Every parent is obliged to monitor the health of their child. And a general blood test is an important assistant in this difficult matter.
After taking a blood test, the results are interpreted and studied by a doctor. The presence of normal indicators indicates the health of the child’s body.
If the doctor finds any deviations from the usual values, the parents will be asked to conduct additional examinations of the child.
The importance of neutrophils in the diagnosis of diseases
Cell characteristics
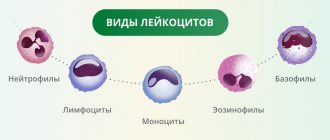
As mentioned above, neutrophils are a type of granulocytic leukocyte. They belong to this group of white blood cells, since they have granules in their composition, or rather in the cytoplasm. They contain various types of compounds: proteins, enzymes, and so on. They provide functions to neutrophilic leukocytes.
Role in the body
Neutrophils make up the majority of all leukocytes. Everyone knows that white blood cells protect our body. How does this happen?
When a foreign agent enters the body, substances are produced that attract neutrophils to the site of penetration. There, neutrophil leukocytes phagocytose, that is, absorb a foreign agent. The granules contained inside the neutrophil help digest the foreign compound.
The difference between neutrophils and other cells that can “eat” other molecules is their viability after phagocytosis. Neutrophils participate in phagocytosis once in their lives (after which they die), while other macrophages can do this many times.
Thus, this type of leukocyte is one of the first factors in the body’s defense against foreign agents.
Type of neutrophils
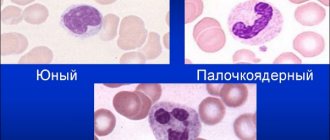
There are several types of leukocytes, differing in maturity. Initially, the maturation of this type of leukocyte begins in the same way as others - from a precursor cell. Then, during differentiation, a myeloblast is formed from it, then a promyelocyte. Already at this stage, granules begin to appear in the cells. Next, a myelocyte is formed, then a metamyelocyte. It is also called a young neutrophil.
Under some conditions, young neutrophilic leukocytes can be detected in the peripheral blood.
A band form is formed from the metamyelocyte. It is named after the shape of the kernel at this stage of maturation. The final, mature cell is the segmented neutrophil. It differs from its predecessor in the structure of the nucleus: segments are formed from the so-called rod, connected by constrictions.
Where are neutrophils formed and what are they responsible for?
Leukocyte granulocytes participate in the body's immune defense against pathogenic environmental factors. Neutrophils are divided into “mature” – segmented and “immature” – precursor cells. In infectious diseases, segmented cells provide immune protection.
The main functions of neutrophil granulocytes:
- Destruction of pathogenic microorganisms (bacteria, fungi) and, to a lesser extent, viruses.
- Regulation of inflammatory processes.
- Control of proliferation of intestinal, epithelial and reproductive microflora.
Before becoming mature neutrophils, cells go through developmental stages. Leukocyte granulocytes are synthesized by red bone marrow and then diffuse into the bloodstream. Stages of neutrophil differentiation:
- Myeloblasts and myelocytes are formed.
- After maturation, the myelocyte leaves the red bone marrow and begins to circulate in the bloodstream. There the further development of the cell continues. The myelocyte differentiates into band neutrophils.
- At the last stage of differentiation, segmented neutrophil granulocytes appear, which provide complete immune protection of the body.
Bone marrow
Indications for referral for analysis
- Determination of neutrophil levels can be carried out as part of an annual preventive examination in children and adults. This is a way to identify hidden diseases that do not yet have clinical symptoms.
- A study of the leukocyte content is determined in order to determine whether there is an infectious process in the body. Perhaps this is the main indication for prescribing an analysis of the level of neutrophil leukocytes in the blood. That is, by analyzing the level of white blood cells, we can draw a conclusion about the body’s ability to resist infections. This is an important characteristic of children's health.
- One of the indications for studying the content of this type of cells is the diagnosis of malignant blood diseases. This may be evidenced by the detection of young and blast forms of neutrophils
- A conclusion about the effectiveness of treatment can also be made based on data on the level of neutrophils over time.
Why does the number of neutrophils decrease?
A decrease in the number of cells (neutropenia) may be hereditary.
If you know about such characteristics in one of the baby’s parents, you should inform your doctor about it. Other factors that can cause neutropenia:
- deficiency of B vitamins, copper, iron, and other microelements;
- long-term use of analgesics, antispasmodics, cytostatics and some other drugs;
- long-term physical activity;
- stress (usually due to a family situation or difficult living conditions, but can also be caused by school workload);
- bacterial and fungal infections;
- viral diseases (measles, chickenpox, rubella, influenza, HIV, herpes, etc.);
- bone marrow pathologies (bone marrow aplasia or hypoplasia, or hereditary diseases affecting the synthesis of cells and their release into the bloodstream).
How does neutropenia manifest in a child?
If the cause of neutropenia is a long-term infection or taking medications, correction of the treatment of underlying diseases is required. If there is no active pathological process, the stages of treatment depend on the child’s well-being:
Chronic moderate neutropenia or a decrease in the number of neutrophils in children under 3 years of age may not manifest itself. In this case, you should focus on the child’s condition and the pace of his development. In most cases, no special treatment is required.
If the cell level has not stabilized after 3 years, or the child is developmentally delayed, gets tired quickly, has a runny nose, or often suffers from colds for a long time, this is a reason for additional examination and treatment. Perhaps the problem can be solved by vitamin therapy, changing the child’s diet and daily routine.
If the cause is stress or school and extracurricular workload, you need to find a way to get rid of them. You may have to give up some clubs during primary school age. The child will be able to return to them when he grows up and gets stronger.
If a decrease in the number of less than 500 in 1 ml of blood is diagnosed, most doctors consider it appropriate to prescribe antibiotic therapy, even if additional examination does not reveal the causes of the disease.
This measure allows both to extinguish a hidden pathological process and protect the child from possible bacterial infection against the background of decreased immunity. As a rule, such therapy gives a positive result.
How is the level of neutrophils in the blood calculated?
To perform a neutrophil count, blood is required. Any one is suitable for this: taken from a vein or capillary. In newborns, blood may be taken from the heel. The study of the type of white blood cells is called leukocyte count. It is performed during a general clinical blood test (CBC).
This study is most often carried out using a microscope and a special cell counter. The specialist examines the blood smear and counts all the types of cells that he saw. Counts one hundred cells in a smear. Next, writes the result on the answer form.
Staining of smears is used to differentiate different cells from each other. The Romanowsky-Giemsa method is most often used for staining blood smears.
For heavy laboratory workloads, it is possible to count cells using an automatic hematology analyzer. But not all laboratories can be equipped with such devices. Which brings us back to the manual method and the value of experts in the field.
Neutrophils are less than normal
Sometimes cases occur when the number of neutrophils is less than normal. This condition is called neutropenia, and it indicates a decrease in immunity. Neutropenia is diagnosed if the number of neutrophils is less than 1.6*10⁹/L. Why are there not enough of these cells in the child’s blood? There may be several reasons for this phenomenon, including:
- neutrophils destroy themselves;
- these particles are produced in insufficient quantities;
- irrationally distributed in the blood.
What can cause destruction or insufficient production of neutrophils? Typically, this result is due to:
- Why are neutrophils elevated in an adult, what does this mean, what to do?
- viral diseases: ARVI, measles, influenza, hepatitis, rubella, scarlet fever;
- fungal infections;
- condition after anaphylactic shock;
- leukemia in acute form (see also: symptoms of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children);
- intoxication with chemical compounds;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- consequences of radiation;
- anemia of various etiologies;
- lack of vitamin B12 and folic acid;
- congenital neutropenia is a rather rare disease.
Also, the level of neutophils in children is affected by taking certain drugs. For example, glucocorticosteroids, anticonvulsants, and various types of painkillers can reduce the number of these cells.
A decrease in neutrophils in the blood may indicate a child’s illness, such as anemia
Sometimes in babies of the first year of life the number of neutrophils is reduced, but this distribution of blood cells does not in any way affect the baby’s well-being. Usually the pediatrician recommends taking tests again after a while. If the results remain the same, the doctor will likely diagnose benign childhood neutropenia. To date, the causes of this disease are not known, but it does not require treatment. As a rule, the level of these particles normalizes on its own. This can happen by one year, or maybe by 2. Such a child is registered with a gemologist, immunologist and pediatrician.
A similar pathology occurs in adults, but it is called cyclic neutropenia. The essence of the disease is that the patient’s level of this type of cell regularly drops, then recovers. The cycle can be a month, or maybe a year.
Do you need any preparation for the analysis?
If the patient wants to get a reliable result of a blood test, then it is necessary to prepare. Moreover, the rules are very simple.
- Blood is donated on an empty stomach. Children under one year of age should not eat for 30–40 minutes before blood sampling. Older people – 3-4 hours.
- emotionally calm before donating blood .
- The level of physical activity also matters. Do not burden yourself or your child with training or sporting events. Even running down a hospital hallway can affect your results.
- There are situations where medications interfere with results . If the patient takes anything, the doctor should be notified so that he takes this into account when interpreting the study results.
Normal values of neutrophils in the blood in adults and children
Due to different methods for calculating the variety of white blood cells, there are different units of measurement: absolute and relative.
Relative values are the number of cells out of a hundred. Expressed as a percentage.
Absolute values - show a specific number of cells in a liter of blood.
The norms of neutrophils in the blood of adults and children are presented in Table 1.
Table 1. Reference values for neutrophil leukocytes.
| Age group | Absolute values | Relative values | |
| Rod | Segmented | ||
| Less than one year | 1.5 – 8.5 * 10*9/liter | 0,5 – 4 % | 15 – 45 % |
| One year – six years | 1.5 – 8.5 * 10*9/liter | 0,5 – 5 % | 25 – 60 % |
| From seven to twelve years | 1.8 – 8 * 10*9/liter | 0,5 – 5 % | 35 – 65 % |
| Over thirteen years of age Adults | 1.8 – 7.7 * 10*9/liter | 0,5 – 6 % | 47 – 72 % |
Deviations from usual values
There are cases when the norm of neutrophils in children is exceeded or, conversely, reduced. Both conditions have certain symptoms, causes and consequences.
Increasing values
The number of granulocytes in a child’s blood exceeding acceptable parameters is fraught with serious consequences.
The absence of any symptoms and a slight increase in neutrophils indicate factors such as:
- Excessive physical activity.
- Stressful situations, overexertion.
- Blood loss.
Usually in such situations, anxiety is not justified.
The presence of the disease can be judged by a large jump in the level of neutrophils in a child after one year. A higher than usual number of granulocytes indicates the development of neutrophilia in the baby.
The causes of this disease are as follows:
- Malignant blood diseases.
- Trophic ulcers.
- Vaccinations.
- Otitis, pneumonia, tonsillitis, sepsis, occurring in acute form.
- Diabetes.
- Purulent tissue inflammation.
Inflammatory processes are directly related to the level of neutrophils in the blood: the higher it is, the stronger the inflammation. To alleviate the condition, it is necessary to immediately identify the cause of the disease and prescribe appropriate therapy.
Decreased neutrophil values in peripheral blood
A decrease in the level of neutrophils indicates a deterioration in the condition of the child’s immune system. This occurs due to insufficient production of blood cells, their rapid destruction or their incorrect distribution. The resulting clinical and laboratory syndrome is called neutropenia.
The reasons for the development of this pathology are as follows:
- Bone marrow disorders.
- Leukemia in acute form.
- Dramatic weight loss.
- Fungal disease.
- ARVI, hepatitis and other viral diseases.
- Intoxication.
- Irradiation.
- History of anaphylactic shock.
- Side effects of taking certain medications.
There is no reason for concern if, despite the low level of neutrophils, the baby under the age of one year feels well. Blood cell levels return to normal when the child reaches three years of age.
The most common causes of increased neutrophil levels in the blood
Band shift
There is such a thing as a shift of the leukocyte formula to the left. This means that the ratio between mature and young forms of neutrophil leukocytes changes towards an increase in the level of the latter.
The shift can be of varying degrees. The result of the analysis will depend on the increase in which forms the shift occurs: stab, juvenile, and so on.
The condition when neutrophils are increased in the blood of a child and an adult is called neutrophilosis.
Band neutrophils may be elevated in the following cases:
- infectious process in the body. Due to the lack of neutrophils, signals are sent to the bone marrow, where cell maturation occurs, to produce new “fighters”. Therefore, not fully matured cells enter the bloodstream;
- blood loss stimulates the bone marrow to synthesize all blood cells, not just leukocytes;
- after intense physical activity and stress;
- after operation;
- pregnancy.
Still, the main reason for the high number of these types of leukocytes is the inflammatory process, which they intensively fight.
With malignant pathologies, almost all forms of neutrophil maturation, including blast cells, can appear in the blood.
High level of segmented neutrophils
Segmented neutrophils are mature cells.
An increase in their number in the blood will be called a shift in the leukocyte formula to the right. There are a number of conditions when segmented neutrophils are elevated in the blood of children and adults. These include:
- deficiency of vitamins necessary for the maturation of new cells, for example, vitamin B12 and folic acid;
- increased background radiation in the surrounding area;
- lung diseases;
- liver pathology;
- kidney diseases;
- recent blood transfusion.
Increased neutrophils during pregnancy
An increase in the number of this type of white blood cells during pregnancy is considered normal. Since at this time everything in the body of the expectant mother is rebuilt and changes.
In response to the appearance of a half genetically foreign child in the body, the synthesis of leukocytes is stimulated. Therefore, their level can be increased. Next, there is constant monitoring of various indicators in a pregnant woman in order to notice deviations in time and have time to influence them.
During pregnancy, the mother's immune system decreases slightly, making the body more susceptible to various infections. An increased number of protective cells helps to avoid serious complications.
Principles of treatment
Neutrophilia is not an independent pathology, so there is no treatment for an increased number of cells.
First of all, the pediatrician determines what caused the deviation and prescribes a repeat examination. Often the main reason is non-compliance with the rules when donating blood. For example, the mother did not follow up, and the child ate before the analysis.
Also, if children have suffered an emotional shock before donating blood or are intensely preparing for sports competitions, there is no need to worry about the test result. Most likely, this is the factor that influenced the active production of neutrophils by the bone marrow. However, re-analysis is mandatory. In other cases, treatment methods depend directly on the disease:
- for diseases of an infectious nature, accompanied by high body temperature and purulent discharge, antibiotics are prescribed;
- for viruses - antiviral agents and measures aimed at increasing immunity;
- if the growth of neutrophils is affected by the baby’s unbalanced diet, menu correction is necessary, as well as taking vitamin complexes;
- for fungi - antimycotic medications;
- for bone marrow pathologies - drugs that inhibit the excessive production of these cells;
- if the cause is the use of certain medications, the course of treatment changes;
- in case of infarction of the brain, myocardium, lungs or kidneys - resuscitation measures.