The first drug with 2000% bioavailability
As long as you wait, your chances of getting rid of hypertension are decreasing!
To learn more…
Many people who measure their blood pressure at home may notice a slight increase in their readings. As a rule, the cause is hidden in hypertension. Various forms of pathology are possible and you need to know what pressure 130 to 110 means and how to deal with it.
Norm or pathology
Pressure is an important value that indicates the state of health, in particular the heart and blood vessels. The norm is 120/80 mmHg. Art., but slight deviations are possible. A pressure of 130 to 110 indicates certain deviations, since both indicators are elevated, but the systolic value is not increased much, while the diastolic value should be 60-90 mm Hg. Art.
High diastolic pressure indicates problems with the heart or serious illness. In addition, this condition causes severe stress on the heart. At levels of 130/110 mmHg. Art. Doctors diagnose isolated diastolic hypertension.
Diagnostic methods
To identify the causes of an increase in blood pressure readings of 130 to 110, patients are prescribed the following types of diagnostic tests:
- Electrocardiogram.
- Laboratory blood test.
- Ultrasound examination of the heart, thyroid gland, brain, renal apparatus, blood vessels;
- Blood test for hormones;
- Laboratory examination of urine.
In addition, the doctor examines the patient, studies the presenting symptoms and medical history. It is necessary to measure blood pressure in both arms. The procedure is done twice with a time interval of about 2 minutes.
To get a complete clinical picture, the doctor conducts a diagnosis
Classification
It is important to know!
STILL STRUGGLE WITH ARTERIAL HYPERTENSION INCORRECTLY? The first bioavailable drug with proven effectiveness Read more »
Increased diastolic value in medicine is divided into 3 main degrees:
- In the first degree, patients' values will not exceed 99 mmHg. Art., fluctuate between 90-99. For older people, such pressure is considered normal as a result of natural aging and wear and tear of blood vessels, but for young people it is a reason for the development of arterial hypertension.
- At grade 2, the level will always be 100-109 mmHg. Art.
- Stage 3 pathology is characterized by a score of 110 or more.
If the diastolic value rises to 85 mmHg. Art., then doctors regard this as prehypertension. Patients need to undergo diagnostics and follow the doctor’s recommendations. The most common cause is atherosclerotic disease.
Secondary hypertension can appear as a result of diseases of internal organs and their dysfunction.
Depending on the pressure indicators, 3 stages are distinguished:
- Mild form - diastolic reading not higher than 114 mm Hg. Art. The heart and other organs are not affected.
- Severe form - the lower value rises to 124 mmHg. Art. The nervous system and eyes are most often affected, rarely the heart.
- Very severe form - lower value up to 130 mm Hg. Art., while the upper pressure can be 200 and higher. The heart and kidneys suffer.
To measure pressure correctly, you must follow some rules:
- Measurements are always taken in a sitting or lying position, in a calm state.
- The hand should lie flat and free.
- Irritating factors are excluded.
- A high-quality, working tonometer is used.
- The bottom of the cuff should be a couple of centimeters above the bend of the elbow.
- The air swings at 20 mmHg. Art. higher than the value at which the pulsation disappears.
After pumping up the air, you need to start deflating it and watch for shocks. They indicate pressure. The upper is determined during the first push, and thanks to the last, the lower is determined.
It is prohibited to take measurements after active exercise or running. In addition, the pressure may be 130 to 110 if measurements are taken immediately after consuming coffee, cigarettes or alcohol. For accuracy, you can take repeated measurements after about 5-10 minutes.
Causes of pressure 130 to 110
Reasons for diastolic pressure of 110 mm Hg. Art. different and among them the following are distinguished:
- The appearance of hypertension in the initial (primary) form.
- Atherosclerosis.
- Diseases of the kidneys and adrenal glands.
- Disorders of the thyroid gland.
- Diabetes.
- Previously suffered a heart attack.
- Heart diseases.
Most often, a pressure of 130 to 110 appears as a result of impaired cardiac function.
The causes of heart problems, both in the male and female half of the population, are hidden in lifestyle, which is not considered correct:
- Eating before bed.
- Overeating, resulting in excess weight.
- Frequent consumption of fats, carbohydrates and salt.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Bad habits.
- Regular stress.
- Strong physical and emotional stress.
Almost always, people who smoke develop hypertension, because tobacco smoke is poison for the body, especially for the heart and blood vessels. In some cases, the cause of pressure surges may be medications that are used to treat a particular disease. This manifestation refers to the side effects of the drug and after stopping their use the condition returns to normal.
Why does the diastolic indicator increase?
Medical experts identify the following, the most common causes of pressure 130 to 110:
- Presence of bad habits (smoking, alcohol abuse);
- Insufficient physical activity, sedentary, sedentary lifestyle;
- The habit of eating before going to bed;
- Frequent stressful situations and psycho-emotional shocks;
- Regular, increased stress (physical, mental, emotional);
- Overweight, obesity;
- Tendency to overeat;
- Improperly balanced diet (abuse of salt, foods high in animal fats and carbohydrates).
The following pathologies can provoke an increase in upper blood pressure in both men and women:
- Diseases of a cardiac nature;
- Atherosclerosis;
- Hypertonic disease;
- Diabetes;
- Pathologies of the renal apparatus;
- Disturbances in the functioning of the thyroid gland;
- Adrenal diseases
- The patient has a history of a previous heart attack.
Often the cause of an increase in blood pressure is smoking, which pathologically affects the function of the heart and blood vessels.
Sometimes the use of certain medications can provoke an increase in diastolic readings, but after stopping the medications, the patient’s condition stabilizes on its own and does not require additional treatment.
Cardiovascular diseases are usually accompanied by high blood pressure
Symptoms
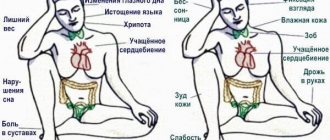
With high lower pressure, symptoms will not always be present; more precisely, it is difficult to determine, since they do not manifest themselves clearly. In addition, the signs may differ depending on the reasons for the increase in indicators.
Most often, attacks can be recognized by the following symptoms:
- Headache.
- Dizziness.
- Nausea.
- Vomit.
- Dyspnea.
- Heart rhythm disturbances.
- Increased pulsation.
- Increased sweating
- Deterioration of vision, loss of sharpness, appearance of “goosebumps” in the eyes.
With a constant pressure of 130 to 110, as well as shortness of breath, this often indicates the development of hypertension. At the very beginning of the development of the pathology, shortness of breath will occur only after exertion, but later it appears even in a calm state. With headaches, localization occurs in the occipital region, at this time there may be tinnitus, nausea, and after vomiting it becomes easier.
Patients have disturbed sleep and have difficulty falling asleep. If the problem is caused by heart pathologies, the patient experiences pain in the chest area, often similar to angina pectoris. In advanced forms, swelling appears and the limbs go numb.
What to do?
If the pressure rises due to a visible reason (workload, a cup of coffee, stress), rest in peace and quiet is enough for the situation to return to normal.
Symptomatic arterial hypertension is controlled by treatment of the underlying pathology. For this purpose, the following groups of drugs are used:
| Group of drugs | Mechanism of action |
| Diuretics: Furosemide, Indapamide, Hypothiazide, Triampur, Veroshpiron | Remove excess fluid from the body, balance the total volume of circulating blood, reducing the load on the heart and blood vessels |
| ACE inhibitors: Captopril, Enalapril, Perindopril, Prestarium | Affects an enzyme that contacts angiotensin, which affects blood pressure growth |
| Beta blockers: Atenolol, Bisoprolol, Metoprolol, Betaloc, Anaprilin | Able to inhibit the effect of adrenaline on special receptors that cause vasoconstriction, stimulate cardiac activity, indirectly increasing blood pressure |
| Calcium antagonists: Verapamil, Nifedipine, Diltiazem, Norvasc, Amlodipine, Lacidipine, Lecarnidipine | They inhibit the penetration of calcium ions through special calcium channels into the cells of the heart and blood vessels, leading to their expansion |
| Angiotensin-2 antagonists: Valsartan, Irbesartan, Candesartan, Losartan, Eprosartan | Block the action of angiotensin 2, which has a strong vasoconstrictor effect |
| Statins: Atorvastatin, Lovastatin, Simvastatin | Regulate lipid metabolism, prevent the deposition of atherosclerotic plaques that narrow the lumen of blood vessels |
| Sedatives: Novopassit, Afobazol, Persen | Relieve stress by indirectly lowering blood pressure |
| Antiplatelet agents: Aspirin, Thrombo-ASS, CardiAsk, Plidol, Trombopol | Block biochemical reactions leading to the formation of blood clots |
If lower blood pressure is elevated due to kidney disease (glomerulonephritis, for example), treatment includes taking antibiotics, steroids (Prednisolone), NSAIDs (Voltaren), and decongestants (Lasix).
Unlike ordinary hypertension, in the treatment of diastolic hypertension with indicators of 130/100-110, non-drug methods of therapy are often used:
- rejection of bad habits;
- weight control (body mass index - less than 25);
- dosed physical activity;
- a balanced diet (mandatory inclusion of seafood, replacing sugar with honey);
- eliminating stress;
- 8 hours sleep.
Sometimes a person has to change jobs to organize the correct work and rest schedule, and include daytime sleep in the daily routine. Hypertensive patients with high diastolic pressure need to relax at a resort at least once every two years.
Main danger
If no treatment is provided at a constant pressure of 130/110 mmHg. Art., then serious consequences and complications are possible. Against the background of this problem, hypertension develops and becomes more severe, when pressure levels increase significantly and hypertensive crises occur.
Complications also include:
- Heart attack.
- Stroke.
- Pulmonary edema.
- Aneurysms.
Most often, crises appear, but at a pressure of 130/110 mm Hg. Art. it's almost impossible. A crisis will occur if the systolic and diastolic values become extremely high, when organs cannot work normally and constant malfunctions occur in their work. There is no specific meaning for a crisis, each person has their own, so exclude the occurrence at 130/110 mm Hg. Art. no need.
Diagnostics
If your blood pressure is constantly high, regardless of the lower or upper value, you must undergo a medical examination.
The essence of this procedure is frequent measurement of pressure, questioning of the patient, percussion, as well as laboratory diagnostic methods:
- Ultrasound.
- ECG.
- Blood and urine tests.
- Other.
In the case of normal heart function, secondary hypertension is possible. Additional examinations of various organs will be required. During the initial visit to the doctor, the doctor takes measurements on both hands 2 times, with an interval of up to 2 minutes. If the data differs, the average value is displayed.
Drug treatment
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW!
STILL STRUGGLE WITH ARTERIAL HYPERTENSION INCORRECTLY? Reduces stress hormone levels and prevents oxygen starvation Read more »
To normalize lower pressure, as well as upper levels, doctors often use the following medications:
- AFP inhibitors – Captopril, Ecalapril.
- Beta blockers – Atenolol, Bisoprolol.
- Diuretics – Indapamide, Hypothiazide.
- Calcium antagonists – Verapamil, Nifedipine.
- Angiotensin-2 antagonists – Losartan.
If a patient is diagnosed with hypertension, then medications must be taken on an ongoing basis, every day, and pressure measurements must be taken additionally. If you stop taking medications quickly, there may be unpleasant consequences. In addition, statins and sedative medications can be added to the course of therapy.
In case of high diastolic pressure due to renal pathologies, doctors add antibiotics and steroids, anti-edema tablets to the course. In certain cases, the patient is hospitalized for stronger and more effective treatment.
Once diagnosed with persistent primary hypertension, people will need to take medications for life, since the disease cannot be completely cured. If you follow all the doctor’s recommendations, the prognosis will be favorable.
Causes of increased diastolic pressure
The diastolic indicator can increase up to 100-110 times: as a result of overexertion, atmospheric fluctuations, dehydration, or taking medications. But when the cause is eliminated, this pressure normalizes on its own.
If DBP is constantly fixed at a high level, then diastolic hypertension is diagnosed, the exact cause of which is still not clear. It is divided into primary (essential) and secondary (symptomatic), with different provoking factors.
| Causes of essential hypertension | Causes of secondary hypertension |
| Hormonal imbalance (menstruation, menopause, pregnancy, puberty) | Initial form of hypertension |
| Impaired reabsorption of salt in the kidneys (abuse of salts) | Atherosclerosis |
| High concentration of vasoconstrictor substances in the blood | Kidney disease, adrenal tumors |
| Overeating with the development of obesity | Thyroid dysfunction |
| Physical inactivity | Diabetes |
| Stress | Cardiovascular pathology |
| Emotional lability | Previous myocardial infarction |
| Bad habits | Pheochromocytoma is a tumor of chromaffin cells of the sympathoadrenal system |
Diastolic pressure usually fluctuates throughout the day, reaching a minimum when a person sleeps. But in patients suffering from diastolic hypertension, the lower reading may increase even during rest.