Is the condition dangerous, severity?
{banner_banstat0}
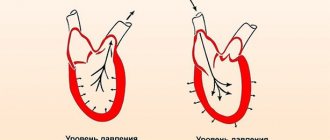
If DBP (diastolic blood pressure) is measured at 100 mm Hg. Art. – this is a direct indication of an emerging or existing pathology of the cardiovascular system.
The pressure is not constant, but normally DBP does not exceed 80 mm Hg. Art. and does not fall below 60.
In children, due to imperfect vascular tone, the lower pressure can be at the level of 40 units, and in older people, due to the loss of compensatory capabilities, it can rise to 95.
An isolated elevated diastolic reading of up to 100 units is no less dangerous than classic hypertension.
Lower pressure 100 mm Hg. Art. and above provokes:
- ACVA (acute cerebrovascular accident) – stroke;
- cardiac ischemia with the development of heart attack;
- acute heart failure with cardiac arrest;
- bleeding in the eye;
- thrombosis;
- paralysis of limbs;
- memory loss;
- renal failure;
- shock
Isolated hypertension is divided according to severity into three groups:
| Degree of pathology | Characteristics of DBP |
| First (beginner, easy) | DBP up to 100 mm. rt. Art. (in older people this is normal) |
| Second (middle) | Lower pressure – from 100 to 110 units |
| Third (extremely difficult) | Diastolic hypertension – pressure above 110 mm. rt. Art. |
Forecast
If you take the necessary measures in a timely manner, you can normalize your blood pressure and achieve lasting results. True, there are situations when you have to take medications and herbal tinctures constantly.
To exclude serious health problems and receive the correct prescription, you should definitely visit a doctor and undergo the recommended diagnostics. In the worst case, there is a high risk of stroke or myocardial infarction.
The main reasons for the increase in DBP
{banner_banstat1}
Increased lower pressure is multifactorial, there are reasons hidden inside the heart and blood vessels (only 20%), and there are extracardiac (80%). In addition, physiological and pathological triggers of elevated diastolic markers are distinguished.
| Causes | The essence of pathology |
| Physiological | |
| Long-term smoking abuse | Nicotine and tar provoke vasospasm, impaired blood flow, hemodynamics, and blood pressure increases. Since cigarette toxins primarily affect the lungs and kidneys, renal blood pressure (RBP) increases. |
| Alcohol | It works in a similar way, only instead of the lungs, the liver is involved in the process, metabolic processes are disrupted, the vessels either dilate or contract, hypertension increases, as soon as the body’s compensatory capabilities end, myocardial ischemia develops with infarction |
| Abuse of salt | More than 5 g/day leads to fluid retention in the body, hemodynamic disturbances, and an increase in DBP |
| Hyperload | Physical or mental stress stimulates the synthesis of catecholamines - this is a natural defense mechanism in which a person does not feel pain or fatigue, but against this background blood pressure rises rapidly, with the lower one overtaking the upper one |
| Stress | Vasospasm provokes an increase in blood pressure |
| Endocrine disruptions | Puberty, menopause, menstruation, pregnancy - cause hormonal changes in the body, change vascular tone, arterial markers |
| Pathological | |
| Myocardial ischemia | General hemodynamics and cardiac output are disrupted, DBP increases |
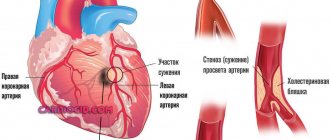
| Atherosclerosis | Reducing the lumen of arteries, capillaries, and veins due to atherosclerotic plaques impairs blood circulation and leads to an increase in diastolic indicator |
| Infringement of the arteries supplying blood to the brain | Causes ischemia of the brain, its centers, pathology of the musculoskeletal system, which increases the lower pressure to 100 units and above |
| Endocrine diseases: diabetes, hyperthyroidism, Cushing's syndrome | The balance of hormones in the body is disrupted, dopamine biologically active substances, thyroid hormones, stress hormones predominate, vascular spasm develops against the background of metabolic disorders, which causes an increase in vascular parameters |
| CRF, CKD (chronic kidney disease) | The synthesis of renin is disrupted, which leads to an imbalance in blood pressure control with the development of malignant hypertension, DBP is a marker of such a process |
| Post-stroke condition | Often a DBP of 100 units indicates a disruption in brain function, which occurs against the background of a stroke, requiring long-term correction |
Right ventricular hypertrophy
Blood from organs and tissues that deplete oxygen reserves and give off carbon dioxide enters the right atrium.
Then it passes through the right ventricle to the lungs to be enriched with oxygen. With minimal malfunctions (with an increase in diastolic pressure), the myocardium begins to work harder, which provokes pathological changes. The mass of the cardiac ventricle begins to increase and the muscle fibers thicken. These changes are called ventricular hypertrophy. The initial stage of the disease does not have pronounced symptoms. They appear later. It becomes difficult for the patient to breathe, shortness of breath occurs, the heart rate increases, dizziness appears with possible loss of consciousness, and the limbs swell.
The consequences of hypertrophy of the right ventricle of the heart are very destructive for the body. Its work is responsible for the pulmonary circulation, which has lower pressure. It connects the myocardium with the lungs, therefore, with hypertensive changes that increase the right ventricle, pulmonary pressure intensifies, which provokes the development of diseases of the bronchopulmonary system.
Cardiac right ventricular hypertrophy is a very rare syndrome that leads to serious illness. If the first signs of the disease occur, you should contact a cardiologist to establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe rational treatment.
Symptoms
{banner_banstat2}
Lower pressure of 100 or more units can occur latently if it occurs rarely and for a short time. But much more often such hypertension is accompanied by severe symptoms and warns of the development of hypertension:
- prostration;
- migraine;
- noise in ears;
- nausea;
- faintness;
- disorientation in space;
- insomnia.
The clinic is correlated by gender, age, constitution.
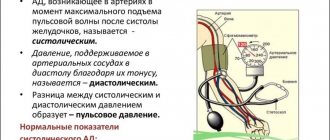
The difference between upper pressure and lower
The pressure indicator is expressed in two numbers: the first is systolic (upper), the second is diastolic (lower). Systole is a measure of blood pressure at the moment the heart contracts, and diastole refers to its degree at the moment when the heart muscle relaxes. This indicator makes it clear whether the vascular walls are in good shape, because diastole is a reaction to their resistance.
Constantly elevated blood pressure indicates high resistance of the vascular wall, which indicates a constant state of spasm. If the vessels are constantly narrowed, blood begins to pass through the walls poorly. As a result, it reaches all tissues and organs in small quantities, which causes oxygen starvation and an acute lack of nutrients in them. For this reason, the functioning of organs can be seriously impaired.
Features of treatment
Any symptom of hypertension is considered dangerous because its consequences are unpredictable. Therefore, if it occurs:
- prolonged dizziness;
- disorientation in space;
- migraine with nausea;
- syncope (fainting);
- tachycardia or bradycardia;
- unruly legs and arms;
- facial asymmetry;
- chest pain of varying intensity;
- neurological symptoms - you need to call an ambulance.
Before the doctors arrive, there is very little that can be done at home.
First aid
{banner_banstat4}
First of all, you need to calm the patient down. Then:
- help him take a comfortable position;
- open the window, loosen tight clothing;
- measure blood pressure.
You can take medications only if you already have a proven regimen for stopping the attack. You can reduce lower pressure without affecting the upper if:
- take a quarter of a Captopril tablet;
- Verapamil tablet or another calcium antagonist;
- No unnecessary movements, basins of hot water, cold douches are allowed.
Upon arrival of doctors, you should agree to hospitalization.
Medicines
The treatment regimen is selected by the doctor depending on the individual characteristics of the person; the following drugs are most likely to be used:
| Group of drugs | Mechanism of action |
| Diuretics (Veroshpiron, Spironolactone, Triampur) | Remove excess fluid from the body, reduce tension in the vascular bed, lower blood pressure |
| Adrenergic blockers (alpha: Doxazosin, Yohimbine, Nicergoline, beta: Atenolol, Bisoprolol, Norvasc) | Reduce arterial tone, affecting endothelial receptors, reduce heart rate, leading to a drop in lower blood pressure |
| ACE inhibitors (Losartan, Telmisartan, Rasilez) | Block the production of biologically active substances that stimulate vasospasm, reducing DBP |
| Calcium antagonists (Amlodipine, Verapamil, Felodipine) | They stop the flow of ions that potentiate vasospasm, cause dilatation of the arteries and a fall in the lower marker |
Isolated arterial diastolic hypertension is insidious, it is difficult to find effective therapy, therefore they use a combination of drugs from different groups and folk recipes, among which the most effective are herbal decoctions:
- bearberry;
- lingonberry leaves;
- rowan.
In addition, tincture of horsetail and pine cones is used. Only regular use of these medications can lower your lower blood pressure.
Left ventricular hypertrophy
The development of cardiac left ventricular hypertrophy is based on a factor such as arterial hypertension, which provokes intense work of the myocardial ventricle. Due to hard work, the walls of the chambers increase, which after some time lose their elasticity and stop working normally.
With the development of left ventricular hypertrophy, cardiac functionality is impaired, which accompanies the appearance of unpleasant symptoms. Prominent among them are:
- dyspnea;
- dizziness;
- loss of consciousness;
- angina pectoris;
- tachycardia;
- fast fatiguability.
Cardiac left ventricular hypertrophy can be a symptom of serious pathologies, among which the most common are pulmonary edema, heart disease, atherosclerosis, heart failure, myocardial infarction and other diseases that can increase the size of muscle tissue.
The left ventricle is the connecting link that is responsible for supplying oxygen-rich blood to organs and tissues. Hypertrophy itself is not a fatal disease, but it can cause a number of dangerous pathologies.
- The heart is unable to pump enough blood, causing heart failure.
- Abnormal disturbances in the heart rhythm lead to arrhythmia.
- Insufficient oxygen supply to the heart and organs causes coronary heart disease.
- A short-term interruption in the blood supply to the heart provokes the development of a stroke.
- Sudden loss of heart function, breathing or consciousness can cause it to stop.
Because of the above possible complications of the disease, it is important to identify it in the early stages, before hypertrophy can provoke heart damage. To diagnose the disease, you need to consult a cardiologist.
Before treating left or right ventricular hypertrophy, it is necessary to determine the cause of the development of the disease, since health therapy is aimed at eliminating the main provocateur, in combination with therapeutic measures that stop pathological changes in the ventricle. By stopping the factors influencing the development of hypertrophy, treatment of the disease becomes very simple.