Medical editor: Strokina O.A. - therapist, functional diagnostics doctor. November, 2021.
Early ventricular repolarization syndrome (EVRS) is a medical concept that includes only ECG changes without characteristic external symptoms. It is believed that SRRS is a normal variant and does not pose a threat to the patient’s life.
However, recently this syndrome has become viewed with caution. It is quite widespread and occurs in 2-8% of cases in healthy people. The older a person gets, the less likely it is that he or she will have SRR; this is due to the emergence of other cardiac problems that are similar in electrocardiographic signs as they age.
Most often, early ventricular repolarization syndrome is diagnosed in young men who are actively involved in sports, in men who lead a sedentary lifestyle, and in people with dark skin (Africans, Asians and Hispanics).
Causes
The exact causes of SRS have not been established to date. However, a number of factors have been identified that contribute to the occurrence of repolarization syndrome:
- taking certain medications, such as α2-agonists (clonidine);
- familial hyperlipidemia (high blood fats);
- connective tissue dysplasia (symptoms are more often found in people with SRGC: joint hypermobility, spider fingers, mitral valve prolapse);
- hypertrophic cardiomyopathies.
In addition, this anomaly is often diagnosed in people with congenital and acquired heart defects and in the presence of congenital pathology of the cardiac conduction system.
The genetic nature of the disease cannot be ruled out either (there are certain genes that are responsible for the occurrence of SRGC).
Main causes of pathology
What exactly causes the disturbance in myocardial repolarization is not precisely determined today. Numerous studies have identified several reasons that can cause changes in myocardial repolarization processes:
- the presence of diseases of the heart muscle, in particular overstrain of ventricular tissue, ischemia, electrolyte imbalance, hypertrophy;
- negative effects of medications when taken uncontrolled;
- increased levels of hormones (adrenaline and norepinephrine) and the sensitivity of heart tissue to them;
- nonspecific reasons. Stress, strong physical activity, general changes in hormonal levels.
Important! This pathology is increasingly being diagnosed in children and adolescents, especially during phases of active growth. In addition, it is often found in pregnant women.
Kinds
There are two options for SRR:
- without damage to the cardiovascular and other systems;
- involving the cardiovascular and other systems.
From the point of view of the nature of the course, a distinction is made between transient and permanent SRGC.
Based on the localization of ECG signs, doctor A.M. Skorobogaty proposed the following classification:
- Type 1 – with a predominance of signs in leads V1-V2;
- Type 2 – with a predominance in leads V4-V6;
- Type 3 (intermediate) – without a predominance of signs in any leads.
T wave on an ECG - norm and pathology
Positive, negative and biphasic T waves on the ECG The T wave reflects on the ECG the process of repolarization of the ventricular myocardium. Depending on the summing vector, it can be positive, negative or biphasic. But besides the vector, its amplitude and morphological shape are also important, we’ll talk about this a little further.
In most leads where there is a high R wave, the T wave is also positive. In this case, the largest R wave corresponds to the largest T wave in amplitude, and vice versa.
- the T wave is always positive in leads I, II, aVF, V3-V6.
- The T wave can be positive, biphasic or negative. in leads III, aVL and V1-V2
- The T wave is always negative in lead aVR
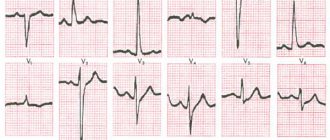
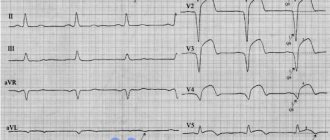
Example ECG No. 1 - Normal variant
Variant of a normal ECG with a negative T wave in leads V1-V2
Example ECG No. 2 - Normal variant
Example of a normal ECG with a negative T wave in lead III. Perhaps it would be more accurate to say that the tooth is two-phase. Note that in the enhanced lead AVF the T wave is positive! as it should be normally
Example ECG No. 3 - Pathological ECG
There are negative T waves in leads V5-V6, which may indicate a previous infarction, although this finding is not specific.
Example ECG No. 4 - Pathological ECG
In leads V3-V4, the T waves are clearly negative, which is not normal. In leads V5-V6, the first phase of the wave is positive, and the second is negative - this is a two-phase or bi-phase T wave, which in these leads is also pathological
Example ECG No. 5 - Pathological ECG
There is a pathological, negative T wave in leads III and AVF.
In addition to the polarity, the T wave has several other important characteristics, such as shape and amplitude, but this article does not set itself the task of covering all the nuances, but only to learn how to find the pathological T wave.
Nevertheless, we will look at several examples of ECGs that every doctor should remember. We are talking about hyperkalemia. There is no high-quality ECG in the archive for this coin, so this recording was borrowed from another resource.
Example ECG No. 6 - Hyperkalemia
Pay attention to the special shape of the T waves. For example, in leads V2, V3, I. The T waves are tall with a sharp apex, if you see an ECG like this, then it is worth checking the level of potassium in the blood - this may be an emergency condition.
If you find any error, please select a piece of text and press “ Ctrl+Enter”
Signs of SRS
There are no characteristic clinical signs of early ventricular repolarization syndrome. There are only specific changes on the ECG:
- ST segment and T wave changes;
- in a number of branches, the ST segment rises above the isoline by 1-2-3 mm;
- often ST segment elevation begins after the notch;
- the ST segment has a rounded shape and directly passes into a tall positive T-wave;
- the convexity of the ST segment is directed downwards;
- The base of the T wave is wide.
Possibilities of Holter monitoring in detecting myocardial ischemia.
Akselrod A.S., Head of the Department of Functional Diagnostics
To the Cardiology Clinic of MMA named after. THEM. Sechenov
Today, the screening method for detecting myocardial ischemia is still the stress ECG test. However, one can find conflicting publications about the capabilities of Holter monitoring in the diagnosis of coronary artery disease, with most authors pointing to the low (from 10 to 50%) sensitivity of this method. Therefore, discussion of the place of Holter monitoring in the algorithm for verifying coronary artery disease seems to be a relevant topic in practical cardiology.
Advantages and disadvantages of Holter monitoring compared to stress testing.
In the publications mentioned above, most authors use two- and three-channel 24-hour ECG recorders. Of course, the sensitivity of the method will be much higher when using a twelve-channel recorder, although, of course, none of the Holter recorders can replace the stress test as a screening method.
These two research methods have one thing in common: ECG dynamics over time. In all other respects they are fundamentally different. At the same time, Holter monitoring has three fundamental disadvantages compared to stress testing:
- during Holter monitoring, the patient himself chooses the load mode, so submaximal heart rate is often not achieved;
- the load is not of a continuously increasing nature;
- the loading regime cannot be immediately controlled by a doctor (only retrospective analysis is possible).
However, Holter monitoring has a number of advantages in detecting myocardial ischemia both compared to standard resting ECG and compared to stress tests. These benefits include:
- the possibility of natural modeling (by collecting anamnesis, you can simulate almost any situation typical for a patient that provokes an ischemic attack);
- the ability to establish a clear cause-and-effect relationship between the attack and the conditions of its occurrence (the diary is used to compare the patient’s activity with the time of the onset and end of the ischemic episode);
- detection of silent myocardial ischemia, especially at night;
- assessment of the effectiveness of antianginal therapy depending on the time of day and the possibility of more precise therapeutic correction taking into account other changes (for example, rhythm disturbances and cardiac conduction).
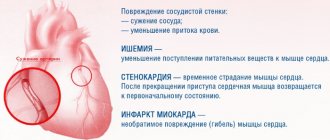
Myocardial ischemia is a situation of insufficient blood supply to the myocardium with two different outcomes: subsequent restoration of metabolism in cardiomyocytes (a disturbance in the repolarization process occurs and the dynamics of the T wave is recorded) or the progressive development of damage to muscle fibers (manifested by certain forms of ST segment displacement above or below the isoline). With further deterioration of the blood supply to the heart, irreversible damage to a larger number of myocardiocytes occurs, the development of inflammation and necrosis. In this case, pronounced dynamics of the ST segment and a change in the QRS complex are noted.
During Holter monitoring, you can clearly see the first two outcomes of coronary insufficiency, which will be discussed in this lecture.
Diagnostics
Since this syndrome is an electrocardiographic phenomenon, it can only be established with a certain examination:
- ECG;
- Ultrasound of the heart (echocardiography): stress echocardiography (for impaired ventricular contractility)
- resting echocardiography;
In addition, tests are carried out on a bicycle ergometer or treadmill: after physical activity, the heart rate increases, and the ECG signs of SIRS disappear.
A potassium test is used: after taking potassium chloride, panangin or rhythmocor at least 2 grams, the severity of ECG signs of repolarization syndrome increases.
A test with isoproterenol and atropine is not used due to severe side effects.
It is important to distinguish between SRR and myocardial infarction, pericarditis, Brugada syndrome. For this purpose, differential diagnosis is carried out.
Symptoms of the disease
In most cases, failure of the repolarization processes of the heart muscle does not have pronounced symptoms. Often, pathology is recorded accidentally during routine examinations or during examinations to confirm another diagnosis - during a graphic recording of heart function (ECG).
If disruption of repolarization processes occurs in the entire myocardium, i.e. diffusely, it provokes a change in blood circulation, which affects the general condition of the body. In this case, symptoms appear that are also characteristic of any other cardiac pathologies:
- change in heart rate;
- chest pain;
- change in emotional state (tearfulness, excessive irritability);
- increased fatigue.
In addition, there are signs that reflect the area of the heart muscle where repolarization processes are disrupted. In particular, repolarization of the left ventricular myocardium is accompanied by a disruption of the heart rhythm.
call me back
A form of this disease, which is often recorded in young people, is the syndrome of early repolarization of the myocardial ventricles. Today it is considered only as an electrocardiographic concept that does not affect the functioning of the heart.
Interesting! This phenomenon, according to statistics, is recorded in 8% of people, most of whom are in excellent health and regularly engage in sports.
Treatment of early ventricular repolarization syndrome
Repolarization syndrome does not require specific treatment. The only thing that is offered to the patient is observation by a cardiologist.
However, a person with SRS should avoid alcohol consumption and intense physical activity to avoid triggering an attack of tachycardia.
In some cases, radiofrequency ablation of an additional beam is performed in an invasive way (a catheter is brought to the site of the beam and destroys it).
Sometimes energotropic therapy (B vitamins, carnitine, phosphorus and magnesium preparations, Mexidol, Kudesan), antiarrhythmic drugs (amiodarone) are used.
Important! The patient should retain all previous ECGs, which is required to exclude the diagnosis of myocardial infarction if heart pain occurs.
How is the pathological process treated?
Violation of myocardial repolarization, the treatment of which completely depends on the root cause of the disease and is aimed at eliminating it, is often considered as normal variants, especially in young people. For people over the age of 50, this pathology, in combination with complaints about the functioning of the heart muscle and a corresponding medical history, may be a manifestation of hypertension or coronary artery disease.
If the exact causes of disturbances in repolarization processes in the heart have not been established, then complex therapy is carried out with the following drugs:
- vitamin complexes that will provide the cardiovascular system with the necessary microelements and vitamins, thereby supporting its full functioning;
- cocarboxylase hydrochloride, which helps restore carbohydrate metabolism and heart function, as well as normalizes trophic processes in the peripheral and central nervous system;
- corticotropic hormones, the active ingredient of which is cortisone. Its main function is to stimulate the synthesis of carbohydrates from proteins, which is necessary for the normal functioning of the body as a whole;
- Panangin or anaprilin, which belong to the group of drugs β-blockers. They are used to treat this disease extremely rarely, only in cases where there is a real threat to the patient’s health.
The selection of drugs and their dosage for each patient is made individually, after a detailed study of the results of tests and examinations.