A stroke is a sudden disruption in the circulatory system of the brain, which leads to damage to various parts of the brain that lose functionality.
Along with the blood, the supply of oxygen to the brain stops. This leads to disruption of cell nutrition.
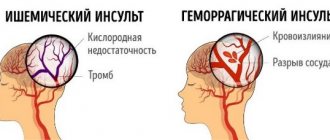
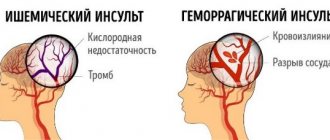
The short answer to the question of how long people live after a stroke depends on the type of brain stroke, as well as how serious the consequences are - with ischemic, mortality in the first 72 hours is no more than 15%; for hemorrhagic – no more than 35%; the most dangerous is subarachnoid hemorrhage - survival rate in the first 72 hours is about 50%. Details are below.
Features of stroke in older people
WHO reports that 5-6 million people suffer from strokes every year. It is one of the 10 most common causes of death. In Russia, the incidence rate is 450 thousand people annually. The disease occurs in people of all ages, but the highest risk of morbidity is in people over 60 years of age (75% of morbidity cases from general statistics). The risk of getting sick doubles every ten years.
Stroke occurs more often in men. In women, more cases are observed over the age of 70-80 years. There is a genetic predisposition to strokes in children whose parents suffered from cerebrovascular accidents.
Vascular pathologies are typical for older people. Due to age-related changes in the body, blood circulation deteriorates, blood vessels become brittle, blood pressure increases, atherosclerosis develops, and heart function is disrupted.
Vascular problems are associated with age-related changes in the nervous system: a decrease in the mass and volume of the brain, degenerative changes in the white matter, deterioration in the activity and atrophy of neurons, pathology of the cerebral ventricles and other reasons. All this creates the basis for the development of a stroke.
In old age, stroke is difficult to bear. It is difficult to select an effective treatment and make a prognosis for the patient’s future condition. There is little chance of full recovery; many people remain disabled for life. There is a high risk of re-bleeding.
Stroke is a serious health problem for retirees. More than 50% of cases of morbidity lead to coma. Recovery after a stroke is difficult and lengthy; there is no guarantee of a full return of body functions.
If you notice the first signs, you should immediately call an ambulance. This is very important: most deaths are due to the fact that a person did not receive medical assistance on time. It is important to recognize an attack as early as possible, provide medical assistance and then carry out long and thorough rehabilitation. In this case, the chances of a good recovery are high.
Forecast
The prognosis depends on many factors: timeliness of assistance provided, general health, quality of treatment. In addition, the consequences of a stroke depend on the type of stroke, namely the area of the brain affected.
Let's look at the main types of stroke by area and their health consequences.
Major stroke
The outcome for the elderly is unfavorable, since the patient does not fully recover. The result is disability.
Unilateral stroke
The prognosis is influenced by the extent of the lesion and the timeliness of medical care. Often the outcome is death or paralysis. Only in isolated cases does the patient recover completely.
Brainstem stroke
The most dangerous species, often leading to death. The survivors remain disabled.
Cerebellar stroke
The prognosis depends on the extent of the lesion. If treatment is started in a timely manner and the patient is properly cared for during the rehabilitation period, he can fully or partially recover. However, most stroke survivors suffer from impaired mobility, which causes them to walk with support.
Spinal stroke
The prognosis is generally favorable and the mortality rate is low. If treatment is not started in time, the patient can be paralyzed. Problems in the functioning of the pelvic organs cannot be ruled out.
If you are over 80 years old
For people over 80 years of age, the prognosis is rarely good, regardless of the type of stroke. The fact is that at such a respectable age the condition is complicated by existing chronic diseases and weakened immunity, which reduces the chances of recovery.
Elderly people at this age most often fall into a coma, during which they do not breathe on their own. Their blood pressure decreases, which leads to impaired blood circulation. Fever may occur. Lives in a coma for an average of 7 days, after which he dies.
In less severe cases (with a unilateral stroke), the patient remains disabled due to paralysis of the side of the body opposite to the lesion and other disorders.
Causes
All the reasons why strokes develop in younger people are also present in older people. But older people are more susceptible to illness due to atherosclerosis, cardiovascular problems and chronic ailments.
Let's look at the main causes of stroke and risk factors for stroke in the elderly:
• Arterial hypertension or persistent high blood pressure. The cause occurs in 70% of older people. After 80 years, it often leads to ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes. • Heart failure and previous myocardial infarction. • Increased blood cholesterol levels. Metabolism deteriorates, because of this cholesterol is processed worse and remains on the vascular walls. Blood flow is disrupted, causing blood clots to form. • Atrial fibrillation. The rhythm of heart contractions is disrupted, causing uneven blood flow to develop. Because of this, blood clots form and spread throughout the body. Once in the brain, such a blood clot can cause a stroke. • Excess weight and impaired metabolism. They increase the load on the heart and provoke illness. These reasons are associated with a sedentary lifestyle and lack of physical activity. Because of them, blood circulation slows down and excess weight is gained. • Diabetes mellitus also causes stroke. • Bad habits: alcohol abuse and tobacco addiction. They harm the heart and blood vessels. • Self-administration of medications that affect heart function and blood circulation. • Stress, nervous tension, excessive mental stress. This is especially dangerous for those who have had a stroke before.
The cause may be atherosclerotic or cholesterol plaque, vascular spasm due to hypertension, rupture of thin capillaries due to large blood clots entering them, cessation of blood circulation in the brain due to a sharp decrease in blood pressure.
If a person has two or more factors from this list, the risk of developing a stroke with severe consequences is increased.
Types of stroke
Stroke is classified into three types:
1. Hemorrhagic. Its cause is a rupture of a brain vessel, which causes blood to accumulate in the surrounding tissues. Neurons are deformed and their functionality is impaired. Hemorrhagic stroke occurs due to bleeding in the brain into the white matter area. The disease is provoked by sudden surges in pressure that the vascular walls are unable to withstand. The vessels rupture, and hematomas form at the site of the ruptures. The resulting tumor puts pressure on the diseased area of the brain, causing its functioning to be disrupted. 2. Ischemic. It develops due to poor blood supply to tissues, since arterial blood is difficult to reach certain parts of the brain. This is facilitated by thrombosis of the vessel. Blood circulation stops, the diseased area of the brain loses oxygen and nutrients, and cells begin to die. This type of stroke is common in old age. Vessel rupture can also occur due to a detached plaque or after a myocardial infarction. 3. Subarachnoid hemorrhage. Occurs due to a rupture of an aneurysm or injury to a vessel, resulting in an accumulation of blood mass in the brain cavity.
What types of stroke do older people suffer from? In elderly patients, all three types can occur, but they are most susceptible to the ischemic type.
A stroke can be:
1. acute (symptoms appear sharply and increase); 2. subacute (slower development - up to a week with a gradual increase in symptoms); 3. chronic (the disease develops gradually - from a week or longer, it is rare).
Symptoms
Brain cells that have lost normal blood supply due to a stroke die. Usually this immediately manifests itself in a person’s condition.
The main signs of a stroke are as follows:
• Dizziness and severe headache; • Loss of consciousness, fainting; • Impaired coordination of movements, disorientation in space; • Problems with speech and pronunciation: poor diction, the patient cannot pronounce sounds, speaks slowly; • Absent-mindedness; • Deterioration of vision: darkening of the eyes, blurred vision.
A stroke in an elderly person can happen at any time of the day, but most often occurs in the early morning or evening. The condition may worsen over several days as bleeding in the brain occurs slowly. Symptoms may wax and wane over several days.
There are certain initial signs that indicate an approaching attack. Older people often don't give them the attention they deserve, but they shouldn't be ignored or overlooked. If you find them, be sure to consult a doctor.
Stroke manifests itself differently depending on the type and location.
Hemorrhagic stroke manifests itself clearly:
• Acute and sharp pain; • Foggy consciousness, lethargy, fainting; • Cramps throughout the body; • Nausea and vomiting; • Feeling as if someone had hit the head; • Pupil dilation – on the side of the head where the stroke occurred.
Ischemic stroke manifests itself more easily and develops gradually. A person has a headache and also experiences these symptoms:
• Memory problems; • Numbness of the muscles at the back of the head; • Incorrect speech; • Paralysis, paresis; • Dementia and other mental disorders.
An ischemic stroke may go away on its own over time. Symptoms increase, then gradually weaken, and the person’s health returns to normal.
First aid for stroke
A quick reaction from relatives who can provide first aid to an old person after a stroke will help prevent serious consequences and provide the necessary treatment in the future.
So what needs to be done:
- position the patient so that the legs are 25–30 degrees below the head;
- try to determine blood pressure and pulse indicators, record them;
- if the patient has lost consciousness, do not try to move him to the bed, just lay him down correctly and leave him alone;
- After the ambulance doctors arrive, talk clearly and intelligently about the person’s previous condition, the medications he is taking, and the visible symptoms of the attack.
There are actions that doctors strictly prohibit taking. Under no circumstances should you:
- use ammonia when recovering from a fainting state;
- hold limbs during convulsions;
- try to offer the patient medications that may get stuck when swallowing (it is better to completely stop taking medications until specialists arrive).
We recommend
“Low blood pressure in an elderly person: treatment and prevention” Read more
Stroke in older women and men: differences
Men suffer less from the consequences of a stroke, and they also have fewer deaths. In women of the same age, these rates are higher.
In women, the following factors increase the risk of suffering from a stroke:
• Vascular problems and heredity; • Difficult pregnancy in the past; • Long-term use of hormonal drugs; • Abundance of stressful situations in life; • Passion for alcohol and smoking.
How do stroke symptoms differ in older women from men? Men are characterized by a “classic” set of symptoms; in women, symptoms resemble migraines:
• Headache in one area of the head, for example, in the temple; • Deterioration of lateral vision, blurriness of small details, points in front of the eye on the affected side; • On the affected side of the body, the limbs tingle and go numb; • The woman speaks unclearly; • There are problems with memory, disorientation in space and time; • Prolonged hiccups occur; • Outbursts of aggression occur.
Diagnostics
How to diagnose a stroke at home
Every person needs to know the signs of a stroke. Being able to recognize a dangerous condition in a loved one in time means saving his life and preserving his health. Remember that anyone can have a stroke.
A stroke affects the nerves of the head and nearby limbs, causing muscles to lose healthy functionality.
Hemorrhagic stroke manifests itself sharply and clearly. You can recognize a dangerous condition by doing a few simple tests:
1. Ask to smile. Normally, both sides of the face are symmetrical, and smiling is effortless. A sick person will not be able to smile straightly; one side of the face will sag and be “late.” 2. Ask to raise both hands and hold them in front of you for a few seconds. A healthy person will be able to raise both arms at the same time, and they will be at the same level. With a stroke, one arm will lag behind the other, or it will not be possible to raise it at all. 3. Ask to repeat a simple phrase. A healthy person will be able to do this, speech will be clear and understandable. The patient's speech is slurred, incomprehensible, and it is difficult to pronounce words. 4. Ask to stick out your tongue - it will tilt to the side. 5. Ask to bare your teeth. You can bare your teeth with only one half of your mouth. 6. Ask to frown. One eyebrow will be furrowed more than the other.
If a person fails these tests, he may be suspected of having a stroke. Call an ambulance immediately.
Ischemic stroke can be detected at home by hypertensive crises and ischemic attacks. This results in a lack of blood supply to the brain. For diagnosis, you can use L. S. Manvelov’s questionnaire. Each “yes” answer receives a point if the symptom has been observed at least once a week over the past 3 months:
1. Headache due to overwork and changes in weather. It is not associated with hypertension, the nature of the pain is non-localized; 2. Tinnitus – regular or periodic; 3. Short loss of consciousness and dizziness when moving (getting out of bed/chair, bending over); 4. Short-term memory loss; 5. Lethargy, insomnia, decreased performance.
If a person answered yes to two or more points, it can be assumed that a stroke will develop in the near future. You need to go to an appointment with a therapist and get a referral to a neurologist from him.
Diagnostics in the hospital
To determine the type of stroke, different techniques are used: magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography, electroencephalography, head X-ray, cerebrospinal fluid examination and blood tests.
The data obtained helps determine the type of stroke, the location of the pathology, and discover connections with parts of the brain. The sooner the patient is taken to the hospital, the more accurate his examination will be and the more effective the assistance. In the first 6 hours after an attack, medical care is most effective. This is especially important in acute strokes, which can severely damage the brain within 3-5 days.
How not to miss a stroke in an old person
We have already said that a stroke in patients over 80 years of age has irreversible consequences. Therefore, as soon as you notice the above signs of illness in your loved ones or acquaintances who have crossed the eighty-year mark, immediately seek help from specialists.
If in young people, during a stroke, only a couple of symptoms appear, then in an old person, a stroke manifests itself in all its diversity, is bright and difficult.
You should be alert to general symptoms: dizziness, headache, poor coordination of movements, numbness on one side of the body.
Hemorrhagic stroke is characterized by the following symptoms:
- sudden and severe headache;
- rapid breathing accompanied by wheezing;
- redness of the skin, especially the face;
- a sharp increase in pressure;
- intermittent heartbeat;
- possible vomiting;
- numbness of the limbs and facial muscles.
In the first minutes of a hemorrhagic attack, immediately after a vessel ruptures, a person may lose consciousness. Depending on how the intracranial hemorrhage is localized, loss of vision and hearing can occur. Vomiting during a stroke can lead to aspiration in an old person, and therefore to respiratory arrest. In the most severe forms, patients experience seizures or even coma.
Signs of ischemic stroke:
- nausea and vomiting due to headache;
- sluggish, impaired movements, inability to lift or even move limbs;
- double vision when looking at objects, a blurry picture before the eyes;
- dizziness and disorientation;
- sensory disturbance;
- numbness of the mouth, inability to speak.
In the ischemic form, symptoms appear gradually. The acute phase is considered to be the first 6 hours after the attack.
If you suspect that an old person has had a stroke, then even before the team of doctors arrives, you can independently determine the primary diagnosis by performing simple tests:
- Ask the patient to smile. If a stroke occurs, one part of the face will remain motionless.
- Have the person try to simultaneously raise or at least stretch their arms forward. In case of a stroke, this can be done with only one hand.
- Try to talk to the victim, pay attention to his articulation. If cerebral circulation is impaired, it is almost impossible to pronounce words.
- Invite a person to stick out his tongue; the tip of the patient will certainly deviate to the side, in the direction of the lesion in the brain tissue.
Even if only one of the tests failed, the patient most likely had a stroke. In this case, there is no time to waste, but it is necessary to provide him with first aid.
Temperature during a stroke in an old person is an important indicator for determining the severity of the attack. The later a person’s temperature rises from the onset of a stroke, the more unfavorable the prognosis for the patient, and the greater the risk of death. High temperature is also a critical indicator that will subsequently prevent the body from recovering. This is due to the fact that hyperthermia worsens the hemorrhage and the hematoma begins to put pressure on the brain.
We recommend
“Recovery of older people after a stroke: tips and practical recommendations” Read more
Treatment and rehabilitation
First aid
If you detect the first signs of a stroke, you should immediately call an ambulance (112 - from a mobile phone, 03 - from a landline).
Next, do the following:
1. The patient's head should be elevated. Lay him on the bed and place pillows under his head, shoulders, and upper back; 2. Open the window to allow fresh air; 3. Unbutton all tight clothing: shirt, belt, tie; 4. Measure your blood pressure; 5. If the patient is vomiting, turn your head to the side - the vomit should not enter the respiratory tract.
No medications should be given until doctors arrive. If the patient has lost consciousness and fallen into a coma, artificial respiration and chest compressions must be performed. In a difficult situation, continue to fight for the life of the victim until the end - there is a chance of salvation. People who suffered severe attacks were saved even in the most difficult cases. Remember that only medical professionals can confirm death. Help the patient and wait for the ambulance.
Treatment in hospital
After arriving at the hospital, the patient is sent to the neurovascular department of the hospital, where he undergoes therapy. The patient must normalize blood pressure, prevent swelling and hypoxia of the brain, restore healthy brain function, normalize blood counts and prevent disability.
An elderly person who has survived a stroke needs constant medical care and care from loved ones. Measures are taken depending on the type of stroke:
• Ischemic: reperfusion treatment. Medications are used along with mechanical treatments to restore healthy blood flow in the blocked vessel. • Hemorrhagic: treated with hemostatic agents that lower blood pressure. In case of major hemorrhage, surgery is performed. Surgery can remove blood clots and reduce hematoma.
In the treatment of stroke in the elderly, drugs are used to lower blood pressure, normalize cholesterol, fight blood clots, improve heart function and circulation, antidepressants and sedatives. Medicines are prescribed depending on the individual situation of the patient.
An elderly patient may be prescribed intra-arterial thrombolysis, and endovascular treatment methods are also used. At the beginning of therapy, antiplatelet agents are used. In the first hours after the onset of a stroke, the patient is given aspirin.
After the first treatment, the patient expects long-term rehabilitation and care. Care for the patient depends on his condition. Bed rest and regular skin hygiene by wiping are recommended to everyone. The bed in the head area should be higher, and you should also change your body position regularly (every 2-3 hours) - this is the prevention of bedsores.
A neurologist treats strokes. It helps restore lost physical and mental functions, and also prevents recurrent attacks.
During rehabilitation, various exercises and techniques are used to restore a person’s speech and motor activity. Teachers and psychologists work with the patient to help him return to the social environment. The person is prescribed medication, nutritional therapy, and physical procedures. It is important to follow a healthy diet: eat boiled or steamed food, limit yourself to sweets, salty, fatty foods. You need to give up alcohol and tobacco.
The effectiveness of restoring lost functions will depend on the size and location of the affected area, the general health of the patient, the participation and assistance of loved ones, and the quality of rehabilitation. It is better to begin recovery a week after the stroke, when the patient’s condition becomes stable.
Rehabilitation lasts from several months to several years. Much depends on the patient’s condition and the quality of rehabilitation. Motor activity may return within six months, speech within 2-3 years. With a high-quality integrated approach, the patient will recover faster.
Rehabilitation: highlights
Rehabilitation after a stroke can be divided into several areas of recovery: speech, motor functions, swallowing and bowel function, memory, vision and facial symmetry.
Speech restoration occurs with the help of special exercises that must be performed regularly. A speech therapist works with the patient. A person is taught to pronounce simple words and phrases, communicate with him by asking easy questions, and learn to understand speech. It is also important to train the muscles of the face and tongue, and develop facial expressions. Next, a person is taught reading and writing. If speech cannot be restored, a person learns to communicate using facial expressions and gestures.
To restore memory, they use short texts to memorize, recall incidents from life, communicate on light topics, use finger games and mental games (for associations, invention, logical connections).
Physical therapy is used to restore movement. Use exercises to flex, rotate and move the limbs. They should be done slowly, gradually increasing the load. There should be no pain or discomfort. They also do exercises for the eyes.
In order for the face to become symmetrical again, it is necessary to restore healthy muscle tone and normal shape. To do this, use special exercises for the facial muscles: smiling, winking, jaw movements.
To restore swallowing, the patient is fed light and tasty foods that are easy to chew and swallow. He also does gymnastics for the tongue and lips.
After a stroke, a person spends a long time in a lying position, and this negatively affects the condition of his intestines. To maintain or restore healthy bowel function, he is prescribed laxatives and enemas, as well as a diet rich in fiber.
After an attack, a person may partially or completely lose vision. To prevent blindness, they do special eye exercises, use medications, or perform surgery.
For recovery, a therapeutic massage may be prescribed: it will help to quickly establish healthy physical activity.
Additional Treatments
In addition to the main methods of treatment and rehabilitation, additional methods are used. Let's take a closer look at them.
• Botox therapy. The muscles of people who have suffered a stroke are in tense tone. To relax them, various techniques are used, including Botox therapy. Botox injections help relieve muscle tension. • Exercise therapy – helps restore limb mobility. • Therapeutic massage will improve blood circulation, help cope with spasms, and improve the functioning of the nervous system. • Physiotherapeutic methods relieve pain, restore healthy blood flow, and improve organ function. They use different techniques – both individually and in combination. Vibromassage, electrical stimulation of muscles, electrophoresis, and laser therapy are popular. • Kinesthetics. The patient gradually learns to make movements that do not cause pain. This allows him to move without an assistant - for example, to turn independently in bed. • Reflexotherapy – impact on biologically active points using needles. Acupuncture helps relieve muscle tension, improve the condition of the musculoskeletal system, and establish healthy functioning of the nervous system. • Bobath therapy – teaches healthy areas of the brain to perform duties instead of damaged ones. The entire therapeutic process is under the supervision of a doctor. • Psychotherapy. A person who has experienced a stroke needs psychotherapeutic help and support. It will help cope with depression and psychological problems. This will support the patient's mental health and brain health, which is very important for successful recovery. • Occupational therapy – helps a person return to normal life and restore ability to work.
Folk remedies for recovery
Folk remedies are good helpers during the rehabilitation period. They cannot replace traditional medications, nor can they be self-prescribed. A suitable folk recipe, agreed upon with the attending physician and used as an addition to the main methods of treatment, will help the elderly patient in recovery.
For people who have suffered a stroke, recipes based on black radish, aloe juice, bay leaf, horse chestnut, hawthorn, rose hips and other herbs are suitable. Herbal infusions are popular.
How to recover and prevent another stroke for an old person
For older people after a stroke, even in a hospital setting, they offer classes on special simulators and select individual exercises that need to be continued at home. The basis of the rehabilitation period, along with taking medications and physiotherapeutic procedures, is a properly selected diet:
- minimum amount of sugar and salt in the diet;
- reducing the consumption of animal fats (pork, lamb, butter, some dairy products);
- The basis of the diet is lean vegetable soups, vegetable oils, cereals, fruits and vegetables.
It is recommended to steam dishes and eat boiled or baked foods. To avoid difficulty chewing, it is better to eat fairly well-chopped food.
In the post-stroke period, many patients have a deteriorating emotional state, feel morally depressed, and have their usual sleep patterns disrupted. What sedatives does a doctor usually prescribe for an old person after a stroke? As a rule, these are sleeping pills and antidepressants: Doxepin, Mirtazapine, Trazodone. Nicergoline is used as an additional medicine, which not only reduces the symptoms of insomnia and mental disorders, but also helps reduce the tone of the cerebral arteries and improves blood flow. It is worth warning that long-term use of these drugs can be addictive. Beware of this and listen to medical advice.
In recent years, PNF therapy (proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation) has been actively recommended for older people who have suffered a stroke, a technique that allows them to regain the ability to move. Simple physical exercises improve motor functions and prevent the development of complications - paralysis and muscle dystrophy.
Other methods are also effective in treating stroke in older people:
- soft tissue manual therapy - working out all muscles allows you to restore their tone;
- Vojta therapy - through targeted pressure on certain areas of the body, the activity of motor muscles and reflexes is triggered. In some cases, completely paralyzed patients after a course of procedures were able to roll over and crawl on their own;
- The Castillo Morales method is a set of exercises that allows you to restore the breathing and swallowing functions, as well as the speech of the victim. Usually carried out in conjunction with psychological therapy;
- kinesio taping - special elastic patches glued to the patient’s skin not only improve microcirculation and lymph outflow, but provide additional support and strengthening to the joints;
- The Mulligan concept is a type of manual therapy method that has proven itself in the treatment of stroke in an old person. Special manipulations by the doctor alleviate the excessive pain of the actions, and the patient, overcoming the pain, can improve the exercises day by day;
- bobat therapy (neurodynamic rehabilitation) is a practice that helps to correct movement patterns and overcome lack of movement.
All these techniques are usually used to treat stroke in an old person in a rehabilitation center under the guidance of experienced doctors. Additionally, patients are prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures, magnetic brain stimulation to restore speech, and transcranial stimulation to improve vascular function.
You can also achieve good results after acupuncture, which helps normalize muscle activity and restore motor functions, improve tissue condition, and form reflexes.
Treatment of a stroke in an old person and the subsequent rehabilitation period is a rather lengthy set of measures that falls on the shoulders of the patient’s relatives and friends. The choice of good doctors, strict adherence to all recommendations, the desire and efforts of the patient himself, the patience and responsibility of relatives help many who have suffered an attack to return to a comfortable standard of living.
The benefits of a boarding house for an elderly patient
Caring for an older person who has had a stroke can be difficult. In order to correctly and effectively help a patient recover, you need to have the necessary knowledge and undergo training. Not every loved one has enough strength, knowledge and time to provide quality assistance to their relative.
Caring for the patient requires monitoring medications, maintaining sleep and eating habits, maintaining regular hygiene, performing physical and cognitive rehabilitation exercises, and observing the prevention of bedsores.
At home, it is difficult to provide full-fledged, high-quality rehabilitation after a stroke. A good option is to go to a boarding house for the elderly, where the person will be surrounded by professional care, and help the relative together with specialists. He needs the support and participation of his loved ones - this is very important for a quick and successful recovery.
Late and remote periods
At a later stage, the body’s potential for rehabilitation after a stroke gradually decreases, but the patient must continue to study and train self-care skills. This period already passes at home, so responsibility for the health and mental state of the patient falls entirely on his loved ones.
You can change your usual exercise therapy complex by adding new exercises and classes with simple exercise equipment, for example, an expander. It is recommended to talk with the patient as often as possible, ask questions, thereby encouraging him to be vocal.
A year after the stroke, the exercises no longer have a pronounced effect, so in the long-term recovery period, the main attention should be paid to consolidating skills and periodic visits to the doctor for follow-up examinations.
Conditions for successful rehabilitation after a stroke
A stroke is a difficult ordeal, especially for older people, who can suffer from it with unpredictable consequences. How long it will take to recover - even doctors cannot answer this question for sure. But in order to shorten the rehabilitation period after a stroke, the patient must provide a number of conditions:
- rehabilitation should take place under the strict guidance of a qualified doctor according to an individually developed program;
- the rehabilitation process must be continuous and comprehensive. This means that it is necessary to work on restoring all body functions simultaneously and sequentially;
- in the home environment, it is necessary to create all the conditions for the successful rehabilitation of the patient: equip the sleeping place with an anti-decubitus mattress, allocate a place for doing therapeutic exercises and purchase the necessary exercise equipment, as well as additional equipment - walkers, wheelchairs, canes, special personal hygiene products;
- provide a balanced diet throughout the entire period of rehabilitation;
- take care to create a favorable home atmosphere, sensitive and caring attitude towards the sick person.
Prognosis after a stroke
A stroke leads to various consequences, doctors do not give guarantees. The first month after a stroke is the most dangerous time. If the patient remains alive after this time, he has a good chance of partial or complete restoration of lost functions. Patient care is of great importance. It determines how quickly the patient will recover and whether a second attack will occur.
Survival statistics for the elderly after a stroke are as follows: in the first month - 35%, in the first year - half of the cases. More women die after their first stroke than men.
A recurrent stroke can occur in 25% of patients within a year, in 30% within 3 years, and in 40% within 5 years.
80% of morbidity cases are ischemic stroke, of which almost half end in death. 20% is hemorrhagic stroke, which is even more dangerous.
To reduce high mortality rates, older people should definitely engage in stroke prevention and immediately seek medical help if warning signs are detected. It is also necessary to educate the population about the disease so that people know how to recognize a stroke and what needs to be done to treat it.
How a stroke will affect the patient’s health depends on various factors: general health, the presence of stress and chronic illnesses, the speed and quality of first aid, the accuracy of diagnosis, the quality of treatment and rehabilitation.
Therapy after ischemic stroke of the left side
The most important factor influencing a positive treatment outcome is efficiency. A quick and correct diagnosis will help you correctly draw up a step-by-step and comprehensive treatment plan. It is important to remember that there is a so-called “therapeutic window” when the process of neuronal changes is still reversible. This usually occurs within a period of 3 to 6 hours from the moment of injury. It is at this time that it is necessary to quickly hospitalize the patient for intensive care or surgery. After emergency assistance is provided, a plan is developed for the subsequent rehabilitation period. Speech therapists and psychologists work with patients who have suffered a left-sided stroke. They are prescribed the following procedures to stimulate the compensatory functions of brain neurons (neuroplasticity):
- Physiotherapy;
- Massage;
- Electrical stimulation;
- Kinesitherapy.
Complications
The consequences of stroke in the elderly are persistent and are observed in more than half of patients. The severity of complications depends on the location of the injury and the amount of hemorrhage.
Most often, a stroke leads to the following consequences:
• Cerebral edema – develops in the first hours after an attack. To avoid swelling, you need to provide medical attention in a timely manner. • Leg swelling – caused by cardiovascular problems and develops gradually. The patient is prescribed diuretics that help remove excess fluid from the body. • Paresis and paralysis – partial or complete, numbness of the limbs. It is not easy to cure paralysis in an elderly person; treatment takes a lot of time. • Speech disorders: from problems with speaking and tongue movement to understanding spoken and written speech. • Joint problems – due to lack of nutrition. • Disorientation in space, loss of the ability to walk. • Loss of control over urination and bowel movements. • Impaired vision, hearing, swallowing. • Mental problems: depression, mood swings, seizures, development of dementia. Mental problems are usually reversible. • Coma is one of the most severe consequences of a stroke. Occurs due to damage and death of neurons. Expressed in fainting, noisy breathing with wheezing, severe redness of the face, loss of muscle tone, urinary incontinence. In a comatose patient, the blood pressure increases, the pulse becomes rapid, and the pupils do not respond to light.
Some older people recover after a stroke and return to their normal lives, while others remain disabled.
People with left-brain strokes recover faster than people with right-brain strokes. Vascular lesions in the right hemisphere are not accompanied by speech problems. Because of this, it is more difficult to detect, the ambulance arrives later - therefore, a right-sided stroke is more dangerous than a left-sided one. Be attentive to all signs so as not to miss time.
People over 70 years old cannot restore lost functions - problems with the body after a stroke remain for life. If the patient recovers slowly within 3 months after the stroke, a medical examination is carried out, based on the results of which the person’s sick leave is extended or a disability group is assigned.
Patients lose the ability to care for themselves and need helpers. After a stroke, it is difficult for a person to communicate even with loved ones, so the patient is usually limited to a narrow circle of people.
Possible consequences
Sagging muscles on the right side of the body, slurred speech or its complete absence, convulsive twitching and difficulties in articulation, difficulties or partial memory loss, difficulties in analyzing the situation, difficulty in perceiving any new information, inadequate perception of what is heard, a depressive state - all this is felt by people, survivors of left-sided ischemic stroke. Not all of the consequences are listed. Despite the fact that the process of treatment and recovery after a stroke is always long and tedious, there is a chance to regain your previous abilities. The main thing is to provide timely assistance to the victim.
Prevention
Preventive measures should be regularly observed by all elderly people over 60 years of age.
1. Regularly undergo a comprehensive examination of the body. In old age, regular examinations are especially important if a person has frequent headaches, dizziness, fainting, hypertension and arrhythmia, elevated cholesterol levels, a traumatic brain injury, or problems with vision, hearing, sleep, attention and memory. 2. Adhere to healthy lifestyle standards. It is especially important to eat right and give up bad habits. 3. Monitor blood pressure and glucose levels and maintain these indicators within normal limits. 4. Do physical therapy. A specialist will help you choose the appropriate exercises individually for the person. 5. Avoid excessive stress, maintain a calm emotional background. 6. Treat chronic diseases.
Remember the main signs of a stroke and how to check for it. Be attentive to the health of a loved one and immediately call an ambulance if you suspect a stroke - time is very important. Provide first aid and then assist the victim in recovery. If your loved one is healthy, teach them about stroke prevention. Correct actions will help protect yourself from a dangerous disease.