Local therapist
Burnatskaya
Svetlana Nikolaevna
33 years of experience
Local therapist, occupational pathologist. Member of the Russian Scientific Medical Society of Therapists
Make an appointment
Dyspnea is the name given to visible disturbances in the depth and frequency of breathing in a person, accompanied by an obsessive feeling of lack of air. Shortness of breath can be observed after intense physical activity or in a state of absolute rest. In what cases is this the norm, and in what cases is it an alarming signal of a health threat?
Types of shortness of breath
In medicine, this problem has its own name - dyspnea. According to the international classification, the following types of shortness of breath are distinguished:
- bradypnea;
- tachypnea.
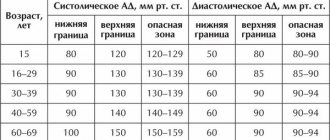
Bradypnea is a decrease in breathing with a slowdown in respiratory rate to 12 or less movements per minute. Tachypnea is an increase in shallow breathing with a frequency of more than 20 movements per minute.
Based on intensity and time interval, dyspnea is divided into types:
- chronic – observed for several years;
- acute – lasts from 2 minutes to several hours;
- subacute – from several hours to 2 days.
Most often, shortness of breath is observed in diseases of the respiratory (bronchopulmonary) and cardiovascular systems. These diseases are extremely life-threatening. Therefore, if you suspect shortness of breath, you should immediately consult a doctor to undergo examination and receive timely treatment.
Classification
Dyspnea can manifest itself in many diseases and pathological conditions, so to facilitate the diagnostic search it is necessary to accurately determine its type. The classification of the symptom is based on the mechanism of development, the degree of change in respiratory function, and the ratio of the inhalation-exhalation phases. There are physiological shortness of breath, when the frequency of inhalations and exhalations changes in proportion to physical activity, and pathological. Most often the symptom is classified in relation to the respiratory phases:
- Inspiratory dyspnea
. This type of disorder is manifested primarily by difficulty in the inhalation phase. Dyspnea is detected in diseases of the diaphragm and pleura, heart failure, and pulmonary fibrosis. Dyspnea in combination with noisy breathing is typical for pathologies of the trachea and large bronchi. - Expiratory dyspnea
. The symptom is usually observed when the patency of small bronchi and bronchioles is impaired, typical of bronchial asthma. Shortness of breath on exhalation also occurs with chronic obstructive bronchitis, pneumosclerosis, and decreased elasticity of the lung tissue as a result of emphysema. - Mixed dyspnea
. Respiratory failure in both phases often develops in severe stages of heart failure and progressive diseases of the respiratory system. This type of dyspnea can be associated with feverish conditions, pathologies of the central nervous system with direct irritation of the respiratory center.
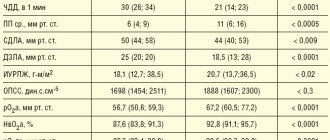
Taking into account changes in respiratory function, several types of shortness of breath are distinguished: tachypnea - an increase in the frequency of breaths more than 40 per minute, bradypnea - a decrease in respiratory movements less than 12 per minute, apnea - a sudden stop in breathing. There is a classification of the symptom according to the main mechanism of development: central dyspnea is observed with organic or functional changes in the functioning of the respiratory center in the medulla oblongata, the neurogenic version is associated with a weakening of inhibitory influences in the cerebral cortex, the hemic form develops with anemia.
Causes of shortness of breath
There can be quite a few reasons for shortness of breath. Among them:
- strong physical activity (sports, work);
- myocardial infarction, irregular heart rhythms, heart defects, myxomas, other heart problems;
- allergies, bronchial asthma, tuberculosis, emphysema, pneumothorax, pneumonia, pulmonary obstruction, cancer;
- vasculitis, primary type hypertension, aneurysm;
- myasthenia gravis, lateral sclerosis;
- ascites;
- uremia;
- anemia;
- pericardium;
- hyperventilation syndrome.
Symptoms
Symptoms of shortness of breath can be very different, but they are always characterized by changes and disturbances in respiratory activity. A person can breathe very quickly and shallowly, or he can take rare and very deep breaths. In both situations, he experiences an acute lack of air, a feeling of suffocation and chest compression.
With inspiratory dyspnea, it is difficult for the patient to take a breath. At the same time, he hears noise while trying to draw oxygen into his lungs. In the case of expiratory dyspnea, it is difficult to exhale, as the lumens of the bronchioles and bronchi begin to narrow.
In medical practice, there are cases of mixed dyspnea, the condition of which is the most dangerous for the body. It can lead to complete respiratory arrest and death.
Are you experiencing symptoms of shortness of breath?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Development mechanism
Shortness of breath is caused by a variety of complex reflex mechanisms involving higher nervous structures, so there are several theories of its development. Many doctors cite changes in oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the blood as the immediate cause of impaired breathing frequency and quality. An increase in the concentration of carbon dioxide, leading to a decrease in pH, has a significant stimulating effect on the bulbar centers, peripheral chemoreceptor zones of the arteries and central receptors located in the medulla oblongata.
At the same time, protective mechanisms are activated, the respiratory center of the brain stem sends activating impulses to the bronchopulmonary system, causing a pathological increase in breathing. The appearance of shortness of breath is associated with impulses from the fusiform nerve endings of the respiratory tract, which are activated as a result of various pathological processes. Sometimes increased work of the respiratory center is observed during descending cortical influences caused by hysterical or neurotic conditions.
The connection of the symptom with the temperature of the internal environment of the body has been proven. With hyperthermia, the sensitive areas of the respiratory center are washed with warmer blood, which causes their activation - so-called thermal shortness of breath occurs. A decrease in body temperature, on the contrary, leads to a decrease in respiratory movements. The development of dyspnea is influenced by the amount of muscle load and metabolic level. Most researchers believe that this mechanism is due to two types of reactions - slow humoral and fast neurogenic.
Subjective sensations in the form of lack of air and suffocation are primarily associated with the spread of excessive excitation from the centers of the medulla oblongata to the limbic structures and the cerebral cortex. This causes the appearance of negative emotional reactions of fear and anxiety in patients with shortness of breath. Sometimes unpleasant symptoms develop due to a discrepancy between the body's needs for ventilation and the functionality of the breathing apparatus to provide it.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of shortness of breath comes down primarily to assessing the general condition of the patient and collecting an anamnesis. Based on the current clinical picture, additional studies are prescribed:
- chest x-ray;
- MRI;
- urine and blood tests;
- Ultrasound of the heart;
- ECG;
- spirometry;
- Ultrasound of the neck.
The exact list of necessary diagnostic measures is prescribed by the doctor after consultation with the patient.
Shortness of breath as a result of a nervous disorder
Often shortness of breath can appear due to nervous shock. Experiences that make you nervous lead to chest pain, difficulty breathing and intestinal upset.
At the same time, experienced stress or prolonged depression can become a reason for further anxiety associated with the fear of suffocation. Shortness of breath that catches the patient in his sleep can cause nightmares and sensations as if someone heavy was sitting on top of his chest and trying to strangle him. With severe nervousness, a groan is observed that accompanies every breath. Shortness of breath of psychological etiology is called psychogenic. Such conditions need to be treated, starting with an examination of the nervous system and consultation with a psychotherapist.
Treatment of shortness of breath
Treatment for shortness of breath is selected depending on what root of the problem is discovered after diagnosis.
- If a foreign body is detected in the respiratory organs, surgical intervention is performed.
- For bronchial asthma, selective beta-agonists are used.
- For heart failure, diuretics, narcotic analgesics, and vasodilators are prescribed.
- If the cause is neurology, then the emphasis is on special breathing exercises.
- For obstructions, anxiolytics, respiratory support, oxygen administration and other measures are prescribed.
Preventing shortness of breath
Since shortness of breath is not an independent disease, but only a symptom, you must first take care of your heart and lungs. For this purpose, the following are recommended as preventive measures:
- stop smoking and drinking alcohol;
- monitor the daily routine (ensure a balance of work and rest, sound, standardized sleep);
- exclude heavy, fatty foods, fast food, carbonated and alcoholic drinks;
- reduce excessive physical activity;
- protect your nervous system from stress and anxiety.
Shortness of breath in people of different age categories
Shortness of breath can occur in people of all ages, from infants to the elderly.
In children, shortness of breath can be both physiological and pathological. The appearance of physiological shortness of breath is caused by physical exertion or high anxiety, which is considered normal. When the respiratory system is immature, pathological shortness of breath occurs in the infant. How to determine the type of shortness of breath and its causes is decided by the pediatrician, selecting the necessary diagnostic methods.
In old age, people's tolerance to physical activity decreases and the efficiency of the respiratory system decreases. Due to age-related changes, the physical strength of the respiratory muscles decreases, as a result of which gas exchange worsens and normal breathing becomes difficult. In addition, older people tend to have diseases of the cardiovascular system and lungs, which lead to shortness of breath. Most often, they do not pay attention to this symptom for a long time, so the diseases that accompany it are diagnosed at advanced stages. As a result, treatment becomes more difficult, the quality of life and its duration are significantly reduced. So it is better to immediately seek medical help if shortness of breath occurs in older people, without waiting for the condition to worsen.
The best pulmonologists in Moscow - Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Alexander Vyacheslavovich Averyanov, Candidate of Medical Sciences Alexander Evgenievich Shuganov are receiving appointments at the therapy center of the Yusupov Hospital. Klina is equipped with innovative high-tech equipment for conducting the most modern diagnostic studies. Thanks to an integrated approach involving specialized specialists in various fields, our doctors identify the exact cause of shortness of breath and select an effective treatment regimen, taking into account the individual characteristics of each patient.
FAQ
Which doctor should you contact if you notice signs of shortness of breath?
First of all, you need to make an appointment with a therapist. He will issue directions for primary tests and diagnostic studies. Based on the results obtained, it will become clear which specialist to refer the patient to. Most often, further treatment is carried out by cardiologists, pulmonologists and neurologists.
Can pregnant women experience shortness of breath? Is it dangerous for the fetus and mother?
Shortness of breath during pregnancy is observed quite often. This is due to constriction of the lungs by the diaphragm. The fetus is constantly growing, the load on the heart and lungs increases. Therefore, shortness of breath should not be considered a danger in this case. The normal respiratory rate in pregnant women is 22-24.
How to deal with systematic shortness of breath?
Of course, you need to understand the reasons for its appearance in the first place. If shortness of breath is not associated with serious illnesses, but is only a consequence of physical weakness of the body (perhaps after an injury or a long-term serious illness), then evening walks in the fresh air will help. You can get a dog, which will become an additional incentive for physical activity and walks.
general characteristics
Dyspnea is perceived by patients as a subjective feeling of lack of air, ineffectiveness of breathing movements, and tightness in the chest.
The symptom is accompanied by characteristic objective signs: increased or slower inhalations and exhalations, pallor or cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle, convulsive loud inhalation, suffocation. Often, to alleviate the condition, a person with dyspnea stops moving, takes a forced position - sits on a chair or bed, leans forward a little, leaning on straight arms. Most often, the appearance of shortness of breath is associated with physical exertion, and at the beginning of the disease the disorder is provoked only by significant activity, and as it progresses, patients feel a lack of air after normal activities. In addition to respiratory disorders, pathological symptoms are possible: pain and discomfort in the chest, headache, dizziness, decreased performance. If shortness of breath is observed when performing usual work or at rest, you should consult a specialist.