Reasons for increased hemoglobin in men
Functional and pathological factors can influence hemoglobin levels. Normal physiological, adaptive and compensatory mechanisms operate under certain conditions of climate, altitude, latitude, etc.
These include:
Long-term presence and residence of a person in high mountain areas. Low atmospheric pressure causes a response from the body, which consists of deepening and increasing breathing in order to compensate for the lack of oxygen supply from the rarefied air. This is a short term reaction. Then a longer adaptive mechanism develops, which increases the number of red blood cells in the blood and, accordingly, hemoglobin. The duration of its formation is from a week to 2 months. After a transition period, breathing evens out and slows down again. The process plays a role in the development of mountain sickness in climbers. This unpleasant pathology develops in the case of a sharp rise to a high altitude without adaptation;
excessive physical stress. From a one-time load, the adaptive mechanisms of increased gas exchange will not have time to work, but if the overload lasts a long time, then the blood will react by increasing the number of red blood cells and the hemoglobin content. This reaction of the body aims to relieve the respiratory system and cardiovascular system. Therefore, often in men associated with constant heavy physical labor, hemoglobin numbers are higher than normal. A similar phenomenon occurs in athletes experiencing monotonous daily overload. For example, long-distance runners, cyclists, skiers, etc.
functional types of dehydration are intermediate between physiological and pathological causes of increased hemoglobin;- living in conditions with insufficient water. For example, working in a hot climate and without proper drinking conditions. In this case, an irreplaceable loss of fluid occurs, leading to “thickening” of the blood. These types of work are more typical for men, so functional dehydration is more common among them.
Please note: the longer a person works and lives in such conditions, the more hyperhemoglobinemia develops and the risk of complications increases.
An increase in hemoglobin in men can develop as a result of diseases:
- occurring with debilitating and prolonged diarrhea, especially accompanied by concomitant vomiting (infectious diseases);
- with excessive urination due to diabetes, chronic stress, kidney disease;
- chronic heart failure, causing swelling of the body and a compensatory increase in fluid secretion by the kidneys;
- malignant polycythemia vera (Vaquez disease).
Long-term use of diuretics and a number of other drugs, and deficiency of cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12) can lead to dehydration and thickening of the blood.
Dangerous consequences
Advertising:
An increase in hemoglobin levels is associated with an increase in blood viscosity. That is, either the protein concentration increased and the blood became thicker, or the blood thickened and its saturation with hemoglobin structures increased. Such phenomena can cause a number of negative consequences for the body.
Why high hemoglobin is dangerous:
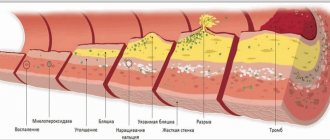
- high saturation of blood protein bodies increases the likelihood of them sticking together - thrombus formation occurs;
- Thick blood moves slowly through the vessels, which leads to the deposition of cholesterol and other harmful substances on the walls of blood vessels - plaques and blockage of blood vessels appear;
- excessively viscous blood requires effort to pump it - the load on the heart and blood vessels increases;
- the low speed of blood movement impairs gas exchange and nutrition throughout the body, blood circulation in the brain is disrupted;
- A high level of hemoglobin that persists for a long time leads to delays and disturbances in the development of children.
An increase in iron-containing protein can cause congestion, strokes, heart attacks, thrombosis, and ischemia. Most of these conditions are fatal, so it is better to prevent their occurrence by promptly starting treatment for high hemoglobin levels.
[media=
https://youtu.be/hmkIHa8swHM
]
How does increased hemoglobin manifest in men?
High hemoglobin can cause a number of nonspecific symptoms (also found in other diseases).
They appear:
- the appearance of reddened areas of the skin, alternating with pale areas, peeling;
- severe weakness and fatigue, decreased appetite;
- decreased hearing and vision;
- alternating constipation and diarrhea;
- superficial sleep, insomnia;
- pain in joints, muscles, bones;
- dizziness, diffuse headache;
- tendency to form blood clots;
- painful sensations in the abdomen and a feeling of fullness.
Signs of high hemoglobin
Typically, elevated levels of iron-containing protein are detected during blood donation, but there are a number of external signs that may indicate such a disorder:
- drowsiness or insomnia;
- joint pain;
- fatigue and lethargy;
- redness or paleness of the skin;
- increased thrombus formation;
- decreased or lack of appetite;
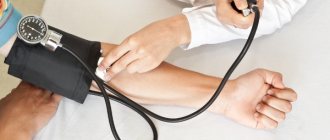
- increased blood pressure;
- decreased hearing or visual acuity;
- dizziness and headaches;
- heavy sweating;
- bone pain;
- painful numbness or burning of the extremities;
- problems with concentration and memory;
- slight increase in temperature;
- frequent digestive disorders;
- itchy skin.
All these are nonspecific symptoms that do not necessarily indicate an excess of hemoglobin. Only blood tests can accurately determine the deviation.
Diagnosis of elevated hemoglobin
Detection of an increased number of red blood cells and hemoglobin is determined during a routine clinical blood test. If the doctor suspects the cause of this process, he may order additional tests. After establishing a diagnosis or functional state, a plan of treatment measures, drug therapy is drawn up, and a diet is prescribed.
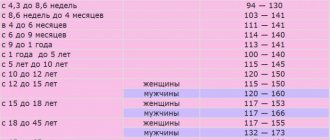
Please note: before you start sounding the alarm, compare the test results with the reference values - they are different for men and women!
| Age | Men (g/l) | Women (g/l) |
| Hemoglobin norms in adults | ||
| Over 65 years old | 126 – 174 | 117 – 161 |
| Over 45 years old | 131 – 172 | 117 – 160 |
| Over 18 years old | 132 – 173 | 117 – 155 |
| Hemoglobin norms in adolescents | ||
| 15 – 18 years old | 115 – 165 | 115 – 155 |
| 12 – 14 years old | 120 – 160 | 115 – 150 |
Treatment methods aimed at reducing hemoglobin in men
If the load is excessive, it is recommended to reduce its intensity. This should be done if the patient has the complaints outlined above.
For diseases of the cardiovascular system, it is necessary to identify the pathology and carry out treatment, which will lead to the normalization of hemoglobin analysis data.
If hemoglobin increases due to diabetes mellitus, it is necessary to reconsider the nutrition plan and introduce correction of insulin doses.
If the treatment does not reduce the level of hemoglobin in the blood, then you should consider prophylactic administration of anticoagulants and antiplatelet medications. These include acetylsalicylic acid, the dose of which must be selected by the doctor.
Insufficient absorption of vitamin B12 should be compensated by prescribing the medication in injection form.
Please note: if the main cause of increased hemoglobin in men is caused by an existing disease, then its treatment, if the tactics are chosen correctly, will itself normalize the deviation of indicators from normal numbers.
How to quickly reduce hemoglobin in the blood at home?
Minor fluctuations in Hb levels caused by sports training or stress do not require the use of special correction methods.
The first thing you have to do to lower hemoglobin is to adjust your daily menu and diet. It has been noted that a diet with increased hemoglobin in men can achieve noticeable results in improving health.
And if the condition is not accompanied by concomitant diseases, it will allow the patient to avoid the need for drug treatment. Therefore, you should pay special attention to this issue and strictly follow nutritional recommendations.
The patient’s attending physician is responsible for preparing the diet, since many factors must be taken into account: the presence of pathologies, intolerance to certain foods and the reason that caused the Hb deviation from the norm. Let's look at the basic principles and recommendations for nutrition.
Read further: All about the norm of hemoglobin in the blood of men by age
Diet therapy
A diet to reduce hemoglobin in the blood does not involve reducing the consumption of iron-containing foods.
It is necessary to sharply reduce the consumption of iron-containing products in case of hemochromatosis - this is a congenital pathology that is accompanied by abnormal deposition of iron in excess quantities.
You should consume soups at least once a day every day. Even in the summer, when it is too hot, it is possible to diversify your diet with cold soups - okroshka, gazpacho or botvinya.
The consumption of red fish and meat, especially fatty varieties, should be limited.
Preference should be given to vegetable and fermented milk dishes. It is worth noting 2 advantages of vegetables: a large amount of liquid in their composition and a low content of iron ions. Dairy products compete with iron ions for absorption, so increasing their share in the diet will significantly slow down the flow of iron into the body.
It is useful to include grapes, tofu cheese, rice, and bread in the menu.
About the importance of water
Some men deliberately limit their fluid intake in the summer in order to sweat less. However, this is an erroneous tactic of behavior that leads to dehydration and a decrease in oxygen in the tissues. The consequence is the manifestation of unwanted symptoms:
- increased craving for sleep;
- frequent headaches;
- state of lethargy;
- general weakness;
- worsening mood.
In parallel with this, blood thickening occurs, the danger of which was discussed above. In order to avoid this condition, it is necessary to consume a minimum amount of fluid, which is calculated taking into account the weight and physical activity of each person.
You should choose green tea, compotes and fruit drinks. It is better to avoid coffee, carbonated drinks and juices. Because they do not quench thirst and increase sweating.
It is optimal if a man drinks 100 ml of unsweetened water at room temperature every hour.
Forbidden foods
Taking any vitamins and nutritional supplements should be discussed with your doctor in advance. Since an excess of certain groups of vitamins can increase the absorption of iron and the production of blood cells. Particular attention should be paid to vitamin C, a sufficient daily amount of which a man receives with food if the menu is properly composed.
A large number of iron ions are typical for seafood, especially sea fish. During treatment, it is advisable to completely exclude them from the diet or minimize them.
You will also have to reduce the amount of sugar consumed, and, accordingly, all sweet baked goods, chocolate and candies. Despite the low iron content in their composition, they create a favorable environment in the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) for enhanced absorption.
It is also necessary to limit the consumption of alcoholic beverages.
Folk remedies
The use of alternative medicine methods cannot act as a full-fledged alternative to traditional methods. Folk remedies are an addition to the prescribed treatment. However, their use must be previously agreed upon with the attending physician. This is necessary to eliminate the risk of reducing the therapeutic effectiveness of drugs by various substances from traditional medicine.
One of the recommended traditional medicines is mumiyo. Available in the form of powder, tablets or capsules. It should be emphasized that during its use it is strictly forbidden to drink alcohol and smoke.
Bloodletting using medicinal leeches was also used to lower Hb levels. However, there is currently no reliable confirmation of the effectiveness of this method.
Preventive measures to prevent increased hemoglobin in men
Regular clinical blood tests will help to recognize hyperhemoglobinemia in time and make the right decision to prevent its development.
Examinations by a doctor will allow you to suspect a possible disease leading to an increase in the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin and begin its treatment.
A proper lifestyle and diet will help prevent the development of dangerous blood thickening processes.
Stepanenko Vladimir, surgeon
110, total, today
( 53 votes, average: 4.62 out of 5)
What foods reduce hemoglobin in the blood: causes of development and methods of treatment of hyperhemoglobinemia
Uric acid in the blood: norms in women and men, reasons for the increase
Related Posts
What is included in the complex
- General blood test extended with leukocyte formula and reticulocytes (venous blood only)
- Total protein
- Cholesterol-HDL
- Glucose (fluoride)
- Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c)
- Alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
- Aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
- Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)
- Gamma-GT
- Creatine kinase
- Albumen
- Total bilirubin
- Direct bilirubin
- Total calcium
- Potassium (K+), sodium (Na+), chlorides
- Creatinine
- Phosphorus, inorganic
- Urea
- C-reactive protein
- Total cholesterol
- LDL cholesterol
- T4 free
- TSH
- Testosterone
- Hepatitis B, HBs Ag (quality)
- Hepatitis C, anti-HCV amounts. (kach)
- AT and AG to HIV 1/2 (screening, quality)
- Syphilis sum. AT (IgG and IgM) (quality)
- Westergren ESR (venous blood)
- Serum iron
- INR (+PTV and PTI)
- Fibrinogen
- Alpha fetoprotein (liver)
- Cyfra 21-1 (non-small cell lung cancer)
- Total PSA (Prostate Specific Antigen)
- Free PSA (prostate)
- CEA (colon, rectum)
- CA 19-9 (pancreas, rectum and sigmoid colon)
- CA 72-4 (stomach)