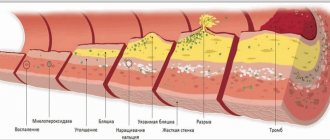
The formed blood cells known as white blood cells are heterogeneous in nature. Moreover, they make up a huge number of the total mass of such structures. They perform an important function of protecting the body from harmful external influences.
They are the defensive force that does not allow viruses, bacteria, or fungi to pass through. Sometimes malfunctions also occur and immune cells begin to attack healthy tissue. This is how allergies develop, for example. But this is a slightly different topic.
As for leukocytes, they can be divided into two large groups:
- Granulocytes. They have a clearly defined core. Perform the task of the primary immune reaction. That is, as soon as pathogenic structures penetrate the body, they are the ones responsible.
- Agranulocytes. Lymphocytes and some others. They enter the “battle” second. They are responsible for the formation of stable and long-term, lifelong immunity to a particular disease.
Segmented neutrophils are granulocytes that are most abundant in the blood. According to research, the number of such formed cells varies from 65 to 75% of the total mass of leukocytes, white blood cells in general.
The indicators of segmented cells are very sensitive to any deviation in the functioning of the body. Whether it is infectious or autoimmune inflammation, the analysis provides informative information that can be used as a basis for further diagnosis.
As a rule, it is not necessary to adjust the indicators of segmented neutrophils. This is a consequence, not a cause.
It is necessary to fight the primary provoking factor. This will be the basis of high-quality, competent therapy.
What are neutrophils
Blood Basics neutrophils are one of the types of leukocytes, white blood cells, thanks to which the body fights all kinds of infections. Moreover, this type of blood cells is the most numerous.
Up to 70% of the Blood Basics of all leukocytes in the human body are neutrophils.
Doctors call them immediate response cells. Having discovered a virus or bacteria, neutrophils rush to attack with lightning speed. Even if it means leaving the bloodstream and going into the tissues of the body.
The more clearly the immune system perceives a threat, the more neutrophils are produced in the bone marrow and the higher their level in the blood.
Reasons for the increase
{banner_banstat1}
An increase in the number of segmented neutrophils is usually observed in the following cases:
Infectious and inflammatory processes
{banner_banstat2}
Classic of the genre. This should include all possible disorders that relate to the penetration of foreign agents into the body. Bacteria, viruses or fungi.
The intensity of the increase in cellular structures, the speed and final volume of leukocytes depend on the specific disorder. The stronger the disease, the more abnormal agents and their waste products, the higher the level of neutrophils.
Symptoms depend on the pathological process. In general, there are always such deviations from the norm:
- Temperature increase. To what extent - you need to look at the situation.
- Weakness.
- Drowsiness.
- Feeling very tired.
- Manifestations of intoxication of the body: nausea, headache. Plus or minus. Everything is determined by the diagnosis.
- There are also focal signs of the pathological process. If it is tonsillitis - sore throat. Pneumonia, bronchitis - shortness of breath, chest discomfort, and so on.
The treatment is specific and is carried out under the supervision of a therapist and a specialized specialist (depending on the disease).
Antibiotics, antivirals, immunomodulators, anti-inflammatory drugs, antipyretics are prescribed to bring down the temperature.
Next, the course of treatment is adjusted based on the dynamics of the patient’s condition. This applies to both dosages and the names of the drugs themselves.
Autoimmune inflammation
They occur no less often, but are fundamentally different from infections. In this case, there are no traces of pathogenic structures. The body begins to react to its own tissues and cells inappropriately and attacks them.
Segmented neutrophils, basophils, and eosinophils also participate in this process. All formed cells of the immune system.
The most common diagnoses are:
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Myocardial damage.
- Gout.
- Lupus erythematosus.
- Thyroiditis.
And much more. This also includes allergic reactions, which will be discussed below.
Treatment is provided by rheumatologists and immunologists. Glucocorticoids are prescribed. Prednisolone is used as a starting point.
Further, the strength of the drug is varied based on the essence of the pathological process and its severity.
In the most extreme cases, if the condition is resistant and does not respond to therapy, immunosuppressants are used. They inhibit the production of protective cells and thereby eliminate the negative impact.
Sepsis
{banner_banstat3}
Occurs against the background of a long-term infection or open injury. The second, not entirely accurate name for this pathological condition is blood poisoning.
In fact, we are talking about a generalized inflammatory process. It covers the entire body, systems and organs suffer. If nothing is done, there is a high probability of rapid death.
Segmented neutrophils are increased to eliminate bacteria, viruses, fungi, and their metabolic products, slow down the inflammatory process and somehow achieve a state of balance. Therefore, the growth is significant, clearly visible and rapid.
Attention:
The combination of speed and high rates often indicates either sepsis or gangrene.
Infectious disease specialists provide treatment. At first, the patient has to be placed in intensive care in order to provide the victim with thorough medical care and provide supervision: the condition can worsen at any moment.
Loading doses of antibiotics are prescribed, as well as anti-inflammatory drugs, medications for viruses and fungi.
Even these measures are sometimes not enough. They resort to hardware blood purification using plasmapheresis methods. But this is more of an auxiliary measure.
Rehydration solutions are administered and infusion therapy is prescribed in order to quickly remove waste products of abnormal agents and toxins from the body’s structures.
The prognosis is vague even with high-quality treatment. It all depends on the moment the correction begins.
Malignant oncology
{banner_banstat4}
Often the reason for the increase in segmented neutrophils is the poisoning of the body with tumor decay products: formed cells, leukocytes act as a kind of scavengers that utilize waste substances and particles. These include dead malignant cells.
You can expect tumor destruction starting from the second or third stage of the pathological process. Because there are so many cytological structures that there is no longer enough “food” for everyone. Some cells die from “gluttony”, others from nutritional deficiency. The bottom line is one thing: tissue breakdown and poisoning of the entire body.
By the way, hence the regular or even constant increase in body temperature, weakness, drowsiness, symptoms of general intoxication, sudden weight loss and other “delights” of this condition.
As for neutrophils, their concentration increases in parallel with the growth of the tumor. The further it goes, the worse the patient will become.
Thermal injuries
{banner_banstat5}
An increase in segmented neutrophils in the blood occurs with massive burns, since the products of protein destruction, which were located in the thickness of the dermis, are released into the channel. The “garbage” needs to be removed. Granulocytes do this job.
The larger the affected area, the worse the situation overall. But that's not the problem. If nothing is done, fatal complications for the patient are very likely.
With burns of more than 20% of the body, there is a high probability of the following problems:
- Kidney failure from too much protein.
- Cardiac arrest due to overload.
- Heart attack.
- Coma.
To prevent this from happening, the patient is placed in a burn department or intensive care unit. Depends on the condition. But no one gives guarantees of survival.
Allergic reactions
{banner_banstat6}
Segmented neutrophils increase due to an autoimmune response, a false attack of the body’s own defense cells on the body’s tissues. There are no objective reasons for this.
As a rule, allergies develop to food dyes, natural pigments of natural origin, dust particles and other harmless substances.
Usually this is the result of hypersensitization of the body. Increased sensitivity to the limit after an infection.
Allergies can manifest themselves in different ways. In some cases it is a common skin rash or urticaria. In others - anaphylactic shock, Quincke's edema. That is, very dangerous, potentially fatal violations.
Immunologists treat patients. The goal is to restore the body's normal sensitivity and reduce the degree of sensitization.
Corticosteroids like Pridnisolone are prescribed. As in other cases, immunosuppressants may be required. Fortunately, this is a relatively rare option.
Attention:
It is impossible to completely cure allergies. All that remains is to stop exacerbations and prevent relapses of the pathological process.
Parasitic infestations
{banner_banstat7}
Simply put, worms. Not necessarily in the classical sense. Those located in the intestines. There are different worms.
- Some prefer the hepatic ducts (giardia, flukes).
- Others, like echinococci, even settle in the lungs, brain, and also in the structures of the digestive tract.
- Opisthorchis, found in river fish, can potentially infest any organ that has a sufficient blood supply. Even the human eye. There are many options.
Be that as it may, parasites release waste products into the bloodstream. This is a kind of signal for the body to start an immune reaction.
Neutrophils attack intruders and destroy them along with eosinophils, which are more adapted for the purpose of combating helminths.
The more worms there are, the more active they are, the more intense the immune response itself. It is necessary to check for parasitic infestation almost in the first place.
The treatment of the pathological process is carried out by specialists in parasitology. Special medications are prescribed. The doctor will choose the exact name; there are many of them and they are usually specific. That is, they act on parasites of a certain type and origin.
It is strongly recommended to undergo treatment in a hospital. Because when they decay, worms poison the body and can cause complications.
Myocardial infarction
{banner_banstat8}
Oddly enough, acute circulatory disorders in the myocardium can become the culprit for the growth of segmented neutrophils.
If you take a closer look, there is nothing unusual. The fact is that in this emergency condition, myocardial cells are destroyed. The accumulated substance known as myoglobin is released. This is protein.
Like all chemical components of this type, it has an increased allergenic potential. The body reacts to the compound as potentially dangerous and produces more formed cells.
In addition, you need to cleanse the body of waste products. These two goals provoke an increase in the content of segmented neutrophils in the blood.
There is no need to do anything special. High levels of formed elements and white blood cells will disappear on their own as soon as the acute condition passes.
It is important to focus on myocardial infarction. Conduct a course of maintenance therapy and prescribe rehabilitation measures. A cardiologist is dealing with the problem.
All symptoms of a pre-infarction condition are described in detail here.
Severe forms of renal failure
{banner_banstat9}
Normally, it is the excretory system that eliminates waste products, cellular debris, and waste proteins.
If the filtering paired organ fails, these poisons are absorbed back into the blood and poison all systems. The increase in neutrophil concentration is due to a reflex attempt to eliminate toxic components.
The most common causes of renal failure are long-term infectious-inflammatory and autoimmune processes. You can also name parasitic type disorders, oncology, anatomical changes (prolapse of the kidney, wrinkling, etc.).
Treatment is carried out by specialists in nephrology (not neurology). Diuretic drugs are prescribed, which stimulate the natural functioning of the paired organ.
If the state is neglected, they cannot be used. Doctors resort to hardware methods of blood purification, hemodialysis.
The only radical and effective way of recovery is a kidney transplant. Finding a suitable donor is not an easy task. That's why patients wait for years.
Many do not have time for the operation and die before the right moment arrives.
Some forms of poisoning
Intoxication with heavy metals. For example, lead, mercury. This also includes pathological processes provoked by volatile compounds. For example, sulfur fumes or other agents.
Most often, employees of hazardous chemical enterprises and people living in areas that are unfavorable from an environmental point of view encounter such problems.
The treatment is specific. It is dealt with by toxicologists or therapists if there are no specialized doctors nearby. A detoxification course is prescribed. When possible, use specific antidotes.
The correction takes place within the walls of the hospital to provide the patient with sufficient supervision.
By the way, some drugs can also lead to poisoning. For example, corticosteroids. The probability must be assessed based on the annotation. Information from the instructions for use.
Injuries suffered
{banner_banstat10}
After any injury, even a bruise, even a fracture, the inflammatory process begins.
So the body, on the one hand, eliminates a possible infection, a secondary septic phenomenon. On the other hand, it increases the local regenerative abilities of tissues and helps restore anatomical integrity.
Granulocytes also participate in this process. In particular, neutrophils. The degree of growth depends on the nature of the pathological condition.
A bruise will practically not provoke changes. The same cannot be said about an open wound with extensive tissue damage.
Treatment is carried out under the supervision of a traumatologist and surgeon. Specific measures are required: operational or conservative. The question remains at the discretion of the doctors.
These are the main, but not all possible provoking factors.
Why are neutrophils elevated?
The most common Neutrophilic Leukocytosis and the most obvious cause of neutrophilia is infection. The number of neutrophils increases more noticeably and most often with bacterial What are the causes of neutrophilia in leukocytosis? diseases.
However, other reasons can also lead to an increase in the level of neutrophils in a blood test. What are neutrophils and what do they do? :
- Serious injuries. For example, fractures, burns, complex surgical operations.
- Inflammatory diseases. These include colitis and other intestinal inflammations, vasculitis (inflammation of blood vessels), hepatitis (inflammation of the liver).
- Taking medications. For example, based on corticosteroids.
- Pregnancy.
- Obesity.
- Emotional or physical (related to overexertion) stress.
- Some types of cancer. For example, leukemia. It affects the bone marrow, which produces blood cells. And may increase neutrophil production.
How many neutrophils should there be?
The fact that there are not enough neutrophils is indicated by a blood test in which the content of phagocyte cells is below 1.6x10⁹. However, the normal options depend on the age of the patient. For example, children in the first year of life should have 30%-50% neutrophils in their blood relative to the total number of leukocytes, and by the age of seven their percentage increases and a figure of up to 55% is considered normal. At the same time, the lower threshold also increases - it starts from 35%. An adult can have from 45% neutrophils in relation to the total number of leukocytes, the upper limit of normal for this age category is 70%.
To make a diagnosis of neutropenia, the true value of the cell number is determined. Mild neutropenia is diagnosed when the level is from 1 to 1.5x10⁹ units per liter of blood. The degree is considered moderate when the content is from 0.5x10⁹, and severe neutropenia is observed when the level is below 0.5x10⁹, or the complete absence of phagocyte cells.
Neutropenia can be congenital or acquired. Blood cell levels may vary depending on your health. The lack of corpuscles can be a separate problem or manifest itself when a specific disease occurs. Congenital forms of neutrophil deficiency are inherited and may not clinically manifest themselves until the blood is taken for analysis for some other reason.
Diagnostics
Detection of neutrophilia requires differential diagnosis. To do this, you need to consult a general practitioner. In order to obtain primary information, anamnesis is collected - how long ago the symptoms appeared, whether there was recent contact with infectious patients, whether there was an increase in body temperature, pain, skin rashes.
If there is a suspicion of acute surgical abdominal pathology, the abdomen must be palpated for tension in the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall and the presence of a positive Shchetkin-Blumberg sign. However, it must be taken into account that these signs are difficult to identify in a child under 9 years of age. To confirm the diagnosis, additional examination is prescribed, including:
- Blood tests
. The total number and percentage of all types of leukocytes are calculated. The concentration of red blood cells, platelets, and inflammatory markers (ESR, CRP) is measured. The morphology of granulocytes (toxic granularity, karyopyknosis) is studied. In a septic condition, the level of presepsin and procalcitonin is determined. The presence of autoantibodies (anti-DNA, topoisomerase, antineutrophil antibodies) is checked. - Identification of the pathogen
. To identify the pathogenic microorganism, bacteriological culture, microscopy of sputum, urine, smear from the throat and tonsils are performed. To diagnose helminthiases, a stool test is performed for worm eggs, a blood test for specific immunoglobulins, and a scraping is taken from the child’s perianal folds. - Ultrasound
. A sign of pyelonephritis on an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity is expansion, thickening of the renal collecting system, pancreatitis - enlargement, diffuse changes in the pancreatic parenchyma, cholecystitis - thickening of the walls of the gallbladder, often the presence of stones. - X-ray
. On chest x-rays with pneumonia, foci of infiltration and darkening are visible. When the ulcer is perforated, the images reveal the presence of free gas in the abdominal cavity (“sickle symptom”). In case of inflammatory diseases of the joints, x-rays show a narrowing of the joint space and marginal osteoporosis. - ECG.
Electrocardiography during myocardial infarction reveals ST segment elevation, left bundle branch block, ventricular tachycardia, and other heart rhythm disturbances. With pulmonary embolism leading to pulmonary infarction, signs of overload of the right parts of the heart are detected - a deep Q wave in III, an S wave in lead I, a high pointed P wave (P-pulmonale) in leads II, III, aVF. - Histological studies
. A definitive diagnosis of cancer can only be made on the basis of a biopsy. The main feature of solid tumors is a large number of atypical cells. In case of leukemia, in the bone marrow biopsy, hyperplasia of the granulocytic lineage and the predominance of blast cells are noted; in the tissues of the lymph node in case of lymphomas, diffuse proliferation of cells with blast morphology is noted.
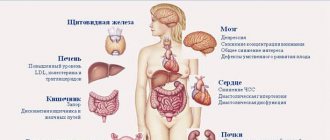
The danger of increased levels of neutrophils in the blood
Neutrophilia without attention is fraught with complications
An increase in the number of neutrophils is not always accompanied by severe symptoms. A person can consider himself absolutely healthy, but detect a deviation from the norm only on a form with test results. This may mean that there is a hidden infection in the body. If no action is taken, the inflammatory process will spread to larger areas.
Malignant and benign tumors are manifested by increased levels of neutrophils. If over a long period the number of cells significantly exceeds the norm, the doctor may suspect the oncological nature of the pathology in the patient.
During pregnancy, a small increase in neutrophils is considered normal. But too high values can lead to miscarriage, since neutrophils perceive the fetus as a foreign organism in the woman’s body.
Forecast
It is impossible to predict prognosis based on neutrophilia alone. It all depends on the disease that served as the background for the occurrence of neutrophilia. For example, a transient increase in the number of neutrophils after stress, food intake, or in a child on the first day of life is absolutely benign and transient. Conversely, severe purulent-septic pathologies and oncological diseases have a fairly high incidence of deaths. Therefore, any excess of the reference values of neutrophils (especially high and persistent ones) requires contacting a doctor.