Starting from the 3rd week, the embryo’s heart already beats, and from the 6th week it can be heard. If the fetus exhibits tachycardia, a disorder of the myocardium, in which the heart beats at a speed of 170-220 beats per minute or more often, additional diagnostic measures must be taken. Since this condition indicates discomfort of the embryo or certain pathologies. Timely identification of the problem will allow you to start treatment on time, correct the process and avoid unpleasant consequences.
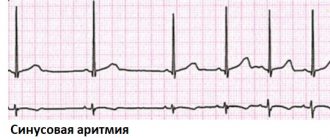
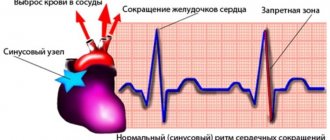
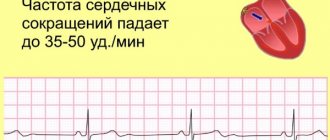
The normal fetal heart rate is 80-86 beats per minute, over time it gradually increases to 160-180.
Causes of tachycardia in a child in the womb
Rapid intrauterine heartbeat in the embryo is provoked by various anomalies in both the pregnant woman and the child. As a rule, they are not serious, but are associated with an increase in the load on a woman’s body. It is important to determine the reasons promptly and accurately. This will help you choose the right treatment and cope with the disease in time, without waiting until it begins to negatively affect the development of the fetus. Causes of pathology in which a pregnant woman becomes the culprit for their development:
- unbalanced diet;
- hyperthyroidism;
- changes in hormonal levels;
- cardiovascular pathologies;
- diabetes;
- rheumatism;
- taking certain medications;
- lack of microelements;
- unstable psycho-emotional state;
- heart disease;
- disruptions in the endocrine system;
- brucellosis and toxicosis;
- blood loss;
- respiratory diseases;
- avitaminosis;
- hypertension;
- water-electrolyte imbalance;
- myocarditis;
- overwork;
- hepatitis;
- drinking coffee and strong tea;
- leukemia;
- smoking;
- chronic and acute infectious diseases;
- cardiopathy.
Other causes of tachycardia that occur depending on the fetus itself:
- hypoxia;
- multiple pregnancy;
- intrauterine infectious diseases;
- anemia;
- chromosomal abnormalities and mutations;
- Rh conflict with mother's blood;
- pathological formation of the placenta;
- increased gas exchange and oxygen demand in the last stages of pregnancy.
Methods for listening to the fetal heartbeat
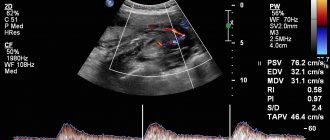
- Ultrasound (ultrasound)
With the help of ultrasound, you can not only hear the baby’s heart, but also see what condition the placenta is in, what size the fetus is, etc. The gynecologist-obstetrician pays special attention to the fetal heart rate if the pregnant woman has developmental defects or children born her in the past, had malformations of the heart and blood vessels.
- Auscultation
To implement this method, an obstetric stethoscope is needed. Relevant only from the 18th or even 20th week of gestation. But this method is not always easy to implement. In these cases, auscultation is difficult (and sometimes impossible):
- oligohydramnios
- polyhydramnios
- location of the placenta along the anterior wall of the uterus
- maternal obesity
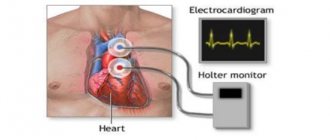
- Cardiotocography (CTG)
The method helps to identify hypoxia and provide the necessary treatment. When measuring heart rate using this method, heartbeats are recorded on a special film. The activity of the uterus is also determined, which is very important during the birth process. The procedure usually takes about an hour, sometimes a little less. This duration is explained by the fact that the baby can sleep for some period, and then wakes up. This affects heart rate and indicators that are recorded during CTG.
Sometimes the doctor decides that the sensors should remain on the woman’s stomach for 24 hours. The first time cardiotocography is performed after the 32nd week of gestation. An earlier date is not advisable. In 9 months you need to undergo CTG 2 times. The procedure is absolutely safe for the fetus and the mother herself. What will be recorded on the tape will not be understood by the average person. The doctor must decipher it, taking into account the data of tests and ultrasound diagnostics.
CTG norms:
- Heart rate 120-160 beats per minute
- the fetal heartbeat does not become less frequent, or is recorded very rarely
- When the fetus moves, the heart rate increases
These three factors are important to determine the PSP index, which should be less than 1.
CTG may show abnormalities when:
- lack of oxygen baby
- pressing the umbilical cord to the fetal head or bones (but then changes will be recorded for a short period of time)
- sensors incorrectly attached to the mother's belly
- Echocardiography
This is another method of listening to the baby's heartbeat. The method is relevant for the 18th – 28th week of gestation if the doctor suspects that the child’s heart is not forming quite correctly. Echocardiography shows the structure of the heart and blood flow.
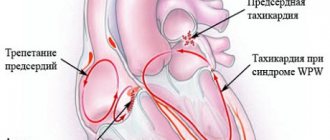
Forms of fetal tachycardia
Often the course of the disease, response to treatment, and favorable prognosis depend on the form of the pathology.
| Form | Peculiarities | Beats per minute | Term | Consequences |
| Reciprocal tachycardia of the supraventricular type | Excess contractions are localized mainly in the atria | 170—250 | 24-33 weeks | Normalization, inflammatory processes, blockade, bradycardia |
| Ectopic tachycardia | Occurs above the sinus node, in different parts of the heart, most often in the appendage and lateral wall of the right atrium | 180—240 | Any | Combination with ventricular form |
| Atrial flutter | Appears due to atrioventricular conduction block | 400 | Different | Normalization |
How long does a CTG take?
CTG is the most commonly used method for recording fetal heart rate. This is a non-invasive test and is not associated with pain or discomfort for the patient. The woman lies on her back, and doctors put two belts with electronic sensors on her stomach.
One of the sensors is an ultrasonic transducer that records the fetal heartbeat. The second sensor measures the strength and duration of uterine contractions. Both sensors are connected to a monitor on which these indicators are displayed in the current time and their dynamics are recorded. As a rule, CTG lasts half an hour; in some cases, the diagnostic procedure can be extended to an hour.
Symptoms
The main signs of the development of tachycardia in a child that a pregnant woman feels:
- increasing your own heart rate to 120 beats per minute;
- nausea;
- excessive anxiety;
- weak immunity;
- signs of oxygen starvation;
- increased fatigue;
- panic attacks;
- discomfort or pain in the heart area;
- sleep disorder;
- numbness of the limbs;
- frequent colds;
- vascular pathologies;
- dizziness;
- severe irritability.
What the study shows
KTG allows you to monitor the condition of the fetal heart. It is important to understand that for a baby, “squeezing” through the birth canal during childbirth is not a pleasant journey, but a tedious job. During labor, the baby is exposed to certain dangers that can be recognized by observing its heart rate. A fetal heart rate that is too low may indicate, for example, hypoxia, and a rapid heart rate may be a signal of intrauterine infection.
Treatment of the anomaly
Treatment depends on the condition of the expectant mother and, most importantly, does not harm the unborn child.
If during diagnosis, using CTG and other research methods, it was possible to detect fetal tachycardia, and, most importantly, find out the cause of the pathology, the doctor prescribes treatment. Therapeutic methods vary greatly depending on many factors:
- general health of the mother;
- chronic and acute diseases of the pregnant woman;
- causes of fetal tachycardia;
- accompanying symptoms and their severity;
- forms and types of pathology;
- gestational age;
- associated fetal anomalies;
- potential harm to the embryo from medications.
Depending on this, the pregnant woman is recommended an inpatient or outpatient course of treatment. If she has a disease that is potentially the cause, pathologists first eliminate them. When, after therapy, further research again shows fetal tachycardia, the risk of which is higher than the potential threat from taking heart medications, I prescribe medications:
- "Magnesium";
- "Sotalol";
- "Lidocaine";
- "Amiodarone";
- "Propranolol";
- "Dexamethasone";
- "Digoxin";
- "Flecainide".
If a sudden attack occurs, women are advised to:
- sit or lie down;
- relax;
- calm down;
- take several slow deep breaths in and out.
Why is the fetal heartbeat determined?
- to establish the fact of pregnancy
When a woman sees a positive result on a home pregnancy test, she should go to the gynecologist. He does an ultrasound to confirm or refute the test result. From the third week, as already noted, you can hear the heartbeat of the embryo. If at the first appointment you are told that there is no fertilized egg in the uterus, or that the embryo’s heartbeat cannot be heard, do not panic! After a week, most likely, your baby's heart will be sufficiently formed and the doctor will hear its beating.
In some cases, a return visit to the gynecologist reveals deformation of the ovum and lack of heart rate. Then the doctor speaks about a frozen pregnancy. Need a medical abortion. The doctor prescribes hormone-based medications. You can try to conceive again 3-6 months after an abortion for medical reasons.
- to assess the condition of the unborn baby
All environmental and maternal health factors affect the baby's heart. Heart rate depends on:
- the percentage of oxygen in the air that the mother is breathing at the moment
- fetal activity
- baby's sleep
- physical activity pregnancy
- mother's illnesses
- the stress that the mother is currently experiencing
But when exposed to these factors, the baby’s heartbeat changes temporarily. If the heart rate is not normal for a long time, the doctor may suspect that the baby is not getting enough blood. A diagnosis of fetoplacental insufficiency is made. It is almost always chronic. Sometimes the condition requires emergency delivery.
- to monitor the condition of the child during childbirth
Childbirth is a difficult stage in a baby’s life. There is a lack of oxygen; it is compressed as it passes through the mother’s birth canal. Basically, babies' hearts can withstand this stress. But in some cases there are emergency conditions, and the child will not survive without the help of qualified doctors. During the birth process, it is customary to check the baby’s heart rate after each contraction, otherwise you may miss the moment when acute hypoxia begins, which is life-threatening for the baby.
How to prevent the problem?
Food should be rich in vitamins and minerals.
To prevent such a problem from occurring, the expectant mother should:
- plan pregnancy;
- undergo regular medical examinations;
- monitor your health, treat acute and chronic diseases in a timely manner;
- take regular walks in the fresh air;
- eat a lot of vegetables, nuts, fruits, fish, white meat;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- take vitamin and mineral complexes;
- do not abuse too fatty, fried, salty, sweet and spicy foods;
- do special gymnastics for pregnant women;
- if discomfort occurs in the heart area, take natural sedatives, but only after consultation with your doctor;
- do not consume caffeine-containing products;
- normalize the daily routine;
- sleep at least 8 hours at night and, if possible, rest during the day;
- drink soothing herbal tea with lemon balm and mint;
- to live an active lifestyle.
Possible complications
What complications can sinus tachycardia cause for a pregnant woman? Pregnancy is a period in a woman’s life when the risks of many diseases increase or existing health problems become more complicated.
If this disease is not treated, allowing its development to take its course, disruption of the nervous system may occur, the emotional background may change, mood swings may intensify, sleep disturbances and a state of lethargy may appear. As a result, the woman’s immunity will decrease, and the already weakened body will constantly remain in a weakened state.
Such problems in a pregnant woman can negatively affect the condition of her body and her quality of life. In addition, with such a disease, the risk of complications during pregnancy and delivery increases. That is why heart problems in the expectant mother must be identified early for the success of their treatment.
Predictions and consequences
The prognosis of this pathology depends on many factors. First of all, it depends on timely diagnosis, timing of development, form of the disease, and correctly selected therapy. An important role is played by the medications used for treatment, as well as the method of their use - tablets, intramuscular injections, injection into the umbilical cord. Sometimes such an anomaly becomes the cause of pathological development of the embryo or heart defect in the future. But in most cases, the pathology has a favorable prognosis. If it is not completely eliminated in the womb, then it completely disappears in the first year of the baby’s life, leaving no unpleasant consequences.
Treatment and its features
Tachycardia in a pregnant woman requires careful diagnosis and the correct treatment regimen. First of all, the patient is prescribed blood tests and an ECG. In some cases, at the doctor’s insistence, additional procedures may be performed.
Treatment of tachycardia during pregnancy cannot be carried out inconsistently. If the doctor has drawn up a treatment regimen using medications, consultations with a psychoanalyst or neurologist, this regimen must be strictly adhered to.
If you are worried about your health and the health of your unborn baby, if symptoms of tachycardia appear, consult a gynecologist or visit a cardiologist. Health-safe diagnostics will help to accurately establish a diagnosis or reassure the expectant mother if fears are not confirmed.
Consequences of tachycardia during intrauterine development
A regular increase in heart rate in the fetus is fraught with the following consequences:
- intrauterine death;
- stillbirth;
- birth earlier than expected;
- insufficient oxygen supply;
- genetic abnormalities;
- heart defects;
- delayed physical and mental development.
When is the examination done and how often?
The study is carried out no earlier than 32 weeks. It is by this time that the nervous and cardiovascular systems reach a certain maturity. By 8 months, the myocardial reflex is formed - the relationship between cardiac activity and motor activity of the fetus. At the same time, the activity-rest cycle is established. Rhythmic changes in fetal sleep and wakefulness follow each other throughout the remaining period of pregnancy.
Cardiotocography must be performed 2 times during the 3rd semester. However, the frequency of the study is determined by the doctor based on the mother’s medical history, pregnancy history, results of other examinations and risk factors.