Not everyone knows what heart failure is. This disease is a condition caused by a decrease in the contractility of the heart muscle. Another reason is stagnation of blood circulation in the small or large circle. Manifestations of the disease can be very diverse. Concern should be caused by shortness of breath, which manifests itself even with minor physical exertion or when a person is at rest. Symptoms include fatigue, a bluish tint to the nails, and the tip of the nose.
Overview of Heart Failure
A decrease in the contractile force of the heart muscle leads to a decrease in the volume of blood ejection and venous stagnation in the pulmonary and systemic circulation. The internal organs do not receive enough oxygen and nutrients, and due to increased venous pressure, edema develops. Stagnation of blood in the lungs leads to respiratory failure and oxygen starvation of tissues. A slowdown in blood flow in the vessels of the legs provokes the formation of blood clots, which can then break off and clog the arteries of the heart, lungs, and brain, causing death.
Signs indicating the presence of heart failure
If a patient has acute heart failure, the activity of any part of the heart is weakened. This could be the left atrium, one of the ventricles. Left ventricular failure occurs when there is a disease that puts stress on this department. It could be hypertension, heart attack.
In this case, there is an increase in pressure in some blood vessels and an increase in their permeability. The consequence of this is interstitial edema, which turns into alveolar edema. A similar type of failure manifests itself in the form of cardiac asthma. Alveolar pulmonary edema is also observed.
Exacerbation of asthma is usually caused by excessive physical activity or great emotional stress. Most often, a person experiences severe and sudden suffocation at night, during sleep. As a result, the patient wakes up in horror.
This type of asthma manifests itself as a feeling of lack of oxygen, increased heart rate, wet cough, and severe weakness. During an attack, the patient becomes covered in cold sweat, and when lying down he experiences severe shortness of breath. The specialist conducting the examination notes that the surface of the skin has turned gray and cyanotic, the person has shortness of breath and cold sweat. The pulse becomes weak and arrhythmic. The borders of the heart expand to the left. Blood pressure decreases. When listening to the lungs, harsh breathing is observed.
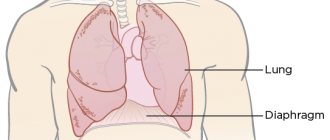
There is an increase in stagnation in the pulmonary circulation. As a result, pulmonary edema develops. The patient experiences a state of suffocation, and sputum is released. It is foamy, has a pinkish tint, and is very abundant. This is due to the presence of blood in it. Even strangers hear heavy, hoarse breathing with bubbling sounds. The patient is forced to be in a vertical position, since in a horizontal position his shortness of breath increases.
The face becomes bluish, the veins in the neck swell, and the patient breaks out in a cold sweat. The pulse is rapid, thread-like, the pressure is low, and wheezing is heard when breathing. If pulmonary edema occurs that requires urgent intervention, intensive care measures must be taken. Otherwise, everything could end very sadly.
Acute heart failure of the left atrium is observed in the case of mitral stenosis. The manifestations of the disease are similar to those found in left ventricular disease.
Damage to the right ventricle is usually a consequence of pulmonary embolism. Congestion appears in the systemic circulation. As a result, the legs begin to swell, the veins of the neck swell, shortness of breath appears, the skin becomes bluish, and there is pressure and pain in the area of the heart. There is a sharp decrease in blood pressure and expansion of the heart to the right.
If a patient has a disease that causes the right ventricle to malfunction, heart failure will appear sooner than if the same happens to the left ventricle. After all, this part of the heart is considered the most powerful. But, if there is a decrease in its functions, the development of heart failure occurs very quickly.
Chronic heart failure is characterized by the fact that at the very beginning its development can be of any type - right and left atrial, right and left ventricular. If there is an aortic defect, arterial hypertension, or some other ailments, congestion is observed in the vessels of the pulmonary circulation, leading to left ventricular failure. At the same time, vascular changes occur in the lungs. A person experiences shortness of breath, suffocation (usually at night), and bluish skin color. There is an increased heart rate, dry cough, and the patient gets tired very quickly.
If there are problems with the left atrium, severe congestion of the small circle appears. This happens in people who have mitral valve stenosis. The patient experiences shortness of breath, constantly coughs, and begins to spit up blood. If stagnation in the veins continues for a long time, sclerosis is observed in the vessels and lungs. Blood circulation in the pulmonary circle worsens, as an additional obstacle appears. The load on the right ventricle increases, and it is this circumstance that explains the occurrence of failure.
If the right ventricle is mainly affected, stagnation covers a large circle. A disease of this type can be a consequence of mitral heart defects, pneumosclerosis, and other ailments. The patient begins to complain that he has pain under his right rib and feels heaviness. He develops swelling, his abdomen becomes enlarged, and shortness of breath occurs with even slight physical activity. Diuresis decreases, the skin becomes cyanotic. Swelling of the veins of the neck and enlargement of the liver are observed.
A lesion that affects only one part of the heart spreads to others after some time. This is how total chronic heart failure occurs, the symptoms and treatment of which should be carried out by a cardiologist. Congestion in the veins is observed in both the small and large circles. A similar problem arises in the following cases: with damage to the heart muscle, myocarditis, coronary artery disease, and some others.
Classification of heart failure
According to the speed of development, acute and chronic heart failure
. The first appears and progresses quickly - within a few days or hours, the chronic one develops gradually.
Acute heart failure (AHF)
can develop according to the right or left ventricular type, depending on the location of myocardial damage.
The following stages are distinguished in the development of chronic heart failure (CHF):
- Symptoms of hemodynamic disturbances appear only during physical activity; nothing bothers the person at rest.
- Signs of venous stagnation: in one of the circulation circles; in large and small circles.
- Development of irreversible dystrophic changes in internal organs.
Classification of the disease
According to the duration of development of symptoms of damage, heart failure is divided into acute and chronic. The first of them can develop in one of two types:
- To the left - left ventricular or left atrial.
- To the right - right ventricular.
Cardiovascular failure is classified, according to Vasilenko-Strazhesko, into three stages:
- First. This is the initial stage, characterized by the fact that hidden symptoms become noticeable only if the person is physically active. He experiences shortness of breath and rapid heartbeat. The patient gets tired quickly. In the absence of physical activity, these signs are absent.
- Second. Symptoms of long-term circulatory failure and stagnation of the entire cardiovascular system also appear when a person is at rest. The patient is considered disabled. This stage has two periods. 2nd A is characterized by moderate hemodynamic lesions in one of the sections of the organ. This is the left or right ventricle. Manifestations of shortness of breath are observed even with normal physical activity. The patient's performance decreases. Other manifestations are cyanotic skin color, swelling of the legs, heavy breathing. 2nd B A is characterized by serious violations. The entire cardiovascular system is involved in this process. External manifestations - a person feels shortness of breath even when at rest. Edema and cyanosis appear. The patient is completely disabled.
- Third. This final stage is characterized by a significant deterioration in blood circulation and metabolism. The structure of many organs, in particular the liver and lungs, is irreversibly damaged. The patient is exhausted.
Causes of acute heart failure
The immediate causes of acute heart failure may be:
- complications of CHF (pulmonary embolism - blockage by a blood clot);
- myocarditis, pericarditis - inflammatory diseases of heart tissue;
- hypertension in the acute phase (hypertensive crisis);
- arrhythmia;
- myocardial infarction, coronary heart disease, major stroke.
Causes of chronic heart failure
The development of CHF is caused by chronic lung diseases, congenital and acquired heart defects and other pathologies, including:
- stenosis and/or insufficiency of heart valves;
- hypertension;
- myocarditis, pericarditis;
- cardiac ischemia;
- hyperthyroidism is an excess of thyroid hormones in the blood.
At first, the compensatory capabilities of the heart allow one to maintain hemodynamics at the proper level, but over time they become depleted and signs of illness appear.
Methods of treating the disease
The main goal of treating patients is to eliminate the factors that cause heart failure. Among them are rheumatism, ischemia, hypertension, etc. In some cases, surgery is required, this happens with heart defects, aneurysm, and other problems that cause a mechanical barrier to the functioning of the organ.
If the patient has severe or acute cardiovascular failure, the specialist prescribes him to adhere to bed rest. In addition, complete rest is recommended for him. If the condition is not so serious, the load may be moderate and will not affect your well-being.
It is not advisable for the patient to consume more than 600 ml of liquid per day; salt should be either completely excluded from the diet or limited to 1-2 grams. Food should be easily digestible, with plenty of vitamins.
Pharmacotherapy brings good results; it makes it possible to significantly improve the condition of patients and improve their quality of life. Treatment of heart failure involves taking several groups of medications:
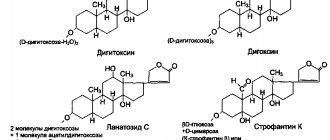
- Cardiac glycosides. They are needed to improve myocardial contractility. As a result, its pumping function and diuresis increase. The products help to tolerate physical activity normally. Among the drugs are strophanthin, digoxin, etc.
- ACE inhibitors, vasodilators. Their effect is a decrease in vascular tone. The drugs cause the blood vessels to dilate. Thus, as the heart contracts, its resistance decreases, therefore, cardiac output becomes greater.
- Nitrates. The purpose of the funds is to improve the filling of blood in the ventricles. Their use allows you to increase cardiac output and make the coronary arteries wider. Among them are sustak, nitroglycerin, etc.
- Diuretics. Prevents the retention of excess water in the body. This is furosemide, etc.
- Beta blockers. Their use leads to a decrease in heartbeats, improvement in its filling with blood, and an increase in cardiac output.
- Anticoagulants. Prevents the formation of blood clots in blood vessels. This is, in particular, aspirin.
- Means leading to improvement of myocardial metabolism. These are vitamins B, C, riboxin.
If a patient develops pulmonary edema, he should be admitted to a hospital where he will receive emergency treatment. He will need to take diuretics and nitrates. The patient is given drugs that increase cardiac output. In addition, he is prescribed oxygen inhalations.
When water accumulates in the abdominal cavity, it is removed using punctures. If pneumothorax occurs, pleural puncture is necessary. If a patient has a low oxygen content in the tissues, oxygen therapy is recommended. That is, if there is heart failure with symptoms, treatment - tablets, other drugs - should be prescribed by a specialist.
Symptoms of heart failure
The clinical picture of this pathology depends on what type of insufficiency develops and in what circle of blood circulation venous stagnation develops.
In right ventricular AHF
The volume of venous blood in the systemic circulation increases, resulting in the following symptoms:
- feeling of increased heartbeat;
- swelling of the limbs;
- swelling of the neck veins;
- a sharp drop in blood pressure, pallor, weakness, dizziness.
For left ventricular AHF
Blood stagnation occurs in the pulmonary circulation (pulmonary), so the following signs appear:
- chest pain;
- cough with pale pink frothy sputum;
- dyspnea;
- the appearance of foam in the corners of the mouth;
- disturbance of consciousness, confusion;
- the patient takes a forced sitting position, slightly leaning forward, in which the condition improves slightly.
A person with AHF needs urgent medical attention. If such symptoms appear, do not hesitate, you must call an ambulance.
Symptoms of chronic heart failure:
- shortness of breath, at first only during physical activity, later - at rest;
- cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle, fingertips;
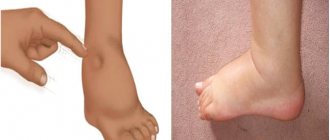
- swelling of the legs, which appears in the evening and disappears in the morning;
- an increase in the volume of the abdomen due to the accumulation of fluid in it (ascites);
- signs of dysfunction of the liver, kidneys, central nervous system.
If such symptoms appear, it is recommended to consult a cardiologist or therapist.
How does heart failure develop?
The acute form of heart failure is often formed on the basis of a heart attack. Its appearance is caused by acute myocarditis and serious arrhythmias. With these diseases, the minute output is reduced quite sharply, as a result of which much less blood enters the arteries. This form, in its clinical manifestations, resembles acute vascular insufficiency. Therefore, in some cases, such phenomena are referred to as acute cardiac collapse.
In the case of a chronic form of heart failure, the pathological processes that form in the heart are balanced for quite a long time by its increased work. At the same time, adaptive mechanisms of the cardiovascular system operate. The rhythm becomes more frequent, the force of contractions increases. Due to the dilation of blood vessels, the pressure in diastole decreases.
With the subsequent development of manifestations of heart failure, a decrease in cardiac output occurs. There is more blood in the ventricles. When the heart muscles relax, they become overfilled. The myocardium is constantly in a tense state, as it strives to maintain normal blood circulation and direct it into the vascular bed. As a result, compensatory hypertrophy of this cardiac muscle occurs. But time comes and the myocardium weakens, which leads to decompensation. As a result, a process of dystrophy develops in the heart muscle, and it itself begins to experience a lack of blood supply and energy.
At this stage, neurohumoral regulation is involved in this process. This phenomenon leads to narrowing of peripheral blood vessels. As a result, cardiac output becomes smaller, and blood pressure in the systemic circle remains at the same level. In the kidneys, a narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels occurs, which, in turn, causes ischemia of this organ. As a result, fluid is retained inside the tissues.
The pituitary gland produces more antidiuretic hormone. The consequence of this is increased fluid absorption. As a result, the amount of circulating blood becomes greater, and the pressure in the veins and capillaries increases. Transudation increases.
Thus, heart failure causes serious hemodynamic damage to the body:
Disturbance of gas exchange.
When blood circulation slows down, the tissue begins to absorb more air from the capillaries. If usually this figure is 30 percent, then in this case it increases to 70. As a result, acidosis is formed. Due to the fact that the respiratory system begins to function more strongly, the basal metabolism is activated. As a result, movement occurs in a vicious circle. The human body requires more and more oxygen, but the circulatory system cannot provide it.
This phenomenon is called oxygen debt. Its development leads to shortness of breath and cyanosis. The latter comes in two types: central or peripheral. The central one is formed during stagnation in the small circle. Peripheral - a consequence of slowing blood circulation. Due to the fact that the lack of blood circulation is more noticeable in peripheral places, patients develop blueness of the arms and legs, the tip of the nose, and ears.
Edema.
The phenomenon of edema appears due to several circumstances. Among them are an increase in capillary pressure and a slowdown in blood circulation. If there is a disorder of water-salt balance, fluid and sodium are retained. If protein metabolism is incorrect, blood plasma pressure is disrupted. If liver function is reduced, there is a loss of activity of certain hormones, in particular aldosterone.
At first, the swelling occurs secretly. Its presence can be guessed by weight gain, while at the same time less urine is produced. First, it becomes noticeable that the legs swell when a person walks. If it is in a horizontal position, the sacrum swells. The disease progresses, after some time cavitary dropsy appears. Fluid accumulates in the abdominal, pleural, and pericardial cavities.
Stagnation in organs.
This phenomenon in the lungs is caused by a disruption in the movement of blood through the vessels of the small circle. At the same time, muscle tone increases, the difference between the volume of the chest at maximum inspiration and the same exhalation decreases. The mobility of the edges of the lungs becomes lower. Manifestations of the disease in patients are coughing up blood, congestive bronchitis, and pneumosclerosis.
Stagnation in the large circle leads to a strong increase in liver volume. This is expressed in the fact that a person experiences heaviness and pain under the right rib. After this, cardiac fibrosis of this organ occurs, connective tissue is formed in it.
If, during heart failure, the cavities of the heart expand, this may result in damage to the atrioventricular valves. The patient experiences swelling of the neck veins, tachycardia, etc.
If stagnant gastritis is observed, a person suffers from the fact that he begins to feel sick, vomit, loses his appetite, and begins to lose weight. As the deficiency progresses, the patient becomes severely exhausted. This condition is called cardiac cachexia.
Stagnation in the kidneys leads to the fact that they begin to separate very little urine, the density of the latter increases, protein and blood appear in it. Damage to the central nervous system in case of insufficiency is expressed in the fact that the patient quickly gets tired, his activity decreases, both physical and mental, he sleeps poorly, and he develops depression.
Diagnosis of heart failure
The examination program for a person with suspected heart failure includes:
- collection of complaints and symptoms;
- initial examination, listening to heart sounds and breathing sounds;
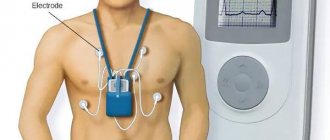
- ECG of the heart;
- Cardiac echocardiography (Echo-CG);
- X-ray of the chest organs;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
Stages of the disease
Stages of development and severity of congestive heart failure. Of the numerous signs of heart failure listed when describing a particular stage, it is necessary to highlight a few, each of which is sufficient to determine a specific stage. Stage I: Subjective symptoms of heart failure during moderate or greater exercise.
Stage IIA:
- pronounced subjective symptoms of heart failure with light loads;
- orthopnea;
- attacks of suffocation;
- radiographic, and in some cases, electrocardiographic signs of secondary pulmonary hypertension;
- reappearance of edema;
- re-enlargement of the liver;
- cardiomegaly without other signs of this stage;
- atrial fibrillation without other signs of this stage.
Stage IIB:
- repeated attacks of cardiac asthma;
- persistent peripheral edema;
- significant abdominal edema - permanent or reoccurring;
- persistent enlargement of the liver, which may shrink during treatment, but remains enlarged;
- atriomegaly;
- cardiomegaly in combination with at least one of the signs of the previous stage;
- atrial fibrillation in combination with at least one of the signs of the previous stage.
Stage III, terminal:
- severe subjective disorders with minimal exertion or at rest;
- repeated episodes of cardiac asthma during the week;
- dystrophic changes in organs and tissues.
If there is at least one sufficient sign of a more severe stage, then this stage should be established. Priority is given to clinical criteria. Negative results of instrumental studies often turn out to be inconclusive. The most obvious final manifestations of heart failure, such as a decrease in cardiac output, insufficient blood supply to organs and tissues and insufficient supply of oxygen to them, may be absent not only at rest, but also with the load available to the patient. Like blood pressure, the corresponding indicators may not go beyond the wide range of normal variants even in severe heart failure - until the last days and hours of the patient’s life (compensation at the pathological level).
Diagnosis and treatment of heart failure in Medical
Our doctors select an individual examination and treatment regimen based on the characteristics of each patient.
All diagnostics and treatment are carried out using expert-class equipment certified in Russia and approved for use by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation.
When should you see a doctor?
The reason for visiting a cardiologist should be alarming symptoms from the cardiovascular system: pain in the heart, dizziness, pressure surges, swelling, palpitations, etc. You should not delay your visit to the doctor, because in the early stages it is much easier to treat and control the disease.
Drug therapy for heart failure
Treatment of heart failure is carried out by prescribing drugs that facilitate the work of the heart, improve the rheological properties of the blood and hemodynamics. Such drugs include:
- B-adrenergic receptor blockers;
- cardiac glycosides;
- angiotensin receptor blockers;
- diuretics;
- nitrates.
Dosages and combinations of drugs are selected by the doctor; during the treatment process, it is often necessary to adjust the prescriptions taking into account the person’s condition.
It is unacceptable to prescribe medications to yourself after reading about the symptoms and treatment of diseases on the Internet or on the advice of a pharmacist at a pharmacy. Do not deprive yourself of the opportunities of modern world cardiology - contact a cardiologist for medical help at the Paracelsus Clinic.
Diagnosis of the disease
Since such an ailment is considered secondary and its development occurs in the presence of other diseases that are already known to specialists, the goal of diagnosis is to identify it at an early stage, even if there are no obvious symptoms.
The first symptoms of heart failure in women and men are fatigue and shortness of breath. Therefore, first of all you should pay attention to them. It is necessary to monitor patients with hypertension and coronary artery disease. People who have suffered a heart attack or rheumatic attacks are at risk. Specific symptoms of the disease include swelling of the legs and accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity. You need to be wary when the 3rd heart sound appears and its boundaries shift.
If there are concerns that the patient is developing heart failure, the gas and electrolyte composition of the blood is analyzed. Acid-base balance studies are carried out and other tests are taken.
The presence of coronary heart disease, arrhythmia, and myocardium can be determined by an electrocardiogram. In addition, a variety of load tests are often used. To do this, they resort to the help of treadmills and exercise bikes. Such testing, in which the load gradually increases, indicates the reserves of the heart.
The use of ultrasound echocardiography helps determine the cause of heart failure. In addition, in this way the pumping activity of the myocardium is assessed. MRI performed on this organ helps to identify ischemia, various heart defects, etc.
Using X-ray examination of the lungs and other organs, it is possible to determine the presence of blood stagnation in the pulmonary circulation. Radioisotope ventriculography, performed in patients with signs of heart failure, makes it possible to accurately determine the contractility of the myocardium. In addition, using this method you can install out of capacity.
If a serious form of the disease is present, an ultrasound examination of the liver, pancreas, and other important organs is performed to assess the condition of the internal organs.