Today, stroke is a common pathology, affecting every fourth person out of a thousand. Moreover, 80% of cases are ischemic and 20% are hemorrhagic strokes. For the patient and his loved ones, the diagnosis is always unexpected. In this case, natural questions arise - what is a stroke, how many days does hospital treatment last, what is the rehabilitation process?
Stroke. How long are they in the hospital?
Poor blood circulation in the brain, in other words, stroke, treatment involves three stages:
- prehospital;
- stay in the intensive care unit;
- treatment in a general ward.
The length of stay of a patient in a hospital, according to treatment standards, is 21 days, provided the patient has no violations of vital functions, and 30 days in case of serious violations. When the length of a patient’s stay in a hospital is insufficient, a medical examination is carried out followed by the development of an individual course of rehabilitation.
The Yusupov Hospital employs highly qualified doctors, and after being treated by them, most of even the most severe patients return to a full life. The professionalism of doctors plays a huge role in the effectiveness of therapy and rehabilitation. Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital develop an individual treatment plan for each patient.
Patients stay in the intensive care unit as long as they need to fully recover. During this period, doctors strictly monitor the patient’s vital functions in order to avoid serious complications caused by damage to brain tissue.
All patients diagnosed with stroke are subject to hospitalization. The length of stay in intensive care depends on a number of factors, including:
- depression of vital functions;
- degree of damage to brain tissue. With a major stroke, patients stay in intensive care longer;
- the need for constant monitoring if there is a high risk of recurrent stroke;
- severity of the clinical picture;
- level of depression of consciousness and others.
How to treat in the intensive care unit
Treatment of stroke in intensive care significantly increases the chances of survival and recovery.
Intensive therapy is carried out comprehensively and provides:
- stabilization of vital signs;
- restoration of cerebral blood supply (drugs are prescribed to reduce blood viscosity and improve nutrition of brain cells);
- life support;
- prevention of complications (bedsores, congestive pneumonia).
What is done in intensive care after a stroke depends on the nature of the brain damage and accompanying symptoms. In severe cases, the patient may be placed on life support.
But, despite timely treatment of stroke in intensive care, it is impossible to say what the chances of survival in the early post-stroke period are. Prognosis depends not only on how it is treated, but on the patient’s body. In medical practice, there are cases where seemingly stable patients experienced a second stroke or developed other serious complications.
Neurological resuscitation is necessary to prevent or promptly detect complications arising after a stroke, increasing the chances of recovery.
Basic and differentiated therapy
Treatment of a patient in the intensive care unit involves basic and differentiated therapy.
Basic treatment is aimed at:
- fight against cerebral edema;
- restoration of normal functioning of the respiratory system;
- patient nutrition;
- maintaining hemodynamics at an acceptable level.
Differentiated therapy involves:
- normalization of arterial and intracranial pressure, elimination of cerebral edema after hemorrhagic stroke. In the first two days, a decision is made regarding the need for surgery. Neurosurgeons at the Yusupov Hospital daily perform surgical interventions to eliminate the consequences of stroke and save the lives of hundreds of patients. All manipulations are carried out using modern medical equipment using effective proven techniques;
- accelerating metabolic processes, improving blood circulation and increasing the resistance of brain tissue to hypoxia when diagnosed with ischemic stroke. The length of stay in intensive care directly depends on the timely and adequate course of treatment.
In most cases, young people recover much faster than older patients.
It is possible to transfer a victim from the intensive care unit to a general ward after meeting a number of criteria:
- the patient can breathe independently, without the support of devices;
- the patient is able to call a nurse or doctor for help;
- there is a stable level of heart rate and blood pressure;
- the possibility of bleeding is excluded.
Only after the patient's condition has stabilized can the doctor transfer the patient to the ward. In a hospital setting, various rehabilitation procedures are prescribed to quickly restore lost functions.
In the neurology department of the Yusupov Hospital, patients are not only developed an individual course of rehabilitation therapy, but also given psychological support.
If necessary, psychologists work with loved ones and relatives of the patient to teach them the basics of caring for a person who has suffered a stroke.
What to do if you have a stroke?
How to prevent a stroke, properly provide assistance and mitigate its consequences, said Inna Borisovna Tsyngeeva, head of the neurology department No. 2 of the Republican Vascular Center of the N.A. Semashko Republican Clinical Hospital.
Strokes happen only in old age.
Is it so? – Indeed, in most cases, people over 60 years of age are susceptible to stroke. However, our lifestyle, unhealthy diet, and physical inactivity lead to strokes becoming younger,” notes Inna Borisovna. – Unfortunately, we have an increased number of patients with strokes, whose age is 35-40 years. If a stroke occurs at a young age, it is worth understanding that the person has a chronic disease, blood disorder, or autoimmune disease. If you are over 60 years old, this is most likely due to vascular diseases: hypertension, atherosclerosis, a consequence of improper correction of risk factors.
Who is at risk and what are the risk factors?
– As with heart attacks, men are more vulnerable. Women before menopause have estrogen protection, explains the doctor. – But women who have reached menopause and older are also at risk. Modern women are workers, breadwinners of the family and at the same time mothers and housewives. And as a result, colossal emotional and physical stress equalizes the risk of stroke.
Speaking about risks, the doctor emphasized the importance of monitoring and timely correction of behavioral risk factors. These are low physical activity, smoking, lack of proper rest, reaction to stressful situations, consumption of large amounts of fatty meat and refined foods. A combination of several factors, which is not uncommon in modern people, further increases the risks of stroke and heart attack.
How is an ischemic stroke different from a hemorrhagic stroke?
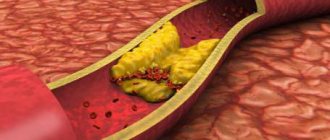
– Ischemic stroke occurs as a result of blockage of a vessel by a detached thrombus or as a result of the growth of an atherosclerotic plaque. There is only one result: blood does not flow, oxygen supply to the brain area is disrupted.
Hemorrhagic stroke is the most dangerous, often ending in death; against the background of high pressure, a vessel ruptures and blood flows into the brain tissue and cranial cavity.
According to statistics from the Republican Vascular Center, every 10-12th person dies, and 50% of patients become disabled after a stroke. Some are to a greater extent completely immobilized and need constant care, others are to a lesser extent, with a slight deficiency, after 3-4 months of rehabilitation they recover and return to normal life.
"Golden time"
“When you have a stroke, every minute is precious, and the patient’s life depends on how quickly the stroke is recognized and timely and correct assistance is provided,” the doctor emphasizes. – It is very important to inform people about risk factors and early signs of stroke, which will help, most importantly, to save life and minimize the patient’s disability. The “golden window” is 4.5 hours when, in the event of an ischemic stroke, a blood clot can be dissolved or, with the help of neurosurgeons, an operation can be performed to remove the blood clot from the lumen of the vessel. Thanks to the new thromboaspiration technique, the patient’s chances of recovery increase significantly. In the event of a hemorrhagic stroke, timely surgery will save life and cause less damage to brain tissue. It is also important to understand that the presence of chronic diseases, such as diabetes, arrhythmia, atherosclerosis, which were the cause of the attack, complicates the course of the stroke and the period of recovery of the body after.
What are the characteristic signs of a stroke that everyone should know?
- So, let's remember. If you notice that something is wrong in the face: if a person cannot smile symmetrically, half of the face is distorted, one eye may not close, the corner of the mouth is drooping. Speech is impaired, as if there is “porridge in the mouth”; the person cannot raise an arm or leg. Sound the alarm, call an ambulance. Remember, your attentiveness will help save the life of a person, perhaps a dad, mom, grandma, grandpa, or even a stranger.
Be attentive to your loved ones,” Inna Borisovna urges. – It happens that a spouse took alcohol, took a steam bath, and he became ill, had a stroke, those around him do not notice, they blame everything on alcohol, and time passes. Don’t be indifferent, don’t pass by on the street, when you see that a person is feeling unwell, come up and ask, maybe it’s a stroke. Then you need to urgently call an ambulance by phone. 03, 103.
How can I help before the doctors arrive?
– Before the ambulance arrives, it is necessary to lay the patient down with his head elevated. If you feel nauseous, turn your head to the side, provide rest and access to fresh air. Take off tight clothes, unfasten your tight belt and tie. Under no circumstances should you give anything to drink or eat, as pharyngeal functions may be impaired and the person may choke. Also, the patient should not get up and walk. Until the ambulance arrives, you need to stay with the patient, then convey to the doctors all the information you know.
How can you prevent a stroke?
– According to experts, most strokes occur due to the growth of atherosclerotic plaques in the vessels. If you have high cholesterol, that is, it is above 5 millimoles per liter, you need to sound the alarm. It is necessary to regularly monitor blood pressure and take a cholesterol test twice a year. If it is elevated, it is necessary to follow a diet, limit fatty meats, and take statins as indicated. And these rules are not discussed, it’s like brushing your teeth,” says the neurologist. – At any age, you need to monitor your weight, the body mass index (BMI) should be less than 25. To do this, you need to consume less refined fats and carbohydrates, give up alcohol and smoking, and walk more. It's advisable if you exercise, but consult your doctor before engaging in strenuous exercise. If the vessels are already changed, then excessive load can lead to rupture - hemorrhagic stroke. Follow your doctor's recommendations and take prescribed medications correctly. Rest, get enough sleep and think positively!
What symptoms require hospitalization?
Signs of a stroke are the following:
- speech is impaired, the person has difficulty pronouncing simple phrases, confuses syllables;
- vision deteriorates sharply;
- an acute headache occurs for no particular reason, dizziness appears;
- on one side of the body there is weakness, numbness, even paralysis of the muscles of the face, arm or leg;
- Coordination and gait are impaired.
If at least one of these symptoms appears, emergency hospitalization and initiation of treatment are necessary.
Symptoms
You are at risk if you agree with one or more of the following:
- one of the blood relatives has already suffered a stroke;
- a tendency to microthrombosis was diagnosed;
- was diagnosed with diabetes mellitus;
- you are a heavy smoker or drink alcohol in large quantities;
- weight significantly exceeds normal;
- Serious circulatory disorders in the brain have already been recorded;
- you suffer from one of the following diseases: angina pectoris, encephalopathy or arterial hypertension.
Inpatient therapy
Treatment methods for stroke in a hospital differ from those used in ARC. The standard of treatment for stroke in a hospital consists of the following measures:
- drug therapy aimed at restoring brain functions;
- rehabilitation.
Rehabilitation activities include physiotherapy, massage, exercise therapy. Patients with speech disorders receive additional treatment from a speech therapist.
How stroke complications are treated depends on the nature of the abnormalities that arise. The nature of the attack has almost no influence on the prescribed therapy. Treatment of ischemic stroke and hemorrhagic lesions follows a similar scheme.
How many days the therapy will continue depends on the prescribed course of treatment. Typically, the treatment period for ischemic stroke is slightly shorter than after cerebral hemorrhage.
Cost of hospitalization in medical institutions
| Calling a medical doctor (by profile) to your home | Transportation by ambulance in Moscow within the Moscow Ring Road | Diagnosis, treatment and hospital stay |
| 3,000 - 5,000 rub. | 7,000 rub. | check with operators |
The cost of hospitalization is calculated individually depending on the severity of the patient’s condition and the hospital.
You can choose a good hospital, find out about the approximate cost and duration of hospitalization from our service specialists by calling our hotline (24 hours a day)
Hospital care after resuscitation
Care after a stroke in the hospital is provided by junior medical staff:
- bedridden people are washed and spoon-fed;
- persons whose capabilities are moderately limited are assisted in performing hygiene procedures.
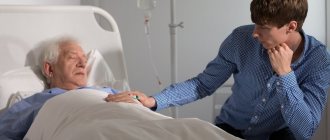
But this does not mean that once you know which department you are admitted to for a stroke, you should limit yourself to visiting a relative. Rehabilitation after resuscitation will be more successful and the recovery prognosis will improve if the stroke patient feels cared for by loved ones.
Although staff provide professional stroke care, it is important to help the person bathe, change clothes or style their hair, and bring home-cooked meals. Attention and care are very important in the post-stroke period.
Duration of inpatient treatment
Relatives have already found out which department the stroke patients are in and even managed to visit the patient. And now relatives are interested in how long they are in the hospital after a stroke.
According to the law, the patient has the right to remain in a hospital until the health-threatening abnormalities disappear:
- A microstroke is treated for 21 days in a general ward.
- A condition of moderate severity, which occurs after an ischemic stroke with right paralysis or moderate hemorrhage, will require inpatient therapy for 3-4 months. In case of a stroke with paralysis of the right side, it is necessary not only to stabilize the patient, but also to carry out primary rehabilitation measures.
- Slow recovery after a hemorrhagic stroke complicated by paralysis on the left side; the time spent in hospital can last up to six months. After a stroke with left paralysis, a person in serious condition often develops complications related to the functioning of the heart.
If a person is in a coma, it is impossible to say how long he will remain in the hospital. Some patients remain unconscious for months and are dependent on medical personnel. Such a person is not discharged from the department.
How long you stay in the hospital after a stroke depends on how long the recovery after the acute period lasts. After discharge, working people are kept on sick leave for several months, giving them the opportunity to complete their rehabilitation course on an outpatient basis.
Sick leave
Inpatient treatment only stabilizes the health condition, and then the person receives further treatment at home. A sick leave certificate after a stroke is opened in the hospital, and after discharge the stroke patient renews the document by visiting a doctor.
The duration of disability depends on the nature of the brain lesion:
- mild ischemic stroke is treated for about 3 months;
- a patient after surgery for removal of an intracranial term requires a minimum of four months of rehabilitation.
Sick leave after a stroke can be extended to 7-8 months. After this time has expired or if the doctor sees that full rehabilitation is impossible, the patient is sent to MSEC to receive disability.
Resuscitation in the early post-stroke period is one of the important stages of rehabilitation treatment. Intensive therapy helps prevent brain swelling and reduce the lesion. If a person has been taken away with a diagnosis of stroke, then there is no need to look for which department to treat stroke - patients after an acute attack are hospitalized in the ARC.
How is a ureteral stent removed?
Removal of a ureteral stent occurs on an outpatient basis and takes much less time than the procedure for its installation. Currently, there are several ways to remove a stent. The first traditional one is cystoscopic. The second is using threads that are tied to a stent and exit through the external opening of the urethra. The third method is applicable only to women and involves using a special sterile loop under X-ray or ultrasound control. The fourth method is less common due to the high cost of the special stent with a magnet used.
In cases of stent encrustation, entanglement, or migration, surgical treatment may be required.