain's resistance to oxygen starvation, reduces the risk of developing cerebral edema, relieves existing edema, and reduces tissue temperature. Brain cooling to reduce temperature is carried out using two methods - non-invasive and invasive. The invasive method involves administering a cooled saline solution intravenously. In this case, it is possible to regulate the temperature, but there are a number of side effects - bleeding, vascular thrombosis. A non-invasive method is cooling the brain through the outer covering. For cooling, both heating pads with ice and special devices in the form of a helmet for the head are used.
How to provide first aid for a stroke
There is a clear algorithm for providing first aid to a person suffering from a stroke :
- Call a medical team . To do this, you need to dial 103 from a landline phone. If you happen to have a smartphone at hand, then the call is made to the single number 112. The doctor must immediately be informed that the person is unwell and there is a suspicion of a stroke.
- The victim must be laid on a flat surface so that his head is higher than his body. They take off his glasses and remove his lenses. If possible, you need to help him get removable dentures.
- If there is no consciousness, then you need to open the patient’s mouth slightly and turn his head to the side . This is done to prevent aspiration of vomit. It is imperative to listen to the patient’s breathing.
- For better access to fresh air, it is recommended to open a window or vent..
- Before the arrival of the medical team, it is necessary to prepare documents, if any..
Doctors need to be informed about the person’s illnesses, as well as what medications he is taking. It is prohibited to give the victim any medications. Medication correction should be carried out by emergency physicians. You should not try to give water or food to a person. This may make the situation worse.
If the patient falls and has an epileptic attack, there is no need to unclench his teeth or try to hold him. It is necessary to protect the victim from injury. To do this, place a soft object, such as a pillow, under his head. If a stroke with an epileptic attack happened on the street, then you can use a jacket or other suitable thing. Foam flowing from the mouth is wiped away with a cloth. The head should be elevated at all times.
There is no need to try to bring a person to his senses with ammonia. Until the end of the attack, it should not be moved from place to place.
If breathing stops, resuscitation measures must be started immediately. To do this, perform a heart massage and breathe mouth to mouth or mouth to nose.
Treatment of stroke at Yusupov Hospital
The neurological department of the Yusupov Hospital is equipped with modern diagnostic equipment, which allows you to diagnose a stroke and quickly determine the extent of brain damage. The hospital team consists of professors and doctors of the highest category, qualified medical personnel. In the hospital, you can undergo studies using ENMG, VEEG, EMG, duplex scanning, neuroimaging and other modern techniques. The neurological department accepts patients with strokes of all severity, the doctor develops a treatment program based on the patient’s condition.
The patient receives medication, round-the-clock care, therapeutic procedures, and psychological assistance. After the patient’s condition has stabilized, rehabilitation specialists work with the patient. A team of specialists constantly monitors the patient’s condition and makes new appointments. Elderly people require a lot of attention - after prolonged physical inactivity, decompensation of the vestibular apparatus occurs. A rehabilitation specialist develops a program with an exact balance between the load, the severity of the stroke and the condition of the blood vessels and heart. You can make an appointment with a neurologist at the Yusupov Hospital by phone.
How to provide first aid for a stroke
There is a clear algorithm for providing first aid to a person suffering from a stroke :
- Call a medical team . To do this, you need to dial 103 from a landline phone. If you happen to have a smartphone at hand, then the call is made to the single number 112. The doctor must immediately be informed that the person is unwell and there is a suspicion of a stroke.
- The victim must be laid on a flat surface so that his head is higher than his body. They take off his glasses and remove his lenses. If possible, you need to help him get removable dentures.
- If there is no consciousness, then you need to open the patient’s mouth slightly and turn his head to the side . This is done to prevent aspiration of vomit. It is imperative to listen to the patient’s breathing.
- For better access to fresh air, it is recommended to open a window or vent..
- Before the arrival of the medical team, it is necessary to prepare documents, if any..
Doctors need to be informed about the person’s illnesses, as well as what medications he is taking. It is prohibited to give the victim any medications. Medication correction should be carried out by emergency physicians. You should not try to give water or food to a person. This may make the situation worse.
If the patient falls and has an epileptic attack, there is no need to unclench his teeth or try to hold him. It is necessary to protect the victim from injury. To do this, place a soft object, such as a pillow, under his head. If a stroke with an epileptic attack happened on the street, then you can use a jacket or other suitable thing. Foam flowing from the mouth is wiped away with a cloth. The head should be elevated at all times.
There is no need to try to bring a person to his senses with ammonia. Until the end of the attack, it should not be moved from place to place.
If breathing stops, resuscitation measures must be started immediately. To do this, perform a heart massage and breathe mouth to mouth or mouth to nose.
Preventive actions
Prevention refers to a set of measures aimed at preventing the development of brain strokes, their relapses, and subsequent complications. Necessary:
- Conduct courses of treatment in a timely manner for existing chronic pathologies.
- If you experience frequent pain in the heart area, be sure to check with a cardiologist.
- Monitor blood pressure.
- Eat properly.
- To refuse from bad habits
Stroke is one of the most dangerous diseases, often resulting in lifelong disability and even death. A timely, competent response to the first symptoms of the disease, an accurate assessment of the patient’s condition, as well as correctly prescribed treatment will facilitate recovery and improve the prognosis.