Home — For the public
- Map of medical organizations
- Vaccination
- Clinical examination
- Fluorography
- Addresses and opening hours of clinics
- Emergency rooms
- Oncology
- Where to take an HIV test
- Healthy child's office
- Services
- Prevention of CVD
- Disease Prevention
- World Patient Safety Day
- Newspaper "Medical News"
- specialist
- School of Health
— Disease prevention
- HIV infection
- All about vaccination
- All about proper nutrition
- Hepatitis
- Flu
- Dementia
- Schoolchildren's health
- STD
- Tick-borne encephalitis
- Whooping cough
- Measles
- Legionellosis
- Meningococcal infection
- Oncology
- Acute intestinal infection
- Pediculosis
- First aid
- Pneumococcal infection
- Pneumonia
- Prevention of rabies
- Dependency Prevention
- Rotavirus infection
- Diabetes
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Injuries
- Tuberculosis
- Tularemia
- Physical activity
- Obstructive pulmonary disease
- Exotic infections
- Ecology
- Why is swimming in ponds dangerous?
— Cardiovascular diseases — First aid for stroke and heart attack
Timely and correctly provided first pre-hospital emergency care for the development of myocardial infarction and stroke is the factor that in many cases determines the outcome of these conditions that are dangerous to the health and life of the patient. Often, the lack of such correct assistance, which should be provided immediately after the development of these dangerous vascular accidents is suspected, becomes the cause of disability or death of people.
Doctors strongly recommend that all people at risk of developing these dangerous conditions know the first signs of stroke and myocardial infarction and be able to provide first aid. Almost every person should have such a reminder, because it can save someone’s life. Heart attack and stroke usually occur suddenly and at this moment it is necessary not to get confused! These simple steps can help save the patient and prevent the development of many complications or death.
General information about myocardial infarction
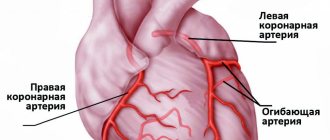
Myocardial infarction
ー this is the death of a section of the heart muscle, which occurs due to a lack of blood supply. As a rule, a heart attack does not develop suddenly; it is preceded by coronary heart disease or other pathology of the organ that leads to disruption of blood flow to the myocardium. Under conditions of oxygen and energy starvation, cells die. At the initial stage, this process is reversible; if blood flow is restored, the area of death can be limited and severe heart failure can be prevented.
First aid
If a heart attack is suspected, the patient should be seated and calmed down; a tight tie or shirt should be loosened or removed. Next, you should measure the pressure, if it is elevated, then it is advisable to give a nitroglycerin . You can also use aspirin - 300-600 mg in tablets that should be chewed is enough.
In case of loss of consciousness, cardiopulmonary resuscitation measures must be performed. If you are in a public place, perhaps an institution (airport, cafe) has a portable defibrillator, its use greatly increases the chance of survival.
Classification of myocardial infarction
Depending on which part of the heart wall is damaged, the following types of heart attacks are distinguished:
- intramural ー the dying zone is located deep in the myocardium;
- transmural - affects the entire thickness of the wall;
- subendocardial - the lesion is located near the inner lining of the heart;
- subepicardial - near the outer sac of the heart.
According to the nature of the flow, they are distinguished:
- acute infarction (primary);
- recurrent, develops within 2 months after acute;
- repeated, develops later than 2 months after the first heart attack.
According to the nature of the symptoms:
- typical form, characterized by chest pain radiating to the left arm and left half of the body;
- atypical forms (abdominal ー abdominal pain, asthmatic ー accompanied by severe shortness of breath, cerebral ー with dizziness, confusion, edematous, peripheral ー pain in the arm, face, neck, painless, combined).
Symptoms
The following manifestations are considered signs of a pathological condition with their subsequent increase:
- numbness of hands, face, pale skin;
- weakness of the body and pulse;
- asymmetrical arrangement of facial muscles on the face (drooping of the corner of the lips, lower eyelid);
- speech problems;
- stupefaction, lack of recognition of acquaintances;
- visual disturbances;
- heart pain;
- soreness in the head, nausea/vomiting;
- clouding of consciousness, sweating;
- involuntary movements, fainting.
If you suspect that something wrong is happening to the person next to you, ask him to do simple things that are difficult for him or will not work out at all: smile, raise both hands up, pronounce his own name or a simple phrase, stick out his tongue ( it will be skewed). Externally, specific symptoms also appear: facial distortion on one side. With ischemia, it is more often possible to provide timely assistance, since the symptoms increase gradually. Hemorrhagic disorder is a rapidly developing condition, based on sharply increased internal pressure. The patient feels a sharp “shock” pain in the head and briefly loses consciousness.
Mechanism of development and causes of myocardial infarction
The lion's share of heart attacks develops against the background of atherosclerotic damage to the coronary vessels and aorta (formation of cholesterol plaques in the wall of blood vessels). Other possible causes of circulatory disorders in the heart muscle are vasospasm and thrombosis. All this leads to the fact that the cells do not receive the required amount of oxygen and die.
The main causes of myocardial infarction:
- coronary heart disease, atherosclerosis;
- sudden physical activity or stress during ischemic heart disease;
- thrombosis of the coronary arteries.
Myocardial infarction in children
It is believed that this pathology only affects older people, but this is not so. A heart attack can also occur in a child in the following cases:
- inflammation of the coronary arteries in infectious diseases, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus and other autoimmune pathologies;
- infectious and rheumatic endocarditis (after a sore throat, for example);
- abnormalities in the structure of heart vessels;
- heart injuries;
- pheochromocytoma - a tumor that constantly produces adrenaline;
- congenital heart defects;
- heart tumors.
Risk factors for myocardial infarction
The following factors lead to the development of atherosclerosis, ischemic heart disease and, as a consequence, heart attack:
- high blood cholesterol (due to poor diet or metabolic diseases);
- obesity;
- hypertonic disease;
- smoking;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- diabetes.
Symptoms of myocardial infarction
Myocardial cells do not die immediately, since hypoxia develops gradually; they “suffer” for 1-2 hours before final death. At this time, they can still be saved, so timely seeking help determines the further outcome.
Pre-infarction state
Warning signs of a heart attack may appear several hours or even days before the attack. By seeking medical help during this period, you can prevent a disaster.
Possible signs of an impending heart attack:
- the appearance of chest pain during physical activity, emotional stress;
- sensations of interruptions in heart function, dizziness, increased heart rate;
- increased frequency of angina attacks;
- Chest pain is not relieved by nitroglycerin tablets.
Important!
Among all registered myocardial infarctions, about 20% are fatal within the first hour of the attack. It is not the doctors or “neglected medicine” that are to blame for this; death occurs even before seeking help due to the fact that the patient himself and those around him cannot recognize the attack and hesitate to call an ambulance. Therefore, if your loved ones have an increased risk of developing a heart attack, study the symptoms and algorithm of actions in case of a heart attack.
Symptoms of acute myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction is manifested by pain. The pain is localized in the chest, radiating to the left arm, shoulder, half of the face, and side. The nature of the pain is pressing, burning. During an attack, a person feels a lack of air, fear of death, cold sticky sweat appears, and the skin turns pale.
A distinctive feature of a heart attack from angina pectoris: with the first, the pain does not subside at rest or after taking nitroglycerin, lasting more than 20 minutes.
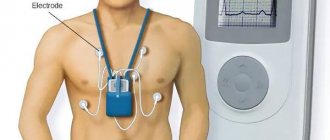
Diagnosis of myocardial infarction
After hospitalization, the patient undergoes the following diagnostic measures:
- ECG;
- clinical and biochemical blood test;
- blood test for creatine phosphokinase (CPK), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), troponin;
- EchoCG (ultrasound of the heart);
- coronary angiography.
These methods help confirm the diagnosis of a heart attack, clarify the location of the necrosis focus, and determine treatment tactics.
How to check?
When the first signs appear, you should immediately call an ambulance. When the victim is taken to a medical facility, he is urgently examined using the following methods:
- Blood pressure monitoring.
- Laboratory blood analysis for general indicators, cholesterol, sugar levels.
- ECG.
- Doppler ultrasound.
- CT scan of the brain.
- MRI of the brain.
If a hemorrhagic lesion is suspected, computed tomography is considered the best way to detect hemorrhage. In subsequent stages of development of stroke damage to the brain, it is better to monitor changes in tissue functionality using MRI, since magnetic tomography best visualizes soft tissue structures, inflammation, and necrotic processes.
Forecast and prevention of heart attack
The greatest mortality from myocardial infarction is observed in the first day; therefore, if medical care was provided in a timely manner, the chances of recovery increase significantly. The overall prognosis depends on the area of damage to the heart muscle.
For prevention, you must follow these principles:
- quitting smoking and alcohol;
- proper, balanced nutrition;
- regular physical activity (check with your doctor);
- regular preventive visits to a cardiologist in the presence of diseases of the cardiovascular system.
How to help the victim
It is absolutely impossible to treat pre-stroke and stroke at home, even if the first symptoms have disappeared on their own. Be sure to call an ambulance and provide first aid to your loved one. It consists of providing bed rest with the head slightly elevated on the pillow. You cannot bend your neck; any external things that impede breathing or blood flow (tie, tight collar) must be removed. Medications that can be given include antipyretics, blood pressure normalizers, and sedatives.
When the victim is admitted to the hospital, his condition is constantly monitored to prevent a stroke or recurrent attack. As medical support, he is prescribed medications that normalize blood pressure, have a positive effect on blood vessels and prevent the formation of blood clots. After discharge, a strict diet, giving up bad habits, and moderate physical activity are prescribed.
Diagnosis and treatment of myocardial infarction and pre-infarction condition in Medical
When should you see a doctor?
A person needs to consult a cardiologist if symptoms of a cardiovascular system pathology appear (chest pain, dizziness, cough, shortness of breath, bluish skin, etc.). You should not self-medicate. Numerous methods of traditional medicine are permissible for use only after the doctor’s permission and after treatment of the acute period of the disease.
Drug treatment of myocardial infarction and pre-infarction condition
Patients in a pre-infarction state are prescribed drugs that improve blood supply to the heart muscle, anti-atherosclerotic agents, and vitamin-mineral complexes.
In the acute period of a heart attack, analgesics, anticoagulants (prevent blood clotting) and thrombolytics (dissolve an already formed blood clot) are indicated.
Surgery
It is possible to more effectively restore blood supply to the myocardium through surgical intervention, which must be carried out in the first hours of a heart attack, then the chances of successful healing are greatest.
Coronary artery bypass grafting
The method of operation is to create a bypass route for blood supply to the affected area of the myocardium. The aorta and coronary vessel beyond the blockage are connected using a section of vein taken from the patient's lower leg.
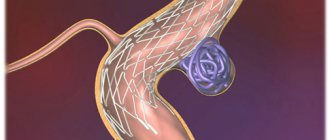
Coronary artery angioplasty
Narrowing of the artery can be relieved by inserting an instrument that widens the artery through the femoral vein. Next, a stent is installed, which fixes the shape of the vessel, preventing its narrowing and restoring blood flow.
Main forms of manifestation
The concept of “pre-infarction state” combines all types of unstable angina and manifests itself in the following types of this pathology:
- Developing angina pectoris for the first time.
- Progressive angina pectoris.
- The appearance of angina at rest after previously occurring exertional angina.
- Early post-infarction angina.
- Prinzmetal's angina.
- Angina after coronary artery bypass surgery.