Experienced hypertensive patients, as a rule, are adapted to living with high blood pressure (BP) levels and are usually well aware of what they need to take to maintain optimal blood pressure values for themselves.
They also know what they should not do so as not to provoke a sharp rise in pressure upward. And the most disciplined ones measure their blood pressure every morning and record the readings in a diary before taking their antihypertensive pills.
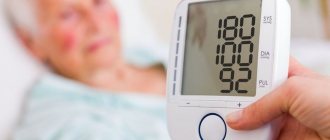
If, with grade 2–3 hypertension, it is possible to keep blood pressure at 140/150 at 90/100 mmHg in this way. Art., which means that this is a relatively stable course of hypertension. But if one day a hypertensive patient suddenly has a blood pressure of 120 over 100, what does this mean? Does such a collapse in the systolic indicator indicate victory over hypertension or is this a new round of pathology fraught with unknown dangers?
What does pressure 120 per 100 mm Hg mean? Art.?
To figure out whether such indicators are optimal for a person accustomed to high blood pressure, consider a pressure of 120 to 100 for each value separately.
- Systolic reading 120 mmHg. Art. for a patient suffering from hypertension, this cannot be called the norm, since his body, in particular, the circulatory system has already adapted to function at higher values, which means that 120 mm in this case is low blood pressure.
- Diastolic reading 100 mmHg. Art. for most hypertensive patients it is quite tolerable, although elevated relative to the classical norm.
- The difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure (pulse pressure) is 20 mm, that is, less than 25% of systolic blood pressure, which means there are serious disturbances in the functioning of the vascular system.
Why could such an imbalance in the indicators arise? What does a pressure of 120 to 100 mean - is this a variant of the norm or is it still low blood pressure? In a specific case, only the “upper” systolic pressure can be considered low, which indicates insufficiency of cardiac output (actually, systole).
Why did the diastolic indicator remain at an elevated level, and not decrease synchronously with the upper blood pressure? A high level of diastolic pressure indicates increased resistance of the peripheral vessels of the bloodstream, which means a narrowing of the capillaries. The reason for this condition may lie in the ordinary “clogging” of small vessels with cholesterol.
When asked what a pressure of 120 over 100 means, we can answer that a person has signs of insufficient cardiac output against the background of increased capillary resistance.
What pressure is considered normal?
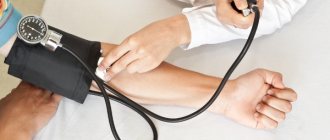
A person’s blood pressure has two indicators - the upper (systolic), recorded at the moment the heart contracts, and the lower (diastolic), noted when the heart relaxes and pushes blood into the arteries. When the heart and capillaries are functioning normally, the tonometer readings are within 120/80 or 110/70; a slight deviation up or down is not considered a pathology.
For each person, the pressure is individual, but, in addition to fixing the two indicators, it is necessary to monitor the difference between them. This difference is called pulse pressure and can also indicate existing health problems. Changes in tonometer readings are affected by:
- Times of Day;
- nervous tension, stress;
- physical exercise;
- binge eating;
- alcohol consumption;
- taking certain medications.
If, after an unexpected increase in blood pressure (BP) levels, the indicators stabilize on their own, and the fact of jumps is rarely observed, there is nothing to worry about. The normal difference between the upper and lower limits should be from 35 to 55 mmHg, and a regular decrease in this indicator indicates the development of cardiovascular pathology.
Why is the heart rate high?
An increased pulse is considered to be an attribute of arterial hypertension, but even with a pressure of 120 per 100, a pulse of 100 or even 120 beats per minute is not uncommon, but rather the rule. Increased heart rate is explained by the heart's attempt to compensate for insufficient cardiac output.
If a compensatory response in the form of an accelerated heartbeat is observed at a pressure of 120 over 100 (pulse 120), it means that the body is trying to prevent a vascular or cerebral catastrophe. But despite the efforts of the cardiovascular system to restore normal blood circulation by increasing the heart rate, this condition cannot be called harmless.
It is necessary to distinguish the norm from the disease
If a person regularly sees a blood pressure of 120/100 during measurement, he should visit a cardiologist. Despite a slight deviation in the normal pulse pressure, this is a demonstration of the onset of pathological changes in the condition of the heart and blood vessels. A constant departure of the lower indicator beyond normal limits, while the upper one remains unchanged, indicates the possible presence of the following problems:
Why does blood pressure jump during menopause?
- sclerotic changes in the capillary system;
- diseases of the renal system;
- hormonal imbalances;
- diseases of the spinal column;
- elevated blood sugar levels;
- problems with the thyroid gland.
Blood pressure of 125/100 and even 130/100 should not frighten a person if it appears once after hard physical work, as a result of stress or mental overstrain. Therefore, in such a situation, it is important to separate a single jump in tonometer readings from the first signs of a developing disease. It is not possible to do this on your own; if your diastolic pressure constantly increases, you should consult a specialist and undergo an examination.
What is the danger?
Why is a noticeable decrease in blood pressure dangerous for hypertensive patients? Isn’t antihypertensive therapy aimed at lowering blood pressure?
- A sharp drop in blood pressure in hypertensive patients is a clear sign of deterioration in perfusion, that is, cerebral circulation, which means that the process of cerebral ischemia has begun, which increases the risk of developing an ischemic stroke.
- There is also a cardiological danger with a pressure of 120 over 100. What kind of danger this is becomes clear when the pulse rises to 100 or 120 beats per minute. This means that the heart begins to pump blood at an increased rate, which is why the heart muscle undergoes additional stress and is depleted faster. The risk of developing a heart attack increases several times.
- In any case, a pressure of 120 to 100 indicates a loss of the body’s ability to compensate for the forces aimed at increased blood circulation, and therefore a decrease in vascular tone.
- Deterioration of vascular tone often causes orthostatic hypotension - a sharp drop in blood pressure when changing body position (from lying to sitting or standing), which can lead to fainting.
The reason for a significant decrease in blood pressure may be a decrease in BCC (circulating blood volume) due to internal bleeding, for example, with ulcers or cancer. This means that pressure of 120 over 100 cannot be ignored. What to do with such blood pressure values - you should consult a therapist or cardiologist.
The first signs of a stroke
Causes
What are the reasons for its occurrence? The abuse of drinks containing caffeine and some other natural causes have already been mentioned above. However, this is not a complete list and cardiologists supplement it:
- pathological processes that occur in the body;
- chronic lack of sleep;
- frequent stress;
- constant overwork;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- poor environment;
- overweight;
- sedentary lifestyle.
Moreover, blood pressure can be affected by:
- Times of Day;
- mood;
- narcotic substances;
- medicines;
- eating heavy food before bed;
- uncomfortable body position during sleep.
What to do immediately?
If a visit to a doctor is not possible in the near future, and a person has a high pulse and blood pressure of 120 over 100, what should be done immediately to provide first aid?
Since an increased pulse poses a threat to the heart muscle and heart activity in general, it is advisable to first lower the pulse so as not to provoke the development of arrhythmia (atrial fibrillation).
To this end, the patient should:
- provide peace;
- free him from tight clothes;
- provide access to fresh air;
- You can wipe the patient's face and chest with a cool, damp towel.
The complexity of the situation lies in the fact that with reduced (for hypertensive) systolic pressure, diastolic blood pressure and pulse remain high. This means that any drugs containing caffeine benzoate will only aggravate the situation if they are used as “symptomatic therapy” - for example, to eliminate a headache. In this case, what to do if the pressure is 120 over 100, and the person clearly needs help?
If the patient's skin turns pale, chills are felt, dizziness and other obvious symptoms occur that indicate a further decrease in blood pressure, it is necessary to call an ambulance.
First aid measures
Before the medical team arrives, the patient needs to be seated comfortably, windows should be opened to allow oxygen in, and clothing should be loosened. You can give a sedative like Corvalol to stop an anxiety attack. Taking any pills on your own is not recommended so as not to aggravate the condition and cause side effects. After first aid has been provided and the patient has been examined by a doctor, the need for medication is assessed.
If a person has a blood pressure of 120–130 over 100, while feeling weak, nauseated, complaining of shortness of breath and severe headaches, you should immediately call a doctor
In the initial stages of isolated diastolic hypertension, when there are no signs of serious diseases in the body, the following treatment methods can be used:
- Diet with limited salty, smoked and spicy foods. Preference should be given to natural products, lean meat, fish, vegetables and fruits. You should avoid caffeine-containing drinks, fast carbohydrates, and foods high in animal fats.
- Moderate physical activity. Morning jogging, yoga, swimming, and walking will help relieve signs of hypertension. Even walking in the fresh air every night helps stabilize blood pressure.
- Limiting stress. We must try to eliminate all factors that cause a regular release of adrenaline into the blood and an increase in tonometer readings. If the problem lies in psychosomatics (when psychological problems are expressed in physiological diseases), it is worth visiting a psychologist.
- Rejection of bad habits. Addiction to smoking and alcoholic beverages has been proven by scientists to affect blood pressure levels and contribute to destructive changes in the functioning of the heart and blood vessels.
- Body weight control. Overstrain of the capillaries and heart muscle is often provoked by extra pounds. Doctors never tire of repeating that every hypertensive patient should lose weight by following a diet and providing the body with regular physical activity to stabilize blood pressure.
Also, to restore normal blood pressure levels, you should get enough sleep and avoid mental and physical exhaustion. Night rest should be at least 7 hours in a row. For symptoms of diastolic hypertension, the patient should regularly take measurements using a tonometer. An increase in lower pressure for no apparent reason is a reason to undergo examination by a cardiologist, identify the causes of the disease and begin appropriate therapy.
While it is possible to do without the use of medications, a person is advised to change their lifestyle, give up bad habits, go on a diet and keep their weight under control. If the diastolic reading regularly increases, over time this can lead to chronic hypertension, when there is a need for lifelong use of antihypertensive drugs, and the risk of dangerous complications also increases.
What medications can help?
If it is unknown for what reasons the pressure dropped to 120/100 and what this means, no matter what medications, the names of which are even well known to hypertensive patients, are taken, they cannot solve the problem of an impending cardiac or cerebral catastrophe. Here, a significant correction of the treatment received by the patient is necessary, which means the assistance of the attending physician. The only thing that can urgently help a patient if he feels unwell is to give him any sedative:
- Valocordin;
- Corvalol;
- tincture of motherwort or valerian.
Of course, a person in such a state must be protected from any unnecessary emotions and experiences, which means trying to calm him down, promising that a doctor will come and definitely help.
Examinations that need to be completed
Patients of this kind are managed by a cardiologist. If necessary, doctors of other profiles are involved: endocrinologist, neurologist and nephrologist. In tandem, they carry out diagnostic activities, each within the scope of their competence.
The general scheme looks like this:
- Anamnesis collection and oral assessment of patient complaints. Objectification of symptoms plays the greatest role; it is a kind of vector that guides doctors in the right direction.
- Blood pressure measurement. Using simple calculations, you can calculate the PD and determine how much it deviates from the norm.
- Daily monitoring. The change may be temporary, but if the process lasts more than 8 hours or almost a full day, there is no doubt about the pathogenicity of the origin.
- Heart rate assessment.
- Palpation of the kidneys. Possible only in thin patients.
- Ultrasound of internal organs.
- Blood tests (general, biochemistry, hormones of the adrenal cortex, pituitary gland, thyroid gland), urine (according to Zimnitsky, clinical).
- Electrocardiography, possibly with stress tests.
- Echocardiography.
- Study of brain rhythms. Encephalography.
Complexity is the key to early verification of the diagnosis, and therefore the determination of therapeutic tactics.
Prevention
To avoid an increase in diastolic pressure and the development of hypertension, adhere to the following rules:
- Increase your level of physical activity if you have a sedentary lifestyle.
- Reduce your salt intake in pure form, as well as in prepared foods (fast food, takeaway, sauces).
- Don't overload your body, give it a rest, walk in the fresh air or do calm, favorite things.
- Reduce your stress levels.
- Cigarettes and booze are your worst enemies, forget about them.
- Give up coffee.
- Distribute your meals, make a meal schedule, and don’t overeat.
- Get rid of excess weight.
The circulatory system will quickly return to normal if you follow these tips. Without pills, you can eliminate hypertension in the initial stages, the main thing is to constantly measure your blood pressure to control it, and lead a healthy lifestyle.
Symptoms
Ignoring the symptoms of high blood pressure can be very dangerous. Main features:
- heart rhythm pathologies, increased heart rate (pulse exceeds 100);
- difficulty breathing;
- dizziness;
- temperature changes (suddenly throws you into the heat, then into the cold);
- intense headache;
- weakness;
- fatigue;
- nosebleeds;
- blurred vision;
- nausea.
Symptoms of hypertension
High blood pressure may indicate the development of hypertension. The presence of this disease is indicated by the following characteristic symptoms:
- Attacks of dizziness;
- Visual impairment;
- Nosebleeds;
- Increased fatigue, weakness, decreased ability to work;
- Difficulty in breathing;
- Arrhythmia, heart rhythm disturbance;
- Tachycardia (increased heart rate to 100 or more);
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Sudden changes in body temperature (periodic sensations of heat followed by chills);
- Severe headaches.
With such a clinical picture, you should immediately consult a doctor and begin treatment for hypertension!
Signs of hypertension