Shortness of breath, constant weakness, unexplained swelling, chest pain - grounds for a cardiological examination. The listed phenomena may indicate a risk of chronic heart failure. The first mild symptoms should not be ignored. Without appropriate therapy, the condition will worsen. The IMMA medical clinics provide therapeutic and cardiological appointments.
In our clinics you can:
- Get a consultation with a cardiologist;
- Take an ECG and get a professional interpretation of the results;
- Complete the ABPM procedure;
- Undergo Holter monitoring;
- Take advantage of other services of our clinics.
For more details and any questions, please contact the number listed on the website
Congestive heart failure - decreased contractions of the heart muscle. This pathological condition is not an independent disease, it is a consequence of various disorders of the cardiovascular system.
The prevalence of heart failure among the population is constantly growing, the disease is considered a social problem along with oncology and AIDS. The reasons for the spread are different: poor environmental conditions, sedentary lifestyle, ignoring healthy eating rules, bad habits. Inattention to health leads to various damage to the circulatory system. Heart failure is a common complication.
About the structure of the cardiovascular system
The heart is a unique organ on which human life depends. It works without rest, has its own control center, which sends electrical impulses that stimulate muscle contractility.
The structure of the heart is widely known: it has two ventricles and two atria. By contracting, they ensure blood circulation through two vascular systems: the small and large blood circles. To more accurately explain the characteristics of different types of heart failure, it is necessary to mention the characteristics of blood flow.
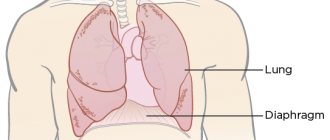
The systemic circulation involves the flow of blood from the left ventricle into the aorta, oxygenation of all important organs and limbs and the return of venous blood to the right atrium. The pulmonary circulation is the flow of blood from the right ventricle to the lungs and the movement of oxygenated blood into the left atrium.
Symptoms of heart failure depend on which part of the heart is affected. This is reflected in disruption of the functioning of blood circulation.
Heart failure, depending on the nature of its course, can be of two types. The chronic form develops over a long period of time and has several stages. Acute heart failure progresses rapidly. The duration of the process is from an hour to two days. This condition requires urgent hospitalization.
The classification of heart failure based on the localization of the pathology distinguishes several types:
- Left ventricular failure;
- Right ventricular failure
- Total form.
As the disease progresses, isolated variants lead to the formation of a general, total form of the lesion. Damage to the left ventricle causes disturbances in the systemic circulation. Pathology of the right ventricle - affects the lungs or pulmonary circulation.
Prevention of exacerbations of heart failure in old age
In chronic heart failure, patients must apply a set of supportive therapeutic measures for the rest of their lives.
For older people, it is especially necessary to adhere to the following recommendations: eliminate smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages, organize a daily diet based on diet No. 10.
General therapy involves moderate physical activity and gradual weight loss. Food can be thermally processed in the following ways:
- cooking,
- baking,
- steam cooking,
- grilling.
Every day you need to drink at least 1.5 liters of clean drinking water. Refrain from fast carbohydrates (sugar, white bread, sweets), replacing them with slow carbohydrates (whole grain bread, cereals, fruits). The diet must be structured in such a way that the total amount of calories does not exceed the permissible norm, taking into account physical activity.
It is important to follow a diet and not skip meals, including breakfast. Avoid snacking between main meals. Every day the patient should have 5 servings of vegetables or fruits, as well as sources of animal protein: seafood, fish, lean poultry.
Proteins, fats and carbohydrates should be supplied in the following ratio: 20%, 30% and 50%, respectively.
Experts are of the opinion that men need at least 7 hours of sleep a day, women - 9 hours. But on average, it is recommended to sleep at least 7-8 hours. It is better to follow this regime: go to bed no later than 23 o’clock, and wake up before 7 o’clock.
At least once a year, even a healthy person should undergo a preventive examination to identify diseases in the initial stages. To diagnose the state of the cardiovascular system, during the examination, blood pressure is measured, an ECG is performed, and body weight is determined. If initial results indicate the presence of symptoms of heart failure in an elderly person, then a number of additional measures are carried out (ultrasound of the heart, Doppler study, coronary angiography, MRI) to identify the exact diseases.
We recommend
“Recovery of older people after a stroke: tips and practical recommendations” Read more
Degrees of chronic pathology
There are several degrees of chronic heart failure. The earlier a problem is identified, the easier it is to treat. In the later stages of the disease, mortality is 50%.
The first stage of chronic insufficiency is characterized by shortness of breath and rapid fatigue after active physical work or sports. Treatment at this time is most effective. Early detection of symptoms of chronic deficiency will not only help to cope with it, but also to determine the true cause.
In the second stage of heart failure, symptoms become more pronounced:
- cyanosis, or blue discoloration of the fingertips, nose and nasolabial folds, lips. The reason is a change in blood composition, insufficient oxygen content.
- With low-intensity loads, typical symptoms appear: shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, weakness.
- Dry cough not associated with a cold.
The second stage is characterized by damage to the pulmonary circulation, the lungs suffer, so a cough occurs, and the blood is poorly saturated with oxygen.
Another variant of the manifestation of the second stage is damage to the systemic circulation. First of all, swelling appears. They can be hidden: fluid accumulates in body cavities, for example, filling the abdominal cavity. Swelling of the legs is more noticeable. This condition is called dropsy.
In addition, stagnation begins in all organs: liver, kidneys, digestive system, brain. Associated pathologies develop and the functioning of these organs is disrupted.
At the third stage, irreversible changes occur. Usually the functioning of the entire circulatory system is disrupted. Lesion of the small circle is characterized by a strong cough with sputum production, the appearance of pink foam not only when coughing, but also at rest. This is explained by a violation of the permeability of numerous vessels, lymphatic fluid fills the lungs, and edema occurs. The condition is fatal and requires urgent hospitalization. Shortness of breath accompanies a person at rest. Worsens when lying down. Periodically there are attacks of suffocation, accompanied by fear of death. They force the patient into a sitting position with his legs down.
At the same time, all vital organs suffer. Signs of congestive liver damage:
- increase in organ volume;
- formation of sclerotic and connective tissue;
- cirrhosis of the liver.
Congestive kidney damage leads to chronic renal failure. At the same time, the amount of urine excreted decreases, swelling increases and no longer goes away under the influence of medications. Intestinal dysfunction occurs, constipation or diarrhea is possible.
The third stage is irreversible. A person completely loses the ability to be active. Even household chores become beyond his power. Usually the patient is assigned a certain form of disability. The survival rate in this case is 50%. Medicine in this case can only offer supportive therapy.
Important! The third stage of the formation of congestive heart failure occurs as a result of the lack of treatment for the disease. If you consult a doctor in a timely manner in the early stages, you can not only stop the progression of the disease, but also be completely cured.
If you notice the following signs of heart failure, you should immediately contact a cardiologist:
- Shortness of breath with minor physical exertion;
- Blueness of fingers, lips, nose;
- Unreasonable dry cough, sometimes accompanied by sputum production;
- Pain in the chest, under the shoulder blade;
- Swelling of the legs, enlargement of the abdomen, which may be hidden edema.
Mild heart failure responds well to treatment, so a preventive examination by a therapist and cardiologist and the necessary diagnostic methods will help avoid serious consequences.
How to treat heart failure in older people?
If your loved one has been diagnosed with heart failure at any stage, it is necessary to immediately eliminate from life all factors that provoke further development of the disease. This applies to lifestyle and especially diet.
Treatment of chronic heart failure is usually carried out in parallel with the treatment of concomitant diseases that are often found in older people.
If swelling is detected in the abdomen and legs, fluid intake is reduced. To normalize water balance, as prescribed by a doctor, use diuretics (usually Furosemide).
To slow down the process of angiotensin formation and prevent narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels, cardiologists prescribe ACE inhibitors, which activate the pumping function of the heart and normalize blood flow.
Also, as prescribed by the attending physician, various vasodilators and cardiac glycosides are used, which have a cardiotonic and antiarrhythmic effect.
To improve blood flow and prevent thrombosis, patients with chronic heart failure aggravated by vascular pathologies are prescribed maintenance therapy with aspirin.
The nurses of our boarding house strictly carry out all procedures provided for by individual rehabilitation programs and recommendations of the attending physicians.
The mechanism of pathology formation
Chronic cardiovascular failure develops slowly due to the body's compensatory mechanisms.
At the compensatory stage of the myocardium, the heart muscle begins to hypertrophy. The vessels expand, causing their walls to become more fragile and permeable over time. Hormones are produced that change the composition of the blood, which becomes more liquid, its volume increases due to increased work of the bone marrow and an increase in the amount of water due to retention.
Compensatory possibilities dry up, and the decompensatory stage begins, which is characterized by a weakening of the functions of the entire cardiovascular system.
As the muscle mass of the myocardium grows, its small vessels lag behind in development, as a result, the heart muscle lacks oxygen and nutrients. Pathological changes occur: the proliferation of connective and sclerotic tissue. The heart becomes unable to pump the increasing volume of blood. Extensive oxygen starvation begins, which covers all organs.
Along with this, the walls of blood vessels become more fragile and permeable. Lymph leaks from the vessels. Swelling begins. These phenomena are especially dangerous in the lungs. They quickly fill with liquid and stretch. A person is tormented by a severe cough, and the discharge of sputum does not provide relief.
How to live with CHF?
13.07.2020
12134
0
Chronic heart failure... The term "failure" does not mean that the heart will soon stop working. The point is that it does not fully cope with the needs of the body (especially under load).
Chronic heart failure (CHF) is a complication of most heart diseases, associated with a dysfunction of the heart as a “pump” that can no longer provide sufficient blood output to maintain the needs of the human body.
The most common causes of the development of CHF include coronary heart disease, previous myocardial infarction, hypertension, congenital or acquired heart defects, and arrhythmias. Heart failure can develop at any age, but is most often seen in older people.
Heart failure manifests itself as shortness of breath during exercise and at rest, often suffocation at night, the appearance and increase of swelling of the legs, an increase in the size of the abdomen, weight gain, severe general weakness and increased fatigue with minor exertion. The reason for this is the excessive accumulation of fluid in all tissues and organs. The stage of compensation, or stable condition of the patient, and the stage of decompensation (unstable condition) are distinguished.
If you suspect you have symptoms of heart failure, you should talk to your doctor (primarily your primary care physician).
The doctor will conduct a thorough examination and ask about symptoms of the disease, medical history and lifestyle. It is extremely important to answer all questions as honestly and thoroughly as possible. Only in this case will the doctor be able to make an accurate diagnosis and develop a treatment plan.
If your doctor suspects you have heart failure, you may need to undergo some tests. These tests will show whether your heart is working well. If a problem is found, research will show what is causing it.
Key studies include:
- history taking and medical examination;
- electrocardiogram (ECG);
- blood tests;
- chest x-ray;
- Ultrasound of the heart.
The symptoms of each patient are individual, depending on them, other additional examination methods may be prescribed to clarify the diagnosis.
The progression of heart failure is unpredictable and occurs individually for each person. In many cases, symptoms remain stable for some time (months or years) before getting worse. In some cases, the severity and symptoms of the disease worsen gradually. Or they can progress rapidly, which could be, for example, a consequence of a new myocardial infarction, heart rhythm disorder or lung disease.
The most common causes of decompensated heart failure:
- Excessive intake of salt and liquid.
- Unauthorized cessation of medication or dose reduction.
- Excessive physical activity.
- Colds.
- Taking painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs (diclofenac, nimesil, ibuprofen, analgin).
- Drinking alcoholic or low-alcohol drinks (in particular beer and kvass).
- Stress, nervous tension.
- Chronic lack of sleep.
Heart failure is a chronic condition that tends to get worse over time. Sometimes it can shorten life expectancy.
The main thing to understand is that careful management of the disease can both relieve symptoms and improve prognosis and prolong life.
If your doctor tells you that a diagnosis of CHF has been made, you must follow four main types of recommendations:
- Lifestyle recommendations.
- Recommendations for home self-control.
- Recommendations for drug therapy.
- Recommendations for physical rehabilitation.
Lifestyle recommendations
The daily intake of liquid is 1.5 liters/day and includes all liquids consumed per day, including tea, juice, kefir, soup, fruits and vegetables. If you experience dry mouth and thirst, you should: rinse your mouth, add lemon or a piece of ice to the water, and take a small sip of water. Do not drink coffee - it increases the feeling of thirst. The intake of table salt is limited, the daily norm of sodium chloride is a teaspoon and do not forget that salt is added to food, so do not add salt to ready-made dishes and do not eat salty foods. It is recommended to stop drinking all types of alcoholic beverages and quit smoking. It is not recommended to take a steam bath or visit a sauna.
Recommendations for home self-monitoring
Body weight monitoring is prescribed daily in the morning on an empty stomach in the same clothes and keeping a self-monitoring diary. There should not be a weight gain of 1-1.5 kg per day, as this may indicate fluid retention and a doctor’s advice on correcting therapy is necessary. Indicators for home self-monitoring also include measuring blood pressure 2 times a day in the morning and evening and monitoring pulse. This can be done using an automatic blood pressure monitor. These indicators should be recorded in the patient’s diary so that they can be shown to the attending physician at the next visit.
Recommendations for drug therapy
The main rule: regular and long-term use of medications. It should not be interrupted or canceled without the consent of the doctor, take breaks for several days, as this may worsen the condition. A combination of drugs is often used for treatment. The number of tablets and treatment regimen are selected by the doctor and are individual for each patient.
General rules regarding taking medications:
- Always keep at hand a list of medications you are taking, indicating their doses and frequency of administration.
- Take your medications at the same time every day.
- Don't skip taking your medications.
- If you forget to take your medications on time, do not take a double dose at your next appointment.
- Do not change the dose of the drug yourself.
Recommendations for physical rehabilitation
Optimal types of exercise: walking, swimming, cycling. It is easier to start physical training with exercises that do not require supporting your own weight. For example, from riding an exercise bike or walking in the pool. This type of physical activity is beneficial at any age.
The first exercises may not exceed 5-10 minutes in duration; their duration can be gradually increased at such a pace that after three to four weeks the physical activity time is 30-40 minutes per day. It is necessary to discuss the limits of physical activity with your doctor and not go beyond them. Physical exercise should be performed two hours after eating and taking medications. It is recommended to avoid exercises that require holding your breath, as well as those that involve hypothermia or overheating. You should not perform any exercise if you feel unwell. It is necessary to immediately stop performing exercises if there is pain in the chest, unusually severe difficulty breathing, severe weakness, severe dizziness, rapid or sharply slow heartbeat. In these cases, you must immediately contact your doctor or call an ambulance.
Today, the most effective approach to getting heart disease under control is to combine medical treatment with lifestyle changes and managing emotions and habits. That's why it's so important to follow all your doctor's advice and do everything you can to change your lifestyle: this will help reduce the symptoms of heart failure and prevent the disease from progressing.
Causes of the disease
The causes of congestive heart failure are pathologies of the cardiovascular and endocrine systems. They can be congenital or acquired:
- genetic predisposition;
- ischemic disease.
- myocarditis
- diseases resulting in thickening of the walls of the myocardium and pericardium;
- thyroid diseases;
- diabetes.
Factors that provoke the occurrence of pathological processes include:
- bad habits, smoking and alcoholism;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- excessive body weight;
- severe infections (usually viral);
- heavy physical activity;
- frequent stress, improper daily routine, lack of sleep.
Congestive heart failure is more common in old age, occurring in 10% of people after sixty years of age. However, the disease also affects young people. In adolescence, it is necessary to carefully monitor the state of the cardiovascular system. The rapid growth of bone and muscle tissue, hormonal changes increase the load on the heart, which does not have time to grow with such rapid growth of the body as a whole.
Young athletes are at risk. Typically, training for teenagers is more gentle; children undergo annual examinations. If signs of congestive heart failure are detected, not only urgent treatment is necessary, but also a temporary refusal to exercise. Doctors recommend taking a break for about a year.
Why is heart failure dangerous?
The result of the development of heart failure is a deterioration in blood flow to all organs and systems of the body. Not only the heart is at risk, but also the liver, kidneys, nerve network and muscles. A person walks as if on a razor blade, since each exacerbation (decompensation) can lead to death.
In order to exclude this scenario, you need to know that heart failure is not a disease, but a complication of various diseases. First of all, arterial hypertension, coronary heart disease, heart rhythm disturbances, myocardial infarction, diabetes mellitus, heart defects and other causes, as well as their combination. The result of heart failure can be chronic kidney disease and anemia. It is extremely important to diagnose a health condition, because identifying warning signs early and promptly treating them will reduce the risk of developing a life-threatening condition.
The risk of developing heart failure increases with age. But if in America and Europe the average age of those diagnosed with heart problems is 70–89 years, in Russia this bar has been lowered to 50–69 years, which is usually associated with late seeking medical help, non-compliance with the recommendations issued by a specialist recommendations and treatment plan. Factors such as severe infection (pneumonia, flu), emotional and physical stress can affect the development of heart failure.
The greatest danger to life comes from periods of exacerbation (decompensation) of heart failure , over and over again the heart muscle, as well as other important organs, are increasingly damaged. As a result of decompensation, the general condition of the body worsens, the following symptoms appear: shortness of breath, cough, swelling in the ankles and abdomen, rapid fatigue, difficulty breathing when lying down, rapid weight gain (which indicates swelling), rapid heartbeat. If the patient exhibits any of the above symptoms, as well as other signs of deterioration in general condition, the patient should immediately contact a medical facility, and in case of severe exacerbation of heart failure, be hospitalized in the cardiac intensive care unit.
We recommend
“Old people in the family: learning to care and communicate” Read more
Acute form
Along with chronic, there is an acute form of heart failure. The reasons for its occurrence are:
- myocardial infarction;
- major stroke;
- structural defects of the heart, congenital and acquired;
- hypertension.
A distinctive feature of acute cardiovascular failure is the suddenness of the attack and the absence of the listed stages of development. The person's condition quickly deteriorates and death is possible within a few minutes. The occurrence of pathology is indicated by a sharp deterioration in condition, suffocation, severe cough with foam or red sputum, blue discoloration of the skin, and cold sweat.
In such cases, first aid is to call an ambulance. Then the victim should be taken out into the open air, the collar and other tight clothing should be unbuttoned. The best pose is considered to be sitting, with legs down. A nitroglycerin tablet should be given under the tongue. Repeat the dose every 10 minutes until the ambulance arrives.
Important! In acute heart failure, you should not take a supine position.
Age and gender factor
Statistical studies prove the connection between the spread of the disease and the gender and age of the patient.
In the age group up to 65 years, women suffer from congestive heart failure to a lesser extent; above this age, the rates become equal. Death as a result of acute heart failure is recorded in men after 45 years.
In old age, symptoms of congestive heart failure are more common, this is explained by chronic diseases, poor lifestyle, and reduced immunity.
Methods of working with the elderly
Treatment of a diagnosed cardiac disease is often performed in three main directions, which are synchronized.
Drug treatment. This type of therapy is the main one for such disorders in elderly and senile people. It is used to ensure that a person is maximally protected from stress of any nature (emotional, mental or physical) on the heart. The most common medications for conservative treatment are divided into three groups:
- Vasodilator drugs. These include: nitrates, which have an effect on venous tone; medications that affect arteriolar tone (Corinfar, Hydralazine, Phentolamine); affecting the tone of veins and arterioles (“Captopril”). These are also ACE inhibitors, weakening the production of the vasoconstrictor hormone angiotensin (II).
- Drugs of the glycoside group (Digoxin).
- Diuretics (diuretics), which include thiazide, loop and potassium-sparing drugs.
It is also necessary to follow the basic rules of medication treatment.
You need to start therapy with small doses of the medicine - often half the usual dose. The increase should occur gradually and evenly. Even the slightest manifestations of side effects of the medications used should be strictly monitored.
Surgical treatment. It also happens that heart failure in old age requires surgical treatment. The most commonly used of them include the following methods:
- Revascularization of the heart muscle (myocardium), that is, restoration of its vascular blood supply.
- Cardiac pacing by implanting special defibrillators into the patient’s body.
- Correction of a heart defect in a patient using closed (not opening the heart cavity), open (opening the heart cavity using a heart-lung machine) and X-ray surgical options.
- Pericardectomy surgery (complete or partial removal of the pericardium, performed for pericarditis).
- Tumor resection (removal of part of the organ in which it is located).
- Transplantation of a donor heart, however, this is the only type of surgical intervention that is practically not used due to the advanced age of patients.
All other types of surgical treatment are not contraindicated for elderly and elderly people.
In addition, types of surgical intervention are also usually classified according to the degree of urgency of their implementation, dividing into emergency (that is, those that do not tolerate the slightest delay), urgent (there is no urgency, as in emergency cases, but surgical intervention must be performed in within several days after diagnosis, since then it may become too late), as well as planned (in other words, elective), which can be postponed for a short time and carried out as planned, at the appointed time.
Lifestyle correction. This measure involves following certain recommendations and instructions from a specialist. These often include:
- Nutrition correction (the patient’s diet, reducing the amount of animal fats he consumes, reducing salt and liquid intake, as well as increasing the mass proportion of vegetables and fruits in food).
- Correction of attitudes towards alcohol and nicotine (complete exclusion or reduction in the amount of their consumption).
- Correction of physical activity (maintaining minimal loads that are feasible for elderly people to perform).
Diagnostics
Symptoms of congestive heart failure are observed by the therapist when examining the patient and listening to heart sounds. He refers the patient to a cardiologist. A number of studies are being carried out:
- ECG;
- ECHOCG
- HMEKG
- Radiography
- Coronary angiography
- MRI, MSCT
Research is being conducted on the characteristics of the heartbeat during physical activity. To do this, the patient is asked to perform a series of simple exercises, such as squats. After this, monitor the change and restoration of the pulse. More in-depth examinations of this kind are performed using a treadmill or exercise bike.
Dangers
Diagnosed heart failure in older people has many dangers. First of all, this lies in the fact that the heart itself, like all other organs of the patient, suffers from blood flow disturbances, which means they are often exposed to oxygen starvation.
Another danger facing patients with heart failure is limitation of physical activity. Depending on the stage of the disease, it can be expressed slightly, or, conversely, too strongly, when any physical activity causes shortness of breath, heart pain and other negative sensations.
Therefore, if you observe a dry cough in a loved one for a long time, shortness of breath, a sharp deterioration in general condition with even the slightest physical activity and other symptoms, you should not postpone a visit to the doctor. Perhaps this will save the life of a loved one. You should also help the patient follow all medical recommendations. Only through the joint efforts of specialists and the patient’s family can the disease be overcome.