What criteria influence the degree of iron accumulation?
The fundamental criteria include the amount of iron consumed in food, taking medications containing iron, the condition of internal organs and tissues, the distinctive characteristics of the menstrual cycle and genetics.
With a lack of iron, iron deficiency anemia can form. However, the most dangerous is the level of iron in the body that exceeds the norm. The substance accumulates in the internal organs, after which it passes into the skin, heart muscle, types of glands, and joints. Such processes have a dark connection with the development of rapid “aging” and disruption of the activity of these organs. The threats of developing cirrhosis and liver cancer, diabetes mellitus, severe heart failure, and dysfunction of the thyroid and gonads are increasing.
The main reasons that can contribute to the accumulation of excess substances include mutations in genes, abuse of certain medications, regular blood transfusions, destruction of red blood cells and chronic dysfunction in the liver.
causes of increased iron in the blood
At this point, these kinds of events can be caused by heredity. The disease in question is called primary hemochromatosis, abnormal genes of which are found in every 250 inhabitants of Northern Europe. The same applies to Russia. The disease is mainly found in representatives of the stronger sex in adulthood, and in representatives of the fair sex - after menopause.
Initially, similar genes with disorders may not be expressed in anything, however, with the further development of liver disease into a chronic form, the genes fully manifest themselves. Approximately 1/4 of cases can be associated with fatty liver disease due to abuse of alcoholic beverages and so on, viral hepatitis of various degrees and forms.
Why does the level of iron in the body go through the roof?
Guests
Leonid Lazebnik professor, doctor of medical sciences, therapist of the highest category, president of the Scientific Society of Gastroenterologists of Russia
Maria Vasilevskaya:
On air, “Medical Examination” is a diagnosis of our healthcare, the temperature of public opinion, pressing issues and useful advice. It’s bad when the body lacks iron, it’s even worse when this microelement is in excess, excessive accumulation of iron, hemochromatosis, leads to the most unenviable consequences: cirrhosis, diabetes mellitus, hormonal imbalance - so why does the iron level begin to go off scale, is it possible to stop this process and who is at risk? These and other questions will be answered by a therapist of the highest category, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, President of the Scientific Society of Gastroenterologists of Russia Leonid Borisovich Lazebnik. Hello, Leonid Borisovich!
Leonid Lazebnik:
Hello!
Maria Vasilevskaya:
Why does the level of iron in the body go off scale?
Leonid Lazebnik:
After all, iron is contained in our red blood cells...
Maria Vasilevskaya:
So…
Leonid Lazebnik:
And if excessive breakdown of red blood cells begins, it does not have time to be absorbed.
Maria Vasilevskaya:
Why does it start?
Leonid Lazebnik:
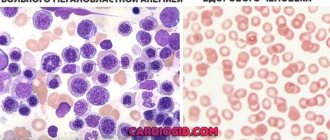
Some kind of intoxication, some kind of anemia, so if a person has anemia, this does not mean that he has little iron in his body, it breaks down in red blood cells and is not absorbed and settles in other places - this is the first thing. Secondly, there are such congenital conditions: some enzymes begin not to repel iron in the duodenum, but to absorb it, and it enters the blood and then begins to be deposited in a variety of organs, the most accumulative organ for the body is the liver, on the left side it is healthy liver.
Maria Vasilevskaya:
The pink one is cute.
Leonid Lazebnik:
Yes, there are these pink liver cells - these are healthy cells, they accumulate a normal amount of iron, they retain it, but on the left is the liver affected by hemochromatosis, you see, there is a lot of fat there...
Maria Vasilevskaya:
Rusty liver.
Leonid Lazebnik:
Yes, fatty liver and, secondly, there are black inclusions there in an asymmetrical order, sometimes even in stripes - these are inclusions of iron, this is called hemochromatosis.
Maria Vasilevskaya:
How does iron get into the human body anyway? We don’t eat nails, do we?
Leonid Lazebnik:
We eat, firstly, enough foods that contain iron, first of all, of course, this is meat, this is buckwheat and some other types, mainly meat and buckwheat.
Maria Vasilevskaya:
Apples probably “rust”?
Leonid Lazebnik:
Not all apples: sour apples, especially those in the skin, contain iron, of course.
Maria Vasilevskaya:
How can I tell? It’s probably obvious from some symptoms: should I eat sour apples or not, how can I tell?
Leonid Lazebnik:
No, you and I can’t understand that, several studies need to be carried out: if we are talking about a serious condition, what is called “bronze” diabetes or “bronze” disease or hemochromatosis, it begins to be deposited not only in the liver, but also in the skin tissues, and the person “turns bronze”, which is why it is called “bronze” disease.
Maria Vasilevskaya:
That is, he appears to have a tan, although he has not tanned?
Leonid Lazebnik:
Yes, and one of the reasons for the increase in sugar may be the so-called “bronze” diabetes or hemochromatosis, but first the person still changes skin color.
Maria Vasilevskaya:
So this is the most important sign?
Leonid Lazebnik:
Yes, it seems that she is tanned and looks great, but symptoms of cirrhosis appear: weakness, peripheral neuropathies, memory impairment. First, the liver enlarges, then it begins to decrease in size, and here two substances need to be examined: ferritin is an indicator of the accumulation of iron in the body and transferrin is a protein that transports iron.
Maria Vasilevskaya:
Do you need to donate blood for transferrin, as you said?
Leonid Lazebnik:
Yes, you need to donate blood. There is appropriate treatment, firstly, traditionally bloodletting.
Maria Vasilevskaya:
Are these leeches or the old fashioned way, like in the Middle Ages?
Leonid Lazebnik:
No, a needle is inserted, excuse me, I’ll show you on myself, 150 or 200 milliliters of blood are released here like this - this is generally a reliable method of treatment that came to us from time immemorial, but it is a reliable method of treatment: excess blood and excess iron are removed.
Maria Vasilevskaya:
As a donor, right?
Leonid Lazebnik:
Yes, but they just pour it out.
Maria Vasilevskaya:
How often do they do this type of bloodletting?
Leonid Lazebnik:
From once a month to once every 3 months.
Maria Vasilevskaya:
If a person has high iron levels and does nothing, what will happen in the end?
Leonid Lazebnik:
It will end sadly, of course.
Maria Vasilevskaya:
Cirrhosis?
Leonid Lazebnik:
It will end in liver failure, cirrhosis of the liver. There are 3 drugs, 2 of them are very powerful, but toxic, the third drug is much softer - it is a hydrolyzate of the human placenta, it works very reliably, by the way, this is both a Japanese and our achievement.
Maria Vasilevskaya:
So this disease can simply be treated with medication?
Leonid Lazebnik:
This disease can be treated with medication, there is no need to be afraid, but first of all, first of all, do not be scared, do not panic, find an intelligent doctor...
Maria Vasilevskaya:
And get treatment.
Leonid Lazebnik:
To repair our cars, we don’t go to the first auto repair shop on the corner, we will find something that inspires confidence in us, and a doctor, find a smart doctor who would not rush to do bloodletting if necessary, yes, if there is a lot of excess blood, it will be necessary to release it, but then you will need drugs that remove iron, either block its absorption, or act gently so that you will not notice anything, and the level of ferritin in your blood will be normal.
Maria Vasilevskaya:
What preventive measures would you recommend to our viewers to prevent excess iron in the body?
Leonid Lazebnik:
Firstly, if you have anemia, you should definitely get it checked, because there are types of anemia...
Maria Vasilevskaya:
What is anemia?
Leonid Lazebnik:
Anemia: if red blood cells disintegrate excessively in the body, then you need to remember that this iron can be deposited in the liver and pancreas. Second: you don’t need... you just want to say: “Gobble up all the multivitamins in a row,” but if your body doesn’t need anything, why eat it, what the body wants, it will ask for itself, if it wants black caviar, buy 2-3 eggs...
Maria Vasilevskaya:
Unscrupulous organism.
Leonid Lazebnik:
At the end of the day, our eating habits are determined by what our microbiota wants.
Maria Vasilevskaya:
Our intestinal microflora.
Leonid Lazebnik:
Yes, our intestinal microflora means don’t eat too much, but if you have an increase in ferritin in the blood, limit yourself to meat, buckwheat and see what foods contain excess iron.
Maria Vasilevskaya:
If a person has a high iron content in the body, what changes in his lifestyle should he make in order to live better, to live a better quality of life?
Leonid Lazebnik:
If diabetes is, of course, drugs that lower blood sugar levels, various insulins and other glucose-lowering drugs, if it is cirrhosis of the liver, then monitor enzyme levels.
Maria Vasilevskaya:
Listen to your doctor in this matter.
Leonid Lazebnik:
Yes, that is, physical activity, volens nolens, is completely excluded.
Maria Vasilevskaya:
Can't you go for a walk?
Leonid Lazebnik:
I said: physical activity, not physiological, but physical activity, that means no sports, but what is associated with everyday stress, for God’s sake, just please control yourself - you don’t need to put everything in your mouth, including recommended nutritional supplements containing microelements and all sorts of multivitamins that supposedly work, think about it, don’t waste your money.
Maria Vasilevskaya:
Everything is clear, we will listen to the doctors, thank you for this conversation!
Leonid Lazebnik:
Thank you.
Maria Vasilevskaya:
Well, be healthy, it was a “Medical Examination”!
Symptoms of too much substance
Symptoms of excess iron in the body:
- Detection of liver enlargement in size or transformation of biochemical criteria. Their reason may not be clear.
- Detection of increased hemoglobin, iron, ferritin, transferrin in the blood.
- The presence of dark spots, cracked skin in the area of the armpits, groin folds, old scars.
- Various combinations of diseases: liver cirrhosis, diabetes mellitus, joint damage, pathology of the heart and endocrine glands.
- Having close blood relatives with hemochromatosis or PWS.
Excess iron
An overdose of iron in a healthy person is quite difficult to achieve as part of a normal diet. Iron is a rather ungrateful mineral component and is only absorbed to a small extent.
Additionally, many other food ingredients can effectively prevent this. We are talking about black tea, coffee, products containing calcium, phytic acids, fiber or polyphenols, which are almost impossible to get rid of.
This looks a little different with iron supplements. A large dose of the element is concentrated into a small tablet that is easy to swallow. Supplement overdose can result from taking too much or too many different medications, most of which contain iron.
In a healthy person, a situation in which the body cannot cope with excessive iron intake is unlikely, including due to natural protective mechanisms. This is an HFE protein that blocks the absorption of iron in the intestines when levels are high. Specific genes are responsible for its production.
Unfortunately, there are people for whom these mechanisms do not work properly. These people suffer from hemochromatosis.
Hemochromatosis is a genetically determined disease. Serious symptoms occur when there is a significant excess of iron in the tissues and hemochromatosis is detected only after 30-40 years. In women, the first symptoms of the disease and its detection may occur even later.
criteria for an excess of a substance in the body?
In such a situation, we recommend that you contact specialists who treat metabolic dysfunctions. A medical professional will help you find the causes, develop a personal research and treatment plan, and establish strict monitoring of your health.
Methods for treating excess iron :
- compliance with dietary nutrition,
- refusal of alcoholic drinks,
- use of antioxidants.
You should always remember that iron is not removed from the body, but remains in it for life!
This is why it is so important to detect this in the early stages and prevent the spread of dangerous substances to stop the functioning of the liver and many other organs, forming liver cancer, which will help you extend the years of your life.
Diet for people with excess iron in the blood
The main means of combating excess iron in the blood are drugs that chelate it in the body. Pharmacological therapy can also be supported by a proper diet. How?
When there is too much iron in the blood, the easiest thing to do is to avoid it in the diet. This is not easy because iron is present in many foods, including fruits, vegetables and other plant foods. However, the right combination and selection of ingredients can either increase or decrease the bioavailability of iron.
First of all, avoid eating red meat, offal and processed foods. These are foods that contain significant amounts of iron. In your diet, you should not rely on egg yolk, parsley, fish and seafood too often.
It is easier for the human body to obtain iron from animal products, so you need to focus on plant products. The fiber they contain, phytic and oxalic acids and polyphenols effectively reduce the absorption of iron. Instead of dark bread, it is better to eat products made from refined flour because they contain less iron.
To further reduce iron absorption, you can add calcium-containing dairy products to your food. This element competes with iron and effectively reduces its absorption. Zinc also has similar properties.
If there is excess iron in the blood, avoid all iron supplements, including multivitamin preparations in which iron may be one of the components.
Particular care should be taken when consuming vitamin C. It plays an important role in the absorption of iron. Taking this vitamin with meals can increase the absorption of iron, but in case of excess, the opposite happens.
The list of prohibited foods should also include foods fortified with iron, such as breakfast cereals or plant-based milks.
Excess iron in the body is a serious health risk and cannot be dealt with only through diet, although its use can greatly help. It is imperative to undergo treatment and regularly undergo blood tests for iron.
The purpose of the medications selected by the doctor is mainly to prevent the accumulation of iron, which helps remove excess amounts of the element from the body.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can make an appointment by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
References
- Federal clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of iron deficiency anemia, 2015. - 58 p.
- Klochkova-Abelyants, S.A., Surzhikova, G.S. Iron deficiency anemia and anemia of chronic diseases: some aspects of pathogenesis and prospects for differential diagnosis. — Medicine in Kuzbass, 2021. — No. 3. — P.25-28.
- Tiglis, M., Neagu, T., Niculae, A. et al. Incidence of Iron Deficiency and the Role of Intravenous Iron Use in the Perioperative Period, 2021. - Vol. 56(10). - P. 528.
Complexes with this research
Biochemistry of blood.
19 indicators Advanced biochemical blood test RUR 3,580 Composition Male check-up No. 1 39 studies for annual preventive examination RUR 11,280 Composition
Biochemistry of blood. 8 indicators Minimum biochemical blood test 990 R Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Female infertility RUB 9,790
- Pregnancy planning. Clinical indicators 3,880 R
- Entry into IVF RUB 15,030
- Women's check-up No. 1 RUB 12,520
- Examination during pregnancy. 3rd trimester 5,730 RUR
Iron and iron health: what role does the microelement play in our body?
Iron is part of hemoglobin. In turn, the protein hemoglobin is a building material for erythrocytes - red blood cells that carry oxygen from the lungs to the organs, and on the way back rid them of carbon dioxide. Actually, this process is called cellular respiration. Without iron it is impossible. And since every cell in our body needs oxygen, iron can be called one of the most important elements.
The synthesis of hemoglobin takes 60–70% of all iron entering the body. The remaining 30–40% is deposited in tissues and spent on solving other problems - metabolic processes, regulation of the thyroid gland, maintaining the body's defense system and connective tissue synthesis.
As you can see, the functions of iron are varied and numerous, but oxygen transport is the most important of them.
Iron is poorly absorbed even with ideal health and proper diet - the human body is able to absorb up to 10% of the iron supplied with food.
Preparing for analysis
The study is carried out on an empty stomach
Usually the study is carried out as planned. The patient comes for analysis in the morning on an empty stomach, after 8-14 hours of complete overnight fasting, and if this condition cannot be met, no earlier than 4 hours after the last meal. You can still drink clean water. 2-3 days before the study, it is not recommended to expose yourself to heavy physical activity, including sports training. You should get more rest, go to bed earlier, avoid stress, alcohol consumption and heavy smoking. You should also not smoke in the morning before the test.
For more accurate results, 7-10 days before the analysis, you should avoid taking iron-containing preparations and foods containing large amounts of iron (seaweed, dried and fresh mushrooms, legumes, hazelnuts, buckwheat, oatmeal, almonds, rose hips, prunes, dried apricots, cocoa). When taking medications that do not contain iron, but those that can lead to an increase in iron in the blood (antibiotics, cytostatics, contraceptives, etc.), you should discuss their discontinuation with your doctor.
If discontinuation of these drugs is not possible now, you should complete the course of therapy with these medications, and then conduct an analysis, or find an alternative to them, for example, replace oral contraceptives with barrier contraceptive methods (condoms, spermicides).
If it is necessary to determine the level of iron in the blood when acute intoxication with this metal is suspected, the above rules may not be followed. Such intoxication is an indication for emergency research and treatment.
Iron intake standards for patients with anemia
Sometimes tests reveal not just a lack of iron, but a more serious situation - iron deficiency anemia. Typically, this condition develops against the background of gastrointestinal diseases, tumor processes, helminthic infestations, and constant bleeding. It is often diagnosed in people who have experienced significant blood loss during injury or surgery.
Iron deficiency anemia is diagnosed if the hemoglobin level drops to 100–70 g/l and serum ferritin drops to 15 ng/ml.
If iron deficiency anemia is diagnosed, you cannot prescribe treatment yourself. The doctor selects the therapy. Perhaps he will prescribe multivitamin complexes and dietary supplements with iron, and in the most severe cases, he may even prescribe iron supplements - quite strong drugs with numerous side effects. You can take such medications only under the supervision of your doctor.
Indications for the study
- Diagnosis and differential diagnosis of anemia of various etiologies, control of therapy for iron deficiency anemia.
- Acute and chronic infectious diseases, systemic inflammatory diseases.
- Malnutrition and absorption, hypo- and avitaminosis, disorders of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Possible poisoning from iron-containing drugs.
In the early stages, iron deficiency may be asymptomatic. If a person is otherwise healthy, then signs of the disease appear only when hemoglobin decreases below 100 g/l. Anemia is characterized by chronic weakness, dizziness, and headaches.
Symptoms of excess iron: joint pain, weakness, fatigue, abdominal pain, decreased sexual desire, heart rhythm disturbances.
What test helps determine iron levels?
Venous blood is required for analysis.
Since iron is never found in the blood in free form, but is bound to its proteins, its level is determined in the serum of venous blood. The colorimetric test with ferrozine is most often used for this. The following values can be considered the norms for this analysis.
| Gender, age | Norms, µmol/l |
| Women >18 years old | 7,2 — 26,9 |
| Men >18 years old | 11,6 — 31,3 |
| Girls 14-18 years old | 9,0 — 30,0 |
| Boys 14-18 years old | 11,5 — 31,5 |
| Children 1-14 years old | 9,0 — 21,5 |
| Children 1 month - 1 year | 7,2 — 17,9 |
| Children under 1 month | 17,9 — 44,8 |
Hemochromatosis is the cause of increased iron
In addition to serum iron, other important indicators can be additionally determined.
- Serum ferritin level. It objectively indicates the amount of iron reserves in the tissues of the body. Quite often, with anemia, along with a high level of serum iron, a decrease in ferritin is observed, and its high level indicates hemochromatosis. The normal ferritin value is 15-150 mcg/l.
- The percentage of iron saturation of transferrin, a transport protein that transports this metal. Norm for the indicator: 20-45%. Its level >55% indicates excess iron in the body.
- TIBC, total serum iron binding capacity, indicates the amount of iron that can bind to transferrin. Norm for the indicator: 45-63 µmol/l. In the above-mentioned pathologies, life-saving blood pressure is often reduced.