With atherosclerosis, the issue of nutrition is acute: what can you eat without harm to your well-being if there is a metabolic disorder in the body. There is no cholesterol in vegetable oil because it is contained in animal products; they contain fats with “harmful” lipids that settle in the form of atherosclerotic plaques. Experts clarify that consuming plant products does not pose any danger and you can eat them without fear - they do not increase cholesterol.
Studies have shown that with regular consumption of olive fat, the concentration of low-density cholesterol decreases due to an increase in the content of substances that destroy cholesterol plaques.
Vegetable oil production technology
Sunflower oil is produced at oil extraction plants. First of all, the sunflower seeds are cleaned, the kernels are separated from the husk. After this, the kernels are passed through rollers, crushed and sent to the pressing department.
When the resulting mint has undergone heat treatment in roasters, it is sent for pressing, where the vegetable oil is squeezed out.
The resulting sunflower oil is infused, and the remaining mint, which contains more than 22 percent of the oil, is sent to the extractor for processing.
The extractor, using special organic solvents, distills off the remaining oil, which is then sent for cleaning and refining. Refining uses the method of centrifugation, sedimentation, filtration, hydration, bleaching, freezing and deodorization.
What's the benefit?
Vegetable oil is a very nutritious product
Vegetable oil is a beneficial substance. It contains many elements necessary for the normal functioning of the body. The benefits of the product are as follows:
- Prevention of vitamin D deficiency in children.
- Skin healing.
- Using the product helps improve the body's immune defense.
- Reduces the risk of cancer.
- Reduces cholesterol.
- Improves the function of the cardiovascular system (cardiovascular system).
- Increases brain activity.
All types of vegetable oils have these beneficial properties.
What does sunflower oil contain?
Vegetable oil contains a huge amount of valuable organic substances, including palmitic, stearic, arachidic, myristic, linoleic, oleic, and linolenic acid. This product is also rich in phosphorus-containing substances and tocopherols.
The main components found in sunflower oil are:
- Fats of vegetable origin, which are better absorbed by the body than fats of animal origin.
- Fatty acids that the body requires for the full functioning of cellular tissues and the harmonious functioning of the nervous system.
- Vitamin A has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the visual system and strengthens the immune system. Vitamin D helps maintain skin and bone tissue in good condition.
- Vitamin E is an essential antioxidant that protects the body from the possible development of cancer and slows down the aging process. Sunflower oil contains a significant amount of tocopherol, compared to other vegetable oils, which has a similar beneficial effect on the body.
Ingredients and usefulness
Vegetable oils have a rich composition that has nutritional value:
- vitamins A, B. D, E;
- phytosterols;
- vegetable saturated, polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fats.
Products obtained from plants are divided according to processing methods, as shown in the table:
| Processing stages | Impact | Advantages | Shelf life |
| Cold pressed | Squeeze out the finished olein using a press | Maximum number of nutrients | Limited |
| Extradition | Extract oil using solvents | Increases the amount of olein | |
| Filtration | Filter crude olein | Cleaning the finished product | |
| Hydrogenation | Treated with hot water | Unrefined oil, less nutrients | Up to 2 months |
| Refining | The product is boiled and passed through filters | Least useful substances | Over 4 months |
The human immune system will work better because the product contains vitamin A.
Plant oleins from seeds are strong antioxidants that slow down the aging process. Thanks to the presence of vitamin A, the immune system and visual organs are strengthened. Fatty acids help the central nervous system function normally and restore tissue at the cellular level. Vitamin complexes normalize the structure of all bones and epidermis. With a high fat content, vegetable oil is cholesterol-free, which means it is not capable of harming atherosclerosis.
Cholesterol and sunflower oil
Does sunflower oil contain cholesterol? This question is asked by many consumers who strive to maintain a healthy diet and eat only healthy foods. In turn, many will be pleasantly surprised to learn that vegetable oil does not contain cholesterol at all.
The fact is that the presence of numerous advertising and attractive labels in order to increase demand for the product has created a myth that some types of vegetable oils may contain cholesterol, while the products offered on the shelves are completely healthy.
In fact, cholesterol cannot be contained in either sunflower or any other vegetable oil. Even a freshly squeezed product does not contain this harmful substance, since the oil is a vegetable product.
Cholesterol can only be found in fats of animal origin. For this reason, all the labels on the packages are just a common advertising gimmick; it is good for the buyer to know which products are high in cholesterol in order to understand exactly what he is buying.
Meanwhile, in addition to the fact that the product does not contain cholesterol, it also does not contain Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, which have an effect on lowering cholesterol in the blood and protecting the heart muscles from damage.
However, the fact that sunflower oil does not contain cholesterol completely compensates for the lack of nutrients.
Thus, sunflower oil is an excellent and only alternative to butter for people suffering from atherosclerosis or hypercholesterolemia.
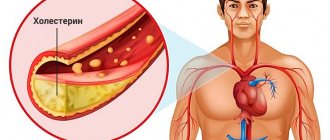
Formation of atherosclerosis by cholesterol
Atherosclerosis is a multifactorial disease of the cardiovascular system with predominant damage to medium and large arteries.
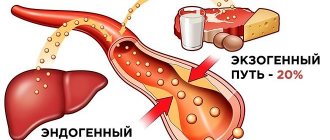
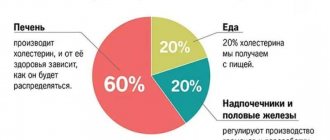
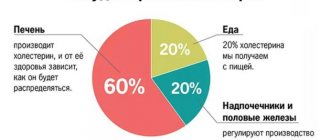
Cholesterol is secreted from the liver with bile in the composition of bile acids, which are 70–90% absorbed in the small intestine and enter the liver, where cholesterol is synthesized from them again. Thus, cholesterol metabolism is a finely regulated system. Excess intake of cholesterol from food is compensated by a decrease in absorption in the intestine, as well as a decrease in synthesis in the liver. If the amount of cholesterol in food decreases, the reverse process occurs - its synthesis in the liver increases and absorption in the small intestine increases. Therefore, the level of cholesterol in the blood is a stable indicator until a failure occurs - a violation of these processes
High-density lipoproteins (HDL) prevent the deposition of cholesterol in blood vessels, and even remove already deposited cholesterol from the vessel wall, sending it for further utilization in the liver. These lipoproteins prevent the formation of atherosclerosis. Low-density lipoproteins (LDL) and very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL) contribute to the formation of atherosclerosis.
Thus, the higher the content of LDL and VLDL, the higher the risk of developing atherosclerosis. The higher the HDL level, the better.
The atherogenicity index (the risk of developing atherosclerosis) can be calculated using the formula: K = Total cholesterol - HDL / HDL, where Total cholesterol is the total cholesterol content in the blood plasma. HDL is the content of high-density lipoproteins in blood plasma. Normal: K = 3-3.5.
The lower this ratio, the better. Standard indicators of lipoproteins in blood plasma are presented in the table. According to European data, LDL should be less than 3.0 mmol/l (Wood D. Et al. Eur. Heart J., 1998).
So why does the failure occur, why does the cholesterol metabolism occur? These mechanisms are very complex and not fully understood. It is known that among a number of peoples of the Far North, where the main foods are venison and fish, atherosclerosis is rare. And at the same time, vegetarians can have high levels of cholesterol and LDL in the blood! Increased cholesterol levels may be due to hereditary factors: heterozygous or homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. However, many scientific data prove that high levels of cholesterol and LDL, among others, are not always an absolutely reliable sign of the development of atherosclerosis. It is also interesting that there is a certain mosaic pattern of vascular lesions, i.e. plaques form in certain areas. A reasonable question arises: why does atherosclerosis form here, and not elsewhere in the vessel?
As already mentioned, atherosclerosis is a multifactorial disease. Significantly in the formation of a plaque in a certain place of the vessel, damage to the wall of the vessel itself contributes. Risk factors for the development of vascular damage and the development of atherosclerosis are as follows:
- Hypercholesterolemia and dyslipidemia.
- Smoking.
- High blood pressure.
- Stress.
- Diabetes.
- Decreased physical activity.
- Age and gender.
These and other risk factors lead to damage to the integrity of the vascular wall, where lipoproteins, fibrin, platelets, and calcium are deposited, which forms an atherosclerotic plaque.
In people who smoke, atherosclerosis develops 2-3 times faster than in non-smokers. Smokers also experience an increase in affected blood vessels.
An increase in blood pressure increases the risk of coronary heart disease by more than 3 times at any level of cholesterol in the blood plasma. In a random selection of Muscovite men aged 40-59 years over 6 years, the percentage of deaths from diseases associated with atherosclerosis was 5 times greater with a combination of dyslipoproteinemia and arterial hypertension than with the presence of one of these factors (Oganov R.G., Zhukovsky G. .S., 1987). More than one million people die in the world from cardiovascular diseases, of which almost half a million from coronary heart disease and 300,000 from cerebral vascular pathology - strokes, etc. (Kukarchuk V.V., 2006). The basis of these diseases is atherosclerotic damage to the arteries of the myocardium and brain. In Russia, mortality from coronary heart disease is one of the first places. The maximum incidence of the disease occurs at the age of 40-50 years (Parfenov A.S., 2006). Hypertension in Russia affects 39.9% of men and 41.1% of women (Kotov S.V., 2006).
Emotional stress leads to neurohumoral changes that increase vascular permeability and facilitate their infiltration of lipids.
However, cerebrovascular accidents are also observed in children. In the structure of childhood neurological pathology, they range from 3-5% to 8 - 10% (Badalyan L.O., 1984; Troshin V.M., 1996; Banker Q., 1992). And children also have strokes. Yes, yes, exactly strokes! In 83% of cases, ischemic strokes in children are caused by congenital vascular anomalies.
The incidence of stroke in children: Canada, Great Britain, France and the USA ranges from 2 to 13 per 100,000 children per year (DeVeber G., 2005; Giroud M. et al., 1995; Kirham F., Hogan A., 2004 ; Lanthier S. et al., 2000, Lynch J., 2004). Research conducted in the Southern Administrative District of Moscow in the period from 1997 to 2004 revealed the prevalence of cerebral stroke in children - 6.94 cases per 100,000 children per year (Zykov V.P., Cherkasov V.G. et al., 2005) .
The risk factor by gender and age seems interesting. The fact is that atherosclerotic changes in the vascular system begin already in childhood! So, according to A.M. Wichert et al. (1981) fibrous plaques in the left descending cardiac artery are observed at the age of 10-19 years in 17.8% of cases, 20-29 years - 45.7%, 30-39 years - 78.6%, 40-49 years - 93 % of cases! Coronary heart disease (CHD) is 3-4 times less common in women under 50 years of age than in men, however, after menopause this ratio gradually levels out. And after 60 years, the ratio of cases of heart attacks and strokes in men and women becomes equal.
However, the most important factor in the development of atherosclerosis is hypercholinesteremia, which is confirmed by the detection of atherosclerosis in children with hereditary hypercholinesteremia! After all, children have no other risk factors. They do not smoke, are active, there is no high blood pressure, excess body weight and diabetes, except for increased cholesterol concentrations. Yes, yes, dear readers. Atherosclerosis occurs in children. And atherosclerosis is steadily getting younger. Interestingly, in addition to familial hypercholesterolemia, the detection of increased cholesterol in children is observed in a number of other hereditary diseases. For example, with Williams syndrome. With this syndrome, a child from birth has an increased level of cholesterol in the blood, which goes away on its own by the age of 2 years.
Sunflower oil and its health benefits
In general, sunflower oil is a very healthy product, which contains many substances necessary for life.
- Sunflower vegetable oil is an excellent remedy for the prevention of rickets in children, as well as skin diseases in adults.
- The product has a beneficial effect on the immune system, strengthening it and reducing the risk of developing cancer.
- Due to the fact that sunflower oil does not contain cholesterol, it allows you to reduce the amount of this substance in your daily diet.
- The substances contained in vegetable oil improve the functionality of brain cells and the cardiovascular system.
However, it is important to consider that all these beneficial properties are available in a product that has undergone minimal processing. Such oil will smell like seeds and smoke when used during cooking.
The same products that are usually sold in stores in a refined and deodorized form contain only fat with a minimal amount of vitamins, and such oil has practically no odor. Accordingly, a product that has undergone complete processing not only has no beneficial properties, but can also cause harm to the body.
The benefits and harms of different types of vegetable oils
The benefits of any product are assessed by the ratio of substances necessary for the body and harmful. From this point of view, almost all vegetable oils are healthy: they contain few saturated fatty acids and many unsaturated and polyunsaturated ones. The exceptions are coconut and palm, and cholesterol has nothing to do with it: they are overloaded with saturated fats.
Sunflower, corn and olive oils are the main suppliers of polyunsaturated and unsaturated acids, since the taste allows them to be added to dishes in sufficient quantities. Their regular use helps improve brain function, normalize intestinal motility, strengthen the heart muscle and vascular walls, cleanse the skin, and get rid of bad cholesterol. Their role has also been proven in accelerating metabolism, preventing osteoporosis, improving visual acuity and coordination of movements. And with proper use of olive oil, the risk of developing breast cancer is also reduced.
Mustard oil, although not actually bitter, has a noticeable antiseptic and bactericidal effect. Sesame, in addition to unsaturated fat, contains phosphorus and calcium - the main microelements of bone tissue. Soybean and rapeseed (canola) are leaders in the fight against high cholesterol. The medicinal properties of sea buckthorn and flaxseed oils are more used in the manufacture of topical medicines for dermatological and gastroenterological patients.
Nut oils have a specific taste and are used in small quantities, although their qualities are not inferior to other vegetable fats. They lower cholesterol levels and also thin the blood, preventing thrombosis.
Sunflower oil and its harm
This product may be harmful if completely processed in a factory. The fact is that when heated, some components can turn into carcinogens hazardous to health. For this reason, nutritionists do not recommend frequently eating fried foods.
After the oil boils, a huge amount of harmful substances are formed in it, which can cause the development of cancerous tumors if you regularly eat a dangerous product. Especially if high cholesterol is observed during pregnancy, in this case, it is generally necessary to reconsider your attitude to nutrition.
Greater harm can be caused by a product repeatedly heated in the same frying pan using the same portion of oil. It is also important to know that after certain processing, foreign chemical substances may accumulate in the oil. Therefore, processed sunflower oil does not need to be used when preparing salads.
Recommendations for correct use
Thus, to obtain the positive effects of vegetable fats, you need to follow these simple rules:
- do not fry food in the same portion of oil more than once,
- set a moderate temperature when cooking,
- normalize the presence of vegetable oil in the menu in order to regulate the calorie content of food.
The most useful option for use is to use vegetable oils in the form of salad dressing or on an empty stomach (preferably in the morning). In this case, the body receives the necessary vitamins and other useful components. The main thing is not to use sunflower oil with cholesterol, that is, together with animal fats. It is better to consume vegetable fats only with vegetables.
Recommendations for the proper use of vegetable fats:
- Check the expiration date of the oil, as oxides accumulated in the product can cause serious metabolic disorders.
- Do not neglect storage rules: refined oil should not come into contact with water. The unrefined product should be stored in a dark container at temperatures up to plus 20 °C. Cold pressed oil is good for up to 5 months, hot pressed oil is good for up to a year. An open container should be used within a month.
Despite the significant benefits of vegetable fats for the body, consuming only one of its types is ineffective. A combination of corn, mustard, sunflower and other oils in equal proportions will help the body receive various types of beneficial microelements.
How to eat sunflower oil correctly
Sunflower oil has no special health contraindications. The main thing is that it should be eaten in limited quantities, since 100 grams of the product contains 900 kilocalories, which is much higher than butter.
- It is not recommended to use vegetable oil to cleanse the body, as this method can provoke the development of acute diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- It is also important to use this product only before the expiration date stated on the package. Over time, sunflower oil becomes harmful due to the accumulation of oxides in it, which disrupt the metabolism in the body.
- This product should be stored at a temperature of 5 to 20 degrees, and contact with water or metal should not be allowed. The oil should always be kept in a dark place, since sunlight destroys many beneficial substances.
- Natural unrefined oil should be stored in a glass container, in the dark and cold. A refrigerator is a great place for storage. At the same time, oil obtained by cold pressing is stored for no more than 4 months, and with hot pressing - no more than 10 months. Once the bottle is opened, you need to use it up within a month.
Cholesterol content in plant foods
Table of the percentage of cholesterol (cholesterol) in products from the category - products of plant origin.
| Product | Content |
| Chocolate cupcake with chocolate icing | 22.00 mg |
| Pancakes | 12.00 mg |
| Mashed potatoes with milk and butter, prepared | 11.00 mg |
| Yogurt | 10.00 mg |
| Iris | 9.00 mg |
| Caramel | 7.00 mg |
| Red beans (Kidney) sprouted fresh | 0.00 mg |
| Almond oil | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh almonds | 0.00 mg |
| Boiled variegated beans (Pinto) | 0.00 mg |
| Roasted almonds | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh sprouted variegated beans (Pinto) | 0.00 mg |
| Boiled pink beans | 0.00 mg |
| Boiled black beans | 0.00 mg |
| Dried goji berries | 0.00 mg |
| Boiled black-eyed beans | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh blueberries | 0.00 mg |
| Carrots raw (fresh) | 0.00 mg |
| Boiled carrots | 0.00 mg |
| Onion rings | 0.00 mg |
| Raw seaweed | 0.00 mg |
| Boiled pigeon peas | 0.00 mg |
| Peas boiled in water (ripe) | 0.00 mg |
| Feijoa fresh | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh green peas | 0.00 mg |
| Fennel, raw (fruit or root) | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh sprouted peas | 0.00 mg |
| Nutmeg spice, ground | 0.00 mg |
| Fennel seeds | 0.00 mg |
| Canned green peas | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh medlar | 0.00 mg |
| Physalis fresh | 0.00 mg |
| Table mustard, paste | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh mint | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh vegetable physalis | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh peppermint | 0.00 mg |
| Jujube (Chinese date) fresh | 0.00 mg |
| Mustard seeds ground mustard | 0.00 mg |
| Dates Deglet nur | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh pomegranate | 0.00 mg |
| Canned pomegranate juice | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh pistachios | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh grapefruit | 0.00 mg |
| Roasted pistachios (no salt) | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh grapefruit juice | 0.00 mg |
| Walnut | 0.00 mg |
| Nori seaweed, raw | 0.00 mg |
| Hazelnut oil | 0.00 mg |
| Walnut oil | 0.00 mg |
| Dry chickpeas | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh hazelnuts | 0.00 mg |
| Buckwheat boiled in water (buckwheat porridge) | 0.00 mg |
| Boiled chickpeas | 0.00 mg |
| Roasted hazelnuts | 0.00 mg |
| Dry green buckwheat | 0.00 mg |
| Oat oil | 0.00 mg |
| Buckwheat flour | 0.00 mg |
| Oat flour | 0.00 mg |
| Wood mushroom raw | 0.00 mg |
| Unheated oat bran | 0.00 mg |
| Shiitake mushrooms, cooked | 0.00 mg |
| Raw oyster mushrooms | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh breadfruit | 0.00 mg |
| Maitake mushrooms raw | 0.00 mg |
| Cottonseed oil | 0.00 mg |
| Fried portobello mushrooms | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh cucumbers | 0.00 mg |
| Horseradish, ready to eat | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh dandelion leaves | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh persimmon | 0.00 mg |
| Enoki mushrooms raw | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh black persimmon (sapota) | 0.00 mg |
| Chicory root, raw | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh pear | 0.00 mg |
| Instant chicory (ready-made coffee) | 0.00 mg |
| Canned pear juice (nectar) | 0.00 mg |
| Canned olives | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh chicory leaves | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh guava | 0.00 mg |
| Olive oil | 0.00 mg |
| Ground savory | 0.00 mg |
| Reveler seeds | 0.00 mg |
| Canned green olives | 0.00 mg |
| Chayote raw | 0.00 mg |
| Prickly pear (fruit) fresh | 0.00 mg |
| Oregano oregano, dried | 0.00 mg |
| Green tea without sugar, prepared | 0.00 mg |
| Butternut | 0.00 mg |
| Green tea with sugar (prepared) | 0.00 mg |
| Black tea without sugar, prepared | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh daikon | 0.00 mg |
| Black tea with sugar and lemon (prepared) | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh jambolan | 0.00 mg |
| Fenugreek seeds | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh jackfruit | 0.00 mg |
| Cherimoya fresh | 0.00 mg |
| Gin 45 degrees alcohol | 0.00 mg |
| Palm oil | 0.00 mg |
| Black Walnut | 0.00 mg |
| Durian fresh | 0.00 mg |
| Canned heart of palm | 0.00 mg |
| Raw garlic | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh melon | 0.00 mg |
| Papaya juice (nectar) canned | 0.00 mg |
| Lentils boiled in water | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh cantaloupe melon | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh papaya | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh sprouted lentils | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh blackberries | 0.00 mg |
| Fern (shoots) raw | 0.00 mg |
| Chia seeds | 0.00 mg |
| Canned blackberry juice | 0.00 mg |
| Parsnip root raw | 0.00 mg |
| Ground sage | 0.00 mg |
| Cooked squash | 0.00 mg |
| Raw champignons | 0.00 mg |
| Raw beetroot | 0.00 mg |
| Pecan | 0.00 mg |
| Fried champignons | 0.00 mg |
| Brown raw champignons | 0.00 mg |
| Ground allspice | 0.00 mg |
| Saffron spice | 0.00 mg |
| Jeera cumin seeds | 0.00 mg |
| Green bell pepper, fresh | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh mulberries | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh red bell pepper | 0.00 mg |
| Seedless raisins | 0.00 mg |
| Ground black pepper | 0.00 mg |
| Ginger extract powder | 0.00 mg |
| Red hot fresh chili pepper | 0.00 mg |
| Raw ginger root | 0.00 mg |
| Ground dry chili pepper | 0.00 mg |
| Hot chili peppers dried in the sun | 0.00 mg |
| Canned peach juice (nectar) | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh peach, pitted | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh parsley | 0.00 mg |
| Walnut drank | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh Suriname cherries | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh figs | 0.00 mg |
| Sunflower oil | 0.00 mg |
| Sunflower flour | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh spinach | 0.00 mg |
| Sunflower seeds, peeled | 0.00 mg |
| Boiled spinach | 0.00 mg |
| Roasted sunflower seeds (hulled) | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh sorrel | 0.00 mg |
| Fried or baked zucchini (without oil) | 0.00 mg |
| Halva | 0.00 mg |
| Cacao butter | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh pomelo | 0.00 mg |
| Escarole cooked | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh tomatoes | 0.00 mg |
| Cooked tomatoes | 0.00 mg |
| Dried tarragon | 0.00 mg |
| Canola oil | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh purslane | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh apples | 0.00 mg |
| Pickled capers | 0.00 mg |
| Bulgur boiled in water (porridge) | 0.00 mg |
| Canned apple juice | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh Brussels sprouts | 0.00 mg |
| Wheat germ oil | 0.00 mg |
| Java apple fresh | 0.00 mg |
| Boiled Brussels sprouts | 0.00 mg |
| All-purpose wheat flour | 0.00 mg |
| Yams cooked | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh cabbage, white cabbage | 0.00 mg |
| Whole grain flour (wheat) | 0.00 mg |
| Barley flour | 0.00 mg |
| Boiled cabbage (white cabbage) | 0.00 mg |
| Unheated wheat bran | 0.00 mg |
| Malted barley flour | 0.00 mg |
| Sauerkraut (kimchi) | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh sprouted wheat | 0.00 mg |
| Barley boiled in water (barley porridge) | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh red cabbage | 0.00 mg |
| White wheat bread | 0.00 mg |
| Raw curly cabbage | 0.00 mg |
| Sprouted wheat bread | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh kale | 0.00 mg |
| Cooked cabbage (boiled) | 0.00 mg |
| Wheat bran bread | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh Chinese cabbage | 0.00 mg |
| Whole grain wheat bread | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh savoy cabbage | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh cauliflower | 0.00 mg |
| Millet boiled in water | 0.00 mg |
| Boiled cauliflower | 0.00 mg |
| Radicchio fresh | 0.00 mg |
| Rambutan canned | 0.00 mg |
| Cardamom | 0.00 mg |
| Rhubarb stem raw | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh carissa fruits | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh radish | 0.00 mg |
| Shea butter (karite) | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh turnip tops | 0.00 mg |
| Turnips raw | 0.00 mg |
| Boiled potatoes | 0.00 mg |
| Cooked turnips | 0.00 mg |
| Baked potatoes | 0.00 mg |
| Rice bran oil | 0.00 mg |
| Raw potatoes | 0.00 mg |
| Brown rice flour | 0.00 mg |
| French fries | 0.00 mg |
| Rice flour | 0.00 mg |
| Unheated rice bran | 0.00 mg |
| Potato starch | 0.00 mg |
| Boiled long grain rice | 0.00 mg |
| Chestnut, peeled, fresh | 0.00 mg |
| Steamed boiled rice | 0.00 mg |
| Pine nut without shell | 0.00 mg |
| Boiled round grain rice | 0.00 mg |
| Boiled rice (in water) | 0.00 mg |
| Dried openwork chervil | 0.00 mg |
| Boiled long grain brown rice | 0.00 mg |
| Boiled brown rice | 0.00 mg |
| Cashew raw | 0.00 mg |
| Boiled wild rice | 0.00 mg |
| Roasted cashews | 0.00 mg |
| Boiled glutinous (sticky) rice | 0.00 mg |
| Rice bran bread | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh kiwi | 0.00 mg |
| Rye flour | 0.00 mg |
| Rye bread | 0.00 mg |
| Cilantro (coriander leaves) fresh | 0.00 mg |
| Rye bread | 0.00 mg |
| Quinoa boiled in water | 0.00 mg |
| Hibiscus flower, fresh | 0.00 mg |
| Fireweed (fireweed leaves) fresh | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh rosemary | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh strawberries | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh cranberries | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh arugula | 0.00 mg |
| Cranberry juice without sugar | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh iceberg lettuce | 0.00 mg |
| Salsify (salf's root) raw | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh head lettuce | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh coconut water | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh lettuce | 0.00 mg |
| Unsweetened coconut flakes | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh red lettuce | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh coconut milk | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh Roman salad | 0.00 mg |
| Coconut oil | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh endive | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh coconut meat | 0.00 mg |
| Sapodilla fruits fresh | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh kohlrabi | 0.00 mg |
| Aspartame sugar substitute | 0.00 mg |
| Boiled kohlrabi (cabbage) | 0.00 mg |
| Stevia (sweetener) sugar substitute | 0.00 mg |
| Hemp seed | 0.00 mg |
| Saccharin sugar substitute | 0.00 mg |
| Coriander seeds | 0.00 mg |
| Sucralose sugar substitute | 0.00 mg |
| Fructose sugar substitute | 0.00 mg |
| Cinnamon powder | 0.00 mg |
| Agave syrup sugar substitute, sweetener | 0.00 mg |
| Brown sugar | 0.00 mg |
| Granulated sugar | 0.00 mg |
| Sugar apple fresh | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh beet tops | 0.00 mg |
| Raw beets | 0.00 mg |
| Boiled beets | 0.00 mg |
| Prepared instant coffee | 0.00 mg |
| Brewed coffee beans | 0.00 mg |
| Ready-made espresso coffee | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh watercress | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh gooseberries | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh celery | 0.00 mg |
| Dry corn kernels | 0.00 mg |
| Celery seeds | 0.00 mg |
| Corn starch | 0.00 mg |
| Raw corn | 0.00 mg |
| Boiled corn | 0.00 mg |
| Canned corn | 0.00 mg |
| Corn oil | 0.00 mg |
| White corn flour (masa) | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh plum | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh apricot | 0.00 mg |
| Corn flour | 0.00 mg |
| Prunes | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh Antillean apricot | 0.00 mg |
| Yellow whole grain corn flour | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh soursop | 0.00 mg |
| Apricot oil | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh kumquat | 0.00 mg |
| Canned soursop juice (nectar) | 0.00 mg |
| Canned apricot juice (nectar) | 0.00 mg |
| Unroasted sesame | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh red or white currants | 0.00 mg |
| Avocado fresh | 0.00 mg |
| Roasted sesame | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh black currant | 0.00 mg |
| Sesame oil | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh quince | 0.00 mg |
| Sesame flour | 0.00 mg |
| Dried apricots | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh amaranth leaves | 0.00 mg |
| Raw asparagus | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh pineapple | 0.00 mg |
| Boiled asparagus | 0.00 mg |
| Anise seeds | 0.00 mg |
| Spirulina raw | 0.00 mg |
| Starfruit (starfruit) fresh | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh oranges | 0.00 mg |
| Canned orange juice | 0.00 mg |
| Peanuts raw | 0.00 mg |
| Roasted peanuts | 0.00 mg |
| Peanut butter | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh watermelon | 0.00 mg |
| Arrowroot flour | 0.00 mg |
| Boiled artichokes | 0.00 mg |
| Boiled Spanish artichokes | 0.00 mg |
| Turmeric spice powder | 0.00 mg |
| Babassu oil | 0.00 mg |
| Couscous boiled in water | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh basil | 0.00 mg |
| Cooked eggplant | 0.00 mg |
| Bay leaf | 0.00 mg |
| Boiled bamboo shoots | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh lime | 0.00 mg |
| Dry soy tofu cheese | 0.00 mg |
| Raw okra | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh lime juice | 0.00 mg |
| Hard tofu cheese (linen) | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh bananas | 0.00 mg |
| Raw milkweed shoots | 0.00 mg |
| Fermented tofu cheese (fuyu) | 0.00 mg |
| Dried bananas | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh plantains | 0.00 mg |
| Raw sweet potato | 0.00 mg |
| Boiled butterbur | 0.00 mg |
| Quinoa fresh | 0.00 mg |
| Flaxseed oil | 0.00 mg |
| Flaxseed | 0.00 mg |
| Boiled beans (ripe) | 0.00 mg |
| Boiled green beans | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh green beans | 0.00 mg |
| Soybean oil | 0.00 mg |
| Soybean cake | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh lemon, without peel | 0.00 mg |
| Soy protein powder | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh lemon juice | 0.00 mg |
| Soy Protein (Isolate) Powder | 0.00 mg |
| Fresh lychees | 0.00 mg |
| Soy protein (concentrate) powder | 0.00 mg |
| Soy sauce (hydrolyzed) | 0.00 mg |
| Frozen logan berry | 0.00 mg |
| Soy sauce (tamari) | 0.00 mg |
A short excursion into history
The plant was brought to Russia almost three hundred years ago, but for a long time it was grown exclusively for decorative purposes.
purpose. Luxurious yellow flowers, always directed towards the sun, enlivened not only palace flower beds and landowners' estates.
For decades, sunflower conquered the space of the Russian Empire. The North Caucasus, Kuban, and Volga region welcomed it into their open spaces. In Ukraine, where the “sun” settled near every hut, peasant women and merchant women not only enjoyed its flowering, but a new entertainment – “clicking seeds” – diversified their holidays on the zavalinka.
While Europe continued to admire sunflowers, which inspired Vincent van Gogh to create an amazing series of paintings of the same name, in Russia they came up with a more practical use for them. Serf peasant Daniil Bokarev invented a method for obtaining oil from sunflower seeds. And soon the first oil mill appeared on the territory of what is now the Belgorod region.
The widespread use of sunflower oil in the mid-19th century was facilitated by the fact that the Orthodox Church recognized it as a Lenten product. This second name even stuck – vegetable oil. Sunflower crops in Russia at the beginning of the last century occupied an area of about a million hectares. Vegetable oil became a national product and began to be exported.