Blood pressure level is used to assess the condition of the entire cardiovascular system. On a par with heart rate, although for these elements they are not directly related to each other.
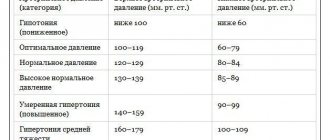
According to the World Health Organization, an indicator from 100 to 139 by 70-89 is considered adequate; this range already includes the individual working norm of a particular person, which can deviate by 10 mmHg, but no more.
Thus, a blood pressure of 150 over 90 is not considered normal; it is hypertension, although mild.
When assessing the general condition of the patient, it is necessary to consider the individual norm for blood pressure, which may be significantly lower. Thus, a hypotensive person will tolerate such a level much worse than a person with values close to the indicated indicators.
Regardless of the physiology, if a blood pressure level of 150 to 90 occurs, you need to be examined under the supervision of a cardiologist.
The condition corresponds to the first degree of hypertension, but can quickly progress, leading to incurability and fatal consequences.
Is 150/90 normal?
No, it can hardly be recognized as such. This is stage 1 headache. At this stage, instability of the tonometer reading occurs, that is, the pressure fluctuates and is not constantly high, which falsely reassures the patient and misleads him about his own health.
This is the best moment for diagnosis and therapy, since stages 2-3 are incurable and difficult to control, and also pose a high threat to the state of the cardiovascular, visual, and excretory systems (the so-called target organ damage within the framework of hypertension).
Everything can end disastrously for the patient: stroke, heart attack, loss of vision, problems with cardiac activity of a potentially fatal kind.
Are such indicators acceptable during pregnancy?
Gestation is generally considered an unpredictable process. While declaring that this is not a disease, doctors nevertheless try to treat such patients carefully.
The efforts of one obstetrician-gynecologist are not enough; depending on the nature of the problem, consultations with an endocrinologist, nephrologist, neurologist, phlebologist, and cardiologist are indicated.
A rise in blood pressure to 150 per 90 mmHg during pregnancy can be a normal physiological phenomenon, but it can be a herald of preeclampsia: a pathological dangerous jump in blood pressure to critical levels.
Determine in advance where and what is impossible: dynamic monitoring of a pregnant woman is necessary, preferably every month. If late toxicosis is suspected, hospitalization in a cardiology or gynecology hospital is mandatory (for preservation).
Symptoms of high blood pressure
High blood pressure is accompanied by symptoms, which, depending on the strength of their manifestation, may be a sign of a hypertensive crisis. This:
What does pressure 100 over 80 and pulse 100 mean?
- severe pain behind the sternum or in the heart area;
- throbbing or pressing headache that does not subside after taking your usual painkiller;
- heart rhythm disturbances - from bradycardia (pulse 60 or below) to tachycardia (pulse 100 or more);
- the appearance of tinnitus;
- dark spots before the eyes;
- dizziness;
- redness of the skin of the face and neck;
- increased sweating, accompanied by chills;
- dyspnea;
- swelling of the face, especially noticeable in the morning;
- feeling of severe weakness in the body;
- loss of coordination of movements;
- blurred vision;
- feeling of uncontrollable panic.
Important! If you notice one or more symptoms of the disease, you should not attribute them to banal overwork. Using a home blood pressure monitor, you can diagnose high blood pressure in time and take measures to lower it.
Reasons for high blood pressure
A significant level of blood pressure develops as a result of physiological, temporary factors or pathological processes of various kinds.
Natural moments
Not accompanied by severe symptoms. There may be isolated vegetative manifestations: sweating, shortness of breath, chills, palpitations. Possible reasons include:
- Intense physical activity. The more trained the human body, the more resistant it is to significant activity. Blood pressure increases slightly, and the same applies to the pulse rate. If an unprepared patient undertakes heavy exercise, nothing good can be expected. There is a clear correlation between blood pressure levels and exercise intensity. The proportionality is direct: the harder you work out, the higher the tonometer reading and the likelihood of complications right away.
- Changes in climatic conditions. Usually as a result of moving from a cold or mild region to a hot, humid one. The increased load on the cardiovascular system affects. In a healthy person, the adaptation period lasts up to 3-4 days, sometimes less.
- Abuse of caffeine the day before or on the same day. Tonic drinks are good for hypotensive patients, but such patients should know when to stop so as not to be trapped by their own body. The rule is: no more than 2 cups per day. Coffee is generally contraindicated for people with hypertension. It is better to replace it with high-quality granulated chicory.
- Excessive water consumption. You should not drink more than two liters a day. Especially if there are diseases of the excretory system. Such people should constantly consult a nephrologist or urologist regarding the regimen.
- Excess salt in the diet. For a healthy person, the figure is within 12 grams per day. For hypertensive patients - 3-7 g, no more. That’s why it’s so important to adjust your diet and give up semi-finished and canned foods: it’s impossible to control the amount of table salt, and the manufacturer either doesn’t write anything at all or outright lies.
These types of causes are distinguished by an important property: with the physiological origin of hypertension, there are no pronounced symptoms. The second significant feature is the short duration of the process, its instability.
Pathological factors
If the pressure rises to 150/90 mmHg. Art. - this is the result of the development of diseases in 60% of cases, which makes this group the most common among patients. What processes provoke hypertension and how to recognize them:
Hyperthyroidism
Excessive amounts of thyroid hormones in the bloodstream. It develops as a result of poor nutrition, tumors of the organ itself or the pituitary gland.
Symptoms make themselves known almost immediately: the voice changes, the relief of the neck changes, the eyes bulge, visually become larger, shortness of breath occurs, fatigue occurs, and performance decreases.
Body temperature stably and regularly rises to subfebrile levels (37-37.5). The pressure is also at a constantly high level. The attending physician is an endocrinologist.
Diabetes
It flows unpredictably even with a complex effect on the body. It hits all systems. Moderately elevated blood pressure may be an indication of a latent process. You need to be examined by an endocrinologist.
Hypercortisolism
Excess of corticosteroids and primarily cortisol. Produced by the adrenal glands. Accordingly, there is a tumor (pheochromocytoma, cancer) in the paired organ itself or the pituitary gland/hypothalamus/chiasmal-sellar region in general.
Clinically it takes the form of Itsenko-Cushing syndrome. The symptoms are typical: severe obesity, without changing the diet, lipid deposition on the face (moon), bone pain, weakness, shortness of breath, inability to perform even minimal physical activity. The doctor is again an endocrinologist.
Renal pathologies
Heterogeneous in character. They are similar in one way: the production of renin increases, which is an intermediate substance and is involved in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone exchange.
Hypertension of renal origin is persistent, pressure increases steadily even at the first stage, up to 150-153 per 90-95, but responds well to specific therapy.
Symptoms: lower back pain, increased daily urine volume, painful urge to visit the toilet, often false, when urine is not released at all or comes out drop by drop, nocturia, changes in the properties of liquid discharge. Treating doctors: neurologist or urologist.
Problems with CNS inhibition
As a result of osteochondrosis and vertebrobasilar insufficiency in the system. Symptoms: neck pain, dizziness, cephalgia, problems with vision, speech, fainting, disorientation in space. Specialist - neurologist.
Heart problems
Mitral valve stenosis, cardiosclerosis, insufficiency, ischemic heart disease, previous heart attack. They are characterized by arrhythmias, shortness of breath, chest pain and high blood pressure. Cardiologist.
Thus, the causes of pressure 150 to 90 are pathologies of the excretory system (kidneys), endocrine structures, cardiovascular diseases, natural physiological factors (less often).
Why does blood pressure rise?
A jump in blood pressure in people of any age can be triggered by physiological factors. The main reasons why the numbers on the tonometer increase and then fall without causing serious disruptions in the body: hypothermia, stress, overwork, consumption of certain foods and drinks, dehydration. It is dangerous when the pressure is 150 to 100 mm Hg. becomes a habitual condition, gradually disrupting the functioning of all organs and systems.
Factors for the development of hypertension are as follows:
- heredity (the tendency to cardiovascular diseases is often transmitted through the female line);
- obesity (every extra kilogram increases blood volume, increases its viscosity, and disrupts vascular tone);
- smoking;
- alcohol;
- abuse of fatty foods rich in animal fats, which contribute to the clogging of blood vessels with cholesterol plaques;
- excess salt in the diet;
- hormonal fluctuations (women often encounter high blood pressure for the first time during pregnancy or menopause, teenagers during a period of active growth);
- kidney and liver pathologies;
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels.
A sedentary lifestyle is one of the main reasons for the development of hypertension in young people
These factors over time cause disturbances in the functioning of the heart, which prevent it from working with proper efficiency, change the composition of the blood, cause the formation of cholesterol plaques, and reduce the elasticity of blood vessels.
Hypertension in men is mainly diagnosed at the age of 40-50 years. Women face this problem after 50 years of age, after menopause. However, the modern lifestyle makes its own adjustments. Constant stress, poor nutrition, and physical inactivity make both schoolchildren and students hypertensive.
What does a high or low heart rate indicate?
Not directly related to blood pressure levels. However, the following trends in the indirect effect of heart rate on blood pressure can be traced:
- Tachycardia increases the risk of fatal complications by 15%.
- An increase in heart rate is inherent in pathologies of the heart, kidneys and endocrine system. In neurological diseases and anemic processes, bradycardia often occurs.
These are general observations and do not claim to be the ultimate truth. You need to understand the problem on the spot, in detail.
Possible complications
Among the consequences:
- Stroke. Acute cerebrovascular accident such as malnutrition or rupture of a vessel with effusion of blood into the cerebral membranes. The second is much more dangerous, since another damaging factor arises: a hematoma, creating a mass effect (compression).
- Heart attack. Necrosis of the middle layer of the muscular structures of the heart. Functionally, it is the most active. At the end of the process, the working tissue is replaced by useless scar tissue. The development of organ dysfunction is likely; death without treatment occurs after 3-5 years as a result of a second heart attack.
- Blindness as a result of hemophthalmos and secondary retinal detachment.
- Pulmonary hypertension. Consequence of a long course of the disease. It consists of an increase in blood pressure in the corresponding artery.
- Kidney failure. Violation of excretory function, fluid filtration. Often ends with an even greater deterioration of the hypertensive process.
The risk of complications is 2-5% over a 10-year period. But the disease progresses quickly, which makes it dangerous. Treatment is needed. Hypotensive patients with a sharp increase in blood pressure have a worse prognosis.
How to reduce blood pressure at home?
First aid measures:
- Take the drug prescribed by your cardiologist in the recommended emergency dosage. If the patient has not yet visited a doctor, taking Captopril or Enalapril to reduce blood pressure by 150 to 90, half a tablet is enough. Sublingually (under the tongue) to achieve a quick effect. It is recommended to purchase these drugs for your home first aid kit.
- For heart pain or tachycardia, take Valocordin, Corvalol, Nitroglycerin (1 tablet), Validol (dissolve 1 tablet). Do not exceed dosage.
- Use a herbal sedative: motherwort or valerian, but not in an alcohol solution: they excite the nervous system. Filter bags or tablets are suitable.
- If available, drink an express decoction (prepared like regular tea) with mint, lemon, St. John's wort. Or chokeberry tincture (2 tablespoons 3 times a day).
- Lie down, calm down. Try to rest.
If blood pressure does not drop, repeat taking the medications. It's important not to overdo it.
Attention:
The maximum dosage for antihypertensive drugs is 1 tablet, for sedatives - 2 tablets, for chokeberry - 8 tablespoons per day.
If there is no effect, call an ambulance to resolve the issue of hospitalization or primary measures to relieve the condition.
Types and degrees of hypertension
Doctors divide arterial hypertension into 2 types - primary (essential) and secondary (symptomatic). In the first case, the disease is caused by factors not related to other organs and systems. Secondary hypertension is always associated with pathologies in the functioning of systems and organs that are involved in the regulation of blood pressure - kidneys, heart, lungs, central nervous system. In this case, it is important not only to reduce the pressure to a normal level, but to eliminate the disease that provoked the disorder.
If measures are not taken to eliminate the first manifestations of the disease, hypertension progresses, going through 4 stages of its development.
- Stage 1 hypertension - mild. The systolic value during attacks ranges from 140 to 159 mm Hg, the diastolic value is 90-99 mm Hg. At this stage, the disease is easily treatable by adjusting lifestyle, nutrition, daily routine, and eliminating risk factors. When blood pressure increases, it is recommended to take medications that can reduce the numbers on the tonometer to optimal levels. The attacks usually pass without consequences for the body, after which a long period of remission occurs.
- Stage 2 hypertension is called moderate. As the condition worsens, the pressure can rise to 179 to 109 mmHg. During the period of remission, the indicators do not return to values that are normal for the patient’s age. Constant blood pressure can remain at the level of 155-156 at 90-100 mm Hg, and may decrease slightly. The disease progresses rapidly, and the risk of complications increases, including death during a hypertensive crisis. At this stage, it is necessary to take extended-release tablets and follow all medical recommendations. Treatment does not always guarantee complete recovery. Restrictions and medication support become lifelong.
- Stages 3 and 4 of hypertension are severe and very severe. Pressure surges become maximum - 180/110 mm Hg. and above, the symptoms are strong and painful. At this stage of the disease, pathological changes in the functioning of the cardiovascular system and other organs and systems become irreversible. Treatment consists of constantly maintaining blood pressure close to normal levels. The patient loses his ability to work and is forced to take many supportive medications.
Important! If the pressure is 150 to 100 mm Hg. is constant, this may indicate a moderate stage of the disease. If such numbers appear on the tonometer monitor only during an attack, it means that the disease is at stage 1 and can be cured in a short time.
Symptoms that require you to see a doctor
The following changes in health should alert you:
- Headache. Localized in the back of the head, crown or covers the entire skull (is diffuse).
- Vertigo. The ground under your feet disappears, it is difficult to coordinate your movements, the world goes around in circles.
- Nausea, rarely vomiting. One-time or recurring. It has a reflex origin, therefore it does not bring relief from poisoning.
- Visual disturbances (floaters, photopsia, glare, blackouts, floating spots and lines). Hearing loss.
Especially dangerous are problems with speech, paralysis, paresis, muscle unruliness, severe chest pain, and facial distortions. In this case, you will need to call an ambulance. Emergency conditions are possible.
If the pressure rises to 150 to 90 and symptoms are present: headache, vertigo, problems with vision, coordination, hearing, etc. - this is a reason to see a doctor in itself.
Diagnosis and treatment
If the pressure is 150 to 100 mm Hg. has become habitual or rises to dangerous levels at the slightest load, it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive examination to identify the cause of the condition and eliminate it. The main diagnostic methods are as follows:
- measuring blood pressure in both arms;
- heart rate measurement (pulse 70-80-90 beats per minute is normal, below 60 is a symptom of bradycardia, above 100 is tachycardia);
- daily blood pressure monitoring;
- ECG;
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- Analysis of urine;
- checking blood sugar levels;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and heart;
- consultations with specialized specialists (ophthalmologist, endocrinologist, cardiologist).
Only after receiving all the examination data can the doctor draw conclusions about the type and stage of the disease, draw up a treatment regimen, and recommend what to take in the event of another pressure surge. Traditionally, to reduce blood pressure during treatment, drugs from the following pharmacological groups are prescribed:
- alpha blockers;
- beta blockers;
- ACE inhibitors;
- diuretics;
- calcium antagonists;
- angiotensin 2 antagonists.
Important! Only the attending physician can tell which medications will be effective in each specific case. You should not select a treatment regimen on your own, since most antihypertensive drugs cause adverse reactions in the body, which can worsen the patient’s condition and accelerate the development of the disease.
Take prescribed medications strictly according to the schedule. Most modern remedies are designed for one dose per day. You cannot reduce the dose on your own. Antihypertensive drugs can cause a “withdrawal syndrome,” which often leads to a sharp deterioration in well-being and a jump in blood pressure. It is also not recommended to increase the dosage without specific medical instructions. A sharp decrease in pressure will lead to an attack of hypotension. And this is not only a headache and weakness, but also fainting or collapse.
What examinations need to be completed?
Management of patients with arterial hypertension of unknown origin is the prerogative of a cardiologist. Other specialists are involved as needed.
The full range of events looks like this:
- Oral questioning, recording complaints, objectifying symptoms.
- Anamnesis collection, including clarification of family history and lifestyle.
- Measuring blood pressure using a mechanical or automatic device.
- Assessment of heart rate and tones during organ beating.
- Electrocardiography. Allows you to identify functional disorders. Requires decryption by an experienced specialist.
- Echocardiography. Ultrasound technique. With long-term hypertension, hypertrophy (thickening) of the ventricles is detected. This is GB's calling card.
- Daily monitoring. It is carried out to study blood pressure dynamics throughout the day, providing accurate information about the state of the patient’s cardiovascular system under normal conditions.
- Other methods: laboratory (blood and urine tests), electroencephalography, assessment of neurological status, ultrasound of the kidneys, abdominal organs, MRI of the brain, adrenal glands. Also angiography if necessary.
The whole process takes from 2 to 7 days. It happens faster in the hospital.
High blood pressure: diagnosis of causes
The disease we are going to talk about has many faces. High blood pressure and everything connected with it is the topic of our conversation today.
Why is high blood pressure so dangerous? Can you trust a tonometer? These and other questions are answered by the general practitioner, cardiologist at Clinic Expert Voronezh LLC, Angelina Anatolyevna Kalinina.
- Angelina Anatolyevna, there is a lot of controversy around high blood pressure. Russian and Western doctors give different numbers. Let's first define what we mean by high pressure? High – how much?
When talking about blood pressure, we use the concept of so-called “upper” (more correctly, systolic) and “lower” (diastolic) pressure. High blood pressure is a situation where the systolic pressure is 140 mmHg. and higher, and diastolic - 90 mmHg. and higher.
Classification also distinguishes such gradations of blood pressure as optimal (systolic less than 120 mmHg, diastolic - less than 80 mmHg, the lower limit of systolic blood pressure is approximately taken to be 110-115 mmHg, diastolic - 70-75 mmHg), normal (systolic - 120-129 mmHg, diastolic - 80-84 mmHg), high normal (systolic - 130-139 mmHg .art., diastolic - 85-89 mmHg).
- It is known that children have their own blood pressure standards for each age stage. Does blood pressure change with age in adults?
Today, medical opinions on this matter differ. The latest clinical recommendations say the following: if in elderly and senile people the systolic pressure is 140-150 mmHg. If you feel well, it is not necessary to strive to unconditionally reduce it below 140 mmHg. However, diastolic pressure should also not exceed 90 mmHg.
- They say that the tonometer can make mistakes. This is true?
This can often be heard, in particular, about electronic blood pressure monitors. Actually this is not true. If the device is working properly, it shows the correct blood pressure numbers. Another point is that these devices may be more sensitive to the conditions and rules for measuring blood pressure. For example, the position of the patient, his arms, and legs matters.
Ideally, half an hour before taking readings, a person should not eat, worry, exercise, or smoke.
If you have doubts, it is recommended to measure the pressure three times at 2-3 minute intervals, and take the average readings for the upper and lower pressure.
- You don’t always have a tonometer at hand. Therefore, it is important to know what symptoms indicate high blood pressure?
The question is very relevant because high blood pressure is not always accompanied by any symptoms.
Those who make complaints note such manifestations as headache, dizziness, nausea; “flickering of flies” before the eyes; blurred vision; feeling of heat, “hot flush”, sometimes chills; discomfort in the chest area; feeling of fear, anxiety, anxiety; urge to urinate. These are the most common symptoms.
- For what reasons does blood pressure increase in an adult?
This is a complex and, unfortunately, not fully explored issue. There are whole groups of diseases of the cardiovascular, endocrine, nervous systems, and kidneys, in which there is an increase in blood pressure. In these pathologies, the cause and mechanism of its increase are well studied. Arterial hypertension that occurs as part of any of these diseases is called symptomatic arterial hypertension.
Taking certain medications can also increase blood pressure.
Speaking about the well-known hypertension (or, in other words, essential arterial hypertension), it is difficult to clearly judge the reasons, since it is based on a whole complex of pathophysiological changes, the research of which continues to this day. If we talk about the factors contributing to the development of this type of hypertension, we can distinguish two groups. External factors include features of a person’s lifestyle, nutrition, bad habits, overweight or obesity, level of physical activity and stress. Internal factors include, for example, genetic predisposition. The combination of these factors leads to the development of hypertension.
- Angelina Anatolyevna, is high blood pressure always a sign of some kind of disease or can it be a random episode?
No, hypertension does not always indicate the presence of any pathology. The ICD even has such a concept as “increased blood pressure without hypertension.” For example, it may increase in response to physical activity and stress. However, it is recommended to take into account the range of such an increase: after certain numbers it is necessary to be observed by a doctor in order to prevent the development of hypertension in the future.
- And if the pressure fluctuates, sometimes high, sometimes low, what could be the reasons for this condition?
This manifestation is relatively common in young people, with increased anxiety and significant psycho-emotional stress. It is based on a disruption in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system, adaptation mechanisms with a defect in the neurohumoral regulation of the cardiovascular system.
- What actions can be taken urgently at home if a person’s blood pressure has increased?
The scope of first aid for high blood pressure should be determined by a doctor (including the ambulance team, if necessary). Firstly, medications to lower blood pressure may not be at hand, and secondly, you need to understand exactly what medications are required in this particular case and how to administer them. Only a doctor can answer these questions competently. As a last resort, until the doctors arrive, and the increase in blood pressure is accompanied by a feeling of fear, anxiety, anxiety, then if you have Valocordin or Corvalol at home, you can take one of these medications (of course, if they are tolerated).
It is necessary to calm the person down; it is better to give him a horizontal position. You can apply a cool towel to your face and forehead.
If we are talking about a patient already taking medications to lower blood pressure, you can take the usual drug in the dosage recommended in such situations by the attending physician.
-Which doctor should I contact with a high blood pressure problem and what diagnostics should I undergo?
Hypertension is treated all over the world by internists and general practitioners. In addition to them, in our country, cardiologists also deal with this disease.
In terms of examination, routine, additional and in-depth methods are distinguished.
The first group includes a complete blood count, a complete urinalysis, albumin in the urine, measurement of fasting blood glucose, total cholesterol, low- and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, triglycerides, creatinine with determination of the glomerular filtration rate, potassium and sodium in the serum, uric acid in serum, 12-lead ECG. Additional methods may include ultrasound of the heart and blood vessels, abdominal organs, kidneys, echocardiography, 24-hour blood pressure monitoring, Holter monitoring and some others.
-Does high blood pressure respond well to treatment? Is this problem curable?
If we are talking about essential arterial hypertension (hypertension), then there is no cure in the sense of “treated with a course and recovered” today. This disease requires continuous lifelong treatment.
But the level of development of modern medicine is already such that this pathology can be easily corrected. The answer to the question of how to reduce high blood pressure and keep it under control lies in the correct selection of medications and strict adherence to all recommendations of the attending physician.
- What preventative measures are needed to keep your blood pressure under control?
You should maintain normal body weight, get rid of bad habits (smoking, alcohol consumption), ensure regular adequate physical activity, eat right and limit your salt intake.
If a person already suffers from high blood pressure, then prevention includes proper self-monitoring, keeping a blood pressure diary, regularly taking prescribed medications, and monitoring with your doctor.
Other related articles:
What to do when the head is cast iron?
How to relieve tension headaches?
What should a child's blood pressure be?
For reference:
Kalinina Angelina Anatolevna
Graduate of the Voronezh State Medical Academy named after. Burdenko 2007.
In 2008, she completed an internship in the specialty “Therapy”.
In 2010, she underwent professional retraining in the specialty “General Medical Practice (Family Medicine)”, in 2017 - in the specialty “Cardiology”.
Since 2015, he has been working as a general practitioner at Clinic Expert Voronezh LLC.
Curation methods
Complex. Taking medications, lifestyle changes, surgical treatment (in extreme cases), and the use of herbal remedies are indicated.
Medicines
Prescribed in minimal dosages to assess the response of hypertension. The following medications are indicated:
- Calcium channel blockers. Do not allow element ions to penetrate blood vessels. Diltiazem and Verapamil.
- Herbal sedatives and tranquilizers (Motherwort, Valerian, Diazepam).
Somewhat less commonly prescribed:
- ACE inhibitors prevent the effect of angiotensin II on the body. It causes an increase in blood pressure. Production is reduced with the help of drugs, which makes vascular stenosis impossible. Names: Perineva, Perindopril, Prestarium.
- Adrenergic blockers (alpha and beta). Reduces the sensitivity of receptors to adrenaline, cortisol and other substances. Carvedilol, Anaprilin, Nebivolol.
Other drugs are rarely prescribed.
For endocrine disorders - replacement or corrective therapy.
Surgical intervention is required in extreme cases: atherosclerosis at an advanced stage, heart defects, rhythm disturbances with Morgagni-Adams-Stokes attacks, pathologies of the kidneys and arteries, tumors of the pituitary gland, adrenal glands, etc.
Phytomethods
Can only be used as an auxiliary method, and not to replace medications.
Recipes:
- Chamomile tea. 100 grams of crushed raw materials per 300 ml of water. Drink 2 glasses a day for a month.
- Chokeberry tincture. 200 grams per 500 ml of vodka or alcohol. Prepared for 21 days, use 2 tablespoons 3 times. Course - 30 days.
- A decoction of valerian, motherwort with mint and St. John's wort. Pour 100 grams of mixture with 300 ml of water. 2 r. per glass for 21 days.
Lifestyle change
The main method of correcting hypertension in the early stages. The following events are scheduled:
- Quitting smoking and alcohol.
- Normalization of physical activity (2-hour walks in the fresh air per day).
- Optimization of the drinking regime (1.5-1.8 liters).
- Sleep at least 8 hours.
The diet is also put in order.
| Consumption shown: | Waiver is required from: |
| Cereal porridge | Fatty meat. |
| Fermented milk products. | Muffins. |
| Eggs. | Coffee. |
| Butter, natural. | Tea. |
| Lean meat, protein. | Semi-finished products and canned food. |
| Natural sweets. | Chocolate. |
| Wholemeal bread, bran. | Spices. |
| Vegetables, fruits. | Salt in large quantities. |