Some people sometimes have a question: how to deceive an ECG? Moreover, some want to achieve a good conclusion in order to get a job, while others, on the contrary, want to make things worse so as not to serve in the army. There are other reasons that prompt a person to deliberately deceive not only the doctor, but also the diagnostic apparatus. Naturally, if you do not follow the doctor’s recommendations for preparing for the procedure, then the results obtained can be distorted, but will this help achieve your goal? And is it possible to simulate angina pectoris, arrhythmia, RGC syndrome and other diseases on an ECG?
Application area
Due to its accessibility, harmlessness, and lack of discomfort, ECG is suitable for examining all categories of the population: pregnant, lactating women, children, elderly people, and seriously ill patients. Using the procedure you can:
- determine the frequency and regularity of heart contractions;
- detect acute or chronic myocardial damage (ischemia, infarction);
- identify disturbances in electrolyte metabolism and intracardiac conduction;
- assess the physical condition of the organ;
- detect signs of non-cardiac diseases (for example, pulmonary embolism).
The ECG diagnostic method has no analogues. In combination with other necessary tests, it makes it possible to quickly and objectively make a diagnosis and select appropriate treatment, including surgical intervention.
Heart organ norms
All basic values are included in this table and mean normal indicators for a healthy person. If minor deviations from the norm occur, then this does not indicate pathology. The reasons for small changes in the heart do not always depend on the functionality of the organ.
How to decipher a cardiogram yourself
Everyone wants to decipher a cardiogram before even reaching the attending doctor’s office.
But in order to read it, you need to know the basic structure of the heart organ and its operating principle. The heart consists of 4 chambers - these are 2 atrium chambers: left and right, as well as 2 ventricular chambers: left ventricle and right.
The main task of the organ is performed by the ventricles. The chambers of the heart have partitions between them that are relatively thin.
The left side of the organ and its right side also differ from each other and have their own functional responsibilities.
The load on the right side of the heart and on its left side is also different.
The right ventricle performs the function of providing biological fluid - pulmonary blood flow, and this is a less energy-consuming load than the function of the left ventricle to push blood flow into the large blood flow system.
The left-sided ventricle is more developed than its right neighbor, but it also suffers much more often. But regardless of the degree of load, the left side of the organ and the right side must work harmoniously and rhythmically.
The structure of the heart does not have a uniform structure. It contains elements that are capable of contracting - this is the myocardium, and elements that are irreducible.
The irreducible elements of the heart include:
- Nerve fibers;
- Arteries;
- valves;
- Fatty fiber.
All these elements differ in the electrical conductivity of the impulse and the response to it.
Types of ECG of the heart
There are several types of ECG of the heart, thanks to which you can evaluate the work of the heart muscle in various conditions and conditions.
Classical electrocardiography
It takes 5-10 minutes and allows you to study the condition of the heart at the time of the procedure. It is used to determine the size of the chambers, heart rate, conductivity of the heart muscle, and evaluate the blood supply to the myocardium at rest. However, many cardiac pathologies appear only during sleep or physical activity, so it is extremely difficult to identify them during a short visit to a cardiologist.
Holter monitoring (Holter ECG)
A complex, in-depth study that provides continuous recording of cardiac muscle parameters for 24-72 hours or up to 10 days (if necessary). Recording is carried out with a special device that is carried with you on a belt or belt. Electrodes are attached to the surface of the skin in certain places. After which the person leads a normal life (works, walks). At the same time, he notes in a notebook when he experiences pain in the heart area, takes medications, and begins active physical activity. The data obtained is reviewed and corrected by the doctor, after which he draws conclusions and prescribes treatment.
Interesting! There are portable devices that are implanted under the skin near the heart to record information throughout the year.
Reading results
After the result of studying the cardiac organ is obtained, it is deciphered.
The result of an electrocardiographic study includes several components:
- Segments - ST, as well as QRST and TP - is the distance that is marked between teeth located nearby;
- Teeth - R, QS, T, P - these are angles that have an acute shape and also have a downward direction;
- The PQ interval is a gap that includes teeth and segments. The intervals include the time period of passage of the impulse from the ventricles to the atrium chamber.
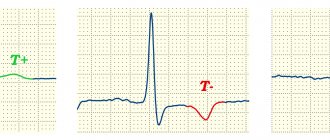
The waves on the electrocardiogram recording are designated by the letters: P, Q, R, S, T, U.
Each letter of the teeth is a position in the parts of the heart organ:
- P - depolarity of the atria of the myocardium;
- QRS - ventricular depolarity;
- T - ventricular repolarization;
- The U wave , which is mild, indicates the process of repolarization of areas of the ventricular conduction system.
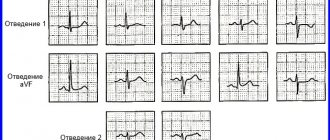
The paths along which the discharges move are indicated on the 12-lead cardiogram. When deciphering, you need to know which leads are responsible for what.
Standard leads:
- 1 - first lead;
- 2 - second:
- 3 - third;
- AVL is analogous to lead No. 1;
- AVF is analogous to lead No. 3;
- AVR - display in mirror format of all three leads.
Thoracic leads (these are points that are located on the left side of the sternum in the area of the heart organ):
The value of each lead records the course of an electrical impulse through a specific location in the cardiac organ.
Thanks to each lead, the following information can be recorded:
- The cardiac axis is designated - this is when the electrical axis of the organ is combined with the anatomical cardiac axis (clear boundaries of the location of the heart in the sternum are indicated);
- The structure of the walls of the atrium and ventricular chambers, as well as their thickness;
- The nature and strength of blood flow in the myocardium;
- The sinus rhythm is determined and whether there are any interruptions in the sinus node;
- Are there any deviations in the parameters of the passage of impulses along the wire pathways of the organ?
Based on the results of the analysis, the cardiologist can see the strength of excitation of the myocardium and determine the time period during which systole passes.
Photo gallery: Indicators of segments and scars
In what cases is an ECG prescribed?
A routine examination is indicated for all patients admitted to the hospital department. Unscheduled and emergency electrocardiography is carried out in case of development or suspicion of myocardial damage of any nature (toxic, inflammatory, ischemic).
Direct indications for an ECG are:
- metabolic syndrome;
- heartbeat instability;
- chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- circulatory disorders;
- changes in myocardial structure;
- endocrine diseases;
- rheumatism;
- monitoring the operation of the pacemaker;
- chronic respiratory pathologies;
- preparation for surgery.
Medical indications for an ECG are:
- periodic pain in the chest, back, neck;
- shortness of breath and difficulty breathing both at rest and after physical exertion;
- high blood pressure;
- swelling of the lower extremities, constant weakness, fainting;
- previous stroke/myocardial infarction;
- age over 40 years (annually).
Pregnant women undergo electrocardiography upon registration, as well as in the presence of alarming symptoms (fainting, dizziness, changes in blood pressure).
An ECG is sometimes recommended in the following situations:
- medical examination (admission to kindergarten, school, secondary and higher educational institutions);
- preventive examination;
- before the driver's license test;
- issuing a certificate for visiting the pool and practicing active sports;
- registration for sanatorium treatment.
The procedure has no contraindications, except for patients with chest deformation, purulent wounds and inflammatory diseases of the skin in the thoracic area.
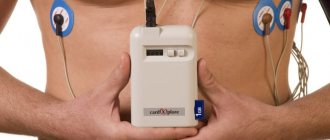
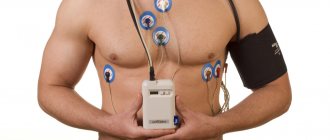
Holter
A holter is attached to the patient, most often on a belt, in a special case and electrodes are applied.
Doctors often use the phrase “hang a holter” or “do a holter,” meaning that the device will be used for 24 hours, on an outpatient basis, in the patient’s usual living conditions - at home, at work, during night sleep. Patients are asked not to wet the device, but otherwise lead their usual lifestyle.
This process of taking readings is called Holter monitoring, named after the American research scientist Norman J. Holter, who first used this technique in 1961.
Why do you need a holter?
It would seem, why do you need a Holter if you can just go to the doctor and take an ECG? Often, people with heart health problems experience the following situation: they have complaints, but they arise when it is not possible to immediately see a doctor - in the evening, at night, during some events.
The next day the person goes to the clinic, an ECG is taken, but no abnormalities are found.
Why might this happen? Because a standard electrocardiogram is a record, like a “snapshot,” that records cardiac activity over a short period of time.
A regular ECG records only a few myocardial contractions: from three to twenty, depending on the cardiograph used for this purpose.
Whereas the heart contracts about 100 thousand times per day! Holter records an ECG throughout the day, and not a single heartbeat during this period will go unnoticed by the device, because the electrocardiogram is recorded continuously. Holter makes available for analysis that information about the patient's heart health that cannot be obtained during a short visit to the doctor, and this is the most important diagnostic value of this device.
Then the holter is removed from the patient, and with the help of a special computer program that processes the data obtained, all types of heart rhythm disturbances, painless and painful attacks of myocardial ischemia, etc. are identified and analyzed.
Holter is a device that allows both accurate diagnosis of heart disease and helps to treat cardiovascular diseases - hypertension, atherosclerosis, heart attack, myocarditis - much more effectively.
24-hour monitoring, which Holter proposed, is a procedure that identifies almost all possible cardiac abnormalities that appear during the day, which cannot be done using other methods of cardiac diagnostics currently used.
Holter monitoring is a simple and safe procedure. In order to carry it out, two visits to the doctor will be required. On the first visit, the holter is programmed and installed on the patient; this procedure takes no more than a quarter of an hour. In a day, the holter will need to be removed and its records analyzed.
These actions usually take the doctor about half an hour or an hour - in more complex cases. Modern clinics often offer Holter monitoring at the patient’s home: all necessary visits are made by the doctor himself.
This is certainly very convenient, especially if the study is required by an elderly, sedentary person.
How to deceive Holter?
Very often, patients of military age try to deceive the holter by running tirelessly up the stairs and bringing themselves to complete exhaustion, imitating tachycardia. But I hasten to disappoint those who came here in the hope of learning how to deceive Holter - Meditech 24-hour blood pressure and ECG monitors are equipped with special sensors that, together with an experienced doctor, always recognize malingerers.
When is a halter needed?
Holter monitoring may be indicated for a patient if:
- there are complaints resulting from heart rhythm disturbances (palpitations, dizziness, loss of consciousness);
- diagnosis of coronary heart disease is required;
- it is necessary to preventively monitor patients with threatening ischemia and arrhythmias;
- it is necessary to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment;
- “white coat” hypertension is present;
- arterial hypertension has been detected for the first time, and the heart needs to be examined in order to decide whether to begin drug therapy;
- the fact of chronic constitutional hypotension was revealed;
- Moderate to severe hypertension, resistant to previous treatment, was diagnosed.
In addition, it is advisable to use a Holter if the patient has congenital heart defects, both unoperated and operated, or if he has suffered a myocardial infarction; to evaluate the performance of a pacemaker; in all cases of acute and chronic heart failure. A Holter monitoring procedure would be useful for people who are overweight (obese) or have diseases of the endocrine system.
How to prepare for Holter monitoring?
If the patient is to wear a halter, then during the 24 hours during which the study will be carried out, he must live his normal life - work, relax, meet people, and perform his usual physical activities.
Some doctors, when installing a holter for their patients, ask them to keep an activity diary during the 24-hour examination. This diary should record everything that affects cardiac activity: sleep, medication, movements, etc. This is not always necessary.
Firstly, because constant attention to the process on the part of the patient can affect the reliability of the result (the person will only think about what the Holter shows in the event of one or another action).
And, secondly, a modern holter can have a built-in sensor that records the patient’s physical activity, from which it is possible to determine at what moment the patient was sleeping and at what point, for example, he was running in the park. During the analysis, these points are clarified.
Modern Holter records not only an electrocardiogram, but also performs actigraphy (this is the recording of the patient’s physical activity) and monitors blood pressure.
The software, which is used to analyze the parameters recorded by Holter, allows you to effectively and quickly identify both heart rhythm disturbances and obtain a clear picture of how the autonomic nervous system regulates the functioning of the heart.
During Holter monitoring, no special actions need to be taken. You just need to remember that a holter is a complex, expensive electronic device, and your attitude towards it should be appropriate. This means:
- The halter should not be wetted - take a bath, shower, or swim in open water with it;
- Do not expose the holter to low or high temperatures (for example, do not go to the bathhouse on the day of the test);
- The device must be protected from shock and vibration. It is advisable to avoid contact with aggressive household chemicals, especially those containing acids, during Holter monitoring.
In addition, heavy, prolonged physical activity is very undesirable, since, firstly, it can distort the results of the study, and secondly, due to increased sweat, the electrodes may come off.
A patient wearing a halter is advised not to be near transformer booths or powerful power lines. And also come close to working electrical household and medical equipment.
During the examination, it is better to give preference to cotton underwear and avoid wearing clothes made of synthetic and silk fabrics, which can accumulate static electricity.
Holter is a medical device with which 24-hour monitoring of heart activity is carried out - an important and serious study, the relevance of which is undeniable these days.
Source: https://formed.ru/glossary/holter/
How to prepare for the procedure, how it is carried out, who does the decoding
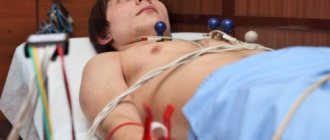
Electrocardiography does not require special preparation. The patient can undergo examination at any time. Before visiting the functional diagnostics office, you need to take care of your appearance, since you will have to expose your chest, forearms and shins, to which the electrodes are attached.
Important! Before the examination, it is not recommended to overeat, smoke, worry, go to the gym or run, drink alcohol, coffee, or energy drinks.
Taking an ECG looks like this: the patient removes the necessary areas of the body from clothing and lies down on the couch. The doctor or nurse degreases the skin with a special product (or water) so that the “suction cups” have better contact with the body, applies electrodes, turns on the device and makes a recording. With the results obtained and a preliminary transcript, the patient is sent to the attending physician.