Goals and objectives of rehabilitation
Healed tissue has limited functionality, which leads to circulatory failure. The main goal of recovery after myocardial infarction is to adapt the body to new conditions. Program objectives:
- restoration of the cardiovascular system;
- psychological preparation of the patient, including the mindset for long-term rehabilitation in compliance with all doctor’s recommendations;
- prevention of possible complications - myocarditis, rhythm disturbances, aneurysm;
- general strengthening, preparing the patient’s body for stress, restoring physical indicators;
- return to work and a full life.
Features of rehabilitation
The most acute period usually lasts up to six hours from the moment of the attack, the acute period - up to seven days. Scarring takes 28 days. Rehabilitation after a heart attack takes place in several stages, requiring the patient to give up bad habits and review all the main aspects of life:
- lifestyle;
- physical activity;
- diet.
The psychological attitude is of great importance. The duration of rehabilitation at the inpatient and outpatient stages depends on the patient’s condition. The final stage has no deadline - it lasts a lifetime.
Risk of heart attack and effectiveness of coronary stenting
A few words about acute myocardial infarction
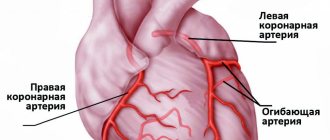
Acute myocardial infarction is necrosis, that is, death of a section of the heart muscle, developing as a result of a sudden, acute disturbance of blood flow in the coronary (cardiac) artery system. Blockage of a branch of the coronary artery can be caused by its thrombosis, less commonly by embolism or prolonged persistent spasm.
The most common cause of heart attack is atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a disease when atherosclerotic plaques form on the walls of blood vessels, which narrow the lumen of the coronary arteries and also contribute to the destruction of their walls, which provokes the formation of blood clots and blockage.
What does a heart attack lead to?
An acute heart attack causes irreversible changes in the heart muscle: the death of part of the functional muscle cells of the heart (necrosis) and their subsequent replacement with connective tissue, that is, the formation of a post-infarction scar. The scar on the myocardium remains for life. It cannot resolve, and the heart always remembers the heart attack. Subsequently, disruption of the blood supply to the myocardium can lead to cardiac dysfunction: heart failure develops, that is, the heart does not perform its functions fully. Thus, for the full existence of the entire organism there is simply not enough “power”.
In simple terms, due to an acute circulatory disorder, the heart gradually begins to “die”, and in order to save a person’s life, it is necessary to restore blood circulation as soon as possible. If medical care is not provided in a timely manner, a person with a heart attack may die within the first 24 hours. In general, the prognosis of the outcome of a heart attack depends on the size of the myocardial lesion, the severity of the course, the age of the patient, and the development of complications. But in any case, the prognosis of the disease is influenced by the timeliness of the start of treatment and its adequacy.
In Kyrgyzstan, this disease remains one of the main causes of premature death. For a long time, the treatment of acute infarction in our area was far from the most advanced strategy. According to indications, thrombolytic therapy was carried out, that is, the administration of drugs that resolve the blood clot and restore the patency of the vessel. Such assistance was provided both by emergency medical teams before hospitalization and in intensive care units of hospitals. The success of treatment often depended on the correct choice of drug and the timely start of its use. Of course, there was no talk of the high effectiveness of drug therapy: a very high percentage of deaths (about 16−20%), and if a person remained alive, he became disabled, his heart could not work properly.
Coronary stenting
Coronary stenting is the most effective way to treat acute myocardial infarction due to the complete elimination of circulatory disorders through direct and immediate impact on the infarction.
The essence of the method
The essence of the method is to install a special stent into the affected vessel through the radial artery (on the wrist) in order to restore blood flow.
A stent is a metal mesh structure that resembles a hollow tube of small diameter. Using a special balloon, a folded stent is inserted into the artery, under the control of an X-ray machine, it is delivered to the site of narrowing of the vessel, then, when the balloon is inflated under pressure, it is expanded and implanted, expanding and supporting the affected vessel in the area of blockage or critical narrowing and restoring blood flow. Also, in order to make the intervention most effective and safe, a wide range of special drugs are used.
Benefits of stenting
The advantages are that this operation is low-traumatic, practically painless, has a small number of complications, reduces the length of hospital stay from 15-17 to 7-11 days, makes it possible for the patient to become active early and refer him for rehabilitation in a sanatorium-resort setting.
Thanks to stenting in acute myocardial infarction, mortality has decreased by almost half, and today it is about 6%. But the most important thing is that after a heart attack the patient can return to a normal, fulfilling life, to his work.
When is stenting effective?
During a heart attack, approximately half the thickness of the heart muscle dies in the first three hours; in the next three hours, the entire thickness of the muscle dies. Therefore, stenting in the acute period of myocardial infarction is effective if it is performed as early as possible, no later than the first 6 hours from the onset of the infarction, optimally - up to 2-3 hours. Restoring blood flow in a clogged artery in this time period, before the development of irreversible changes in the myocardium, sharply reduces the area of the infarction, and sometimes makes it possible to “interrupt” its development.
How not to “live to have a heart attack”
There are major risk factors that can lead to the development of myocardial infarction. We can influence some of them, but not others. You cannot influence, for example, gender (men are more susceptible to coronary heart disease), age, family history, or hereditary predisposition. However, we can significantly reduce the adverse effects of factors such as arterial hypertension, smoking, diabetes, high cholesterol, excess weight, and a sedentary lifestyle. All these factors, both in combination and each independently, provoke the development of atherosclerosis, which, as I have already said, is the main cause of myocardial infarction.
Prevention of myocardial infarction
The number of patients in whom a heart attack is not associated with atherosclerosis, but is most likely caused by a sharp spasm of the coronary artery against the background of severe stress or a large loss of fluid and, as a consequence, thickening of the blood and the formation of a blood clot, is very, very small in the study group.
People think little about their health, they ignore alarming symptoms due to an irresponsible attitude towards themselves or out of ignorance, although there is enough necessary information in the media and on the Internet, there are very good social advertising videos. But citizens simply do not pay attention to this.
Today, medical capabilities make it possible to save the lives of patients even with severe heart attacks. But not only doctors, but also ordinary people should be wary in this regard. Without this, no technology will help.
Give up bad habits and “fast food”, add more physical activity to your life, devote at least 30 minutes a day to physical exercise and walking in the fresh air. Also, do not skip medical examinations and consult a doctor on time.
How to choose a stent?
The choice of a stent is up to the doctor who will install it. However, the patient may be offered an alternative between a plain stent and a drug-eluting stent. If the doctor, due to the patient’s characteristics of atherosclerotic lesions, advises using a covered stent, this is worth listening to. But in some cases, you can get by with a simple stent when a more expensive covered stent is not necessary. The main thing is to be sure that you are consulting on this matter with a highly qualified specialist with extensive experience in intravascular operations, since only he can take into account all the features of your condition, the influence of concomitant diseases, and the tolerability of medications that are necessary after stenting. If you suspect that your doctor is choosing a stent based on other considerations, such as the cost of the stents, you may want to consult with another specialist. Therefore, the patient’s problem is the choice of a competent and responsible doctor, and not the method of treatment. If necessary, BOSTI is ready to help with this.
What is the main reason why experts recommend the use of drug-eluting stents?
It is known that in some cases (with severe types of vascular lesions, concomitant diabetes mellitus, etc.) the likelihood of developing restenosis, that is, repeated stenosis developing inside a simple metal stent, is quite high. In such cases, drug-eluting stents are used. However, it should be borne in mind that after the installation of covered stents, the requirements for taking antiplatelet drugs are much stricter, and the duration of their course is longer - until the release of the drug from the surface of the stent ends (12 months). If these requirements are not followed, conditions may be created for stent thrombosis throughout this time, and this is a very dangerous complication.
Dr. BOSTI recommends high-quality stents from the German company BIOTRONIK
The German company BIOTRONIK is a world leader in the production of coronary stents, introducing innovative and high-tech methods of diagnosis and treatment. In 2015, the highest level in this area was achieved - they put the Magmaris bioabsorbable stent into production and implantation. This stent consists of a magnesium alloy, which is not foreign to the human body. Magmaris gradually dissolves inside the vessel; after 12 months it is almost completely dissolved (95%), this time is enough for us to “heal” the place of narrowing and/or occlusion. And in terms of its parameters (patency, deliverability, flexibility, strength and efficiency), Magmaris is in no way inferior to conventional stents.
1) Orsiro drug-eluting stent from Biotronik containing a biodegradable polymer
The advanced crimping technique gives the stent a very small cross-section (0.99 mm/0.039″) and ensures stable retention of the stent on the balloon without damaging the BIOlute® coating.
- Thanks to our state-of-the-art balloon technology, delivery of the stent to the lesion site is effortless and easy. The shaft with the Enhanced Impact Transmission (EFT) system gives this high-quality device greater ability to move, also through tortuous vessels.
- The Orsiro stent system is based on PRO-Kinetic Energy, our sixth generation metal stent. The stent material is a cobalt-chromium alloy, which makes the ribs of the structure thinner while maintaining optimal radial strength and radiopacity. The diameter of the thin ribs of the stent is only 60 microns, which provides exceptional flexibility and ease of movement to the installation site - even in the most complex vessels.
A unique solution for the treatment of coronary artery stenosis, a hybrid design with a combination of passive and active components.
Passive component:
Passive PROBIO® coating covers the stent frame and eliminates interaction between the metal parts of the stent and surrounding tissues.
Active ingredient:
BIOlute® is a polymer matrix that is absorbable in the body and releases a drug from the limus group in a controlled manner. Over time, only the PROBIO® covered stent remains in the patient's body.
2) Magmaris scaffold
The Swiss Magmaris scaffold is recognized as a physiological and high-quality scaffold - its wall thickness is 150 microns.
The surgeon performs the entire operation under local anesthesia, through a small puncture in the artery on the thigh or arm.
When straightened, the scaffold restores normal blood flow in the vessel and prevents its walls from closing again. Oxygen and nutrients begin to flow to the affected area of the heart muscle - the development of a heart attack stops.
You can purchase high-quality coronary stents Orsiro, Magmaris. They are also available for order throughout Kyrgyzstan.
You can find detailed information about them on our website, as well as
consult
about treatment with BOSTI - call or write to the following.
numbers: 0555 71 08 85 0555 71 08 18 0551 71 77 13
Recovery methods
Basic means of rehabilitation after myocardial infarction:
- drug treatment of circulatory disorders;
- Exercise therapy and physiotherapy;
- psychological support and training at a health school for patients with coronary artery disease;
- Spa treatment.
The doctor develops a recovery program after myocardial infarction individually, taking into account the patient’s condition:
- the extent of the lesion (small focal or transmural infarction can be diagnosed);
- localization of ischemic necrosis (apex, septum, wall are affected);
- presence of concomitant diseases.
Definition of clinical group
There are three clinical groups of patients:
- 1 (mild) – the body responds normally to stress, there are no symptoms of heart failure, conduction and rhythm are preserved;
- 2 (moderate) – against the background of arterial hypertension, drug therapy is required, conduction disturbances, heart failure of the 2nd degree, and a permanent form of atrial fibrillation are diagnosed;
- 3 (severe) – a thrombus is present in the heart cavity, ventricular rhythm disturbances are detected at rest and during exercise, the patient is diagnosed with acute aneurysm and heart failure of 3-4 degrees.
Physical rehabilitation
Recovery is impossible without a gradual and systematic expansion of physical activity. Prolonged bed rest increases the risk of developing congestive pneumonia and thromboembolic complications. Lack of physical activity leads to disruption of the gastrointestinal tract and weakening of muscles. This increases the duration of rehabilitation and negatively affects the quality of life.
Taking into account the type of response, a physical therapy program is selected. The intensity of the load is determined individually. They increase gradually with constant monitoring of all indicators.
Psychological rehabilitation
A heart attack is a disease that requires immediate hospitalization. The need for long-term treatment, fear of death, and restriction of activity lead to serious disturbances in a person’s psychological state. This explains the importance of conducting psychological and psychotherapeutic work with the patient.
In addition to the help of professionals, support from loved ones is also required. This allows you to avoid neurosis and depression, which negatively affect health and adaptive capabilities.
Patients often cease to correctly assess their capabilities. There are two extremes: they are afraid of any physical activity or exceed the permissible limits. Here you also have to work with a psychologist.
Drug therapy
Drug therapy during the rehabilitation period is necessary for:
- blood pressure control;
- prevention of angina pectoris, arrhythmia;
- normalization of lipid metabolism and blood clotting;
- treatment of chronic heart failure.
Main groups of drugs:
- antiarrhythmic - used to prevent disturbances in the rhythm, frequency, and sequence of heart contractions;
- antiplatelet agents - used to prevent thrombosis, reduce the risk of strokes and heart attacks;
- beta-blockers – reduce myocardial oxygen demand;
- hypotensive - they are necessary to normalize blood pressure in hypertension;
- nitro drugs – effective for angina pectoris;
- statins – prevent the formation of atherosclerotic plaques and serve as the prevention of atherosclerosis.
Drug therapy is prescribed by a cardiologist. He monitors the patient’s condition and, if necessary, adjusts the treatment program.
Prevention
Rehabilitation after a heart attack will be incomplete if the patient does not eliminate risk factors. Your lifestyle will have to change. Necessary:
- stop smoking - nicotine negatively affects the inner lining of blood vessels (endothelium), increases cholesterol levels (low-density lipoproteins), causes vasospasm, increases blood pressure;
- minimize alcohol consumption (no more than 30 g for men, 20 g for women) or completely abandon it - alcohol increases blood pressure, causes arrhythmia, tachycardia, has a toxic effect, can provoke a heart attack and death;
- give up unhealthy foods, control your weight (body mass index should be between 25-27 kg/m2).
When preparing your diet, it is necessary to reduce the proportion of animal fats - they contain cholesterol. Smoked meats, canned food, and pickles are excluded. Products are steamed, stewed, baked. Frying is excluded. The basis of the menu after a heart attack:
- sea fish;
- lean meats;
- fruits and vegetables;
- nuts;
- whole grain cereals;
- wholemeal bread;
- dairy products;
- beans, lentils;
- olive oil.
Symptoms
General signs of a heart attack are considered (Fig. 3):
- pain, feeling of squeezing, high pressure, heaviness, burning in the chest. These sensations may spread to the arms, the area of the back between the shoulder blades, the jaw or neck;
- fatigue, weakness, dizziness.
Figure 3. Heart attack symptoms.
Source: MedPortal Symptoms of a heart attack are not always the same. Some people experience severe pain, for others it may be mild, and for others it is almost unnoticeable. Pain can spread to the arms, neck and throat, and the area between the shoulder blades. During a heart attack, pain can increase with any, even minor physical activity: when trying to stand up or change position, when walking. Often a heart attack is accompanied by fear, a feeling of intense melancholy, and doom. Because of this, behavior can become anxious and agitated.
The heart rate during a heart attack can increase to 90-100 beats per minute, but blood pressure does not increase or increases slightly. The skin looks pale, becomes damp to the touch, and the nails and nasolabial triangle may turn blue. In some cases, nausea and vomiting may occur.
Men and women experience heart attacks differently. In women, shortness of breath, nausea or vomiting, and pain in the back and jaw are often added to the standard symptoms (Fig. 4).
Figure 4. Symptoms of heart attack in men and women. Source: MedPortal
A few weeks, days or hours before a heart attack, in some cases, warning signs or precursors appear. This is pain or a feeling of compression, pressure in the chest that occurs during physical activity and goes away at rest. You may also feel weak and short of breath.
Stages and terms of rehabilitation of patients with myocardial infarction
In cardiological practice there are three stages:
- inpatient - the patient is in the intensive care unit for up to three days, he spends about two weeks in the cardiology department;
- inpatient-outpatient – its duration depends on the severity of the condition (usually 28 days);
- remote (supportive, outpatient) – people who have had a heart attack are monitored by a cardiologist.
Hospital treatment
The inpatient treatment stage begins from the moment the patient is admitted. It involves being under constant observation, first in the intensive care unit, then in the cardiology department. During this period, intensive treatment is carried out. On the first day, physical exercise is contraindicated. From the second, primary physical skills begin to be restored with the help of exercise therapy (under the supervision of a therapeutic exercises instructor).
The first 2-4 days of exercises are performed in a lying position. The patient can:
- bend/extend fingers and toes (up to eight times);
- Without lifting your feet from the bed, bend your knees and straighten them (up to six times);
- lower your legs bent at the knees to the left and right (up to six times);
- perform other simple exercises recommended by the instructor.
The patient must rest before starting the next exercise - it takes from 10 to 30 seconds.
After transfer to the cardiology department, physical activity expands. From days 4 to 12, the second stage of exercise therapy begins. The patient performs the complex in a hospital, sitting in bed. It is recommended to do:
- not sharp turns of the head left and right (up to 10 times);
- raising your arms forward and up, then returning to the starting position (up to five times);
- movement of the feet forward/backward without lifting off the floor (up to 15 times);
- other simple movements included in the exercise therapy complex.
At home, the patient also performs a set of exercises with a dosed and systematic increase in load. It is convenient to use special mobile applications.
Along with physical treatment, psychological support is provided. The patient learns about his disease, the correct lifestyle and the changes that have occurred in the body.
Inpatient-outpatient recovery
The patient is ready for the inpatient-outpatient stage after discharge from the hospital. By this time:
- his condition becomes stable;
- motor activity expands (the patient can walk up to 500 m in steps).
Recovery from illness is possible in a specialized sanatorium or in a cardiac rehabilitation center. The patient is referred for sanatorium-resort treatment by a doctor and a medical advisory commission based on a conclusion from the hospital. There he goes:
- training at the health school - individual and group classes are provided;
- psychotherapy;
- drug therapy - special medications, metabolic agents, vitamin and mineral complexes are prescribed;
- physiotherapy (electrophoresis, baths, thermal power station) – the course includes 10-15 procedures.
An important stage in the patient’s recovery is physical rehabilitation after myocardial infarction. Massage, exercise therapy according to a more intensive program, classes on special simulators, and measured walking are indicated. To select exercises, at the first stage the patient undergoes a test:
- a load is prescribed - walking for six minutes, an exercise bike, a treadmill (walking);
- The body's reaction to it is monitored - the patient's degree of fatigue, the presence of shortness of breath, blood pressure and pulse indicators, ECG.
In accordance with the results obtained, the doctor determines the type of response:
- physiological – moderate fatigue, blood pressure within normal limits taking into account the load;
- intermediate – slight shortness of breath, fatigue disappears within five minutes, moderate changes on the ECG, disturbances in blood pressure and pulse with recovery within 10 minutes;
- pathological – severe shortness of breath, fatigue, chest pain, ECG changes, prolonged increase in blood pressure/pulse limit.
Self-recovery
The long-term (maintenance) stage begins from the moment the patient’s condition is completely stabilized. The doctor’s recommendations on lifestyle, quality of nutrition, and physical activity must be strictly followed. During the first year, the patient visits a cardiologist every three months and undergoes coagulogram and lipidogram monitoring. In the future, the frequency of visits and tests will be once every six months. Blood pressure should be measured daily.
Life after a heart attack
Mortality from myocardial infarction has been reduced thanks to:
- raising public awareness;
- new diagnostic methods;
- availability of high-tech medical care;
- improvement of outpatient preventive measures.
With proper recovery after myocardial infarction, the quality of life can be improved, and patients can live to a ripe old age. Necessary measures:
- compliance with the medication regimen prescribed by the doctor;
- dosed physical activity;
- weight control;
- proper nutrition;
- positive psychological attitude.
The quality of rehabilitation after a heart attack at home depends on the patient and his family. You should not violate the recommendations, as this may provoke a second heart attack with possible death.
Diagnostics
In case of a heart attack, the diagnosis is made based on the clinical picture, the results of electrocardiography and laboratory diagnostics. A heart attack develops quickly, and therefore, if its symptoms appear, you should immediately call an ambulance. Later, when the condition is stabilized, you will need to undergo extensive diagnostics with a cardiologist.
Diagnostic signs of a heart attack are:
- long-lasting chest pain that lasts more than 30 minutes (can be felt as a burning sensation, squeezing);
- leukocytosis and increased ESR in the results of a clinical blood test;
- increased levels of sialic acids, fibrinogen and the presence of C-reactive protein in a biochemical blood test;
- the presence in the blood of markers of ischemic necrosis, cardiac muscle (troponin).
Differential diagnosis may be of some importance during a heart attack. Usually, myocardial infarction is easy to distinguish from other diseases accompanied by pain in the heart (intercostal neuralgia, angina pectoris, pulmonary embolism, pleurisy and others). With an atypical course of a heart attack, diagnosis may become more complicated. The abdominal form can be similar to pancreatitis, peptic ulcers or food poisoning, and the cerebral form can be mistaken for a stroke.