Iron deficiency
Hepatitis
Menopause
23345 April 16
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. We remind you that independent interpretation of the results is unacceptable, the information below is for reference only
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) is a plasma membrane-anchored enzyme that participates in the dephospholation reaction. The reaction is the process of detaching phosphorus from certain organic substances.
Alkaline phosphatase: indications for use, rules for preparing for the test, interpretation of results and normal indicators.
Indications for the purpose of the study
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) is present in many tissues of the human body, but its greatest amount is determined in the epithelium of the small intestine, osteoblasts (cells that synthesize the intercellular substance of bone tissue), in hepatocytes (liver cells), placenta, renal tubules and intestinal mucosa.
Several isoenzymes of alkaline phosphatase are detected in blood serum (isoenzymes are enzymes that differ in amino acid sequence, existing in the same organism, but in different cells):
- bone alkaline phosphatase is secreted by osteoblasts and is involved in the maturation of the intercellular substance of bone tissue and its mineralization. The level of bone alkaline phosphatase can be elevated during active bone growth in children - up to puberty, during fractures, in postmenopausal women, and also as a result of diseases associated with the process of bone tissue destruction;
- hepatic alkaline phosphatase is represented by two isoenzymes: the first increases in the blood serum in case of stagnation of bile in the liver and/or a decrease in its secretion; the second isoenzyme increases with the destruction of liver cells;
- intestinal ALP is synthesized by cells lining the intestinal lumen, enters the lumen of the small intestine and is partially absorbed into the blood. Intestinal alkaline phosphatase activity may increase after meals and in intestinal diseases;
- Placental alkaline phosphatase is present in the blood serum during pregnancy, its level increases during normal pregnancy and reaches a maximum in the third trimester. Due to damage to the placenta in preeclampsia, there is a marked increase in alkaline phosphatase. Low activity of alkaline phosphatase in pregnant women is a sign of insufficient development of the placenta.
In clinical practice, the total activity of alkaline phosphatase is determined.
The liver and bone isoenzymes of alkaline phosphatase are predominantly found in blood serum (up to half of the total amount in adults). The ratio of these forms in blood serum depends on age.
Thus, the following conditions and diseases may be indications for prescribing a blood test for alkaline phosphatase:
- liver diseases;
- bone diseases;
- diseases that occur with damage to the liver and/or bone tissue (tuberculosis, kidney disease, metastatic liver cancer, metastatic bone tissue, etc.);
- infectious mononucleosis (at the onset of the disease."
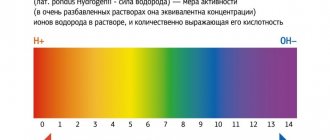
Reference values
Important! Standards may vary depending on the reagents and equipment used in each particular laboratory. That is why, when interpreting the results, it is necessary to use the standards adopted in the laboratory where the analysis was carried out. You also need to pay attention to the units of measurement.
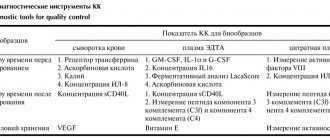
Alkaline phosphatase standards according to the independent laboratory Invitro:
| Floor | Age | Norms (U/l) |
| Both boys and girls | up to 15 days | 90-273 |
| 15 days - 1 year | 134-518 | |
| 1 year - 10 years | 156-369 | |
| 10 years - 13 years | 141-460 | |
| Women | 13 years - 15 years | 62-280 |
| over 15 years old | 40-150 | |
| Men | 13 years – 15 years | 127-517 |
| 15 years - 17 years | 89-365 | |
| 17 years -19 years | 59-164 | |
| over 19 years old | 40-150 |
Helix laboratory standards:
| Age, gender | Reference values | |
| up to 15 days | 83 - 248 U/l | |
| 15 days - 1 year | 122 - 469 U/l | |
| 1-10 years | 142 - 335 U/l | |
| 10-13 years | 129 – 417 U/l | |
| 13-15 years old | female | 57 - 254 U/l |
| male | 116 - 468 U/l | |
| 15-17 years old | female | 50 - 117 U/l |
| male | 82 - 331 U/l | |
| 17-19 years old | female | 45 - 87 U/l |
| male | 55 - 149 U/l | |
| over 19 years old | female | 35 - 105 U/l |
| male | 40 – 130 U/l | |
Laboratory Diagnostic Manual Alkaline Phosphatase Data:
| Age | Total, IU/l | Bone,% |
| Newborns | 35 — 106 | |
| 1 month | 71 — 213 | 85 |
| 3 years | 71 — 142 | 85 |
| 10 years | 106 — 213 | 85 |
| Adults under 31 years old | 39 — 92 | 60 |
| Adults over 31 years of age | 39 — 117 | 40 |
Preparation for the procedure
It is preferable to take blood in the morning on an empty stomach, after 8-14 hours of overnight fasting (you can drink water), or 4 hours after a light meal during the day.
On the eve of the study, you should adhere to a standard diet without excessive consumption of foods rich in proteins and purines (meat, liver, kidneys, fish, meat broths, mushrooms, beans, beans and lentils).
Avoid increased psycho-emotional and physical stress (sports training), alcohol intake.
3.How the analysis is carried out and the risks of analysis
How is a blood alkaline phosphatase test performed?
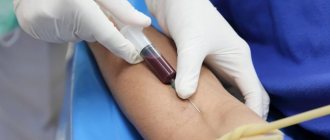
A blood alkaline phosphatase test is performed after drawing blood from a vein. Blood sampling from a vein is carried out according to a standard procedure.
Risks of Alkaline Phosphatase Blood Tests
If you are donating blood for an alkaline phosphatase blood test, then possible risks may only be associated with taking blood from a vein. In particular, the appearance of bruises at the site of blood sampling and inflammation of the vein (phlebitis). Warm compresses several times a day will relieve phlebitis. If you are taking blood thinning medications, you may bleed at the puncture site.
Treatment of cholestasis
The first measure when cholestasis is detected or suspected is nutritional correction.
A special feature of this diet is the replacement of animal fats with vegetable fats. It is recommended to eat more vegetables and fruits, choose lean meats and types of dairy products. Cereal-based porridges are also useful. It is necessary to limit fried, smoked and spicy foods. You should completely avoid alcohol, strong coffee and tea. For the treatment of cholestasis, medications of different groups can be prescribed:
- hepatoprotectors;
- antibiotics;
- cytostatics;
- ursodeoxycholic acid preparations.
For signs of hypovitaminosis, multivitamin complexes are also recommended.
In the fight against skin itching, the first-line drugs are bile acid derivatives, which bind bile acids from bile in the lumen and prevent their transport into the bloodstream. The effectiveness of CNS opiate receptor blockers has been proven. During the rehabilitation period, non-drug methods are used to increase the body's defenses - physiotherapy, massage, physical therapy. Treatment of pregnant women is complicated by risks to the fetus when using medications, therefore, to reduce symptoms, they resort first of all to simple and safe means - oatmeal masks, chamomile decoction, and the use of baby cream.
Cold water and sleeping in a cool room relieve itchy skin. However, if it is strengthened, the doctor may prescribe bile acid preparations approved for use in pregnant women (in particular, ursodeoxycholic acid). These drugs are determined by the American Food and Drug Administration (FDA) based on clinical studies. Drugs for which sufficient data have been accumulated on their use in pregnant women are assigned by this organization to the appropriate group (category of action on the fetus).
For successful treatment of cholestasis in children, it is important to promptly establish the cause of this syndrome. Often the pathology in this group of patients cannot be cured with medications alone; then surgery is performed.
In adults, surgical intervention is also often required to relieve the causes of cholestasis. There are several surgical treatment options available:
- plastic surgery of the biliary tract and anastomosis;
- external drainage of the bile ducts;
- removal of stones from the cavity of the gallbladder or the organ itself.
Symptoms and signs of low ALP levels
Jaundice is not a specific sign of decreased alkaline phosphatase
Manifestations of a reduced level of alkaline phosphatase are also symptoms of the disease that provoked the disorder. In most cases, patients notice the following conditions:
- migraine-type headaches;
- joint pain;
- decreased mobility;
- pale skin;
- jaundice;
- stool disorders;
- pain in the liver area of an acute, aching or spastic nature;
- a sharp change in weight up or down.
Usually, only some of the above symptoms are present. Even if only one of them occurs, this is a reason to seek medical help.
Attempts at self-medication pose a serious danger for the patient, since the pathology causing the symptoms will progress without proper therapy.
Manifestations of bile stagnation
Symptoms of cholestasis may differ in different forms of the disease, and in some cases are almost completely absent. The following manifestations help to suspect pathology:
- Skin itching. The symptom worsens in the evening and after contact of the skin with warm water. This provokes the appearance of scratches and pustular rashes on the skin. The patient becomes anxious, irritable, and suffers from insomnia.
- Feeling of fullness and pain in the hypochondrium on the right side. The latter can “give” to the right shoulder blade, arm, collarbone, and lumbar region.
- Changes in skin and mucous color. This usually manifests itself as yellowing of the sclera of the eyes, then the yellowness spreads to other parts of the body. Hyperpigmentation, a darkening of the skin, may also occur.
- Abnormal stool. Cholestasis is characterized by discolored yellow, gray or white stool. Due to the abundance of fats, it becomes liquid and has a foul odor. Later, indigestion and constipation occur.
- Skin formations. You can see xanthomas (thickened areas of rough skin on the body that are brown or yellow) on the chest, back, and elbows. Symmetrical yellow formations on the eyelids are called xanthelasmas. They appear when the amount of cholesterol in the blood increases for three or more months and may disappear after it normalizes.
- Dyspeptic disorders. There is a bitter taste in the mouth, nausea and vomiting are noted. Appetite is often reduced or absent, causing the patient to lose weight.
- Darkening of urine. The released liquid changes from straw-yellow to the color of “dark beer.”
- Signs of hypovitaminosis (due to impaired absorption of fats, the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins - A, D, E, K) is impaired. With prolonged cholestasis, vitamin K is not sufficiently absorbed from the intestine, and increased bleeding occurs. Vitamin D deficiency is accompanied by brittle bones and pain in the limbs and back. With poor absorption of vitamin A, distance vision deteriorates, and a person sees worse in the dark. Vitamin E deficiency reduces libido.
Reasons for decreased normal ALP levels
Low ALP can be caused by anemia
The reasons why alkaline phosphatase levels decrease are quite varied. The main doctors among them are the following:
- severe anemia;
- decreased activity of the thyroid gland;
- hypophosphatasia is a congenital pathology in which softening of the bones occurs;
- age-related osteoporosis;
- lack of vitamins C, B6 and B12;
- deficiency of zinc, magnesium and folic acid;
- cretinism.
During pregnancy, a decrease in enzyme levels may indicate the development of placental insufficiency.
Taking medications that affect the functioning of the liver can also cause a decrease in the level of the enzyme in the blood.
In a small percentage of patients, due to the individual characteristics of the body, the enzyme level is slightly reduced, but there are no pathologies. This feature is determined after the examination, if no health problems are detected during the examination.
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)
An enzyme that is contained in organs responsible for processing glucose, and in an oxygen-free cycle.
Yes, to begin with, it must be said that the main path of glucose breakdown occurs with the participation of oxygen, and oxygen-free oxidation is a “backup” process, but necessary in the early stages, when the oxygen cycle has not yet “turned on.” Why is glucose breakdown needed at all? This is the main process by which we obtain energy. LDH actively manifests itself in the heart, liver, kidneys, spleen, pancreas, and muscles. It converts lactate (the product of oxygen-free oxidation of glucose) into pyruvate, which then enters the final oxidation cycle and produces the maximum possible amount of energy. Interestingly, LDH has several isoforms - from LDH1 to LDH5, and all of them are found in different organs (LDH 1.2 - in the heart, a late marker of myocardial infarction, LDH4.5 - in the liver, during the destruction of liver tissue). Norm:
140-350 units/l.
Increase:
physiological - can be caused during pregnancy, after exercise and drinking alcohol, as well as taking caffeine, aspirin, insulin, heparin, interferon, and some antibiotics.
Pathological - occurs with myocardial infarction, acute or toxic hepatitis, cirrhosis and tumors in the liver, muscle injuries, acute pancreatitis, acute kidney pathologies and blood diseases (hemolytic anemia, B12-deficiency anemia, leukemia). Decrease:
in destructive kidney diseases, when the process has been going on for a long time, the function gradually decreases and the filtration of urea is impaired, which eventually appears in the blood (uremia).
Prevention of low ALP levels
Timely seeking help is the best prevention
There are no exact preventive measures against a decrease in alkaline phosphatase, since the pathologies that cause changes in the indicator are varied. General preventative measures that help reduce the risk of health problems include:
- proper nutrition;
- giving up alcohol and tobacco;
- taking enough vitamins;
- seeking medical help if even minor health problems occur.
These recommendations will be useful for the prevention of most diseases, as they are aimed at the general maintenance of the body.
Causes and types of cholestatic syndrome
There are two main forms of pathology - extrahepatic and intrahepatic.
The first develops in the case of complete or partial blockage of the bile ducts, most often with stones in cholelithiasis and choledocholithiasis, as well as in tumors of the organs of the hepatobiliary system, dysfunction of the sphincter of Oddi, opisthorchiasis, congenital anomalies of the biliary tract. Intrahepatic cholestasis is a consequence of diseases of the hepatocellular system, such as hepatitis of viral, alcoholic and drug origin, fatty liver disease (a fairly common pathology of modern humans, affecting up to 20% of people or more, depending on age and body weight) and its autoimmune lesions, defects intrahepatic ducts.
Frequent causes of pathology also include congenital metabolic disorders (galactosemia, cystic fibrosis and others), sarcoidosis, and hormonal changes, for example, during pregnancy.
Clinically, cholestatic syndrome can manifest itself in anicteric and icteric forms, and also have an acute or chronic course. There are three types of violations:
- Partial cholestasis - decreased bile secretion.
- Dissociated cholestasis is the retention of individual components of bile.
- Total cholestasis is characterized by severe disturbances in the flow of bile into the intestines.
Features of the analysis
In medical practice, the level of alkaline phosphatase is very important in diagnosing various diseases in children. It is determined by conducting a biochemical blood test. It is necessary to monitor the condition of children and adolescents with a history of diseases of the liver, kidneys, endocrine system and digestive tract. Biochemistry analysis is prescribed for both inpatient and outpatient patients.
To carry out the analysis correctly, a venous blood sample is required, which is carried out on an empty stomach. Also, before the analysis, the child should not experience increased physical activity. Deciphering the results of the analysis with alkaline phosphatase indicators should be carried out exclusively by a qualified specialist, as well as prescribing additional diagnostics.