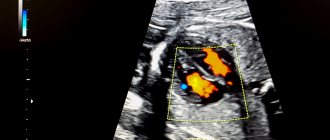
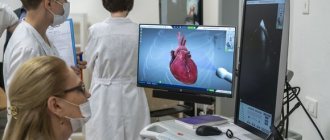
Cardiac echocardiography is an effective technique for visualizing the structures of the heart and heart valve to identify pathological functional and morphological changes. Diagnostics with ultrasonic waves helps to evaluate the functioning of the organ over time, to see on the display the contraction of the heart muscle and the functioning of the valve. Ultrasound examination is possible at any age: the technology is non-invasive, safe, and has virtually no contraindications. In addition, the method is informative and allows you to get results in just a few minutes.
What can and cannot be done before a cardiac ultrasound and how to prepare for an adult
No special preparation required. It is enough to approach the procedure in a normal state. In practice, this means that before an ultrasound of the heart at home you cannot:
- Smoking. You must stop smoking at least 3 hours before the test.
- Drinking alcohol. It is advisable to give up alcoholic drinks at least 24 hours in advance.
- Worry. Try to spend the previous day as relaxed as possible.
- Do gymnastics immediately before the procedure. Spend a few hours in peace.
Is it possible to eat before a cardiac ultrasound? Yes. You can eat before the test, but it is advisable to avoid overeating, which can overload the body and affect your well-being.
Preparation for cardiac ultrasound is no different for men and women, but the results will be different, since the norms of the sexes differ.
Carrying out an ultrasound examination
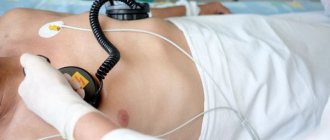
During a cardiac ultrasound, the patient lies quietly on the couch. Special sensors are placed on the chest, with their help the condition and functioning of the blood vessels and parts of the heart are assessed. Cardiac muscle contractions are also assessed. The duration of the study is about 20 minutes. The obtained data is stored in the clinic database.
Immediately before the procedure, the doctor should check your pulse and blood pressure. The gel that lubricates the body can be easily removed with a napkin. The gel ensures close contact between the sensor and the surface of the skin, otherwise the remaining air will degrade the quality of the image obtained on the monitor.
Preparation for echocardiography of the heart when diagnosing the condition of the internal organ after exercise
In rare cases, it becomes necessary to determine the condition of the heart muscle during and after exercise. This procedure is most often prescribed to athletes to determine the optimal training regimen. The test can also be prescribed to people with cardiac pathologies, for example, coronary heart disease, to make a diagnosis in the early stages.
In this case, special preparation for echocardiographic examination is also not required. The procedure itself is most often performed using an exercise bike. The doctor takes data during and after exercise.
Indications for use
Typically, cardiovascular diseases do not manifest themselves clearly and can “masquerade” as other diseases, so doctors prescribe an ultrasound of the heart
even with dizziness, excessive sweating and shortness of breath. What an ultrasound of the heart shows can clarify the clinical picture of identified vascular diseases.
Aortic diseases
The aorta is the largest artery that begins from the left ventricle of the heart, therefore, with ultrasound of the heart, which shows the condition of the aorta, diseases such as atherosclerosis and aortic aneurysm, as well as its dissection and occlusion, can be monitored. Since ultrasound of the heart can be performed frequently in an adult, this is one of the most accessible research methods.
Hypertonic disease
Hypertension affects the condition of all blood vessels, so periodic studies with interpretation of ultrasound of the heart are necessary for the doctor to adjust treatment, depending on the patient’s condition. Common consequences of hypertension are coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction, aortic aneurysm, etc.
Myocardial infarction
Ultrasound of the heart shows what is happening to the myocardium as well. The procedure is carried out in a standard manner. Interpretation of the results of cardiac ultrasound during myocardial infarction allows us to identify the focus and degree of myocardial necrosis, as well as its contractility. Also, ultrasound of the heart reveals a pre-infarction state, thereby preventing an attack.
IHD
Coronary heart disease (CHD) is one of the most formidable and serious, and therefore its many symptoms cannot be detected except by ultrasound of the heart. This is the fastest and most effective way. The most effective method to determine IHD is a stress test, as a result of which numerous symptoms of the disease appear.
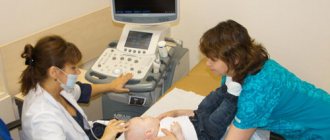
How to prepare for an ultrasound of a child's heart
Children, like adults, do not require special preparation. It is enough to feed the baby so that he behaves calmly during the procedure. It is allowed and even desirable to carry out the procedure during sleep. Before rocking the baby to sleep, you need to put on a vest that allows access to the body from the front.
How to prepare for cardiac echocardiography if your baby is not feeling well
If the diagnosis is scheduled for hours when the baby is not sleeping, or it was not possible to put him to sleep, you need to prepare a pacifier or bottle with food to distract the child from the doctor’s manipulations. During the echocardiography, he will not experience any unpleasant sensations; only the presence and touch of a stranger can confuse or cause tears. Therefore, equipment may be required to distract from the frightening factor.
Ultrasound of the prostate gland - Preparation
This study, or TRUS as it is also called, is performed through the rectum. Therefore, it will need to be cleaned. This is done as follows. A couple of hours before the start of the study, the patient is given a microenema. Its volume is 200 ml. To do this, take plain water and use a special bulb to inject it into the rectum. The patient empties within a few minutes. It is necessary to fill the bladder by taking liquid an hour before the procedure. If the patient is unable to tolerate it, you can go to the toilet. But then you will need to drink some liquid again.
Ultrasound cost
| Duplex study of the arteries of the upper or lower extremities | 3000 | rub |
| Duplex examination of the veins of the upper or lower extremities | 3000 | rub |
| Duplex examination of veins and arteries of the lower extremities | 4900 | rub |
| Duplex examination of veins and arteries of the upper extremities | 4900 | rub |
| Duplex examination of the portal system | 3500 | rub |
| Duplex scanning of brachiocephalic and transcranial vessels | 5200 | rub |
| Duplex scanning of brachiocephalic vessels | 3000 | rub |
| Duplex scanning of hemorrhoids | 1900 | rub |
| Duplex scanning of the renal arteries | 3100 | rub |
| Comprehensive examination of the gastrointestinal tract (ultrasound) | 5200 | rub |
| Neurosonography | 3100 | rub |
| Stress echocardiography | 4200 | rub |
| Transcranial duplex scanning of blood vessels | 3100 | rub |
| TRUS of the prostate gland + bladder + scrotum (without CD) | 3400 | rub |
| TRUS of the prostate gland + bladder + scrotum (with color circulation) | 3600 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity (to exclude free fluid) | 1600 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal aorta | 3000 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the maxillary sinuses | 1900 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the eyeball and paraorbital space with color circulation | 1900 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the stomach | 1650 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the gallbladder | 1600 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the retroperitoneum | 2200 | rub |
| Ultrasound examination of the salivary glands | 1800 | rub |
| Ultrasound examination of gallbladder function (before food load and after 30-40 minutes) | 1800 | rub |
| Ultrasound of complex MPS in women TA, without CDK (kidneys, ureters, bladder) | 2800 | rub |
| Ultrasound of complex MPS in women with TA with CD (kidneys, ureters, bladder) | 2900 | rub |
| Ultrasound of complex MPS in men TA without CDK (kidneys, ureters, bladder, residual urine, prostate gland) | 3500 | rub |
| Ultrasound of complex MPS in men TA and TRUS without color circulation (kidneys, ureters, bladder, residual urine, prostate gland) | 3800 | rub |
| Ultrasound of complex MPS in men TA and TRUS with color circulation (kidneys, ureters, bladder, residual urine, prostate gland) | 4000 | rub |
| Ultrasound of complex MPS in men TA with CDK (kidneys, ureters, bladder, residual urine, prostate gland) | 3800 | rub |
| Comprehensive ultrasound in men of the TA (bladder, prostate gland, residual urine) with color circulation | 2500 | rub |
| Comprehensive ultrasound in men TA (bladder, prostate gland, residual urine) without color circulation | 2100 | rub |
| Ultrasound of large joints (1 joint) | 2000 | rub |
| Ultrasound of large joints (2 joints of the same name) | 2900 | rub |
| Ultrasound of lymph nodes (group 1) | 1900 | rub |
| Ultrasound of any part of the large or small intestine | 1450 | rub |
| Ultrasound of small joints (up to 2 joints) | 1800 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the mammary glands with regional lymph nodes (without colorectal circulation) | 2200 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the mammary glands with regional lymph nodes (with color circulation) | 2400 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the bladder (without colorectal dosage) | 1700 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the bladder (with color circulation) | 1900 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the bladder + prostate gland TA (with color circulation) | 2400 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the bladder + prostate gland TA (in men) without color circulation | 2200 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the scrotum (without color circulation) | 1600 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the scrotum (with color circulation) | 1900 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the scrotum and spermatic cord (without color circulation) | 2000 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the scrotum and spermatic cord with color circulation | 2000 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the adrenal glands (without color circulation) | 1700 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the adrenal glands (with color circulation) | 1900 | rub |
| Ultrasound OBP + Kidneys | 2900 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs (liver, gall bladder, pancreas, spleen) (without colorectal dosage) | 2300 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs (liver, gall bladder, pancreas, spleen) with colorectal dosage | 2500 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the liver | 1600 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the liver with colorectal dosage | 1800 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the liver + gallbladder without color circulation | 2050 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the liver + gallbladder with color circulation | 2250 | rub |
| Ultrasound of pleural cavities | 1800 | rub |
| Ultrasound of superficial structures (soft tissues) without color circulation | 1800 | rub |
| Ultrasound of superficial structures (soft tissues) with color circulation | 2000 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the pancreas | 1500 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the pancreas with color circulation | 1600 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the spine (1st section) without color circulation | 2200 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the spine (1st section) with color circulation | 2400 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the penis (without color circulation) | 2200 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the penis (with color flow) | 2400 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the kidneys (without colorectal dosage) | 1800 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the kidneys (with color flow) | 1900 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder (without colorectal dosage) | 2400 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder (with colorectal dosage) | 2600 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the kidneys and ureters | 2100 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the kidneys and adrenal glands | 2200 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the prostate gland (PA) with a full bladder (without CDB) | 1400 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the prostate gland (PA) with a full bladder (with color circulation) | 1500 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the prostate gland (TRUS) (without colorectal dosage) | 1900 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the prostate gland (TRUS) (with color doppler) | 2300 | rub |
| Comprehensive ultrasound of the prostate gland (TA and TRUS) without CD | 2400 | rub |
| Comprehensive ultrasound of the prostate gland (TA and TRUS) with color circulation | 2450 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the spleen | 1500 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the spleen with color circulation | 1500 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the heart without Dopplerography | 2700 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the heart with color circulation (Echocardiography) | 3100 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the hip joints (children) | 2200 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the thyroid gland with regional lymph nodes (without CDK) | 2100 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the thyroid gland with regional lymph nodes (with color circulation) | 2300 | rub |
| Ultrasound guidance (1 organ, 1 area) | 1700 | rub |
| Ultrasound mark (marker) 1 study | 1500 | rub |
| Echohydrosalpingoscopy (with consumables) | 9300 | rub |
| Ultrasonic densitometry | 2000 | rub |
| Ultrasound elastography of parenchymal organs (1 organ) | 3500 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the stomach with water-siphon test | 2500 | rub |
| Ultrasound in gynecology | ||
| Volumetric 3D/4D ultrasound during pregnancy 2-3 trimester with recording on a flash drive/disc | 3800 | rub |
| Volumetric 3D/4D ultrasound during pregnancy 2-3 trimester (with recording on a flash drive) with calculations | 4800 | rub |
| Volumetric 3D/4D ultrasound during pregnancy 2-3 trimester | 3300 | rub |
| Volumetric 3D/4D ultrasound for twins in any trimester (optional) | 1300 | rub |
| Dopplerography (assessment of uteroplacental blood flow) | 2100 | rub |
| Dopplerography in gynecology | 1600 | rub |
| Dopplerography (assessment of uteroplacental blood flow) (twins) | 2900 | rub |
| Dopplerography (assessment of uteroplacental blood flow) according to the program | 0,00 | rub |
| Ultrasound monitoring of the luteal phase, category 1 | 2800 | rub |
| Ultrasound monitoring of the luteal phase, category 2 | 3500 | rub |
| Ultrasound monitoring of the luteal phase, category 3 | 4500 | rub |
| Ultrasound monitoring of follicle and/or endometrial growth without stimulation of superovulation, category 1 | 1600 | rub |
| Ultrasound monitoring of follicle and/or endometrial growth without stimulation of superovulation, category 2 | 1800 | rub |
| Ultrasound monitoring of follicle and/or endometrial growth without stimulation of superovulation, category 3 | 2100 | rub |
| Ultrasound in the first trimester of pregnancy transabdominal (without CD) | 2100 | rub |
| Ultrasound in the first trimester of pregnancy transabdominal (without CDK) according to the program | 0,00 | rub |
| Ultrasound in the first trimester of pregnancy transabdominal (with color doppler) | 2500 | rub |
| Ultrasound in the first trimester of pregnancy transabdominal (twins) (without colorectal doppler) | 2900 | rub |
| Ultrasound in the first trimester of pregnancy transabdominal (twins) (with color doppler) | 3600 | rub |
| Ultrasound in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy (twins) transabdominal (without CD) | 3900 | rub |
| Ultrasound in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy (twins) transabdominally (with color dispersion) | 4800 | rub |
| Ultrasound in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy transabdominally (calculation of fetal size) (without color circulation) | 2800 | rub |
| Ultrasound in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy transabdominal (calculation of fetal size) (without color circulation) according to the program | 0,00 | rub |
| Transabdominal ultrasound in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy (calculation of fetal size) (with color doppler) | 4100 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the symphysis pubis | 1900 | rub |
| Ultrasound determination of fetal sex (without calculations) | 1800 | rub |
| Comprehensive ultrasound of the pelvic organs (TA and TVUS) | 2900 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the pelvic organs (PA) without color circulation | 1900 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the pelvic organs (PA) with color doppler | 2050 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the pelvic organs (TVUS) (with color doppler) | 2300 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the pelvic organs (TVUS) without color circulation | 2100 | rub |
| CDC in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy | 1900 | rub |
| Cervicometry | 2200 | rub |
In what situations is echocardiography performed?
The procedure is carried out as prescribed by a doctor. Most often it is needed when:
- pain in the chest or behind the sternum;
- there is a disturbance in heart rhythm;
- shortness of breath, accompanied by edema, is troubling;
- changes in the functioning of the cardiac apparatus were diagnosed during an ECG study;
- neoplasms were identified.
If you have diagnosed diseases of the cardiovascular system, it is recommended to undergo an ultrasound (echocardiogram) of the heart twice a year. To correctly interpret the results, the doctor should provide the data from the previous study. If it is necessary to diagnose the condition of blood vessels, Doppler ultrasound or Doppler sonography is used.
Decoding the results
The results of the study are influenced by various factors: the patient’s pathologies, chronic diseases, emotional state, age, lifestyle and the quality of the equipment itself. The protocol obtained at the end of the procedure is provided to the cardiologist. It contains all the necessary data: size, condition of the organs being examined, the thickness of their walls, the presence of scars, heart rate and other indicators. The results are interpreted by the doctor who performed the ultrasound.
You should not attempt to evaluate the examination results yourself. A person who is not knowledgeable in ultrasound diagnostics simply will not be able to decipher the data.
How is a cardiac ultrasound performed at home?
To conduct an examination of the heart muscle and chest cavity at home in Moscow, a doctor at the Ultrasound+ clinic uses a modern mobile diagnostic device.
When performing cardiac echocardiography at home, it is necessary to prepare a place where the patient can lie down for a few minutes. For example, you can cover the surface of the sofa with a sheet. You should also place a towel nearby so that after the diagnostician’s work is completed, you can quickly clean the skin of the silicone gel. Before starting ultrasound diagnostics, you must remove your belt, jewelry, clear the chest area and lie down.
The doctor will apply a special gel to the skin and begin the examination. The specialist will move the device first in the chest area, and then, if necessary, in the back area. The doctor may also ask you to lie on your side. The whole process takes no more than 20 minutes, after which the specialist begins to study and interpret the results.
You can find out the survey data immediately. If necessary, the specialist will make a conclusion about the changes that have occurred in the condition of the organ over the past year. To do this, he will need a picture or conclusion from a previous ultrasound of the heart.
To find out in detail how to prepare for an examination in your case and to sign up for an ultrasound at home, leave a request on the website or call the Ultrasound+ clinic by phone.
Methods for performing echocardiography of the heart
- M – method (one-dimensional). With its help, the dimensions of the heart chambers and the work of the ventricles during their contraction are accurately determined. The indicators are presented in the form of a graph.
- B – method (two-dimensional). Allows you to see tumors, blood clots and aneurysms. With its help, the thickness of the heart walls and valves is measured, and the degree of contractility of the ventricles is determined.
- Electrocardiography with Doppler. The procedure is necessary to diagnose heart defects and other serious disorders.
Ultrasound can be performed through the esophagus or during periods of active physical activity.
Echocardiography through the esophagus is prescribed in situations such as:
- Infectious endocarditis.
- Routine examination before installation of an artificial valve.
- After a stroke and in cases of cerebral circulation disorders and atrial fibrillation.
- Cardio version.
- Defect of the septum between the atria.
- The impossibility of traditional ultrasound of the heart. This occurs in the presence of costal ossification and other disturbances in the structure of the chest.
It is prohibited to perform cardiac echocardiography through the esophagus if there is:
- Varicose veins of the esophagus.
- Strong gag reflex.
- Radiation therapy of the esophagus.
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine in acute form.
- Enlarged hernia on the diaphragm.
- Gastric and intestinal bleeding.
- Intestinal perforation.
- Spasms, tumors, intestinal diverticula.
- Pathological mobility of the cervical spine.
Rules for preparing and conducting echocardiography through the esophagus:
- Stop eating and drinking at least 4 hours before the ultrasound
- Pull out dentures and gastric tube
- Before the procedure, the patient's mouth and throat are irrigated with lidocaine.
- The patient lies on his left side, a mouthpiece is inserted into his mouth and an endoscope is carefully inserted into the esophagus, through which ultrasonic waves penetrate
- The procedure takes from 15 to 20 minutes and is recorded on video.
How to eat properly?
Is it possible to eat before an ultrasound? Ultrasound examination is performed on an empty stomach. Therefore, you cannot eat for 8-10 hours and drink for 2-3 hours. For children, the duration of fasting is reduced. Infants are not allowed to eat for 3 hours, 1-3 year olds for 4 hours, and children aged 3-12 years for 6-8 hours. It is not recommended for children to drink water within an hour.
People diagnosed with diabetes should not fast for long periods of time. Therefore, before the session, they can drink tea and eat a piece of dried white bread. You need to eat little by little, but often (every 3-4 hours). You can't wash down your food. Drinking is allowed only 40 minutes after a meal or an hour before it. While eating, you should not rush or talk to prevent swallowing air.
During the day, you should drink about one and a half liters of liquid: purified or mineral still water, unsweetened lightly brewed tea, herbal teas, unsweetened compote, liquid jelly.
Dinner on the eve of diagnosis should be light; meat and fish dishes should not be consumed. You cannot have breakfast on the day of the diagnosis. If the examination is scheduled for the afternoon, then a light breakfast is allowed, but a couple of hours before going to the clinic you need to take enterosorbents.
Study parameters and diagnoses
Ultrasound allows you to determine:
- actual size of the ventricles, cardiac muscle, atria;
- the thickness of the walls of the heart, as well as the actual condition of the tissues;
- heartbeat rhythm.
The image obtained by the diagnostician may reflect the presence of scars, tumors, and blood clots on the heart. Ultrasound reflects the state of the pericardium and myocardium and characterizes the valve located between the atrium and the ventricle. If an ultrasound with Doppler ultrasound is performed, the doctor can even tell what condition the vessels are in and can give an answer whether they are partially blocked or not.
What heart problems can a doctor detect during an ultrasound examination of the heart muscle?
During the examination, the doctor may find:
- circulatory disorders;
- partial necrosis of the heart muscle;
- hypotension;
- stage of hypertension;
- abnormalities in the structure of the heart muscle;
- disturbances in the functioning of valves;
- disruption of heart rhythm;
- myocarditis;
- inflammatory process in the cardiac lining;
- stenosis;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Important! To accurately determine any of the diseases listed above, the doctor will have to decipher the picture of the cardiovascular system that he receives on his computer.
Analysis of survey parameters
Thanks to ultrasound testing of the heart muscle, doctors are given the opportunity to examine in detail the work of the heart, which is in the interval of one contraction and one relaxation (the norm is 75 heart beats over one minute, the cycle period is 0.8 seconds).
Analysis of data obtained from echocardiography is performed in a certain order. Each heart node is sequentially deciphered and recorded in the examination protocol. It should be understood that the protocol cannot be considered as a final document. The diagnosis is made by a cardiologist by carefully analyzing the protocol indicators. Therefore, doctors do not recommend independently comparing the data obtained with the normative ones.
Standard ultrasound values are averaged and are based on the gender and age of the person. For example, in women, the cardiac tissue of the left ventricle, its volume and mass index coefficient are smaller than in men.
For children, different standards have been adopted for the functioning of the heart, its dimensions, volume and weight. At the same time, there are differences in indicators between girls and boys in all age categories, starting from infancy. From the age of 14, standards are already comparable to adult indicators.
In the decryption protocol, parameters are written in abbreviated form according to the first letters of their names.
Echocardiography of children: normative values and parameters
Let's consider deciphering an ultrasound of the heart of a newborn baby. The rules are:
- The interatrial septum is also called the left atrium (LA). Size in diameter 11–16/12–17 mm (girl/boy).
- Right ventricle (RV): 5–23/6–14 mm (girl/boy).
- Final LV dimension in a relaxed state (LV FED): 16–21/17–22 mm (girl/boy).
- The final size of the LV in the contracted state (LV FSD): 11–15 mm, typical for both sexes.
- Thickness of the posterior wall of the left ventricle (PLW): 2–4/3–4 mm (virgin/minor).
- Thickness of the intergastric septum (IGS): 2–5/3–6 mm (virgin/minor).
- Free wall (FW): 0.2 – 0.3 cm (the value is the same for all sexes).
- Ejection fraction (EF). This is the amount of blood expelled from the ventricle during contraction. Determined as a percentage - 65-75%.
- The speed of blood passing through the pulmonary valve is 1.42-1.6 m/s.
Heart ultrasound is performed routinely in infants at one month and one year of age.