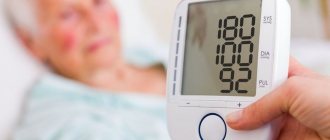
Indicators for measuring blood pressure
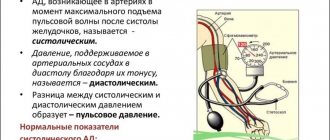
When measuring pressure, two values appear: the first is systolic pressure, the second is diastolic.
If the blood pressure monitor shows 140/60
- it means it has deviated from the norm. A person with such indicators needs to consult a specialist and undergo an immediate medical examination.
The difference between the upper and lower values is called the pulse. Its norm is 40 millimeters of mercury. This indicator is also influenced by physical activity and the psychological state of a person. However, even if this indicator changes, over time the pulse difference should return to the average value.
In an elderly person, such changes should not cause a feeling of malaise.
If blood pressure is 140 over 50
, the pulse difference is 80 mm. mercury column. This indicates that the body's cardiovascular system is not in order.
What could a blood pressure of 130/90 indicate?
When the tonometer monitor displays a pressure of 130 to 90 or 134 to 94 mm Hg. Art., doctors begin to talk about possible hypertension at the initial stage. In this case, systolic pressure is within normal limits. Only the lower (renal) blood pressure is elevated. This type of hypertension is classified as secondary. This means that the pressure increases not because of the physiological characteristics of the body, but because of the presence of concomitant disorders. Among the main reasons:
- pathologies of the kidneys and renal arteries;
- adrenal gland diseases;
- renal stenosis, including congenital;
- atherosclerosis;
- disorders of the thyroid gland, including those associated with benign neoplasms.
You can suspect that changes in blood pressure are caused by kidney disease by looking at your heart rate. A pulse of 90 or a pulse of 100 is not normal and requires contacting a doctor, who will prescribe an additional examination to determine the cause of the increase in renal pressure. To an increase in pressure to 129 by 90 mmHg. Art. and above are also conditions that cause fluid retention. This is the period of menstruation, abuse of salty and fatty foods. Expectant mothers also face this problem.
Pregnancy is an increased load on the entire cardiovascular system. Therefore, pressure drops during this period are normal, provided that the difference between the readings in the first and third trimester does not exceed 20 mmHg. Art. But any deviations from the norm should be monitored by a doctor. Medicines are prescribed with extreme caution. An alternative to tablets are herbal preparations, herbal remedies, and physiotherapy.
Excess weight is a multiple increase in the load on the heart muscle, which also causes the development of hypertension.
Risks of high blood pressure
With such blood pressure, it is recommended to immediately consult a cardiologist: the doctor will prescribe the necessary examinations and make the correct diagnosis. It is important to remember that the greater the pulse difference when measuring pressure, the greater the load on the heart.
If the pulse difference remains high for a long time, this may indicate internal bleeding or heart failure.
signs of pressure 140 to 60
The first symptoms of hypertension
At a pressure of 135 to 85 or 128 to 90 mmHg. Art. A person may experience no unpleasant symptoms at all. But with nervous or physical stress, the manifestations become obvious. This:
Blood pressure 150 over 100
- headache (headache in the back of the head or in the temporal region);
- nosebleeds;
- increased heart rate;
- flashing black dots before the eyes;
- tinnitus;
- painful sensations in the chest;
- sleep disturbance.
Such symptoms are transitory. During remission, the person feels normal and does not notice any problems with well-being. This is the main insidiousness of the disease. Over time, the pressure of 135 to 95 becomes constant, increasing during attacks to critical values.
Important! The situation is also dangerous when diastolic pressure drops below acceptable values and the pulse difference increases. Blood pressure 130 at 65 mm Hg. Art. Such values are a symptom of a malfunction of the excretory system, which can lead to a stroke. But for professional athletes who daily subject their bodies to increased stress, such pressure is normal.
High blood pressure during pregnancy
Experts point out to patients that low blood pressure during the first trimester is normal during pregnancy. The closer the moment of birth, the more often high blood pressure is observed.
If a pregnant woman has a blood pressure of 140 over 40
, you must immediately consult a doctor: high blood pressure can cause fetal hypoxia.
If the pressure is 140 over 50, what does this mean?
? It is possible that high blood pressure is a short-term phenomenon caused by a stressful situation or physical activity. The doctor will prescribe sedatives and evaluate the pregnant woman’s diet.
However, situations often occur when the pressure does not return to normal: it is necessary to begin drug therapy. In this case, only a specialist can prescribe treatment, taking into account all possible risks to the health of the unborn child.
blood pressure during pregnancy
Diagnostic measures
If there is a periodic increase in blood pressure, it is recommended to purchase a home tonometer, which allows you to quickly and extremely accurately measure blood pressure without medical assistance. Automatic and semi-automatic devices are best suited for these purposes, the use of which does not require special medical skills.
It is important to follow some rules on which the reliability of the results reflected on the monitor depends:
- 30–60 minutes before the start of the diagnostic procedure, you should not smoke, eat salty or fatty foods, drink alcohol or drink coffee;
- the person should be as relaxed and calm as possible; you cannot move or talk during the procedure;
- the best position is sitting on a comfortable chair, leaning your back on the back and placing your hand on the table;
- pressure is measured first on one arm, after 10 minutes - on the second;
- Blood pressure should be monitored twice a day - in the morning and in the evening, unless the doctor determines another monitoring time;
- the obtained data is entered into the pressure monitoring log.
When the values are 130–137 at 90 mmHg. Art. become permanent, the person is sent for examination, which includes the following activities:
- blood pressure measurement according to a schedule determined by a specialist at home and daily monitoring in a hospital setting;
- an electrocardiogram to assess the stability of the heart;
- blood test for the concentration of potassium and hormones in the blood;
- urine test to check the condition of the kidneys and excretory system;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and heart;
- renal arteriogram, radiography.
Causes of isolated systolic hypertension
This disease indicates that adverse changes are occurring in the cardiovascular system that require the intervention of specialists. Timely treatment will help avoid complications.
Most often, hypertension is a short-term phenomenon, to eliminate which you just need to give up physical activity, review your diet, and give up coffee and other energy drinks.
Many people are at risk due to a sedentary lifestyle, hard work and poor diet. All these factors negatively affect health, and make themselves felt in old age.
Patients with arterial hypertension (AH) have a high risk of complications, including cardiovascular complications, so it is important to achieve a reduction in blood pressure (BP) to target values. The optimal target blood pressure values in this case are still being discussed. Thus, in the 2021 clinical guidelines of the American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association, target blood pressure levels for patients receiving treatment were ≤130/80 mm Hg. Art. In the 2007 European Society of Cardiology guidelines, the target values were ≤140/90 mmHg. Art. for patients with low and moderate cardiovascular risk and ≤130/80 mmHg. Art. for high-risk patients, but in 2013 they were revised, as the decrease in blood pressure below 140/90 mm Hg. Art. did not lead to improved outcomes in any of the patient groups. Discussion of this situation led to the formation of two competing concepts: “the lower the achieved BP levels, the better the outcome” and the “J-shaped curve of outcomes depending on the BP level.” The first is based on a direct relationship between blood pressure and the incidence of cardiovascular complications, up to values of 115/75 mmHg, the second is based on the fact that the benefits of reducing blood pressure to low values will be less than from reducing them to average values. This hypothesis remains very popular due to the idea that there is a threshold of low blood pressure for the regulation of organ blood flow, and in vascular diseases this threshold may increase.
In this regard, the Cochrane Society conducted a meta-analysis of studies comparing patients with complicated hypertension with “low” achieved BP (≤ 135/85 mm Hg) and “standard” achieved BP (≤ 140-160/90-100 mm Hg .st.). The analysis included studies from the Cochrane Hypertension Specialized Register, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE, Embase, LILACS, the World Health Organization database and the ClinicalTrials.gov registry. Adult patients receiving hypertension therapy and having coronary heart disease with clinical angina or chronic occlusive peripheral vascular disease, myocardial infarction or stroke were included. A total of 6 randomized controlled trials were selected, including a total of 9484 patients followed for 1-4.7 years (mean follow-up period 3.7 years), which analyzed the difference between overall mortality, cardiovascular mortality, number of cardiovascular -vascular complications, side effects of antihypertensive drugs and cases of hospitalization with “low” and “standard” blood pressure achieved.
The study authors found no differences in all-cause mortality (hazard ratio (HR) 1.06, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.91-1.23) or cardiovascular mortality (HR 1.03, 95 % CI 0.28-1.29). There was also no difference in the incidence of treatment side effects (RR 1.01, 95% CI 0.94-1.08) and in the incidence of cardiovascular events, including myocardial infarction, stroke, sudden death, hospitalization or death from congestive heart disease. failure (OR 0.89, 95% CI 0.80-1.00). In the “low” group, the achieved blood pressure values were lower by 8.9/4.5 mm Hg.
Ultimately, there was no evidence that a blood pressure reduction ≤ 135/85 mmHg. reduces mortality or the number of major cardiovascular complications. The authors conclude that in patients with complicated hypertension, there is currently insufficient evidence to justify lower BP targets than currently available.
Prepared based on materials:
https://cochranelibrary-wiley.com/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD010315.pub3/full
Preventing high blood pressure
In order to maintain normal blood pressure, you must:
- Maintain a daily routine.
- Avoid unhealthy foods, the consumption of which can lead to obesity and increased cholesterol levels.
- Stop drinking alcohol and tobacco products.
- Avoid stressful situations.
A healthy lifestyle is a great way to normalize blood pressure over the long term. Elderly people are recommended to undergo systematic examination by a cardiologist, as well as regularly take medications, the main task of which is to control vascular tone.