Does your stomach or heart hurt? Abdominal form of myocardial infarction
A heart attack does not always cause chest pain. Sometimes it manifests itself as nausea, vomiting, indigestion, and abdominal pain. Which makes us wonder about the root cause of such complaints. Abdominal form of myocardial infarction. Is it worth doing a cardiogram for abdominal pain?
Why does my stomach hurt and my heart cells die?
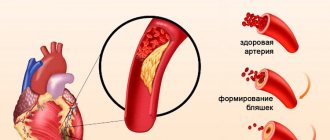
The reasons for the development of an atypical heart attack are no different from the classic one: progressive atherosclerosis, high cholesterol, vasoconstriction, high blood pressure. Where do abdominal pains come from? It turns out that the pain syndrome is caused by damage to the lower wall of the heart muscle, which is located close to the diaphragm. This explains why the pain radiates to the stomach. After a few days, necrosis (death) spreads throughout the heart muscle so much that the pressure drops and the pain moves to the chest. The name of the abdominal form is directly related to abdominal pain (from the Latin abdomen - belly).
Cholecystitis, pancreatitis, diarrhea... How not to miss a heart attack
The most understandable option is when abdominal pain first appeared due to dietary errors. We suspect gastritis and are looking for the cause. It is more difficult if chronic gastritis, cholecystitis, pancreatitis or an ulcer were identified a long time ago. Then the usual painkillers are used, despite the lack of effect. Having consumed a week's supply of medications in a few days, pale due to low blood pressure, they only then seek medical help.
If digestive disorders (loose stools, vomiting, abdominal pain) come to the fore, patients can go to the infectious diseases department with suspected poisoning.
Consider a heart attack if you have digestive disorders
With the abdominal form of a heart attack, the upper abdomen hurts (under the stomach, right half, especially the right hypochondrium). The pain is severe, suddenly onset, burning, accompanied by nausea, vomiting, bloating, and loose stools.
The alarming thing is that they are provoked, in addition to physical activity and stress, by eating. The pain changes in character: it intensifies, is less tolerated, becomes oppressive, changes location, lengthens (gradually increasing, reaching its peak within an hour), makes you panic and be afraid of death. The effect of nitroglycerin is short-term, sometimes it is not at all.
Don't forget about an electrocardiogram for abdominal pain
Sudden severe abdominal pain is an indication for taking an electrocardiogram before prescribing pills and injections. Therefore, if atypical abdominal pain appears, radiating to the middle of the chest, it would be more correct to contact a medical institution to conduct this research method.
What to do before the ambulance arrives
Treatment of the abdominal form of heart attack is carried out in a hospital. But what about emergency medical care before entering the hospital if the pain occurs at home? You won’t chew aspirin every time you experience stomach pain or nausea. After 5-6 such attempts, your stomach will answer you with an ulcer, with which you will certainly end up in the hands of doctors. If the attack drags on and the pressure allows (figures greater than 140/80 mm Hg), take a tablet or nitroglycerin spray and listen to the pain. If it becomes dull, call an ambulance and rely on their professionalism.
What is the danger of abdominal pain associated with a heart attack?
The prognosis of any heart attack is always worse if the time from the onset of the first symptoms to medical care and admission to the hospital is delayed. In the case of the abdominal form, the likelihood of delaying treatment is high. The patient, of course, will not die, but the dead heart cells cannot be resurrected.
Cardiologist at the Lutik polyclinic Irina
Atypical heart attacks
The classic symptoms of myocardial infarction are known to many people today. A sign of this formidable cardiac pathology is sudden sharp - so-called "dagger" - pain in the heart or behind the sternum, which can radiate to the left lower jaw, left arm, left shoulder or under the left shoulder blade. Along with the pain, there is a feeling of lack of air, shortness of breath, fear of death, cold pouring sweat and severe weakness.
This is a typical full-blown clinical picture of a heart attack, the so-called anginal variant. It allows you to immediately suspect a heart problem, provide first aid and promptly call an ambulance. However, unfortunately, not all heart attacks have a typical course. This is especially true for people over 75 years of age, in whom the proportion of atypical heart attacks is about 30%.
Forecast and prevention of heart attack
The greatest mortality from myocardial infarction is observed in the first day; therefore, if medical care was provided in a timely manner, the chances of recovery increase significantly. The overall prognosis depends on the area of damage to the heart muscle.
For prevention, you must follow these principles:
- quitting smoking and alcohol;
- proper, balanced nutrition;
- regular physical activity (check with your doctor);
- regular preventive visits to a cardiologist in the presence of diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Diagnosis of myocardial infarction
After hospitalization, the patient undergoes the following diagnostic measures:
- ECG;
- clinical and biochemical blood test;
- blood test for creatine phosphokinase (CPK), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), troponin;
- EchoCG (ultrasound of the heart);
- coronary angiography.
These methods help confirm the diagnosis of a heart attack, clarify the location of the necrosis focus, and determine treatment tactics.
Diagnosis and treatment of myocardial infarction and pre-infarction condition in Medical
When should you see a doctor?
A person needs to consult a cardiologist if symptoms of a cardiovascular system pathology appear (chest pain, dizziness, cough, shortness of breath, bluish skin, etc.). You should not self-medicate. Numerous methods of traditional medicine are permissible for use only after the doctor’s permission and after treatment of the acute period of the disease.
Drug treatment of myocardial infarction and pre-infarction condition
Patients in a pre-infarction state are prescribed drugs that improve blood supply to the heart muscle, anti-atherosclerotic agents, and vitamin-mineral complexes.
In the acute period of a heart attack, analgesics, anticoagulants (prevent blood clotting) and thrombolytics (dissolve an already formed blood clot) are indicated.
Surgery
It is possible to more effectively restore blood supply to the myocardium through surgical intervention, which must be carried out in the first hours of a heart attack, then the chances of successful healing are greatest.
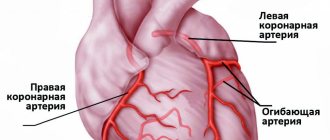
Coronary artery bypass grafting
The method of operation is to create a bypass route for blood supply to the affected area of the myocardium. The aorta and coronary vessel beyond the blockage are connected using a section of vein taken from the patient's lower leg.
Coronary artery angioplasty
Narrowing of the artery can be relieved by inserting an instrument that widens the artery through the femoral vein. Next, a stent is installed, which fixes the shape of the vessel, preventing its narrowing and restoring blood flow.
Myocardial infarction in children
It is believed that this pathology only affects older people, but this is not so. A heart attack can also occur in a child in the following cases:
- inflammation of the coronary arteries in infectious diseases, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus and other autoimmune pathologies;
- infectious and rheumatic endocarditis (after a sore throat, for example);
- abnormalities in the structure of heart vessels;
- heart injuries;
- pheochromocytoma - a tumor that constantly produces adrenaline;
- congenital heart defects;
- heart tumors.
Risk factors for myocardial infarction
The following factors lead to the development of atherosclerosis, ischemic heart disease and, as a consequence, heart attack:
- high blood cholesterol (due to poor diet or metabolic diseases);
- obesity;
- hypertonic disease;
- smoking;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- diabetes.
Causes of poisoning
More than 12% of drug poisoning and overdose cases involve NSAIDs. Non-opioid analgesics are widely available and can be purchased at any pharmacy, as they are vital supplies. However, it is impossible to buy narcotic painkillers without a prescription. Their free distribution without a prescription is punishable by law. Painkillers often contain codeine, which is sought after by drug addicts.
Why does poisoning occur with painkillers:
- failure to comply with instructions or doctor's prescription;
- incorrect reception;
- doctor's error;
- increasing dosage;
- lack of knowledge about taking medication;
- low body resistance;
- combination with alcohol, drugs, other drugs;
- cumulative effect due to prolongation of the course of treatment;
- taking the drug for recreational purposes;
- intake during pregnancy;
- when attempting suicide.
Among the most dangerous non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is phenacetin, previously contained in such drugs as Sedalgin and Askofen. This analgesic quite often caused the development of allergic reactions and disruption of internal organs. Today, a substance used as an antipyretic, paracetamol, is used to a greater extent in medicine.
If the patient takes the medicine as prescribed and prescribed by the doctor, an overdose of analgesics and local anesthetics occurs quite rarely. However, most often an overdose of anesthetics is used by drug addicts to achieve euphoria. Pharmacy drugs have long become a source of cheap “high” for them.
Mechanism of development and causes of myocardial infarction
The lion's share of heart attacks develops against the background of atherosclerotic damage to the coronary vessels and aorta (formation of cholesterol plaques in the wall of blood vessels). Other possible causes of circulatory disorders in the heart muscle are vasospasm and thrombosis. All this leads to the fact that the cells do not receive the required amount of oxygen and die.
The main causes of myocardial infarction:
- coronary heart disease, atherosclerosis;
- sudden physical activity or stress during ischemic heart disease;
- thrombosis of the coronary arteries.