The concentration of cholesterol (in chemistry - cholesterol) in the blood is one of the key markers of the state of lipid (fat) metabolism in the body. In clinical hematology, analysis of HDL and LDL cholesterol is performed using a colorimetric, photometric or electrophoretic method.
The study is called a lipidogram, otherwise the lipid profile (status) of the patient. If prescribed by a doctor, indicators of cholesterol metabolism can be included in a detailed biochemical analysis of venous blood.
What are HDL and LDL in cholesterol metabolism?
Cholesterol refers to fat-containing alcohols. The substance is concentrated in cell membranes and serves to protect cells. The body needs cholesterol as a participant in the most important processes that support life:
- hormonal synthesis (steroid and sex hormones);
- production of bile acids;
- absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, E, D);
- maintaining pregnancy;
- interaction between the spinal cord and brain.
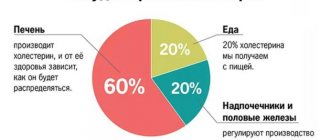
Cholesterol is divided into two types: exogenous, entering the body with animal fats (butter, meat, milk, etc.); endogenous, produced by liver cells (hepatocytes) inside the body.
Reference: The share of exogenous cholesterol is 20% of the total amount.
Cholesterol, like fat, cannot move through the bloodstream on its own. Once in the blood, its molecules combine with apoprotein proteins and other lipids (triglycerides, phospholipids), forming courier lipoproteins of different densities. The less protein there is in lipoproteins, the lower their density.
20% of cholesterol enters the body with food, and 80% is produced by liver cells
Triglycerides (TG or TG) are formed from fatty foods and are stored in fatty tissues. Essentially, this is the body's lipid reserves, used to replenish energy. Phospholipids are a special type of fat that is not synthesized by the body; they consist of fatty acids, polyhydric alcohols and phosphoric acid and are necessary for the construction of cell membranes.
Types of lipoproteins
Five main types of lipoproteins are involved in cholesterol metabolism.
Accepted classification of lipoproteins and main functions
| Full title | Function | Abbreviation | The average size | |
| Latin | Russian | |||
| low density lipoproteins | transport endogenous cholesterol from the liver to peripheral tissues and cells of the body | LDL | LDL | 18-26 nm |
| very low density lipoproteins | VLDL | VLDL | 30-80 nm | |
| lipoproteins of average (otherwise, intermediate) density | BOB | 25-35 nm | ||
| high density lipoproteins | collects excess LDL and VLDL and delivers them to the liver for excretion | HDL | HDL | 8-11 nm |
| chylomicrons | transport exogenous cholesterol from the intestines to the liver and body tissues | HM | 75-1200 nm | |
LDL and VLDL are positioned as “bad” cholesterol. When moving through arteries and capillaries, they “cling” to microdamages in the intima (the inner layer of the vascular wall) and settle.
A cholesterol stain forms inside the vessel, on the basis of which a cholesterol plaque is subsequently formed, which becomes the cause of atherosclerosis. HDL is called “good” cholesterol because it escorts low-density and very low-density lipoproteins out of blood vessels, preventing them from sticking to the intima.
Components of lipoproteins in percentage
The table shows that chylomicrons and low-density lipoproteins contain the most fat (triglycerides).
Where do they come from?
“Bad” cholesterol is formed in the liver. As they form, they combine with protein and enter the bloodstream, moving throughout the human body to various tissues.
LDL appears as a result of the metabolism of very low and intermediate density lipoproteins.
Lipid profile parameters
The laboratory measurement value for total cholesterol and its fractions is mmol/l. Indicators included in the lipid profile:
Normal blood cholesterol levels
- OX (Cho);
- HDL;
- LDL;
- VLDL;
- HM;
- TG;
- KA (IA).
TC – total cholesterol level. KA – coefficient (otherwise, index) of atherogenicity. When assessed by electrophoretic method, fractions are divided:
- alpha lipoproteins or HDL;
- beta lipoproteins – LDL;
- prebeta lipoproteins – VLDL.
The CA value is a laboratory marker that reflects the degree of danger of atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels. It is calculated using the formulas: KA = (LDL + VLDL) / HDL or IA = (Cho – HDL) / HDL.
Drug-induced LDL-lowering
Therapy for elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein is prescribed by a general practitioner after a medical examination based on the results obtained. If necessary, taking into account the cause of the pathological condition, a consultation with a cardiologist may be necessary.
Therapy involves the use of the following medications:
| Group of drugs | Name | Application |
| Statins | Lovastatin, Atorvastatin | The medications increase the production of enzymes that control cholesterol levels in the blood. The adult dosage is 1 tablet. in a day. It is recommended to take the drug in the evening. |
| Fibrates | Fenofibrate, Gemfibrozil | The drugs improve metabolism. Adults are prescribed 1 tablet. per day. The maximum daily dosage is 145 mg. |
| Bile acid sequestrants | Holestan, Holestipol | The drugs reduce cholesterol synthesis. It is recommended to take medications in 2 drops. 2 r. per day before meals. The duration of treatment is 3-6 weeks. |
| Nicotinic acid derivatives | Niceritrol, Niacin | The recommended daily dosage for adults is 18-25 mg. |
In some situations, your doctor may prescribe dietary supplements that contain omega-3 fatty acids.
A slight increase in the concentration of low-density lipoproteins will help to adjust proper nutrition and preventive actions. High research rates mean that drug therapy is indispensable.
In the absence of timely and correct treatment, the patient will face complications in the form of atherosclerotic plaques. Severe consequences include heart attack, stroke, and death.
Article design: Vladimir the Great
Preparing to donate blood for a lipid profile
Preliminary preparation for analysis is necessary to obtain accurate results. 2-3 days before the prescribed procedure, it is recommended to refuse foods rich in animal fats and alcoholic beverages (including weak alcohol), and stop taking any medications other than those necessary for medical reasons.
The day before the procedure:
- reduce physical activity;
- limit sugar intake.
Blood sampling is performed strictly on an empty stomach. The fasting regime should be at least 8 hours.
Symptoms of high cholesterol
It is possible to determine the exact level of cholesterol in the body only after an analysis, but there are symptoms that may indicate the presence of disturbances in the functioning of the body. This will not allow you to make a diagnosis, but it should be a reason to visit a lipidologist or cardiologist. Make an appointment for a preventive appointment if:
- physical activity or excessive anxiety provokes the appearance of aching pain in the chest;
- even minor physical activity causes a feeling of lack of oxygen;
- you begin to get tired faster, and fatigue is accompanied by a feeling of heaviness in the chest area;
- you often have a headache for no reason, there is noise in your ears, you feel oxygen starvation to the point of fainting.
If you notice the symptoms described, make an appointment with your doctor. It will be enough to visit a therapist so that he can conduct a preventive examination and, if necessary, refer you to other specialized specialists.
The diagnosis of atherosclerosis is difficult to make without biochemical and instrumental examination, so be prepared for the fact that you will have to undergo a series of tests. The examination usually begins with a blood test and an ECG.
. Then, depending on the results obtained, a treatment program is prescribed, if necessary. The patient’s blood is usually taken from a vein, but if a quick result is needed, it can be obtained using the express method by drawing blood from a finger. To obtain more accurate results, it is recommended to donate blood on an empty stomach.
Normal lipid status
The norms for total cholesterol do not depend on gender. For men and women from 20 to 45 years old, the indicators should fall within the range of 3.2-5.2 mmol/l. If the result is equal to or greater than 6.7 mmol/l, then the patient is diagnosed with hypercholesterolemia.
At values below the norm of 3.2 mmol/l – hypocholesterolemia. Both disorders are considered pathologies. Reference values for high-density and low-density lipoproteins differ by gender and age category.
Normal indicators
The values of triglycerides and very low density lipoproteins for men and women are identical:
- TG – 0.41-1.8 mmol/l;
- VLDL – 0.26-1.04 mmol/l.
For the atherogenicity coefficient, only inflated values are of diagnostic value. The higher the KA, the higher the risk of atherosclerosis.
CA norm table
What does it mean if low density lipoproteins are elevated?
When cholesterol plaques form on the walls of the arteries, blood circulation worsens. Internal organs and systems do not receive the necessary substances and oxygen to function normally.
Low-density lipoproteins are elevated - this means that the following pathologies develop in the human body:
| Name | Description |
| Cardiac ischemia (CHD) | A pathological condition that often occurs together with atherosclerosis. The disease is characterized by a lack of oxygen in the tissues of the heart. Provokes shortness of breath, chest pain, and a sharp increase in blood pressure. |
| Thrombophlebitis | Blood clots form in the vessels and veins of the lower extremities due to high cholesterol levels. The walls are affected by the inflammatory process. They stretch and deform. The disease is accompanied by redness of the skin, pain in the legs and the appearance of varicose veins. |
| Atherosclerosis | Chronic pathology that affects arteries and blood vessels. Cholesterol plaque provokes the formation of plaques that clog the arteries. In some situations, blood clots also form, narrowing the lumen of the vessel. The disease develops slowly and often requires surgical intervention. |
Low-density lipoproteins are elevated - this means that it is necessary to begin treatment to prevent negative consequences. Diagnostics will help to establish the cause of the disorders and select the most effective therapeutic methods.
Deviation from normal levels of LDL and HDL
Non-standardized lipoprotein values should be considered only in conjunction with triglyceride values and the level of total cholesterol in the blood. When HDL cholesterol is elevated with normal levels of TC and other fractions, this indicates good lipid metabolism. An unfavorable combination is when the level of LDL and TC is increased, and the level of HDL is decreased.
The following indicators accompany chronic diseases:
- hepatobiliary system (hepatosis, cirrhosis, cholecystitis, cholangitis, etc.);
- renal apparatus (pyelonephritis, nephritis, etc.);
- endocrine system (diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism);
- cardiovascular system (hypertension, atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, pericarditis, myocarditis, endocarditis, etc.).
As well as some autoimmune and oncological pathologies. If there are no such diagnoses, then the cause may be an unhealthy lifestyle:
- unhealthy diet (predominance of animal fats in the diet, deficiency of vegetables and fruits);
- alcohol and nicotine addiction;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- long-term stress.
In this case, the results of the lipid profile should be regarded as a high risk of developing atherosclerosis and heart disease. With a decrease in HDL, “bad” cholesterol settles on the inner wall of blood vessels, forming cholesterol spots, from which atherosclerotic plaques eventually form. Such growths inside the vessel block blood flow, which causes heart attack, stroke, and dry gangrene of the lower extremities.
Hypocholesterolemia is also harmful to the body. Lack of cholesterol threatens hemorrhagic stroke, destruction of cell membranes, anemia (anemia), osteoporosis, neuropsychological disorders and depression.
With cholesterol deficiency, the synthesis of sex hormones is disrupted. As a result, libido decreases, men experience problems with potency, women's menstrual cycles become disrupted, and there is a risk of infertility.
Complexes with this research
Lipidogram.
Diagnostics of atherosclerosis Analysis of pathologies of lipid metabolism and the risk of heart and vascular diseases 480 R Composition Male check-up No. 1 39 studies for annual preventive examination 18 570 R Composition
Male anti-aging diagnostics Monitoring of basic indicators in men aged 40+ 13,300 RUR Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Advanced anti-aging diagnostics in postmenopause RUB 29,230
- Advanced women's anti-aging diagnostics RUB 28,680
- Nutritionist recommends RUB 7,570
- Metabolic profile RUB 5,900
- Preventive check-up RUB 11,960
Results
HDL and LDL are the most important participants in cholesterol metabolism, the amount of which in the blood must meet certain standards. Low-density lipoproteins supply the body's cells with cholesterol, which is produced by the liver. High-density lipoproteins cleanse blood vessels of excess fat, preventing the development of atherosclerosis.
Dyslipidemia, otherwise an imbalance of LDL and HDL, accompanies a number of chronic diseases or is a consequence of unhealthy eating behavior, bad habits, and physical inactivity. You can check your fat metabolism levels by donating blood for a special test - a lipid profile.
What increases cholesterol?
Increased cholesterol levels can be due to various factors. The first thing you should pay attention to is your diet
.
If a person has a slight increase in cholesterol levels, doctors usually recommend that they eat less foods high in saturated fat, but certain health problems can also contribute to high cholesterol levels. For example, chronic renal failure or decreased thyroid function. Some people may have high cholesterol levels “naturally” and be inherited. This genetic abnormality is called “ familial hypercholesterolemia
”.
When shaping your diet, you need to remember that cholesterol is found only in products of animal origin. This argument is often made in favor of a plant-based diet by vegetarians. However, this does not mean that if animal food is excluded, the rest of the diet can be uncontrolled. Food fried in vegetable oil and products containing palm oil can also have a negative effect on lipid metabolism.
Important Notes
Material for research Capillary blood.
Children under 7 years of age: venous blood/capillary blood (for special indications). Children over 7 years of age and adults: venous blood. Capillary blood collection for research is carried out only for children under 7 years of age (for special indications)! According to GOST R 53079.4-2008, indications for taking capillary blood are possible: in newborns, in patients with very small or hard-to-reach veins, with large-area burns, and in severely obese patients.
Pathological reasons for the increase
There are other causes of elevated low-density lipoprotein (LDL) levels. Mostly related to diseases.
Diabetes
A chronic, serious disease in which the level of glucose in the body increases. Usually associated with a condition of the pancreas. When little insulin is produced. On the other hand, a situation is possible in which the tissues are simply insensitive to this substance.
Both options are equally dangerous. The disease is accompanied by critical metabolic disorders. And that's the minimum. Low-density lipoproteins in diabetes constantly increase, so therapy is carried out systematically. For many years.
For immediate treatment, statins are prescribed, as well as fibrates as needed. As well as nicotinic acid.
But this is not enough. Insulin is used to stop attacks. In addition, a strict diet is indicated. Avoid sweets and sugar from your diet, and don’t get carried away with starch.
Herbal products are required. It is necessary to reduce body weight. The issue is resolved under the supervision of a competent endocrinologist.
Liver pathologies
Diseases in which an organ stops working as it should. Be it hepatitis, inflammation or cirrhosis (that is, death of the tissues of the largest gland).
Since the liver is primarily responsible for fat metabolism, all functions begin to be disrupted, including lipid processing.
What is the therapy? It is necessary to prescribe hepatoprotectors. Karsin, Essentiale, Phosphogliv. These are special means that prevent organ destruction.
The main diagnosis is being corrected. For example, hepatitis. Drugs are used. Next, the patient’s condition is monitored over time. Check how the prescribed course works.
Treatment is the prerogative of the hepatologist. If there is no such doctor within reach, a consultation with a gastroenterologist is indicated.
Cholecystitis
Inflammation of the gallbladder. Accompanied by impaired bile production. This substance is involved in the processing of fats.
If there is not enough compound after eating, problems with lipid storage begin. At a minimum, over-deposition occurs. When there is too much fat. This means that the concentration of low-density lipoproteins increases. It is very dangerous.
Treatment is carried out on site. Necessary choleretic drugs. Allohol and others. They help the substance to be evacuated faster through special ducts. This means there will be no stagnation.
Attention:
The drug is not used for cholestasis with inflection and organic disorders of the gallbladder. His anatomical disorders.
Then, if necessary, diet therapy is used. A diet high in protein is prescribed.
Plus, they review the amount of food they eat per day. There should be about 5-6 of them so that each time the portion fits in the palm of your hand. This will reduce the load on an organ that is already out of order.
Insufficient production of thyroid hormones
The so-called hypothyroidism. This small organ, along with the pituitary gland, can be called the “conductor” of the entire endocrine system.
All deviations in the functioning of the thyroid gland immediately lead to an increase in the concentration of low-density lipoproteins, therefore, the amount of cholesterol also increases. Depending on the degree of violation, it is very significant.
Attention:
This is a threatening condition fraught with atherosclerosis.
Therapy is carried out under the supervision of an endocrinologist. Possibly in a hospital if there are life-threatening complications.
Special iodine preparations are prescribed. Also a diet high in this substance.
A huge role is played by correcting the primary cause. Often thyroid diseases are secondary. Caused by other factors. For example, problems in the functioning of the pituitary gland, etc.
Adrenal gland disorders
Diseases in which the concentration of adrenaline, cortisol and other substances is disrupted. They indirectly participate in the normal synthesis of LDL and correction of the concentration of low-density lipoproteins.
As soon as the amount of hormones decreases, problems begin. There can be many reasons: for example, Addison's disease or surgery. Correction is carried out immediately. Under the supervision of an endocrinologist.
Treatment is conservative. Substitute drugs are prescribed. Hormonal agents. If possible, artificial stimulation of the adrenal glands is performed. To achieve restoration of their functions.
The process is not fast. Complete rehabilitation requires at least 2-3 months. Often much more. It all depends on the primary factor.
Atherosclerosis
It is quite difficult to say exactly what is the cause and what is the effect. The essence of the pathological process is the deposition of cholesterol on the walls of the arteries.
The vessels cannot bear such a load. Local and even general pressure increases, the nutrition of body tissues is disrupted.
Therapy is carried out under the supervision of an endocrinologist. Prescribed drugs of the statin group. If the plaque becomes calcified and inorganic salts are deposited, there is no point in such medications. The formation is removed surgically. Through minimally invasive intervention.
If LDL is elevated, this means that normal metabolism is disrupted (slowed down). Usually there are two reasons. The first depends on the patient himself. For example, he doesn't eat well. And the second concerns the pathological process. Primary in relation to atherosclerosis.
The result is always the same. If left untreated, dangerous complications develop. Up to stroke, heart attack, arterial aneurysms.
References
- Francois, M., Baigent, C., Catapano, A. et al. 2021 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk, 2021. - Vol. 41(1). — P. 111-188.
- Arthur, C., John, E. Physiology Review, 2015.
- Severin, E.S., Aleynikova, T.L., Osipov, E.V. and others - M.: Medical Information Agency LLC, 2008. - 364 p.
- Kumar, V., Abbas, A., Fausto, N. et al. Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease, 2014. - 1464 p.
Indications for the study
Periodic lipid testing is recommended for all adults. This makes it possible to timely identify violations and take the necessary measures. The period between studies should be no more than 5 years. In some cases, it is recommended to undergo examination more often. It is recommended to take a blood test for VLDL cholesterol annually or several times a year if the patient is at risk for the development of vascular and heart pathologies. The risk of their development is increased in smokers, patients suffering from high blood pressure, diabetes, and increases with age. Measurement of indicators can be carried out directly or performed using a calculation method.