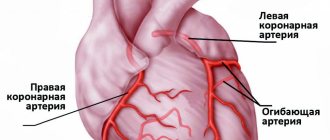
Myocardial infarction is always a great risk to a person’s life. The cause of almost every third death in our country is cardiac arrest due to insufficient blood supply (ischemia) to the heart muscle (myocardium), as a result of which the organ tissue begins to die. Up to 40% of people with this diagnosis die in the first 15-20 minutes after the onset of the disease. That is why it is so important for patients with pathologies of the cardiovascular system to undergo examinations, to know the first signs of the development of myocardial infarction in women and men, and to always be ready to call an ambulance. Your health and life, as well as the lives of your loved ones, next to whom you find yourself at the right moment, may depend on the ability to correctly identify the symptoms of the disease, competent and prompt actions.
Symptoms of myocardial infarction at different stages of the disease
Signs of myocardial infarction differ at different stages of pathology development. During the disease there are 4 stages:
- stage of ischemia or acute period;
- stage of necrosis (acute period);
- stage of organization or subacute period;
- post-infarction period (scarring stage).
About 40% of all recorded heart attacks come as a surprise to the patient. Most often, doctors explain these by people’s inattention to their health. In the remaining 60% of cases, the disease is preceded for a long time by angina attacks.
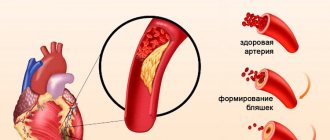
The first signal to show concern is the appearance of pain in the chest, back, left shoulder or forearm, sometimes radiating to the jaw, ear and, less often, to the stomach and lower back. The nature of the pain varies: from mild and sluggish to acute and cutting. Typically, such pain appears after playing sports or during everyday physical activity, during emotional experiences and stress. These are the first signs of coronary heart disease. In nine out of ten cases, IHD develops due to vascular atherosclerosis (deposits of cholesterol in the inner walls of blood vessels) that supply blood to the heart muscle.
Such attacks can be observed in a patient from several weeks to two, three or more years and often, if not intervened, end in myocardial infarction. Have you noticed these in yours? Contact specialists immediately! Timely measures taken, diagnosis and observation by doctors will help avoid the development of the disease.
If coronary heart disease is not treated, then the next stage may be the most acute period of a heart attack.
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation after a heart attack lasts a lifetime. First, it helps to recover and avoid a second heart attack, and in the future it maintains the health of an elderly person.
Features of rehabilitation are related to the severity and consequences of the stroke, age and general condition of the patient. During recovery you need to do the following:
• Eat a special diet; • Get rid of extra pounds; • Gradually increase physical activity; • Prevent and prevent stress; • Carry out suitable procedures to restore the body; • Undergo preventive treatment with medications and be observed by a doctor.
After a heart attack, a person gradually returns to an active lifestyle. The patient has many limitations; recovery must occur competently. You can sit on the bed with your legs down only on the 5th day; before that, the person lies and learns to sit up in bed. After a week you can take your first steps, and after two weeks you can walk at a slow pace with your doctor’s permission. After about a month, you can go outside the ward, accompanied by a relative or medical professional.
It is necessary to monitor the patient's condition, measure blood pressure and heart rate. Next, physical therapy and exercises on simulators are prescribed. Daily walks of half an hour are recommended.
Psychological (the patient is accustomed to an active life) and social rehabilitation (reinstatement in society with the help of relatives) is important for a person.
With successful rehabilitation, the pensioner is sent to a cardiological sanatorium, where he engages in physical therapy with specialists, eats a diet and takes the necessary medications.
An elderly person is recommended to undergo rehabilitation at home under the supervision of responsible relatives or in special boarding houses, where the pensioner will receive professional care.
The therapeutic diet involves eating small meals frequently, usually 5-7 times a day. The initial diet should consist of low-calorie nutritious foods: soups, cereals, vegetables, fruits. After a two-week light diet, you can add dairy products and fish to the menu. You should avoid salty, smoked foods, coffee and alcohol.
Folk remedies are a good addition to traditional medications during the recovery period. Together with medications, folk recipes will help reduce swelling, normalize blood pressure and nourish the heart cells. They use products based on valerian, rose hips, hawthorn, motherwort, calendula, immortelle and other herbs. They are used to make infusions and decoctions for regular oral administration.
Features of rehabilitation in old age:
• A heart attack in old age is fraught with recurrence and serious consequences. Recurrent infarction in 70% of cases occurs in the first three years after the first (in 1/3 of patients). Many die three years after leaving the hospital because they did not pay enough attention to rehabilitation. It is no less important than treating a heart attack. • Rehabilitation is needed to restore myocardial function, restore motor function, psychological adaptation, and prevent negative consequences. The patient is assisted in the recovery process by a cardiologist, nutritionist, physiotherapist and psychiatrist. Under the supervision of specialists, the elderly person gradually returns to normal life. • Care for a patient during the rehabilitation period can be organized in different ways: home treatment with a nurse, a rehabilitation center, a sanatorium, a private boarding house. Rehabilitation in a specialized institution is the best option. An elderly person is always under the supervision of specialists and receives professional care. Recovery in a sanatorium after a heart attack usually occurs within 2 weeks to a month and then continues at home. In general, recovery takes about a year. In the future, you will need to adhere to medical recommendations for the rest of your life. It is necessary to maintain healthy physical activity, regularly visit a cardiologist, eat healthy, and give up bad habits. • In the first year after a heart attack, it is recommended to visit a cardiologist once every two weeks, in the second year - once every 3 months, then once a year. Periodically, the pensioner undergoes an ECG and other tests, and donates blood for lipid levels.
Remember the following signs and symptoms of myocardial infarction:
- The first symptom of myocardial infarction is acute, squeezing or pressing pain in the chest, radiating to adjacent organs, the left ear, jaw, left arm, and sometimes the upper abdomen. The pain can last from half an hour to a day and, unlike angina, is not relieved by taking nitroglycerin;
- patients with the first signs of a heart attack may complain of toothache;
- the painful condition is accompanied by chills, weakness and dizziness, sometimes shortness of breath and cold sweat;
- arrhythmia develops, the pulse increases noticeably;
- the skin becomes pale gray due to lack of blood supply.
The nature and severity of pain during a heart attack depend on the location of the muscle damage. The larger it is, the stronger the pain. Sometimes the only symptom of a heart attack is sudden cardiac arrest.
The acute period is one of the most dangerous stages of the disease. Some of the cardiac muscle tissue is already dead, and the heart, finding itself in unusual conditions, may not withstand the load and stop. If you feel such symptoms and make sure that the usual remedies for angina pectoris do not help, immediately call an ambulance.
Symptoms during the acute stage of myocardial infarction become less pronounced. The pain subsides. As a result of tissue necrosis, the patient's temperature rises, which, depending on the focus of necrosis, may not subside for up to 7-10 days.
In the subacute period, the signs of myocardial infarction disappear, heartbeat and body temperature normalize. A week or two after a heart attack, the dead portion of the heart muscle begins to scar.
In the post-infarction period, there are no symptoms of the disease. But angina attacks will not simply disappear, so if measures are not taken, there is a high probability of developing a recurrent myocardial infarction. To avoid this, it is necessary to treat the root causes of the pathology: coronary disease and atherosclerosis. Due to damage to blood vessels by cholesterol plaques, not only the heart suffers, but also the limbs, digestive organs and brain (cerebral infarction).
Diagnostics
• In myocardial infarction, it is important to detect necrosis as soon as possible. In the primary diagnosis, anamnesis is collected, pain is analyzed, the heart area is listened to and palpated, and the patient’s condition is assessed. These methods help to identify the pulse rate, study systolic murmurs, and detect cardiac tone abnormalities. • The specialist conducts visual diagnostics, ECG, and takes blood for analysis. • Laboratory diagnostics, during which the patient’s blood is examined, is of great importance. In the first 6 hours after an attack, the patient’s level of myoglobin, necessary for the transport of oxygen, increases. This and other important changes will be shown by the composition of the blood during the study. The level of leukocytes, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, biochemical signs of inflammation and myocardial necrosis are determined in the blood. Specialists do several tests to make sure there is no heart attack or to track its development. • Instrumental diagnostics examines the patient using instruments. Using an ECG, you can determine the location and size of the lesion, assess the contractility of the heart muscle, find out data on necrosis and the risk of complications. Coronary angiography helps detect the location and extent of narrowing of the coronary artery. Additionally, radioisotope scintigraphy, echocardiography, CT and MRI may be prescribed.
Symptoms and signs of myocardial infarction in women
Female heart attacks have a number of atypical features and are less studied compared to male ones. The thing is that women are less likely to suffer from coronary heart disease. They are helped in this by estrogen, a hormone that is produced by the female body almost throughout life. It prevents the development of atherosclerosis. After menopause, the amount of estrogen in the body decreases and the chances of developing coronary heart disease in women increase.
Precursors of myocardial infarction in women are often swelling of the extremities that appear at the end of the day, chronic fatigue, shortness of breath, and digestive problems.
Often, a heart attack in women occurs without severe chest pain and may be accompanied by nausea, high fever and high blood pressure. Sometimes a false toothache develops. There are also cases of asymptomatic heart attacks.
This course of the disease is much more dangerous, since the patient can endure the first signs of the disease without attaching much importance to them. Some patients who have experienced a heart attack find out about it only after a while, undergoing diagnostics.
Complications
Consequences for the patient are inevitable, even with timely professional help. A scar remains at the site of necrosis, which can cause complications.
Within three days after the attack, the following complications develop: intraventricular block, extrasystole, atrial fibrillation, tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, which can turn into fibrillation and cause death.
Typical complications after a heart attack: cardiac asthma, cardiogenic shock, pulmonary edema, congestive wheezing, low blood pressure, decreased diuresis, cyanosis, cardiac hemorrhage, heart failure, aneurysm, pleurisy, pericarditis, pulmonary embolism, embolism of the brain, kidneys, lungs, post-infarction syndrome, neuropsychiatric disorders, etc. Complications are individual in nature and depend on the general health of the patient.
For a patient who has suffered a heart attack, high-quality rehabilitation is especially important in order to avoid the development of severe consequences.
Symptoms and signs of myocardial infarction in men
In men, the course of the disease has all the characteristic signs:
- sharp pain behind the sternum, in the left arm, shoulder and forearm;
- sticky cold sweat;
- weakness, dizziness, pale gray skin color;
- shortness of breath, rapid pulse;
- high blood pressure.
Despite the development of medicine, acute myocardial infarction is increasingly being diagnosed in both men and women under 40 years of age. The reason for this is a sedentary lifestyle; a diet with a predominance of unhealthy fats, which are rich in fast food products; obesity; smoking; diabetes. Young patients often have an asymptomatic form of heart attack.
Classification
The forms of myocardial infarction differ in the depth of the lesion, topography and ECG data, localization of pain, dynamics and periods of development, frequency of occurrence, and development of complications. There are different types of heart attack:
• Small and large lesions. Small-focal lesions do not cause severe consequences, but in a third of patients they can develop into a large-focal form. Large lesions cause aneurysm and cardiac rupture; • According to the depth of the lesion: subepicardial (close to the outer lining of the heart), subendocardial (located in the inner layer of the lining of the ventricular wall), intramural (inside the muscle fiber), transmural (the entire thickness of the heart wall is affected).
Signs of atypical myocardial infarction in women and men
Atypical signs of the disease are observed in elderly patients who have experienced one or more myocardial infarctions. Based on the nature of the symptoms, several atypical forms are distinguished:
- the abdominal form is characterized by indigestion, nausea, vomiting, hiccups;
- in the asthmatic form, the patient feels suffocated and may develop a cough;
- the cerebral form is represented by dizziness, presyncope;
- atypical pain syndrome (toothache, pain in the neck, left ear, spine, left leg, left fingers).
Often, acute myocardial infarction occurs without signs or symptoms in both women and men and is detected only after a while, after the patient has done an ECG. A silent heart attack is typical for patients with diabetes mellitus because it dulls the pain syndrome. This course of the disease is much more dangerous: the absence of symptoms of myocardial infarction makes it difficult to provide first aid to the patient. The only way to avoid the development of coronary heart disease and prevent myocardial infarction is to undergo timely and regular diagnostics of the cardiovascular system. At the Center for Circulatory Pathology, our specialists work with the latest equipment from Europe, the USA and Asia, which is capable of diagnosing the disease long before the first signs and symptoms of myocardial infarction. Treatment in our center is based on the best experience of domestic and foreign medical practices.
For patients whose health does not allow them to come to our Center, there is a special on-site diagnostics department. Based on a special method of non-surgical treatment of cardiovascular diseases, we develop a unique set of therapy and diagnostics for everyone who comes to our clinic.
Professional treatment. Why should you only contact experienced doctors?
As soon as myocardial infarction is suspected, the patient should be immediately admitted to the local cardiac intensive care unit. If an acute period is recorded, then the person first needs to remain in bed. Any psychological stress during this period is excluded! As for nutrition, it is severely limited in volume and calorie content. When the subacute period begins, the person can already be transferred from the intensive care unit to cardiology, where he will continue the recovery course after a severe attack. Treatment of myocardial infarction can take a long time, when the patient will systematically have to be checked by the attending physician, take various tests and undergo a bunch of examinations.
To relieve severe pain, the doctor prescribes narcotic analgesics. In this case, treatment is carried out in combination with antipsychotics, as well as the administration of nitroglycerin through an injection into a vein.
Therapy carried out by experienced specialists in case of a heart attack is necessary in order to prevent and eliminate interruptions in the heart and cardiogenic shock. As a rule, during this period the patient takes antiarrhythmic drugs, including thrombolytics, antispasmodics and nitrates.
It is extremely important that treatment for myocardial infarction is carried out by an experienced doctor. Only a prestigious clinic employs specialists who can correctly assess the patient’s condition. When a person survives an attack, this does not mean that the danger is over. There is a long course of treatment ahead, and the success of the process depends on the selection of medications, the experience of doctors and the technical equipment of the clinic.
Of course, when a person loses consciousness as a result of a heart attack, it is not advisable for family and friends to go to a private clinic. But the recovery period is better spent in a commercial medical institution. When the patient can walk normally, you can make an appointment with a specialist who will help minimize the consequences of a serious illness.
Constant shortness of breath
Shortness of breath is one of the most common symptoms in older men, indicating complications with the heart. Therefore, it is important to monitor your own breathing, noticing changes:
Advertising:
- So, if shortness of breath occurs over several days when walking increasingly shorter distances, you should think about the possible consequences.
- You also need to pay attention to the behavior of the body at night. A noticeable increase in breathing during sleep may indicate a pre-heart attack.
- In addition, a sick person needs more pillows to fall asleep - he uses them to raise the upper body, thereby facilitating the process of air intake.
If this happens on an ongoing basis and the situation gets worse every day, such symptoms indicate the progression of the pathology. Shortness of breath is caused by the accumulation of fluid in the lungs, which appears due to the inability of the heart to push blood out effectively enough.
Sore throat often occurs with various viral diseases of the respiratory system. To reduce pain and discomfort, sprays, syrups and tablets are used, some of which contain an antibiotic to suppress pathogens. Read more in the article: “antibiotic throat tablets.”