Normal values are considered to be 7.5-11 fl.
In the resulting histogram, which is a curve displaying the quantitative and qualitative composition of the blood, you can calculate how many young cells there are and how many are already preparing to die. The following ratio is within normal limits:
- mature cells – 90% of the total platelet mass;
- old – 5-6%;
- newly formed – 0.2-0.8%;
- degenerative – no more than 0.2%.
Taking into account such features, during the study a curve is formed that shifts to the left if the number of immature and degenerative cells is greater, to the right - if most of the cells are old. Decoding already gives numerical indicators that facilitate perception.
In childhood, the indicators are somewhat different - 6.8-11.5 fl. The width of the spread is dictated by the immaturity of the hormonal system. This is taken into account when carrying out the analysis, since in children deviations in MPV are observed extremely rarely and only in cases of pathologies.
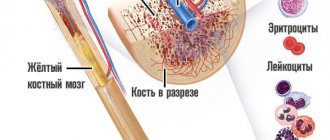
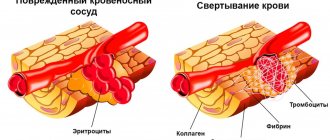
An important part of a clinical blood test is determining the level of platelets - red blood cells. Thanks to these components, normal blood clotting is maintained, which helps prevent large blood loss during injuries and operations, and also provides the ability to correct blood vessels in case of damage.
Elevated mean platelet volume (MPV) is a completely different indicator. Determining both has great diagnostic value, allows you to identify serious pathological processes in the body and prevent their negative impact on humans.
General information
It should be noted that an increase in the number of platelets and an increase in their average volume are different phenomena. The detection of a high level of red blood cells indicates their quantitative increase and does not characterize the qualitative composition.
Analysis of the average volume of platelets of platelets does not reflect their quantitative presence in the blood, but the ratio of mature and young elements. That is, this indicator is decisive for assessing the usefulness of platelets.
Their activity and ability to form a life-saving thrombus at the site of vessel injury depends on the size and quality of the plates.
Mature cells, characterized by their small size, make up a smaller portion of the total volume of blood studied. Immature (young) blood cells are larger and, accordingly, occupy most of the fluid volume.
This ratio is considered normal. Its violation indicates the presence of pathology in the body.
Different characteristics of platelets
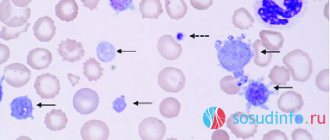
Fragments of megakaryocytes, giant bone marrow cells, anucleate blood plates - platelets (PLT - platelet), circulating in the blood, look like biconvex disks with a diameter of 1.8 microns to 4 microns. Young blood platelets are larger in size than mature cells, aged platelets are the smallest. In blood smears, platelets appear pale blue or lilac in color and are often collected in groups.
In an inactive state, platelets have a round or oval shape, but as soon as they “sense” a violation of the integrity of blood vessels and bleeding, they almost instantly change shape, increase up to 10 times in size, “acquire” pseudopodia and begin to stick together (platelet aggregation) . The blood platelets perform all these actions in order to rush in the form of a conglomerate to the scene of the accident, where the platelets that arrived earlier are already waiting.
Therefore, platelets are very prone to change their size , since they have a very important function in the human body - participation in vascular-platelet hemostasis or, more simply, these blood platelets help blood clotting in case of various damages in the microcirculation zone.
Symptoms
Due to a disturbance in the normal balance between mature and immature blood components, accompanied by an increase in the average volume, the following symptoms are observed:
- the occurrence of itching of the skin, which cannot be eliminated by taking antihistamines;
- frequent nosebleeds;
- bloody discharge from the ears;
- hemoptysis;
- subcutaneous hemorrhages (bruises) that occur without visible factors contributing to their formation;
- bluish or reddish tint to the skin;
- general weakness, malaise;
- increased sensitivity to changes in atmospheric pressure;
- lethargy, drowsiness, apathy.
The most alarming symptom is the unreasonable appearance of bruises.
Indications for examination
The described manifestations are not observed in the initial stages of pathological processes, so the disorder is often detected by chance during routine examinations.
To avoid an advanced condition, in which the treatment process will be longer, it is necessary to do a blood test twice a year to determine MPV.
The collection of biomaterial for blood testing is done from a finger.
The study is carried out under a microscope using hematological analyzers. A deviation upward or downward in the average volume indicates serious illness.
Who should check the MPV level
A general blood test is one of the most common tests that is prescribed to rule out various diseases or find out their causes.
The MPV indicator (as well as other platelet tests) should be evaluated in people who:
- experience frequent nosebleeds
- have prolonged monthly bleeding
- have problems healing small skin cuts
- prone to bruising and hematomas
- have petechiae on the skin or mucous membranes
- noticed blood in the stool
- underwent surgery
- have chronic liver or kidney disease
- suffer from cardiovascular diseases
- have used hormonal contraception for many years
- are taking anticoagulants
Norm
Indicators are measured in femtoliters. Normal values range from 7.5 to 11 fl. The percentage of young platelets is about 0.8. Mature - no more than 5.7%.
These indicators are different for children and adults. For example, in a three-year-old child they are no more than 8.8 units. Women have lower values than men. Such differences are a consequence of menstruation.
Low levels of MPV are observed in pregnant women. The danger is a condition in which a decrease in the quantitative level of platelets is detected
. This is fraught with the possibility of spontaneous miscarriage or premature birth.
What to do if the MVP level is increased?
A thrombus, circulating with blood throughout the body, can enter a vessel of the heart or brain.
An increase in MVP production indicates that more cells are being produced than required.
Due to this, the consistency of the blood increases and the concentration becomes thicker. This disease is called thrombocytosis.
Thrombocytosis is dangerous because in excess blood clots begin to be created, which, reaching impressive sizes, can block the vessel and limit the blood supply.
Fatal outcomes are quite possible. Subsequently, it leads to heart attack and stroke, after which a third of sick people die.
Thrombocytosis is of two types:
- Relative – the norm is not significantly exceeded (from 20 to 30%)
- Critical - the norm is exceeded by 3-5 times.
In a critical case, urgent medical intervention is required!
An increase in MVP indicators is possible in two options:
- Certain physiological states of the body,
- Development of pathologies.
Physiological condition includes:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Certain medications
- Features of the child's body,
- Various types of bleeding.
The development of such pathologies affects the increase in MVP:
- Injuries (mostly in large numbers),
- Surgical interventions
- Various types of bleeding.
The main reasons for increasing MVP are some diseases:
- Alcoholism,
- Atherosclerosis,
- Diabetes
- Deterioration of the thyroid gland,
- Blood cancer,
- and others.
A peculiarity in pregnant women is a frequent increase in platelets, which in the vast majority of cases is as it should be. Since the body of the expectant mother changes and adapts to more comfortable conditions for gestation. This can be explained by the fact that the fetus needs its own circulatory system. It is for this purpose that a woman’s circulatory system produces more platelets.
Increasing the indicator
If the values are higher or lower than normal, what does this mean?
The conclusion is clear: the detection of such deviations indicates pathological changes in the body associated both with the process of platelet production and with the presence of various diseases.
A sharp decrease in values is fraught with intense bleeding. Inflated values indicate the likelihood of thrombosis, which develops against the background of thickening and increase in blood viscosity.
The result of an increase in indicators is a significant slowdown in blood flow, a tendency to the formation of blood clots - thrombi, which can lead to blockage of the lumen of the vessel.
This entails the likelihood of stroke, heart attack, and thromboembolism.
Additional examinations
A blood test gives an approximate idea of the state of the body. It only allows us to state a fact: there is a problem. Why it arose is a different question, and the answer to it is sought using auxiliary techniques.
The examination is carried out by a hematologist. Third party specialists are brought in as needed.
- Oral interview with the patient. Complaints are informative in some cases. Symptoms indicate damage to one or another organ.
- Anamnesis collection. Lifestyle, past and current diseases, family history, genetics and other points. The doctor collects them for interpretation and determines the possible source of the problem. Its origins.
- Ultrasound of the digestive tract. First of all, specialists are interested in the liver.
- To study the functional state of the largest gland in the body, scintigraphy is prescribed. Radioisotope technique.
- A blood test for hormones helps identify thyroid diseases.
- Specific, extreme measures are possible. Bone marrow puncture, histological evaluation of the obtained material.
- If necessary, diabetes is diagnosed with special tests: sugar curve and others.
The question of examination is within the competence of the doctor. The list can be expanded or narrowed. Of necessity.
Main reasons
The indicator increases in the presence of predisposing factors such as:
- diabetes mellitus due to pancreatic dysfunction;
- hyperthyroidism, which provokes hormonal imbalance;
- infectious and inflammatory diseases;
- posthemorrhagic anemia caused by large blood loss due to injuries and internal bleeding;
- tuberculosis;
- liver pathologies;
- splenomegaly (enlarged spleen);
- oncological diseases;
- autoimmune diseases.
The possibility of MPV rising above normal as a result of removal of the spleen cannot be ruled out.
In addition, the indicators may be exceeded due to uncontrolled use of medications that can activate excessive platelet production. Therefore, you should warn your doctor before performing a blood test about all the medications you are taking. In this case, this situation will be taken into account when decrypting.
What it is
When patients notice the abbreviation MPV on the test form, rarely does anyone understand what it is. This is the platelet index or average platelet volume. This allows you to assess the condition of peripheral blood and its coagulation system. This indicator is determined during a general clinical analysis. Usually blood is taken from a finger or a vein. It must be taken on an empty stomach, in the morning. The study is carried out no later than 2 hours after collection, otherwise the results will be unreliable.
Determining this indicator allows you to detect pathologies at the initial stage. The presence of thrombosis, internal bleeding, and some chronic diseases can be detected. Therefore, it is recommended for adults to have a blood test annually, and for children twice a year. The study of MPV levels is also regularly carried out for women during pregnancy, patients with liver pathologies, autoimmune diseases, and circulatory disorders.
Platelets and their role in the body
Platelets are blood cells. They are flat plates without nuclei, colorless, round or oval. They are responsible for the coagulation process. Produced in the bone marrow. Not all platelets are in the blood; some of them are deposited in the spleen, liver, and lungs. When injured, they are released into the blood and travel to the site of injury. At the same time, they change and stick together, forming blood clots. With their help, bleeding stops and the walls of blood vessels are restored.
To prevent bleeding, platelets change shape and stick together
Platelets perform many functions in the body:
- support the structure of the walls of blood vessels;
- prevent bleeding;
- stimulate tissue restoration;
- strengthen cell membranes;
- secrete growth factors involved in cell division.
Platelets of different ages and sizes are constantly present in the blood. The average lifespan of such a cell is 10 days. The younger she is, the larger in size. Mature platelets decrease in size and become more active. MPV shows not only the total number of these formed elements. The platelet index allows you to determine which cells are more mature. The ability of blood to clot depends on this.
When is an increase considered normal?
Active production of a large number of platelets by the bone marrow becomes a consequence of the body’s compensatory reaction.
It helps stop bleeding, but leads to an imbalance between mature and young cells. The reason for the increase in the indicator in such situations is associated with restorative physiological processes in the body.
Such deviations are considered normal; they do not indicate pathology. Among them are the following situations:
- after surgical operations;
- in women during the menstrual cycle;
- multiple injuries accompanied by heavy bleeding;
- the use of drugs that stimulate hematopoiesis;
- features of processes in children caused by inferiority of the hematopoietic system.
The absence of a natural increase in platelets against the background of the described situations indicates bone marrow failure and necessitates further examination and correction of the condition.
Average platelet volume is reduced
Platelets are elements of the blood that play an important role in clotting. Under certain pathological conditions, the average volume may decrease. To accurately determine the cause of the decrease in volume, a detailed examination must be carried out.
Formation of a primary plug and stopping bleeding
Normal indicators
The following values are considered normal values for the total platelet count:
- adult men and women - 150-400x109 cells/l;
- women during menstruation - 75-220x109 cells/l;
- children - 100-480x109kl/l.
Indicators may vary depending on the individual characteristics of the person. During pregnancy, your platelet cell count may fall. It is recommended to undergo analysis periodically in order to know your personal norm and, if necessary, detect deviations from the usual values.
Normal average volume is 7-10 Fl. In men, the average volume is slightly more than 10-11 Fl. The indicator is reflected in the general analysis. Based on the results of the study, the state of human health is judged.
More details about platelets, their number and average in the video:
Treatment
The main directions of therapeutic effects on the level of average platelet volume are:
- The use of medications that thin the blood. This can significantly improve its movement within the body and thereby facilitate the functioning of the heart muscle.
- Normalization of platelet production using hormonal drugs.
Attempts to decipher test results on your own, and even more so to treat deviations from the norm without a doctor’s recommendations, lead to a complication of the situation. Therefore, the use of any drugs is allowed only after consultation with specialists.
What does the MPV index mean?
When automatically processing blood samples, platelets are counted in the same channel with red blood cells - erythrocytes, so the hematology analyzer can separate particles by signal height in accordance with volume, which allows the device to immediately differentiate them:
- Macroplatelet cells (this group includes elements from 1.8 to 30 femtoliters - in principle, these are the cells that are currently interesting to us);
- Microerythrocytes;
- Fragments of red blood cells - schizocytes;
- Remains of the cytoplasm of white cells - leukocytes or, as it is called, cellular debris.
a – normal platelets b – platelets of different volumes (pronounced anisocytosis) c – huge macroplatelets
Meanwhile, this information alone is very little to characterize the state of platelets. At other times they would have been seen on a stained slide, but now most automated hematology analysis systems provide the various indicators present in the hemogram - mean platelet volume (MPV) and other platelet indices. The average volume of blood platelets is calculated by the automatic hemoanalyzer program using the formula:
MPV = [PCT,% x 1000] /
In addition, the device also includes a histogram for its calculations, which is subsequently studied by the doctor when deciphering the results.
Necessary Precautions
Particular caution is required when choosing medications for the treatment of diseases that are viral and inflammatory in nature.
Their components can cause a significant release of young platelets into the bloodstream and upset the balance of the average volume of red blood cells.
The presence of diabetes mellitus, vasculitis, hyperthyroidism and thyroid diseases in a patient requires a mandatory analysis to determine the average volume of blood platelets at least once a quarter. This will eliminate the likelihood of exacerbation of existing pathologies and the development of other diseases against their background.
Increased level
The most common situation is that MPV in a blood test is increased. This can happen after an injury, surgery, in the presence of chronic diseases, or taking certain medications. An elevated level indicates the presence of a large number of platelets in the blood. In this case, they speak of the presence of thrombocytosis.
When there are too many platelets in the blood, this is thrombocytosis.
If the volume of red blood plates is increased by 1-2 units, this is relative thrombocytosis. It can occur for physiological reasons, such as after bleeding. The MPV level increases with atherosclerosis, smoking, alcoholism, and also with age - after 60 years it is 11-12 fl.
Causes of Low Blood Platelets
But such a result often means that pathological processes are occurring in the body. In this case, critical thrombocytosis can be diagnosed when MPV almost doubles. This happens for the following reasons:
- for some congenital pathologies;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- with hyperthyroidism;
- for diabetes mellitus;
- due to anemia after heavy blood loss.
Note! This indicator certainly increases after removal of the spleen, but only for a short time.
What to do
If the increase in platelet count is caused by physiological processes and no pathologies are detected, no treatment is required. To find out the cause of this condition, the patient is prescribed a repeat OAC. A biochemical blood test, urine test, and ultrasound of the abdominal organs are also performed.
With a pathological increase in MPV, the risk of blood clots increases, so measures are taken to restore the structure of the blood. Anticoagulants are used, as well as hormonal agents to normalize platelet production. Treatment should take place under the supervision of a doctor, preferably in a hospital.
Possible complications and consequences
Blood thickening caused by an excess of platelets is a serious prerequisite for such negative consequences as:
- tendency for platelets to stick to the walls of blood vessels and develop thrombosis;
- myocardial infarction;
- iron deficiency anemia due to the predominance of mature platelets in the blood.
To prevent the development of complications, you should undergo a preventive examination at least once a year. This will make it possible to identify existing problems in the body and eliminate them, resorting to qualified help from specialists.
In order to have an idea of the concentration of platelets in the blood, a special laboratory method for determining it is used -. Thanks to the results obtained, it is possible to determine what number of platelets is produced, what part of them is subject to adhesia, and how quickly the process of their gluing occurs (indicates an enzyme such as fibrinogen). As a result, the data obtained can be used in the diagnosis of various diseases of the circulatory system, including hematopoietic dysfunction (oncological diseases of the bone marrow). What is the average volume of platelets in a healthy person, and what does an increase in the number of these blood cells indicate, we will analyze further.
Platelets are the smallest but extremely important blood particles
.
They do not have a core, but this does not prevent them from fully performing their functions. Their main task is to regulate blood viscosity and density. This function is achieved due to the ability of platelets to stick together, forming a dense microstructure. This important feature allows you to quickly eliminate bleeding in the presence of microtraumas, preventing life-threatening blood loss.
The life expectancy and distribution of platelets is short - only 10 days. Their synthesis occurs in the bone marrow, and the concentration in the blood is determined in a special analysis - MPV. There are certain standards by which platelet concentration is determined. The average platelet volume in a healthy person is 7-11 femtoliters. This indicator is formed from calculations of the number of new and old cells, which are easy to identify externally: young cells are larger in volume and mobile, while aging cells are small in size and inactive. Indicators below or above the norm are considered deviations.
The MPV test is carried out using blood from a finger, which is smeared into a thin layer on a glass slide and placed under a microscope. The peculiarity of the analysis is that it needs to be performed only in the first 1.5-2 hours after blood sampling, after which the width of the indicators and the final result may be inaccurate.
Deviations from the norm indicate the presence of
diseases or pathologies
.
If the bone marrow produces more platelets over a certain period of time than their number has time to die off, the blood becomes too viscous, provoking the formation of blood clots. If there is insufficient platelet synthesis, the risk of bleeding increases significantly (the blood clotting process is disrupted).
- The average platelet volume in men and women over 18 years of age is 150-350x109/l.
- The average platelet volume in a newborn baby is 100-400x109/l.
- The average platelet volume in childhood is 150-380x109/l.
- The average platelet volume in women during pregnancy is 150-38-x109/l.
Deviations are any non-compliance with the specified and generally accepted standards of indicators.
The deviations themselves may be pathological in nature (if the deviations are more than 10-25 units), or they may be caused by any side processes. However, the danger lies not only in a sharp decrease in the platelet count, which threatens heavy bleeding, but also in an uncontrolled increase in the number of blood cells, as a result of which thrombosis develops and the blood becomes thick and excessively viscous.
General blood analysis
A complete blood count (CBC, clinical blood test) is one of the most important and frequently prescribed laboratory tests. This analysis makes it possible to assess the condition of the body as a whole, confirm or exclude the suspected diagnosis, and monitor the progress of treatment.
Platelets are blood cells that stop bleeding if a blood vessel is damaged.
The first general blood test is performed for children in the maternity hospital. As the child grows up, it is recommended to carry it out regularly during routine medical examinations, which will make it possible to promptly identify abnormalities (for example, the development of iron deficiency anemia) and take the necessary measures in a timely manner. For preventive purposes, it is recommended to conduct a general blood test for adults once, and for children twice a year.
A general blood test includes determination of hemoglobin concentration, number of red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets, hematocrit level, as well as erythrocyte and platelet indices and erythrocyte sedimentation rate. A detailed blood test also includes a leukocyte count, which consists of determining the percentage of different types of leukocytes in the peripheral blood.
Counting the number of platelets and determining MPV is mandatory for women during pregnancy, as well as for patients with autoimmune diseases, varicose veins, liver pathologies, etc.
Increased platelet volume: what does this mean, and what are the reasons for this?
If, as a result of the MPV analysis, the patient's average platelet volume is increased, this means that there is a risk of developing thrombocytosis
.
In this case, the blood becomes more viscous, which leads to a slowdown in blood flow, as well as to the formation of blood clots. If no measures are taken in time and treatment is not prescribed that could regulate the synthesis of platelets by the bone marrow, the consequences are the most dire: myocardial infarction, stroke, thromboembolism.
When the average platelet volume is increased, it is important to determine which microparticles are causing the imbalance - young or old. If the number of new young platelets exceeds this, this indicates possible internal bleeding or significant blood loss (during surgery, for example). When the rate of old platelets goes off scale, this is a sure sign of cancer, in which such an imbalance is the first indicator suggesting the presence of health problems that are asymptomatic.
One of the components of a detailed blood test is such a parameter as the average platelet volume. These small blood platelets perform important functions in the body: they take part in blood clotting, ensure the formation of a blood clot and restore the integrity of the vessel. In fact, they are not cells, although they are commonly called that. They are disc-shaped fragments of cytoplasm that do not have a nucleus. They are formed in the bone marrow, two thirds are in the bloodstream and one third in the spleen.
The average platelet volume is the platelet index, which characterizes the maturity of blood platelets, the lifespan of which is about 10 days. In blood tests it is designated as MPV. Old cells decrease in size, while young cells, on the contrary, increase in size.
Blood for MPV is donated in the morning on an empty stomach, taken from a vein or from a finger. The analysis result is obtained using hematological analyzers. They draw a curve that shows the distribution of platelets by volume. The histogram is shifted to the right if immature forms predominate. If the blood contains predominantly old cells, a shift to the left occurs.
Reasons for increasing MPV
A high level of average platelet volume is an alarming sign that indicates the development of dangerous diseases
If the average platelet volume is elevated, this indicates that large, young platelets predominate in the blood. This does not always indicate increased thrombus formation, since immature cells are quickly and constantly produced, but can also die quickly.
The reasons for the increase in the average platelet volume can be physiological and pathological:
- Injuries and operations. If a person has recently undergone major abdominal surgery or multiple traumas, the body begins to actively fight blood loss and produce more young platelets, which leads to an increase in MPV levels.
- Menstruation. Sometimes, with heavy menstruation, a woman suffers from anemia. During this period, the body begins to replenish blood loss by producing new immature platelets, so the average volume increases. To avoid incorrect results, it is better to take the test after the end of menstruation.
- Thrombocytopenia. With thrombocytopenia, the number of platelets in the blood decreases. This is often due to the fact that a large number of young immature bodies are produced, which increase the MPV rate, but quickly die off and do not perform their function. Immature platelets cannot stick together quickly to form a blood clot. All this leads to various bleeding and hemorrhages.
- Alcoholism. Alcohol can cause many problems and cause abnormal blood counts. For example, ethyl alcohol causes the death of blood cells, which causes the spinal cord to produce immature cells in large quantities.
- Atherosclerosis. With this disease, fats settle on the walls of blood vessels, forming plaques. The lumen of the vessel narrows and the blood supply to organs and tissues becomes insufficient. Due to the accumulation of fats, the walls of blood vessels become less elastic and more fragile. This is a dangerous disease that can be fatal when vital arteries are blocked. At the same time, atherosclerosis and thrombosis are often interrelated.
- Diabetes. Diabetes mellitus is a serious disease associated with metabolic disorders. With this disease, hormonal disruption occurs, all body systems suffer, including blood vessels and the hematopoietic system.
Signs and possible consequences
The signs and consequences of elevated MPV levels depend on the reasons for the increase, the diagnosis, and the severity of the patient's condition. An increased platelet volume is not always associated with an increase in their number.
Therefore, symptoms can be very different:
- Hemorrhages. Small hemorrhages on the skin and mucous membranes are also called purpura. They often occur with thrombocytopenia, when the number of platelets decreases and the vessels become more fragile. Thrombocytopenic purpura can occur with minor blows, injections, or injuries. They can vary from small spider veins to large bruises. Sometimes such skin hemorrhages are painful on palpation.
- Frequent bleeding. This is a common sign of an abnormal platelet count or average volume. Bleeding often occurs spontaneously. Usually these are nosebleeds and bleeding gums, which appears even when brushing your teeth with a soft-bristled brush. In rare cases, blood may be found in the urine. If you have an anal fissure or hemorrhoids, the healing process takes a very long time.
- Soreness in fingertips. This symptom is observed with increased MPV, which is accompanied by thrombocytosis, that is, an increase in the number of platelets, and not a decrease. The tips of the fingers become very sensitive and hurt when pressed.
- Weakness in the body and pale skin. As a rule, these are signs of anemia and internal bleeding, which can also be accompanied by an increase in the average platelet volume.
- Visual impairment. Problems with platelets often cause visual disturbances and hemorrhages on the sclera of the eyes.
- Skin itching. This is a rather indirect sign that can manifest itself in various diseases, dermatitis, allergic reactions, so it is first recommended to go to a dermatologist and take a blood test.
The most severe consequences are heart attacks, strokes, and thromboembolism. They occur when elevated MPV levels are associated with increased platelet counts and susceptibility to thrombosis. In this case, important arteries and vessels may become blocked, leading to severe complications and sometimes death.
Diagnostic value
Unlike the total number of platelets in a unit of blood, MPV reflects qualitative characteristics, that is, by this indicator one can judge their usefulness. Old cells are smaller in size, while young forms are large in size and have a structureless structure. Their activity, tendency to stick together, and the content of biologically active substances in them depend on the size of the plates.
The physician can obtain important information based on the MPV. If this indicator is elevated, it means that young cells are present in the blood. The higher the value, the more immature forms there are. If this indicator is low, this indicates that small forms are present in the bloodstream. MPV may be increased or decreased if the platelet count is normal.
By assessing the average platelet volume in the blood, your doctor may find the following:
- increased adhesion of platelet plates to each other, development of thrombosis;
- blood loss in people with iron deficiency anemia when large forms of platelets are detected;
- This test does not make it possible to determine myeloproliferative disease.
MPV in a blood test: decoding, norms in women and men
Determination of MPV is important for assessing the hematopoietic function of the body. Using the MPV platelet index in a blood test, you can detect increased platelet aggregation, thrombosis, and active blood loss (if large platelets are detected in people with iron deficiency anemia). In addition, the MPV indicator in a blood test acts as an additional marker of chronic myeloproliferative diseases (the presence of large platelets in the peripheral blood).
The normal MPV in adults is the same for women and men and is 6–13 fl. In children under one year old, the MPV norm is 7–7.9 fl, 1–5 years old – 8–8.8 fl. For children over 5 years of age, the normal values are the same as for adults.
An elevated MPV platelet index indicates the presence of large platelets in the patient's peripheral blood. If the MPV in the blood test is low, this means a predominance of small platelets.
MPV increased
A slight increase in MPV may indicate several physiological conditions, including:
- various injuries, usually multiple;
- surgical interventions;
- heavy periods;
- taking medications that promote hematopoiesis;
- features of hematopoiesis in childhood;
- bleeding, including internal bleeding.
MPV may be elevated as a result of blood loss
If MPV is elevated, the reasons may be:
- idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura;
- thrombocytopenia;
- diabetes;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- atherosclerosis;
- enlarged spleen;
- erythremia;
- splenectomy;
- myeloid leukemia;
- May-Hegglin anomaly;
- cell degeneration;
- alcoholism.
When MPV in a blood test is increased and decreased
An increase in MPV may indicate the presence of thrombocytopenia, myeloproliferative diseases, posthemorrhagic anemia, hyperthyroidism, diabetes mellitus, infectious and inflammatory diseases, neoplasms, preeclampsia, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, impaired platelet formation due to a lack of vitamin B12 or folic acid in the body, May-Hegglin anomaly , Bernard–Soulier syndrome. The index also increases after surgical removal of the spleen (splenectomy), in smoking patients with atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels, with alcoholism and taking certain medications, and in the elderly.
When the balance between the formation and destruction of platelets is disturbed, a tendency to thrombosis or increased bleeding occurs.
MPV reduced
If the average platelet volume is low, this may indicate the following pathological conditions:
- enlarged spleen (splenomegaly);
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- anemia;
- some hereditary diseases lead to a decrease in MPV (for example, this indicator is low in Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome).
- oncological diseases: sarcoma, leukemia, lymphoma, lymphogranulomatosis, carcinoma;
- inflammatory diseases;
- autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, hemorrhagic vasculitis and others);
- myocardial infarction;
- uremia, renal amyloidosis, glomerulonephritis;
- hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism;
- hypoproteinemia;
- taking certain medications.
Low MPV may be found during pregnancy. If the platelet level is also low, then there is a risk of miscarriage and premature birth.
Preparation and delivery of a general blood test
To take a general blood test, standard preparation rules are used. Blood sampling is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach. On the eve of the study, you should avoid excessive physical and mental stress, and give up fatty foods. Before donating blood, you should not smoke; the patient should be completely at rest for half an hour before the test. Blood for general analysis can be taken either from a finger or from a vein.
Determination of MPV in a general blood test is carried out within two hours after collecting the material, since with a later study the result may be distorted.
A decrease in MPV may mean an enlarged spleen (splenomegaly), the presence of liver cirrhosis, hypoproteinemia, kidney disease, and thyroid pathologies.
Prevention
It is necessary to regularly monitor blood composition. This will help to identify serious violations in time. You should consult a doctor for an analysis if bruises often appear, the skin changes color, you feel constant fatigue, tachycardia, or there is causeless weight loss. If you have chronic diseases, it is recommended to donate blood every 3 months.
To prevent hematopoietic disorders, you need to eat right, replacing animal fats with vegetable ones. It is also necessary to maintain a drinking regime and not take any medications without a doctor’s prescription.
Determining the platelet index or MPV helps to detect pathological changes in the body in a timely manner. If deviations from the norm are detected, the doctor will prescribe treatment.