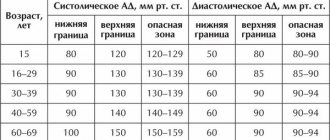
One of the first places in the world is occupied by mortality from cardiovascular diseases. Vascular diseases, blockage of arteries and veins negatively affect the functioning of all organs of the body.
Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood throughout the body. With the bloodstream, the necessary vitamins, hormones, and nutrients are carried to every part of the human body. Healthy blood vessels have smooth inner walls, and blood flows smoothly through them.
What is vascular blockage?
Blockage of blood vessels occurs due to various factors:
- thrombosis;
- injuries;
- the appearance of atherosclerotic plaques on the walls.
A thrombus is a blood clot that forms as a result of damage to the inner wall of an artery. The plaque is formed from substances circulating in the blood: calcium, cholesterol, fibrin. The body evaluates this formation as a defect and the process of thrombus formation begins. Unlike arterial thrombosis, venous thrombosis is not characterized by cholesterol deposition.
As deposits build up in the arteries, a condition called atherosclerosis occurs. This condition leads to narrowing and hardening of blood vessels.
Risk factors contributing to vascular blockage:
- increased cholesterol levels;
- high blood pressure;
- diabetes;
- smoking;
- obesity;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- genetic predisposition.
Symptoms of vascular blockage
Often, poor arterial patency does not cause any pain until a serious complication such as a stroke develops.
In other cases, especially when more than half of the artery is blocked, symptoms such as:
- discomfort, chest pain;
- severe shortness of breath;
- rapid heartbeat;
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- weakness;
- sweating
Due to a decrease in blood flow to the heart, chest pain (angina) appears, then coronary heart disease develops.
Peripheral artery blockage can cause:
- Leg pain.
- Poor healing of foot injuries.
- Gangrene.
If there is obstruction of the cerebral vessels, a person experiences headaches, constant or periodic, increased blood pressure, dizziness, vomiting, and unclear consciousness.
Consequences of the disease
Depending on the location of the damaged vessel, various complications arise. With obstruction in the extremities, nagging pain in the legs first appears, then trophic ulcers and tissue necrosis. Amputation is indicated, otherwise gangrene may develop. With prolonged ischemia of the heart vessels, myocardial infarction occurs. Long-term obstruction of blood vessels in the brain causes a stroke.
Classification
There are several stages of damage to the coronary arteries:
- Initial. At this stage, there is a slowdown in blood flow and the appearance of microcracks in the vascular endothelium. Such changes lead to lipid deposition and the formation of greasy stains.
- Average. As the pathology develops, clear plaques are already observed. Blood clots may also form. Their danger is that they can come off and close the lumen of the artery.
- Heavy. At this stage, the plaques thicken as calcium salts are deposited in them. Therefore, the coronary artery is deformed, and its lumen narrows.
Diagnostics
If poor patency of arteries and veins is suspected, the following studies are performed:
- Cholesterol analysis.
- Chest X-ray.
- CT scan.
- Ultrasound.
- Echocardiogram.
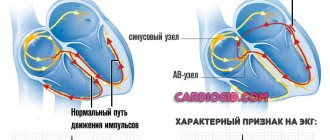
- ECG.
- MRI scan.
- Angiogram.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses magnets and radio waves to produce images inside the body without a surgical incision. Unlike CT scans, MRIs do not use ionizing radiation. This is considered a safer alternative.
Symptoms
Symptoms of coronary artery disease may vary from case to case. It is also not uncommon for patients to feel nothing strange about their condition until one day, for example, a myocardial infarction occurs.
Among the most characteristic symptoms of coronary insufficiency are:
Angina pain is a pressing, squeezing, burning pain behind the sternum lasting up to 10 minutes. Often appear during physical activity. May begin behind the sternum and then spread to the neck, back, shoulders, arms, jaws;
- Dizziness;
- Cold sweat;
- Pain in the stomach;
- Shortness of breath, especially with exertion;
- Sleep disorders;
- Weakness.
Important! If you notice such symptoms, especially against the background of unusual physical activity, you should immediately call an ambulance. This should also be done if angina has already been diagnosed, but the symptoms are not relieved by nitroglycerin and last longer than 15 minutes.
Source: Pavel Danilyuk: Pexels
The listed symptoms are characteristic of a chronic (reversible) version of coronary insufficiency, which manifests itself as angina pectoris. In the acute (irreversible) version, the described symptoms are more pronounced and last much longer - up to several days (with myocardial infarction). The pain is not relieved by nitroglycerin and can be so severe that it is necessary to resort to narcotic drugs.
Despite the fact that the main symptom of a heart attack is most often severe chest pain (80% of cases), there are other manifestations of the disease:
- Cough and shortness of breath;
- Sharp pain in the upper abdomen;
- Symptoms of brain damage.
An asymptomatic form of myocardial infarction is rare. The area of damage in the heart is not so extensive, and changes are recorded instrumentally after the fact.
Treatment of vascular blockages
There are many options for preventing and treating blood clots. Depending on the severity of the condition and the patient's medical history, the doctor prescribes various methods.
Disease prevention:
Quitting bad habits, urgent lifestyle changes:
- a diet low in saturated fat and cholesterol, less sugar and simple carbohydrates, and high in fruits and vegetables;
- body weight loss;
- ban on smoking and alcohol;
- fitness classes;
- minimizing stress;
- lowering blood pressure and cholesterol using folk remedies;
- maintaining low blood sugar levels by avoiding large amounts of sweets, jam, and sweets.
Drug treatment
Some medications help prevent clogged arteries, such as:
- cholesterol-lowering medications;
- drugs that lower blood pressure;
- blood thinners, which reduce the chance of dangerous blood clots.
Surgical intervention.
In the later stages of the disease, drug measures do not help improve the situation and then surgical procedures are used:
Stenting
A small tube called a stent is placed in the artery to maintain good blood flow. A catheter is inserted through an artery in the leg to reach the heart, and a stent is inserted through the catheter into the area of the blockage.
Coronary artery bypass grafting
In this surgery, arteries from other parts of the body are moved to the site of blocked arteries to help the blood reach its target destination.
Balloon angioplasty
A device is used that pushes the plaque towards the side walls of the arteries, resulting in the opening of the vessel lumen.
But in advanced cases, especially when the vessels of the legs are damaged, it is not possible to save the limbs, amputation is indicated.
Disease prevention
Like any other disease, it is easier to prevent than to treat.
General preventive measures include:
- Elimination of existing risk factors for the development of atherosclerosis.
- Prevention of any foot injuries.
- Preventive and hygienic foot care.
- Wearing comfortable shoes.
Patients with various pathologies of the cardiovascular system require systematic courses of therapy.
If an obstruction has already been detected, reconstructive surgery should be performed as soon as possible. It will allow you to save the limb. By using the help of specialists, you can significantly improve the quality of your life.
Important! Any prevention will be effective if you carry it out under the constant supervision of your doctor. Often a whole group of specialists (surgeons, therapists, cardiologists, phlebologists) is involved in the manipulations.
Sudden coronary death
Sudden coronary death (SCD) is said to occur when a person dies within no more than 6 hours against the background of apparent well-being due to a cardinal malfunction of the heart. At the same time, the patient loses consciousness and falls.
As a rule, the immediate cause of VCS is ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation. These are severe rhythm disturbances in which the efficiency of myocardial contraction decreases so much that blood does not flow to vital organs in sufficient volume.
WHO recommends at least 150 minutes of physical activity per week to help reduce the risk of VCS. Source: Mario Ohibsky from Pixabay
However, these arrhythmias are most often preceded by a severe attack of acute coronary insufficiency. Extensive myocardial damage as a result of this attack not only in itself reduces the contractility of the ventricles of the heart, but also contributes to the occurrence of arrhythmias.
Sometimes death can be prevented with timely assistance, but this is more typical for sudden cardiac death of an arrhythmogenic nature. In this case, the developing arrhythmia is of paramount importance, and coronary causes are secondary. Patients with diabetes are at increased risk of VCS.
Important! If you see a person suddenly lose consciousness, you should call an ambulance and, if you have the appropriate skills, perform primary resuscitation measures. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation should be resorted to if you do not detect a pulse and/or breathing in the victim.
Despite this threat in patients with coronary insufficiency, with well-chosen treatment and strict adherence to doctor’s orders, the likelihood of VCS becomes significantly lower. It is also important to seek medical help in a timely manner. It is known that several weeks before an attack, patients sometimes complain of pain in the chest, worsening mood, and fatigue. This means that some treatment measures can be taken before an attack occurs.
Atherosclerosis of the cerebral arteries
When cholesterol plaques form and the arteries of the brain narrow, the brain cells experience a lack of blood and nutrients. The following symptoms may indicate this condition:
- periodic dizziness,
- noise in ears,
- headache,
- increased fatigue,
- disturbances in coordination of movements.
The narrowing of the main carotid artery supplying the brain is identified as a separate diagnosis - carotid artery stenosis. Damage to the vessels supplying the brain carries the threat of a serious disease - ischemic stroke of the brain.
Frequently asked questions from our patients on the Internet about deep vein thrombosis
How to understand that there are blood clots in the veins?
Only a specialist, phlebologist or vascular surgeon can reliably understand that there are blood clots in the veins. And even a specialized specialist will need instrumental support and ultrasound examination of blood vessels. You can assume that you have blood clots in your veins based on the following signs:
- Edema.
- Blueness of the skin.
- Soreness, swelling of tissues, redness of the skin along the veins.
If there are blood clots in the veins, how to recognize them, symptoms and treatment?
Blood clots in veins can be recognized using duplex ultrasound scanning. The presence of blood clots in the veins is indicated by the following symptoms: swelling, pain, discoloration of the limb. The best option for diagnosis, as well as subsequent treatment, is to contact a good phlebological center.
How to recognize a blood clot on the leg?
In order to recognize a blood clot on the leg, you must seek professional medical help. As an option, do an ultrasound examination of the vessels of the lower limb. The best solution would be to consult a specialist, a phlebologist.
How to identify blood clots in the legs?
From the point of view of modern diagnostics, the best way to determine blood clots in the legs is ultrasound examination of the vessels of the lower extremities.
A blood clot in a vein, how does it form?
A blood clot in a vein is formed as a result of a complex chain of biochemical reactions, during which a network of insoluble fibrin molecules is formed from fibrinogen molecules. Blood cells are fixed in the latter, creating a dense intravascular structure, which is a thrombus.
How to identify a blood clot?
A thrombus can be detected using various methods, such as computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and good ultrasound. The latter method has the best price-quality ratio and is the gold standard for diagnosing thrombosis.
Chronic form
A typical manifestation of chronic coronary insufficiency is angina. Most often it is caused by atherosclerotic damage to the coronary arteries of the heart, which causes a narrowing of their lumen. During physical activity, the myocardium requires more blood, while the permeability of the artery is reduced - ischemia occurs with characteristic symptoms.
When attacks are predictable and repeated in response to a load of the same severity, they speak of a stable version of angina. Its course is relatively favorable and can be easily controlled. There are other options:
- Unstable angina is a form of angina in which a plaque in a coronary vessel undergoes ulceration, a thrombus gradually grows in the lumen, causing attacks to constantly progress and ultimately lead to myocardial infarction.
- Prinzmetal's angina (vasospastic angina) - occurs as a result of a sudden spasm of the coronary arteries.
We wrote about angina in more detail here.
Until this point, we were talking mostly about absolute coronary insufficiency, when the direct cause of the pathological condition was pathological processes in the coronary vessels. But there is also a relative form that occurs against the background of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, which was discussed in the causes of coronary insufficiency. During this process, the myocardium increases in size due to the increased load, while new vessels do not appear. In this case, ischemia of poorly supplied areas also develops.
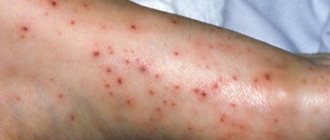
Deep vein thrombosis with varicose veins
Very often, deep vein thrombosis becomes a complication of varicose veins.
Deep vein thrombosis is often a complication of varicose veins
The severity of the disease will depend on the location of the blood clot and its size. If there is no complete blockage of the vessel, there may be no symptoms of the disease.