Band neutrophils are a special type of white blood cells responsible for the body's immune defense. These cellular structures are formed in the bone marrow, from where they enter the vessels of the circulatory system.
The main mechanism of the protective function is phagocytosis. Many people remember what this is from their school days. Neutrophils capture and destroy foreign microorganisms, and having fulfilled their extremely important purpose, they die and are excreted from the body.
Neutrophil maturation occurs in several stages. Final stages:
- stab;
- segmented neutrophils.
The rods are the predecessors of the segmented ones, their younger form. The term “band” indicates differences in the structure of the cell nucleus. If mature neutrophils are characterized by segmentation, then in functionally immature neutrophils this cell component is a rod-shaped solid formation.
The number of segmented forms in the bloodstream significantly exceeds the number of immature ones. In general, they cope with the protective function. But what happens if the proportion of band neutrophils in the blood increases noticeably? This means that the body is under attack from harmful microbes.
Based on the increase in the number of neutrophils, doctors conclude that there is an infection - bacterial or fungal, and also determine the degree of its activity.
Table by age
The source of information about the number of neutrophils is a detailed general blood test.
The normal content of these cellular structures for healthy people depends on the age group they belong to. Relative values of normal levels for all age groups are presented in the table.
| Patient age | Band neutrophils (%) |
| Newborns | 3—17 |
| Children from 1 month to 1 year | 0,5—4 |
| Children from one to 13 years old | 0,7—5 |
| Teenagers (13-15 years old) | 1—6 |
| Men | 1—6 |
| Women | 1—6 |
Normal for women
The table by age shows the relative norms for women in the range of 1 - 6 percent. The absolute normal values for women are 1.8-6.5 × 109 cells per liter.
Is there any cause for concern if the number of band neutrophils does not exceed 6 percent? What does this mean? First of all, there is no health-threatening bacterial infection. In other words, at this moment the bone marrow is not active, sending young neutrophils into the blood vessels.
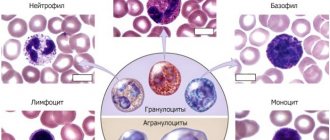
Types of neutrophils
But what happens if a blood test shows a quantitative increase in leukocytes of this type (above 6 percent in women)? Perhaps the patient is sick. This situation occurs in a number of diseases and conditions, including
- leukemia;
- inflammation in the ear, bronchi, tonsils, lungs;
- blood poisoning;
- peritonitis;
- burns;
- abscess;
- trophic ulcers.
Rod-shaped neutrophils in men
If in the leukocyte formula of healthy adults, regardless of gender, band neutrophils make up from 1 to 6%, this is the norm. The absolute levels of immature neutrophils in the blood of men are 1.8-6.5 × 109 units per liter. These same values are the norm for women. In other words, the norm is for all adults.
In the child's blood
The normal number of young neutrophils corresponds to the age of the babies. The maximum acceptable value in infants (up to 17 percent) is much higher than in healthy older children (band neutrophils no more than 4-5 percent).
The norm differs noticeably only in the initial period of the baby’s life, when the mother’s blood cells change to new, the child’s own blood components.
Deviations from the norm in children:
- Neutrophils are reduced or completely absent in the child’s blood, and no noticeable deterioration in well-being is observed. If a repeat test shows the same results (insignificant or 0 in the child), the pediatrician diagnoses benign neutropenia of childhood and recommends contacting a hematologist and immunologist. The causes of this disease have not been studied, but it does not require special therapy. The level of neutrophils levels out on its own by 1 year, and sometimes by two.
- In the analysis of a completely healthy child, there are moderately increased values of the level of leukocytes in this group. This happens if shortly before blood sampling the baby suffered from an illness or simply had a hearty breakfast.
Neutrophils - what kind of cells are they?
Neutrophils are a group of white blood cells that fight the spread of infection in the body. They are formed by bone marrow cells and are sent through the body tissues to the site of infection. Having detected foreign cells, neutrophils capture and engulf them. This process is called phagocytosis.
The lack of neutrophils has a scientific name - neutropenia. This is a condition in which blood cells break down too quickly, without having time to build a reliable defense. In some situations, we have to talk about disorders of the hematopoietic system, when the bone marrow does not produce enough protective cells or about the fact of a pronounced decrease in immunity.
To determine the number of neutrophils, two types of measurements are used:
- true;
- relative.
When determining the true number of cells, their content in the analyzed volume of blood is taken into account. When identifying a relative indicator, the total number of leukocytes is taken into account and the percentage that neutrophils make up of the total number is calculated.
Neutrophils are very mobile blood cells; they have access to areas and tissues where the main leukocytes do not penetrate. All neutrophils, depending on their maturity, are divided into band and segmented. The second group is mature cells, their number increases significantly when an inflammatory process occurs. They are the main phagocytes filling the bloodstream, but when infection develops, they quickly migrate to the site of inflammation, overcoming the walls of blood vessels.
How are they indicated in the analysis?
The relative abundance of neutrophils is indicated in a line beginning with the character set NEUT% (NE%) (neutrophils). The designation for the absolute content of neutrophils in a blood test looks somewhat different. The form contains a ciphergram in which the % sign is replaced by #: NEUT# (NE#) (neutrophils).
Form with blood test results
Reasons for deviations from the norm
There are many reasons that can provoke deviations from the norm. The same factors can lead to low and high cell levels.
- Reduced neutrophils in the blood
Reasons for the increase
The human immune system reacts sharply to various external and internal factors. That is why there can be many reasons for the increase in the number of band cells.
The most common of them:
- Progressive type 1 diabetes mellitus.
- Long-term use of antibacterial medications, which provokes a weakening of the immune system.
- Viral and cold pathologists in the acute stage.
- Burns, cuts and other injuries to the skin, especially when a large area is affected.
- Gastric ulcer in the acute stage, gastritis.
- Bronchitis in acute and chronic form.
- Myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke.
- Poisoning by the breakdown products of ethyl alcohol.
- Allergic reaction to medications, food or other substances.
- Anemia of varying severity.
- Inflammatory pathologies of joints.
- Infection of the body with intestinal parasites.
- The presence of trophic ulcers on the patient’s body.
- Blood poisoning of the initial or advanced stage.
- The presence of malignant tumors in the body and their decay.
In addition, pathologies of muscles and nerve endings of inflammatory origin can provoke an increase in cell levels.
Reasons for the downgrade
Factors that influence an increase in indicators can also cause a decrease in them.
However, there are other reasons that can lead to deviation:
- Damage to the bone marrow by malignant neoplasms, spread of metastases in the body.
- Systemic diseases.
- Viral pathologies, such as hepatitis or rubella.
- Severe anaphylactic shock threatening the patient's life.
- Advanced tuberculosis.
- Endocarditis.
- Deficiency of folic acid in the body.
- Exhaustion of the body as a result of excessive stress and malnutrition.
- Bacterial pathologies of internal organs and skin.
One or more reasons lead to changes in indicators and aggravation of the patient’s condition.
If absent in the blood
A number of diseases and factors lead to a quantitative decrease in immature defender cells. For example:
- viral diseases (measles, rubella, etc.);
- mycoses;
- anemia;
- chemical poisoning;
- oncological processes and consequences of radiation;
- hyperthyroidism;
- taking certain medications.
The absence of band neutrophils in the blood of an adult does not always mean that he is sick or is under the influence of factors leading to neutropenia.
In most cases, 0 in an adult is a laboratory error. 1 percent in an adult is an indicator of health.
When is a test ordered?
Band neutrophils can be increased or decreased in patients of different genders and ages.
However, the study is prescribed if there are specific indications in the form of various symptoms and signs of diseases:
- Colds and inflammatory pathologies at the initial stage.
- Increased fatigue and weakness that does not disappear after a long rest.
- Loss of appetite and weight loss for no apparent reason.
- Decreased concentration and memory impairment.
- Dry skin, bleeding gums.
- Indigestion.
- Increased body temperature in the absence of other symptoms of the disease.
- Inflammatory pathologies of the liver, pancreas, gall bladder.
- Kidney diseases in acute and chronic stages.
- Suspicion of acute respiratory tract diseases.
- Oncological diseases in latent form.
- Infectious pathologies of the digestive tract.
- Blood pathologies characterized by a decrease in the level of red blood cells and hemoglobin.
Diagnostics can be prescribed for preventive purposes, which makes it possible to detect abnormalities at the initial stage. This analysis is a standard examination method, therefore, immediately upon admission of a patient to a hospital in any department, blood is drawn and tested. Thanks to the simplicity and speed of diagnostics, it is possible to identify deviations on the day the biomaterial is submitted.
Causes in children
In younger patients, the list of diseases will be approximately the same. There are some additions. A number of conditions occur only in young patients and appear immediately.
Pediatric infectious diseases
Scarlet fever, rubella, chicken pox, whooping cough, mumps (mumps) and much more.
They are not fundamentally different from other infectious pathologies. All white blood cells rush to fight foreign agents.
Pediatricians are involved in recovery. Antibiotics are prescribed in strictly controlled dosages. Anti-inflammatory drugs, also drugs for viral infections, antipyretics. An individual regimen is prescribed.
Regular monitoring of the condition is indicated.
Congenital bone marrow disorders
Segmented neutrophils in a child can be increased as a result of hyperfunction of the bone marrow, when too many formed cells are produced: including leukocytes in different variations.
This is usually a genetically determined disorder. It is difficult to correct. All that remains is to deal with the symptoms.
Corticosteroids and immunosuppressants are prescribed. The disease often occurs in periods. The violation is replaced by remission and so on in a circle. You need to be constantly monitored by a hematologist.
Indications for analysis
A general blood test is the most common hematological test, so the range of indications for its use is wide. Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell whose main task is to destroy pathogenic microorganisms. Therefore, the main goal of the analysis for the content of neutrophils is to identify potentially dangerous conditions accompanied by infectious and inflammatory processes. In other words, a blood test for neutrophils can be informative both for colds and for kidney or liver diseases.
Neutrophil norms and their functions
{banner_banstat0}
Without specifying individual levels in men and women by age (they are described here), the average number of formed cells will be from 51 to 60% of the total mass of white blood cells.
Another approximately 7-10% is accounted for by immature forms of structures. The so-called band neutrophils, which are yet to enter “adult”, functionally active life.
The main task of formed cells, white blood cells of this type, is to bind antigens and fight pathological structures, be they bacteria or other offenders. These bodies play a major role in eliminating helminthic infestations and in the development of an allergic reaction.
The laboratory, artificial function is to mark inflammatory processes, oncological phenomena and other pathological conditions, which will be discussed further.