Causes
The reasons that lead to this phenomenon can be different - from infections and inflammations to allergic reactions. It can also be caused by a foreign body getting into the ear. Anemia, high blood pressure, and other illnesses (including something as serious as Meniere's disease, a swelling of the inside of the ear canal) can cause a person to experience a humming, buzzing, or squeaking sound. Also, similar sensations can be caused by the use of alcohol and drugs, large doses of caffeine and certain medications. Sometimes tinnitus can occur after stress or loud noise. Excessive earwax can also cause tinnitus.
Causes
Noise in the head appears against the background of the development of many diseases. In some cases, it is not a harbinger of any dangerous condition. Endogenous sounds appear as a result of contraction of muscles and ligaments, crunching of joints, and blood pulsation.
Objective noise occurs due to several reasons:
- neuromuscular;
- muscular-articular;
- vascular.
Tinnitus is the result of the development of the following pathologies:
- vascular atherosclerosis;
- hepatitis A;
- diabetes mellitus;
- hypoglycemia;
- hypo- and hyperthyroidism;
- diseases of the outer, middle, inner ear;
- sulfur plugs;
- otitis;
- otosclerosis;
- Meniere's disease;
- hearing loss;
- acoustic and barotrauma;
- malignant neoplasms of the cerebellopontine angle, brain;
- intoxication;
- pathologies of the cervical spine;
- psychoneurological diseases;
- chronic fatigue syndrome;
- stress.
Subjective noise in some cases is the result of industrial factors, exposure to a sharp loud sound.
Elderly people more often suffer from noise in the head due to cardiac dysfunction, high blood pressure, and age-related changes.
Symptoms of tinnitus
If a person experiences a buzzing, humming, ringing or squeaking sound, as well as hissing, whistling or clicking noises that have no actual sound source, then they may have a disorder called tinnitus. The strength of this noise may vary. Sounds may be felt in one ear or heard in both. Tinnitus may be accompanied by other symptoms, the most common of which are:
- Headache
- Severe weakness
- Confusion, dizziness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Increased body temperature
- Discharge from the ears and discomfort in them
- Sudden changes in blood pressure
Which doctor treats
Since noise in the head is a symptom of ear diseases, as well as neurological pathologies, if an unpleasant symptom appears, you should contact an otolaryngologist or neurologist.
Why suffer from noise in your head if you can turn to a specialist at the Kuntsevo Medical and Rehabilitation Center to solve the problem?
IMPORTANT! You should not self-medicate, because noise in the head is a neurological symptom that may indicate the development of serious pathologies.
Our neurologist and otolaryngologist will conduct a detailed study of the causes of the symptom and indicate a direct path to solving the problem and getting rid of noise in the head. You just need to make an appointment with our doctor, who will not only help you get rid of the symptom, but will also describe a detailed course of rehabilitation.
Sign up
Treatment for tinnitus
As soon as the diagnosis is made, treatment must begin immediately. Lack of proper treatment for this disease can have a serious impact on the patient's life. The constant unpleasant sounds that he experiences interfere with normal sleep and rest, prevent him from working, lead to a state of constant stress and can even cause depression.
After a medical examination, treatment for the disorder (or underlying disease) is prescribed. Usually, in order to eliminate the symptoms, it is enough to take special medications that eliminate inflammation. But sometimes surgery may be required if a specialist deems it necessary.
If this disorder is not treated, the consequences can be very tragic - tumors and infections can lead to complete hearing loss and other serious disorders. It is important that the patient does not self-medicate, but consults a specialist in connection with tinnitus.
Why "Movement"
- The clinic is located in the Vyborg district of St. Petersburg, near the Ozerki metro station.
- Reception is carried out by qualified doctors who have many years of experience in treating various neurological diseases and problems of the musculoskeletal system.
- Comprehensive treatment programs developed by our specialists, in the vast majority of cases, make it possible to avoid surgical intervention even in very complex clinical situations.
- Prices for medical services are affordable.
Our specialists
Tarasova Svetlana Vitalievna
Expert No. 1 in the treatment of headaches and migraines. Head of the Center for the Treatment of Pain and Multiple Sclerosis.
Somnologist.
Epileptologist. Botulinum therapist. The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Physiotherapist. Doctor of Medical Sciences.
Experience: 23 years.Derevianko Leonid Sergeevich
Head of the Center for Diagnostics and Treatment of Sleep Disorders.
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Vertebrologist. Somnologist. Epileptologist. Botulinum therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 23 years.
Palagin Maxim Anatolievich
The doctor is a neurologist. Somnologist. Epileptologist. Botulinum therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 6 years.
Zhuravleva Nadezhda Vladimirovna
Head of the center for diagnosis and treatment of myasthenia gravis.
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Physiotherapist. Experience: 16 years.
Mizonov Sergey Vladimirovich
The doctor is a neurologist. Chiropractor. Osteopath. Physiotherapist. Experience: 8 years.
Bezgina Elena Vladimirovna
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Botulinum therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 24 years.
Drozdova Lyubov Vladimirovna
The doctor is a neurologist. Vertebroneurologist. Ozone therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 17 years.
Dyachenko Ksenia Vasilievna
Head of the center for the treatment of dizziness and balance disorders.
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category.
Angioneurologist. Neurorehabilitation specialist. Physiotherapist. Candidate of Medical Sciences.
Experience: 19 years.Volkova Svetlana Anatolevna
Head of the Center for Parkinsonism and Extrapyramidal Diseases.
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Epileptologist. Ozone therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 26 years.
Take a hearing test online
What does a hearing test tell you?
An online hearing test allows you to quickly and easily determine your hearing status. In just 3 minutes you can determine its spiciness. The result of the hearing test is called an “audiogram” and is an indication for doctor’s prescriptions.
We suggest the following hearing tests: signs of hearing loss; online frequency hearing test; hearing test in noise; speech recognition; modeling signs of hearing loss.
Take a hearing test
Causes of tinnitus
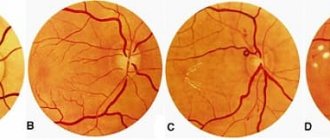
Key research findings interpret tinnitus as a disorder of auditory processing function. Tinnitus can be caused in many places in our peripheral and central auditory processing systems. Often these are changes in the inner ear, resulting in tinnitus as a neurophysiological reaction, and symptoms of altered hearing perception. (Fig. 3).
If we are talking about temporary (reversible) damage to some part of the auditory pathway, then the effect of tinnitus often disappears after a noise pause. If hearing loss persists, tinnitus often remains.
There are various molecular biological models for the occurrence of tinnitus. One form is tinnitus transduction (lesion on the left). These are thin elementary threads (connections) that mechanically connect stereotypes to each other and open or close transduction channels at the top of stereotypes. Damage to the left, for example due to noise, leads to permanently open transductive channels. Constant polarization occurs and intracellular calcium concentration increases. The consequence of this is prolonged constant concentration with a decrease in cochlear amplifier function and deformation of the organ of Corti, which may play a role in the occurrence of hearing impairment (eg, hyperacusis) and the appearance of tinnitus.
Alterations in auditory input due to hearing loss result in hyperactivity in the auditory pathway and the neural correlate of tinnitus. The altered spontaneous activity irritates the auditory system, and tinnitus is perceived in the auditory cortex as an abnormal pattern, as a consequence of processes of reorganization of the central auditory system. These processes are probably facilitated by the increased number of neurons involved, which increase exponentially from the auditory organ (3,500) to the auditory plug (100,000) and synchronize and amplify the effect.
So, tinnitus arises as a perceptual phenomenon always in the auditory plug. This knowledge is very important for therapeutic use, since all auditory psychosomatic centers are connected in the brain. The perception of tinnitus is controlled through the central nervous system and emotionally assessed through the limbic system. From this comes the individual burden of tinnitus in the patient.
McKenna's model describes the relationships between tinnitus, its severity, and the patient's physical and emotional response (Figures 4–7).
This model implies three significant points regarding tinnitus:
- reducing negative thoughts;
- reduction in the response of the autonomic nervous system;
- change in conscious perception of tinnitus.
Classification and its significance for acoustic hearing support
The concept of tinnitus is a figurative expression; it does not say anything about the cause of the disease, its treatment and consequences. The word Tinnitus comes from the Latin word “tinnire”, meaning “to sound”. Having tinnitus means hearing noise without an external sound source. In the diagnosis of tinnitus, it is first determined whether it is an objective or materialized tinnitus, and thus the treatment method is determined. The incidence of objective tinnitus is very rare (0.01%).
Subjective tinnitus is the most often overtly occurring form. In this case, it is impossible to determine the place of origin of tinnitus. Typically, the deciding factor for therapy is how well the patient can cope with their tinnitus, as well as how much they suffer from it.
The chosen treatment concept traditionally depends on the tinnitus condition. Thus, it is determined whether we are talking about tinnitus without hearing loss or with hearing loss. If you have existing hearing loss, it is very important to understand whether this loss can be compensated for. Often we are talking about minor or moderate hearing loss. If the auditory perception is completely normal, then tinnitus can be considered as a consequence of general irritation, as improper processing in the auditory tube.
Acute or chronic tinnitus
If the perception of tinnitus continues for up to three months, then it is said to be acute tinnitus. Acute, new-onset tinnitus is often spontaneous and disappears after appropriate therapy or simply rest. If tinnitus persists for more than three months, then we are talking about chronic tinnitus. Both conditions require action.
Thus, during the acute phase, the patient usually undergoes treatment by an otolaryngologist. In most cases, therapy is prescribed to promote blood circulation. Unfortunately, there is no clear evidence to support the effectiveness of these measures.
In the chronic stage, the most realistic goal is to get used to the tinnitus. Treatment from a medical point of view can be excluded. All measures focus on reducing tension (burdening).
Why are sick people often irritable?
People with tinnitus in the first stage of occurrence are often irritated, restless, and frightened, because they do not understand what is happening and cannot obtain complete and objective information about this condition. People despair even more when they hear a specialist’s phrase: “Unfortunately, we can’t do anything here, you have to live with it.”
The specialist needs to explain the cause of tinnitus in order to reduce the patient’s fears and doubts. In this case, it is very important to eliminate the negative thoughts that arise.
Material taken from Hörakustik magazine, No. 12 2021.
Conclusion
Tinnitus is an auditory phenomenon that occurs as a result of dysfunction of the inner ear and the central portions of the auditory pathway.
In rare cases, tinnitus is caused by objective reasons. The severity and severity of tinnitus depends less on the site of excitation (auditory pathway) than on the site of treatment. All load amplification factors that arise after this are combined in the upper cycle.
Primarily, the autonomic nervous system is responsible for controlling perception, the limbic system as the center of emotional evaluation, and the amygdala as the “fear center.” This functional connection controls the tinnitus phenomenon, maintains it and also intensifies or weakens it. Stress and similar illnesses affect whether a patient experiences tinnitus or not.
Read also
Fainting
Attacks of dizziness and fainting are pathological conditions that occur when the body overreacts to certain triggers, such as extreme emotional...
Read more
Benign positional paroxysmal vertigo
How great it is when you feel dizzy with happiness, but unfortunately there are people who are afraid of this symptom because this symptom greatly interferes with their quality of life. Dizziness is not a diagnosis, it is a symptom...
More details
Meniere's disease
Meniere's disease is a disease in which the leading symptoms are systemic dizziness, accompanied by hearing loss, a feeling of fullness and tinnitus. Paroxysmal dizziness,…
More details
Vestibular paroxysmia
Attacks of systemic dizziness lasting several seconds, less often minutes, and are accompanied in most cases by tinnitus and hearing loss. Seizures often occur during hyperventilation...
More details
Cerebellar ataxia
Cerebellar ataxia is a syndrome associated with damage to the cerebellum and its connections in the brain stem. Cerebellar ataxia is a frequently encountered symptom complex in the population. The reasons for the occurrence...
More details
Fainting
VSD with syncope (fainting) also refers to paroxysmal manifestations. This is a neurogenic type of VSD, the main role in the development of which is played by a sharp decrease in blood pressure. Short-term loss of consciousness is more often observed in young people with increased emotional lability. Fainting occurs under the influence of a specific factor (uncomfortable environment, change in ambient temperature, etc.). An attack is usually caused by the same factor, which is individual for each patient.
Often before an attack, the patient’s ears become blocked due to VSD. Presyncope with VSD can also be accompanied by suffocation, rapid heartbeat, and dizziness. Fainting is a particularly dangerous condition because a fall can cause serious injury. Therefore, VSD with this type of attack requires careful monitoring.