What is sinus bradyarrhythmia in children?
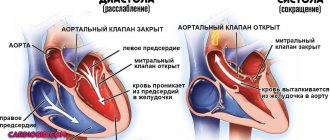
Sinus bradyarrhythmia is a congenital or acquired heart disease in which the beat frequency decreases to a critical level. As a result, the patient’s blood circulation slows down, internal organs and systems receive less oxygen and nutrients, and suffer from hypoxia. Pathology can occur at any age, but the most dangerous consequences are observed in children.
Sinus bradyarrhythmia in a child is diagnosed if the number of beats per minute does not exceed 60 times. The development of the disease is not always accompanied by visible symptoms and disorders.
It occurs more often in premature babies, with some forms of cerebral palsy. The reason lies in the dysfunction of the sinus node, better known as the pacemaker. There are moderate and severe forms of the disease.
Moderate
Moderate bradyarrhythmia in rare cases is a congenital anomaly of the body. Sometimes this feature appears in children who are actively involved in sports. But any form is dangerous to health and can disrupt the formation of organs and brain development. Unpleasant symptoms often appear when air is exhaled from the lungs.
Sinus bradyarrhythmia in a child is when the number of beats per minute is less than normal
Often, a moderate form of the disease appears with constant hypothermia and is formed as a protective reaction to low temperatures. On inspiration, the pulse is restored to normal levels, so diagnosis is difficult and requires a combination of different techniques.
Expressed
When the heart rate drops below 40–45 beats per minute, a diagnosis of severe bradyarrhythmia is made.
The following signs indicate it:
- frequent burning in the heart area;
- the child looks weak, sick, drowsy;
- The baby gets tired quickly with light loads.
The form of the disease is dangerous due to sudden attacks with loss of consciousness and memory. They worsen children’s general well-being, school performance, and limit communication with peers.
Treatment of arrhythmia in children
Treatment of arrhythmia in children is carried out only after a thorough examination of the body and determination of the cause of its occurrence. Sinus tachycardia is treated in cases where the patient cannot easily tolerate the state of accelerated heart rate or further maintenance of such a rhythm will infringe on the body’s needs for oxygenated blood. If tachycardia is psychogenic in nature, auto-training or psychological assistance is possible. It is recommended to give up stimulants, strong coffee, tea, and spicy foods, as well as review the medications the child is taking.
The same thing - medications - must be carefully studied again, paying special attention to the list of side effects, and for bradyarrhythmia. In this case, it is also necessary to study the acid-base state of the child’s body, the volume of circulating fluid, as well as determine blood pressure. Treatment of sinus arrhythmia in children is not carried out if it is respiratory in nature and does not bring inconvenience to the child’s life. In opposite cases, contacting a pediatric cardiologist cannot be delayed, which has a positive side: everyone knows that early diagnosis is the direction in which modern medicine is moving. In addition, as mentioned above, arrhythmia in a child can be caused by concomitant diseases, the treatment of which in half of the cases gives a positive result without the need to act directly on the heart.
However, for timely, and more importantly, correct treatment, correct diagnosis is necessary, and in Moscow you will not find doctors more competent in this narrow specialty than the doctors working at the Svyatoslav Fedorov Children's Medical Center. Doctors here provide assistance every day and will take care of your child as if it were their own child. A friendly, open, pleasant atmosphere on the one hand and many years of experience in the relevant field on the other will make treatment for your child a comfortable and serious process at the same time. You will receive a diagnosis of the child’s objective condition, a careful analysis of each of the symptoms, strict implementation of the necessary diagnostic procedures and strict adherence to treatment protocols.
Regardless of how you are treated depending on the decision of the cardiologist - outpatient or inpatient, you can count on maintaining quality standards of care. The introduction of the latest examination technologies and maintaining experience with standard methods, modern diagnostic equipment, properly selected rational treatment, optimal timing of therapy and preventive examinations in the future - this and more is happily offered by the Svyatoslav Fedorov Children's Medical Center. By making the right choice in a medical facility for the treatment of your child, you ensure many years of health and a fulfilling life for your baby.
With prices for services of the medical center named after. Fedorov, check out the “Prices” page
Why does the disease develop in children and adolescents?
In newborn babies, the heart beats at a frequency of 120–140 beats per minute. As you grow and mature, your heart rate decreases to a stable rate of 65–75 times. If the level drops below 60 beats, an examination is necessary to exclude dangerous pathologies. They develop as a result of inflammatory or congenital anomalies of the sinus node, increased tone of the vagus nerve.
Among the causes of sinus bradyarrhythmia in preschool age:
- complications after suffering from pneumonia, tonsillitis, otitis media;
- constant hypothermia;
- intracranial pressure;
- predisposition to cardiovascular pathologies;
- metabolic disorders and thyroid dysfunction;
- oncology.
In adolescents, the cause of sinus bradyarrhythmia is often associated with improper formation of hormonal levels. In rare cases, the child’s body reacts to taking energy drinks, illegal drugs, or poor eating habits (bulimia or anorexia in girls 13–15 years old).
Expert advice
If your child suffers from any cardiac disease and is prescribed drugs such as beta-blockers (Bisoprolol, Metoprolol) and calcium channel blockers (Verapamil, Diltiazem) for treatment, you need to remember that the pulse may slow down while taking them. A decrease in heart rate by approximately 5-10 beats from the lower limit of the age norm is not dangerous. But, if the child’s heart rate decreases more, the cardiologist must be informed about this so that he can adjust the dosage.
Signs of illness
Sinus bradyarrhythmia in a child is sometimes asymptomatic and is detected by chance during a comprehensive diagnosis of other diseases. The main signs depend on the age, developmental characteristics of children, and the stage of the disease. Depending on the cause, the problem may be physiological, organic, neurogenic, drug-related or toxic.
Your child may have the following symptoms:
- increased sweating at rest;
- feeling of lack of air;
- loss or confusion of consciousness;
- heaviness in the chest;
- poor appetite;
- low concentration, deterioration in school performance;
- discharge on the face of the nasolabial triangle.
Tingling or burning in the heart with bradyarrhythmia always occurs when exhaling. If you hold your breath for a few seconds, the discomfort disappears.
Physiological
For natural reasons, a slowdown in heart rate is observed during a night's rest or daytime sleep, after waking up. At rest, the pulse drops to 65–60 beats, the changes are practically not felt by the child. During physical activity or active play, the indicator rises to a normal and comfortable level.
Among the dangerous physiological causes of the disease is the appearance of benign or malignant tumors in the heart area, on the myocardial muscle. The child complains of shortness of breath and tingling in the chest, has pale skin, and may lag behind peers in development in terms of weight and height.
Organic
Bradyarrhythmia can form due to improper development of the sinus node in the heart. The number of beats per minute decreases to 45–50 units, and deformation and necrosis of myocardial tissue begins.
The problem occurs against the background of serious diseases:
- vascular ischemia;
- cardiosclerosis;
- cardiomyopathy.
In a young child, sinus bradyarrhythmia of the organic type develops with inflammation of the pericardium of the heart. This is a dangerous complication after a sore throat or otitis media, in which characteristic symptoms are observed: constant low-grade fever, muscle weakness, low activity in play and study, joint pain.
Neurogenic
Sinus bradyarrhythmia in a child can be a consequence of pathologies of the nervous system: intracranial pressure, childhood neuroses, vegetative-vascular dystonia.
In addition to pain in the heart area, young patients feel:
- dizziness;
- low blood pressure;
- attacks of panic or irritability.
The problem requires an integrated approach to treatment, the help of an endocrinologist, cardiologist and neurologist.
Medicinal
In childhood, bradyarrhythmia of this type develops extremely rarely. It occurs in children with asthma, kidney pathologies or severe lung diseases, who constantly take potent drugs to maintain vital functions. Damage to the sinus node of the heart can occur as a side effect after undergoing chemotherapy for oncology.
Toxic
Increasingly, doctors are observing babies who have sinus bradyarrhythmia after toxic poisoning. The reason is associated with living in a disadvantaged area, constant contact with toxic substances in the house, kindergarten, and school. Damage to the heart is caused by pathogenic bacteria and viruses in typhoid fever, hepatitis A or B.
Signs and symptoms
The clinical picture directly depends on the degree of bradycardia. With a slight slowdown in heart rate, the child can feel great without experiencing any discomfort.
With a more pronounced decrease in heart rate, the child becomes less energetic, he gets tired quickly, he is constantly sleepy, and his skin becomes pale. His head is spinning and his vision is getting dark. He may even faint.
Sometimes I had to observe children who, due to severe bradycardia, lost consciousness, their heart stopped beating for a while and their breathing stopped, then convulsions began. After a few seconds or a couple of minutes, the child comes to his senses. This resembles an epileptic seizure. This phenomenon is called Morgagni-Adams-Stokes syndrome. It develops when the heartbeat is very slow. Its occurrence is due to severe hypoxia (oxygen starvation) of the brain.
An attack of Morgagni-Adams-Stokes syndrome is a very dangerous condition, as it can lead to the rapid death of a child.
In what cases should you immediately consult a doctor?
If your child does not exercise seriously and his heart rate is lower than normal for his age, he should be seen by a cardiologist, but not necessarily right away. It’s another matter if he is lethargic, sleepy all the time, and faints. In this case, a visit to the doctor should not be postponed. And finally, if a child develops an attack of Morgagni-Adams-Stokes syndrome, you need to call an ambulance.
Is it normal for a child who plays sports to develop the disease?
At the initial stage of bradyarrhythmia, the child leads an active lifestyle. But excessive sports activities in preschool age can provoke disturbances in the development of certain parts of the heart. This causes the appearance of painful symptoms during the transition period.
With regular sports activities in children, in 90% of cases the physiological type of the disease is diagnosed.
With a constant load, the heart gets used to working at an increased pace for several hours a day, so at rest the pulse drops to 60 beats per minute: this is how the body “forces” the myocardial muscles to rest between heavy workouts. This condition does not cause concern among doctors, does not entail dangerous complications, and is detected in 50% of professional athletes, football players, and cyclists.
general information
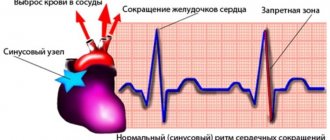
Modern medicine does not identify a decrease in heart rate as an independent disease, but regards it as a symptom of certain pathological processes. As a rule, in children (including newborns) and adolescents, a sinus form of cardiac bradycardia is detected, which may also be accompanied by arrhythmia.
Assessing the presence or absence of pathology requires an integrated approach, since heart rate norms depending on age are only average values.
How dangerous is the disease?
More severe complications occur with severe forms of the disease. The child’s body constantly experiences a lack of oxygen, the blood supply to soft tissues deteriorates, and the elimination of toxins and decay products slows down. This leads to the death of heart tissue and nerve fibers, and concomitant diseases of the kidneys, liver, and thyroid gland develop.
Among the dangerous complications:
- fainting;
- brain hypoxia;
- heart failure;
- thrombosis;
- increased risk of ischemic stroke;
- tachycardia.
In the absence of treatment or ignoring the recommendations of doctors, the child develops cardiopathy or angina pectoris, requiring surgical intervention.
Which sport is not suitable
- diving;
- Horseback Riding;
- cycling;
- gymnastics;
- karate;
- skiing;
- judo;
- body-building.
These types of sports are not suitable for children with this disease, since each of them involves excessive constant physical activity, and even increased before competitions, which is contraindicated in case of bradycardia in a child.
Is treatment necessary?
Moderate sinus bradycardia in a child does not always require drug treatment. After diagnosis and identification of the cause, most children continue to play sports, attend school and clubs without restrictions. Doctors recommend annual ultrasound examinations to monitor the condition of the myocardium and sinus node.
In severe cases, treatment with special medications, physiotherapy, and vitamin complexes is required. The task of doctors is to prevent the development of complications that can lead to disability. If the situation worsens as you get older, corrective surgery is performed or a pacemaker is installed.
Diagnostics and treatment at NEARMEDIC
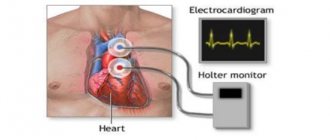
In most cases, to make a diagnosis, NEARMEDIC cardiologists prescribe standard electrocardiography, Holter (24-hour) monitoring - HM ECG. If there are initial changes on the ECG, pharmacological tests are recommended. In a number of doubtful cases, the doctor prescribes EPI - an electrophysiological study, which helps to develop treatment tactics and determine the electrophysiological indications for pacemaker implantation.
Mild sinus dysfunction does not require treatment. You can limit yourself to monitoring the patient’s condition and conducting non-drug therapy: quitting smoking and alcohol, avoiding taking certain medications. To avoid irritation of the sinocarotid area, it is not recommended to wear tight scarves and ties that put pressure on the neck. Physical therapy classes and swimming are shown.
The most effective treatment for bradyarrhythmia, regardless of its classification, is cardiac pacing. The patient undergoes a mini-operation - a pacemaker is implanted that generates electrical impulses. The operation is performed under local anesthesia.
Diagnostic measures
Measuring your pulse daily can help detect irregular heart rhythms. If a decrease is observed for more than 7–10 days, it is better to consult a pediatrician or cardiologist for advice.
For a comprehensive examination, the following diagnostic methods are recommended:
- Taking an anamnesis, interviewing parents (doctors are interested in the presence of a genetic predisposition to diseases of the cardiovascular system).
- Daily monitoring of rhythm and blood pressure using a special device (Holter technique).
- Electrocardiogram.
- Ultrasound of the heart or echocardiography.
- MRI of the chest in severe forms of the disease.
- Analysis of thyroid hormones.
- Doppler of the arteries and vessels of the brain in the neurogenic form.
A clinical blood test helps identify hidden inflammation, shows anemia and other disorders. Diagnosis is carried out without hospitalizing the child to the hospital.
Methods for treating bradyarrhythmia
Only after a comprehensive examination does the doctor select a treatment method. For moderate forms of the disease in children and adolescents, a special diet and correction of the daily routine are recommended. A vitamin complex with magnesium, potassium and Omega-3 amino acids strengthens the heart muscle and immunity, helping the child cope with the stress of school and section.
If the heart rate is 40–50 beats, a therapeutic course in a hospital is recommended. The child is given special medications to eliminate hormonal imbalance or infectious inflammation due to pericarditis. In the organic or toxic form, treatment of the underlying cause is required.
Drug therapy
If the heart rate is slow, drugs are administered to normalize the heartbeat.
These are special cholinergic protectors that stimulate myocardial function without sudden surges in blood pressure:
- Metacin. Taken intravenously or subcutaneously 2–3 times a day, 0.5–1 mg. For a child, the daily dose should not exceed 6 mg.
- Atropine. When the heart rate decreases to 20–25 beats, the medicine is administered at a dose of 300 mcg every 6 hours. During an attack of bradyarrhythmia, a one-time dosage of 10 mcg per 1 kg of baby’s weight is used.
- Amiodarone. Improves coronary blood flow, used in the form of tablets or injections. For children, the dose is up to 10 mg per day. Course duration is up to 2 months.
To stimulate signal conduction from the sinus node, it is recommended to take beta-agonists:
- Ephedrine (Norepinephrine, Adrenaline);
- Izadrina;
- Alupenta (Eufillina).
For neurological problems that provoke attacks of bradyarrhythmia, doctors select sedative medications. When treating children, preference is given to herbal remedies with minimal risk of complications: Glycine, Pantogam, Citral.
Surgery
If drug therapy does not help stabilize the heart rhythm, surgery is performed. A common method is radiofrequency cardiac ablation, or RFA.
With its help, the cardiac surgeon cauterizes the area of the muscle that causes the signal to slow down or removes excessive tissue growth on the wall of the sinus node. As a result, the incorrect path of impulses is interrupted, the frequency enters the normal range of 65–75 beats.
Before the operation, the child in the hospital undergoes a comprehensive examination for blood clotting time, viral hepatitis, and receives consultation with an otolaryngologist.
The cauterization procedure is as follows:
- Anesthetic and sedative drugs are injected into the femoral artery for anesthesia.
- Through a vein, the doctor passes a thin probe from sensors directly to the inflamed area of the heart.
- Using a visual intravascular sensor, the surgeon determines the point of impact.
- After cauterization, a change in heart rhythm is observed for 10–15 minutes, after which the probe is removed and the patient is sent for rehabilitation.
The operation has minimal complications: there are no painful incisions, healing and recovery time is reduced. Already on the first day the baby can get up, move and eat. On days 3–5 he is discharged for home treatment.
A more traumatic method is to install a pacemaker. The miniature device becomes an artificial pacemaker, replacing the function lost by the heart. The device is permanently implanted into the child and is adjusted individually.
The procedure for installing a pacemaker is carried out by experienced cardiac surgeons and includes the following steps:
- Electrodes are inserted into the device through a puncture in the vein. They will pass through large vessels directly to the device.
- A subcutaneous pocket no larger than 5 cm in size is formed in the armpit, into which the pacemaker is placed.
- The connection occurs through the lateral vein of the arm.
- The electrodes are additionally attached to the endocardium using reliable hooks.
- Additionally, the device is tested and the results are recorded in a computer program.
The operation to install a pacemaker lasts at least 3 hours. The child receives antibiotics for 3–5 days to prevent rejection of the implanted device. Complete rehabilitation takes no more than 10 days.
Recipes for folk remedies
At the initial stage of the disease, drug treatment and traditional methods can be combined. Some plants contain beneficial substances that stimulate the functioning of the heart muscle and saturate tissues with mineral compounds and phytoncides. The most accessible recipes at home:
| Hawthorn decoction | In a clean container you need to brew 2 tbsp. l. herbs, pouring 0.5 liters of boiling water over it. This tea calms the child after an attack and restores sleep. |
| Calendula tea | Dried flowers are crushed, brewed at the rate of 250 ml of hot water and 2 tsp. plants. The product should be drunk 2 times a day for up to 10–14 days. |
| Honey with dried fruits | In a clean bowl, chop 200 g of dried apricots, prunes and walnuts, mix with 0.5 liters of natural honey. The composition is given to the baby 3 times a day in a spoon after meals. The vitamin mixture saturates with magnesium, potassium, amino acids, supporting heart function. |
With an integrated approach, sinus bradyarrhythmia is treatable. Many children “outgrow” the disease by the age of 16–18 and get rid of shortness of breath and muscle weakness. Modern methods make it possible to completely relieve a child from the consequences of the disease and reduce the risk of dangerous complications, disability or death by 90%.
Article design: Vladimir the Great
Medical indications
Among the main symptoms of bradycardia in children are:
- pale skin;
- fast fatiguability;
- shortness of breath;
- dizziness that occurs in attacks;
- pain in the chest area;
- fainting and semi-fainting states.
To prevent bradycardia and reduce symptoms, doctors advise following a special diet:
- Drink as much fluid as possible. Ideally, one and a half to two liters per day.
- Eat a lot of vegetables. It’s good if carrots, parsley, and cabbage predominate in the diet.
- Give preference to lean meat.
- From fruits, choose apples, bananas and citrus fruits that are good for your heart.
- Eat fermented milk products.
- Don't give up seafood.
In addition to diet, hardening and moderate physical activity are useful.
When choosing a sport for a child with cardiac bradycardia, its degree should be taken into account. To do this, you need to do an ECG, which will help you understand what kind of bradycardia is taking place: sinus or heterotopic.
Be sure to consult a cardiologist. It will help you decide on the type of load that will be optimal for a particular type and diagnosis.