March 15, 2021
When the acute stage after a stroke ends, the patient is discharged from the hospital, then a new period begins - the person’s recovery after a stroke at home.
In this article we tell you how to properly care for victims, restore their movement and cognitive functions, and provide psychological support so that rehabilitation after a stroke at home is systematic and gives the desired effect.
What to do immediately after a stroke at home?
Proper recovery after a stroke at home with the support of relatives and under the supervision of doctors brings good results. It is important to start rehabilitation immediately and not to miss the “rehabilitation window” - this is the year after the stroke, when treatment gives the maximum result.
Recovery after strokes is divided into several periods; the time may shift depending on the patient’s condition.
| The most acute period | Acute period | Early recovery period | Late recovery period | Period of residual effects |
| First 5 days | 3-4 weeks | Up to 6 months | 6-12 months | After 1 year |
How long does it take for speech to recover?
How quickly function can be restored, and what the prognosis for speech loss is, depends on the level of pathological changes in the brain. The recovery period is also influenced by the speed of learning and the characteristics of the rehabilitation period.
Approximate recovery times can be marked in the table:
| Type of attack and presence of consequences | Recovery time |
| Ischemic type: minimal neurological defects, including changes in speech function | Complete rehabilitation after 2-3 months |
| Ischemic or hemorrhagic type: pronounced neurological changes, persistent deficit of speech function | Complete rehabilitation after several years, and sometimes more |
| Ischemic or hemorrhagic type: severe neurological changes, complete loss of speech, paralysis of one side of the body | Complete rehabilitation is impossible |
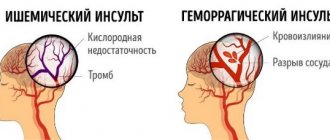
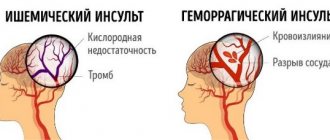
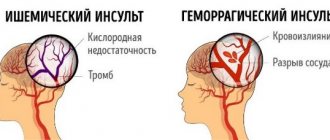
According to statistics, complete restoration of speech is often possible in cases of ischemic stroke. Longer recovery of function is observed in persons who have suffered a hemorrhagic attack.
If you were unable to avoid a stroke, there is no need to despair and give up. A person’s attitude is of great importance in recovery. It has been scientifically proven that a positive attitude towards the problem and the desire to return lost functions many times faster helps to fully recover.
Rules for caring for victims after a stroke
When a loved one has a stroke, rehabilitation at home is a high responsibility and a lot of physical activity for his relatives. It is important to prepare and create a comfortable atmosphere for the person. And then keep the order in the room and its cleanliness, prepare healthy food. Proper living will improve the mood and condition of the patient, thanks to this the person’s recovery after a stroke at home will progress.
Preparing the room and bed
After a stroke, rehabilitation at home should be comfortable for the patient. You need a spacious and bright room where there are large windows and no unnecessary noise is heard. All the furniture in the room is stable; in the future it will be a support when walking.
It is important to place a functional bed with an anti-bedsore mattress with the head of the bed against the wall so that the patient can be approached from all sides. Adjust the height of the bed, elevate the head or legs, and install protective bars to prevent the patient from falling.
The bed should consist of a pillow that supports the head, a light blanket, and a sheet without folds. Next to the bed you need a bedside table with water and necessary things for a person, and below there is a toilet chair.
While lying on the bed, let your healthy arm and leg be next to the wall so that you can see what is happening in the room through the sore side. Seeing a changing situation, a person’s affected areas of the brain are activated, accelerating recovery.
There are several tips on how to improve a person’s life after a stroke:
- arrange things at home so that the patient does not bend over or rise “on his tiptoes” behind them; long handles on brushes, brooms or mops will help avoid unnecessary bending;
- Place a damp towel or non-slip board on the table to prevent the dishes from slipping;
- support the patient’s forearm at a certain height, so his hand will not get tired quickly. This can be done using a height-adjustable table, a bed tray with legs, or a special forearm support that is attached to the armrests of the chair;
- Place a foam attachment on the handle of a brush, razor, spoon, or comb or buy a special “smart” item.
Body hygiene and the fight against bedsores
Bedsores harm the patient's recovery. They appear when the hard surface of a bed, chair, orthopedic devices, a lump from a sheet or pajamas presses on the person’s body. Bedsores can also form when moving, turning or improperly changing bed linen.
Most often, redness, blisters, like a burn, and small abrasions appear above the protrusions of the bones in the area of the back of the head, shoulder blades and sacrum. An anti-bedsore mattress, body hygiene and proper care will help to avoid the appearance of bedsores. You need to change your position in bed as often as possible, turning every two hours. It is necessary to keep the skin clean and ensure that it is not too wet or dry. You can treat it 1-2 times daily with camphor alcohol.
When caring for someone at home after a stroke, it is important to examine the patient every day. It is necessary to ensure that there are no folds or food crumbs on the sheet. When changing linen, do not pull the sheet out from under the patient, but pull it out carefully. You should not put oilcloth under your body; it is better to use diapers or an absorbent disposable sheet.
If bedsores do appear, use hydrogen peroxide to treat wounds and special ointments.
Nutrition
Food for the patient should be tasty and warm. It is necessary to take 4-5 doses a day, with dinner no later than 2 hours before bedtime. All food is prepared without salt, but sometimes the doctor allows you to add up to 5 g, he will definitely inform you about this at the appointment.
For the patient, food is prepared either boiled or baked. It is allowed to eat bread, soups, cereals, dairy products, fruits, eggs, vegetables and herbs, pasta, and for sweets - honey.
There are certain recommendations about what foods a patient can eat after a stroke:
| Can | Limit | Exclude |
| no oil | vegetable oil | lard, butter, margarine |
| red river fish | fatty fish: sturgeon, halibut | caviar |
| skinless chicken | all types of meat without fat | sausages, frankfurters, meat with fat |
| low-fat milk, kefir, cottage cheese | whole milk, cheese | fat milk, sour cream, cream |
| bananas, cucumbers, tomatoes, legumes | potato | preserves, jams |
| oatmeal, rice, buckwheat porridge, black bread | white bread, pasta | baking, muffin |
| green tea, mineral water, natural juices | sugar | chocolate, candy, pastille |
Sometimes patients after a stroke have problems swallowing. Such a person should be given soft food, not liquids, since liquids immediately enter the trachea and cause coughing. If swallowing is impaired, the patient should not be left alone; it is important to ensure that he concentrates on eating and tilts his head when chewing. A speech therapist-aphasiologist helps with swallowing problems.
Sample menu for 1 day:
Breakfast : 2 egg white omelette or oatmeal, tea or coffee with milk.
Second breakfast : boiled beef stroganoff, cottage cheese, apple or rose hip decoction.
Lunch : soup, boiled meat with vegetables, apple compote.
Dinner : boiled fish with mashed potatoes, pilaf with fruit, tea with milk. At night : a glass of curdled milk or prunes
Etiopathogenesis
If the patient is paralyzed, then a stroke (hemorrhage) has occurred. Violation of the integrity of the arterial wall leads to the formation of a hematoma. As blood accumulates outside the vessel, it begins to put pressure on neighboring brain structures. Under these conditions, nerve cells responsible for key brain functions, such as muscle control, die, causing entire parts of the body to go numb.
A stroke with paralysis of the right side can be caused by the following factors:
- Wrong diet. It is very important to monitor the amount of calcium in the foods you eat, as it is a key element in maintaining the health of arterial walls. A lack of calcium leads to weakening of blood vessels and increases the risk of their damage. In this case, even small blood congestions can provoke hemorrhage.
- High blood pressure. Excessive blood pressure on the walls of the arteries can lead to their damage in the weakest places. As a rule, people at high risk are older people who experience deterioration in the elasticity of the vascular walls due to natural aging and low calcium levels.
- Hereditary predisposition. Recently, it was found that patients with a family history of stroke are likely to have a heart attack or stroke at some point in their lives. These are mainly patients with hypertension. While the specific inherited cause of the disease has not yet been established, it may be weak blood vessels and problems with neurohumoral regulation.
- Excess weight. Fat people tend to have low levels of minerals in the blood and high blood pressure - leading causes of stroke, which can paralyze the body.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system. Impaired blood flow and rupture of a vessel in the brain can provoke pathologies such as heart defects, heart failure, the formation of atherosclerotic plaques and blood clots.
- Endocrine diseases. The most common cause of stroke among this group of pathologies is diabetes. People with this condition often suffer from high blood pressure. Also at risk are patients with low levels of thyroid hormones and problems in the adrenal cortex.
- Alcohol and tobacco abuse. Nicotine reduces the strength of arterial walls and increases cholesterol levels in the blood. High-quality alcoholic drinks in small quantities can even be beneficial, but frequent and excessive consumption of alcohol easily provokes hemorrhage with subsequent paralysis.
The causes of paralysis of both the right and left parts of the body are indicated above. Statistics show that bad habits are the most common factor in paralysis, in which it is much more likely to help the patient survive if diagnosed in time.
Motor rehabilitation
Restoration of movements should be gradual. This path is similar to a high ladder: first you need to learn to roll over, then control your head, then sit, stand, gradually walk and increase speed.
The most important thing is not to step over these steps in order to quickly reach the pinnacle of recovery. Each missed step is harmful, so it is important to learn how to move correctly and strengthen these skills with exercises. Below we have collected some tips on what to do at home after a stroke - when and how to roll over in bed, sit down and stand up.
How to lie down and turn over
You cannot always be in a lying position, as this will strain your back, arms and legs, and this will cause pain in the body.
To reduce pain and fatigue, use pillows. If your hand hurts, place it on a soft surface with your palm facing up. The same can be done with a sore leg. Place your limb on a pillow and bend your knee. The hip will rest on the pillow, and the sore leg will not roll off. It is important that raising the head of the bed is only possible during rehabilitation of ischemic stroke at home.
Learning to turn over in bed is the first step to recovery. An assistant is needed to turn to the paralyzed side. A caregiver or relative stands on the person's affected side and helps him turn by holding his healthy shoulder, knee or hip.
When and how to sit down and stand up
If the patient can sit up, change the position every day. It is necessary to move closer to the head of the bed and sit up straight, and distribute the weight evenly on both buttocks.
After the doctor's permission, you should learn to change seats. In the future, this skill will help you use the bathroom and toilet and be more independent. When transplanting for the first time, you need to monitor every movement in order to accustom your body to the correct technique. It is necessary to place your feet shoulder-width apart in one line, move your legs to the legs of a chair or armchair. Lean forward, resting your hands on the armrest, then straighten up and, maintaining your balance, gradually stand up, straightening your legs.
After a stroke, special training will help you recover at home. The number and time of their implementation are prescribed by the doctor, but you can use simple exercises yourself.
Therapeutic exercises to restore movement:
Each exercise should be done 4-6 times under the supervision of relatives or a caregiver.
Lying on your back, place your arms along your body, calmly inhale and exhale:
- Flex your feet vigorously, tensing your legs;
- make wide circular rotations with your feet in both directions;
- lift your legs up one by one;
- alternately bend your legs at the knee, clasping them with your hands;
- straighten your limbs.
Sitting on a chair:
- simultaneously and alternately rise onto your toes, straining your calf muscles;
- straighten your legs forward with tension in your hips;
- sit on the tip of the chair, holding onto the seat, move your straight leg to the side one at a time.
While standing, walk in place:
- raise your knee higher;
- lower your arms and rotate your straight arm in and out;
- put your hands on your belt, slightly bend your torso to the side;
- step forward, spreading your arms to the sides.
How to improve coordination of movements
After a stroke, areas of the brain that are responsible for coordinating movements are often damaged. As a result, the patient may lose his balance when standing, sway when walking, and move his arms randomly. To improve coordination, you can do daily training.
Exercises to improve coordination of movements:
- throw an object at a target. Gradually you need to increase the mass of the object, move the target away and reduce its area;
- swing movements in large joints, turns and tilts of the body, according to the patient’s condition;
- eye movements in different directions with a motionless head, also depending on the patient’s condition.
Self-massage
A patient after a stroke needs massage. It calms the body and reduces pain. Only a specialist can use the correct technique, but sometimes self-massage can be done to improve the patient’s condition. It consists of four actions: stroking, rubbing, kneading and vibration.
When stroking, the hands move evenly over the massaged area and glide easily over the skin. You need to move from the fingertips to the armpit, on the back - from the lower back upward, in the lumbar region - from the spine to the sides, the joints are massaged in a circle in any direction.
Rubbing is more effective than stroking. It increases blood circulation and improves tissue nutrition. Rubbing is performed using the same technique as stroking, only a little stronger.
Kneading is a complex technique and should be done carefully. Performed with the palm, fist, several fingers, thumb.
Vibrating massagers are used for vibration. Shock movements with vibration increase muscle tone.
There are some tips that will help you do self-massage correctly and avoid mistakes:
- massage movements should not cause pain. After correct movements, there are no bruises and the skin is not damaged;
- the duration of self-massage is from 3 to 25 minutes, depending on the patient’s condition;
- The patient’s position should be comfortable, all muscles of the massaged area should be relaxed;
- You cannot do self-massage during feverish conditions, during inflammatory processes, in areas where there is eczema, lichen, boils, fungus, thrombophlebitis, varicose veins;
- you can use products for better glide. But it is better to perform self-massage simply with clean, warm hands.
Treatment
Therapy after a stroke helps restore normal blood flow to the damaged area of the brain and reduce the risk of developing vascular problems and having another stroke. The patient may be prescribed a complex of medications and folk remedies.
Drug therapy
If the right side of the body is paralyzed after a stroke, the doctor first prescribes medications.
- Anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents (for example, Warfarin and Curantil) - prevent the formation of blood clots, making it more fluid, which improves blood flow even through the narrowest sections of blood vessels. These drugs help improve the condition of patients with atherosclerosis, blood clots, or narrowed blood vessels.
- Agnioprotectors (“Alprostan”, “Parmidin”) - normalize the functioning of the walls of blood vessels, reducing the risk of reducing the lumen in the arteries.
- Antispasmodic drugs (such as Vincamine and Papaverine) help relax the vascular walls, which increases blood flow.
- Diuretics (“Veroshpiron”, “Hypothiazide”) - help remove excess fluid from the body, reducing the risk of developing cerebral edema and exacerbation of hypertension.
- Nootropics (“Actovegin”, “Piracetam”) - increase brain performance. Nootropics are prescribed throughout recovery and for some time after full recovery.
Drug therapy is selected individually, based on the diagnosis and the general health of the patient. In case of serious disorders, the patient is given all types of medications and his blood pressure is monitored.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine provides additional assistance in recovery and is prescribed along with basic medications. In case of serious health problems, consultation with a specialist is necessary to draw up a specific treatment and preventive program.
Let's consider the most effective folk remedies.
- Taking a bath with the medicinal plant oregano. First you need to boil water along with the herb in the proportion of a liter per spoon and then pour it into the bath. For an average bath, 5 or 6 liters of decoction is enough.
- Honey and propolis are thoroughly mixed in a vessel with a ratio of 100 to 1, after which they are left to infuse for three days. The finished product is taken a couple of drops twice a day.
Folk remedies help improve blood flow and supply brain tissue with essential nutrients, as well as improve the functioning of the immune system.
Restoration of cognitive functions
After a stroke, the patient often experiences speech and memory impairments. It is important to pay special attention to this, since impaired cognitive functions make it difficult to communicate normally and cause strong feelings.
How to get your speech back
After a stroke, many patients experience speech impairment. Disorders manifest in the patient while he is still in the hospital. Most often, recovery is carried out by a speech therapist at the hospital, or you can invite a doctor to your home.
The specialist works with the patient himself and gives recommendations to the family or caregiver on how to help perform the exercises. It is important for loved ones to change their behavior in everyday life so that the person’s speech recovers faster. You need to speak more slowly than usual, use simple words and phrases, accompany them with gestures and, if necessary, drawings. You can give the patient a notebook and pencil, ask him to write a series of numbers, letters, or his own name. Near each piece of furniture in the house it is necessary to put a card with its name, so the patient will remember the words again.
Useful tips to help a person restore speech:
- involve him in the conversation: say hello and goodbye;
- if there is a discussion, make sure that the patient listens and participates at least non-verbally;
- if there is a discussion, make sure that the patient listens and participates at least non-verbally;
- if it is difficult for a person to name some objects, use their names more often in your speech;
- As the patient recovers, correct his speech errors. Increase his vocabulary;
- Monitor the patient's emotions. If the person becomes upset or irritated, change the subject.
How to resist memory changes
After a stroke, it will be more difficult to solve ordinary problems. To return to your normal routine, you need to divide all tasks into small subtasks and take your time. It’s worth planning your day, setting aside more time to complete a task, focusing on only one thing and taking breaks to rest.
Several rules of behavior for the patient that will help him restore his memory and feel better:
- take care of your brain. Do not overload it, and if you feel that you are tired and have begun to think more slowly, rest;
- remove everything unnecessary. If you are busy with important work, choose a quiet place where you will not be distracted;
- concentrate on only one thing;
- get rid of anxiety. Restless thoughts interfere and distract. Often it is sadness, apathy and depression that interfere with memory functioning. It is important to concentrate on interesting activities, develop talents, and be more in nature if your health allows it. Pleasant actions distract from negative thoughts. It is important to change the attitudes: “I no longer need a good memory” or “I am not able to improve my memory” are not suitable.
Exercises to train attention and memory
- describe your yesterday minute by minute, recreate the complete picture of that day. If you forgot something, be distracted by something else or take a rest. After half an hour, return to the exercise and try to remember again;
- Make a mental shopping list, imagine what the products look like: their color, size, packaging. After an hour, try to reproduce this list;
- close your eyes, imagine the number 1. When you see it clearly, erase it and imagine 2 in its place. Do this until 10.
Psychological support
An important point in rehabilitation after a stroke at home is the patient’s motivation. His optimistic attitude and desire to achieve his rehabilitation goal.
After a stroke, care at home should be psychologically comfortable. A person who has had a stroke may have problems controlling their emotions. He may often get angry, cry, scream and laugh. Such a person's mood changes quickly, he may be depressed or confused, experiencing anxiety, fear, frustration, hostility and anger. Psycho-emotional disorders can hinder recovery of health.
At such moments, the patient cannot be left alone for a long time; you need to talk to him, even if it seems that he does not hear or does not understand you. You should definitely involve him in household chores, for example, asking him to help peel potatoes or serve an item, if possible.
Be sure to walk with the patient, leave the house more often, so that he feels part of society. If a person cannot walk yet, invite acquaintances and friends to visit so that he can see other people and communicate with them.
If you follow all these tips, the patient’s recovery will progress, rehabilitation after a stroke at home will have its effect, and the person will definitely achieve the goals that the doctor prescribes for him.
You will see certain signs that the patient is getting better:
- shows interest in the environment, becomes proactive;
- sits down and walks on his own with a walker or without orthopedic devices at all;
- does some things independently: can wash the dishes or prepare a salad;
- expects your arrival at the appointed time or remembers an appointment, for example, on Tuesday at 14:00;
- can find a word in a dictionary or a name in a notebook;
- follows his own meal and medication schedule.
Find out how to get comprehensive rehabilitation at home in St. Petersburg with an effectiveness of 95% of the intended result
To know
Classes with a speech therapist
Special lessons with a speech therapist after a stroke are the most important component of treatment. You should start visiting a specialist immediately after determining the type of speech impairment. The sooner the patient begins to train the ability to speak fully, the greater the chance of achieving the desired result. All classes are divided into 2 stages.
First stage
Classes at the first stage are aimed at restoring basic speech functions. It is applicable for both adults and children. If the patient suffers from mild aphasia, then the first stage can be shortened. It involves the use of the following practical exercises:
- Conversation between a speech therapist and a patient, forcing the perception of information. To do this, the specialist speaks on various topics, making the patient understand the speech.
- Posing questions that require a detailed answer. The doctor asks the patient a special question, in which there is no possibility of answering only with an affirmative or negative gesture.
- Photo recognition. The patient is shown photos with objects or familiar people, and he must name what exactly he sees.
- Reading letters or numbers. The patient is shown numerical or letter series where the elements are arranged without any ordering. His job is to read what he sees.
- Writing and reading. For minor speech impairments, the patient is asked to write phrases or sentences, as well as read prepared texts aloud.
If classes bring poor results, they can be repeated in a more simplified form.
Second phase
At the second stage, the patient is offered a more complex set of tasks. It is very important to exclude unnecessary load, because... it can reduce the effectiveness of classes. Therefore, the speech therapist must carefully monitor the patient’s condition and give him time to rest.
Exercises:
- Restoring the connection between words and images. To do this, the patient is given complicated tasks similar to the exercises from the first stage. He is also asked to compose stories based on related pictures, work on intonation, retell texts, and also independently read and write short essays or letters.
- Speech recognition. The patient must classify the words he hears according to certain criteria, follow instructions expressed in complex sentences, improvise on any topic, and strive for standard speech.
- Correction of articulation and pronunciation. Working through template phrases, trying to pronounce phrases as clearly as possible, developing intonation and speech coloring skills, and verbally expressing all thoughts.
- Restoring basic abilities. Reading books or letters, analyzing what you read, working on recognizing letters and numbers, writing long essays with a gradual increase in the complexity of tasks.
Full recovery may require extensive sessions with a speech therapist. If progress has become noticeable, then you cannot stop lessons with a specialist, because Maximum results should be achieved, as well as consolidated, so that speech skills do not begin to deteriorate again.
Speech therapists can use additional exercises to achieve even greater results.