Electrocardiography (ECG) is one of the leading medical technologies used to diagnose diseases in the field of cardiology, which is based on recording heart impulses during muscle activity. Electrocardiography is a method that allows you to identify a wide range of ailments that negatively affect the functioning of the heart and blood vessels. At the same time, special equipment allows you to obtain accurate results, regardless of the stage, beating rhythm and other factors. Using the technique, it is clarified in which area the myocardial infarction is located.
An electrocardiogram of the heart reflects electrical activity, which allows for preventive studies, for example, in pregnant women, children, the elderly, and also makes it possible to clarify diagnoses for prompt decision-making in favor of effective treatment. Latum Clinic invites patients to undergo electrocardiography - a procedure that becomes decisive in making a diagnosis. Using our services, you can count on high-quality medical service, provided by competent specialists and modern technical equipment. With us, you don’t have to waste time on queues and appointments - the procedure is available on any day and time convenient for you. You can undergo the examination at a branch convenient for you: Seligerskaya metro station, Korovinskoe highway, metro station st. 800th anniversary of Moscow, Dmitrovskoe highway. The cost of electrocardiography varies and allows everyone to receive quality service with informative results.
What is an ECG?
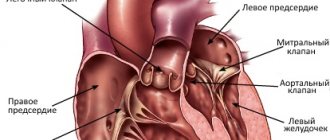
Electrocardiography is a non-invasive technology for graphically recording the potential difference in the electric field generated during the work of the heart. It is carried out using an electrocardiograph.
Electrocardiograph
The device has electrodes that are attached to certain points on the patient's body. They capture the electrical impulses of the heart, which, after amplification, are recorded by a galvanometer and recorded on paper using curved lines. The result is a cardiogram, which is subject to further interpretation by a cardiologist or therapist.
Goal and tasks
Taking an electrocardiogram is necessary for diagnosing disorders of the heart, and is also a mandatory element of the annual medical examination of the population. Cardiologists recommend an ECG every year for all people over 40 years of age.
Looking at the cardiogram, the doctor will evaluate:
- Frequency (pulse), rhythm and regularity of heart contractions.
- Physical condition of the heart.
- The presence of disturbances in electrolyte metabolism (potassium, calcium, magnesium and others).
- Conducting system of the heart (various blockades and arrhythmias).
- The effectiveness of treatment in acute and chronic diseases.
- Localization, size and degree of damage during ischemia and myocardial infarction.
- The presence of cardiac complications in diseases of other organs and systems (pulmonary embolism).
Reasons to get tested
A cardiogram is done at the slightest complaint:
- for interruptions in heart function;
- shortness of breath;
- heaviness and pain in the chest;
- weakness, dizziness;
- high blood pressure;
- pain in the back, chest and neck.
And:
- before operations;
- at medical examinations;
- during pregnancy;
- if there is a risk of developing heart disease;
- to obtain a medical record when applying for a job.
For a complete diagnosis, one cardiogram is not enough. The doctor will be able to draw conclusions about your health based on a comprehensive examination, taking into account the results of other examinations, tests, your complaints and medical history.
What kind of doctor does it?
At the clinic, a referral for cardiography is given by a therapist. And the doctor who deciphers it is called a cardiologist.
The following can also be concluded:
- functional diagnostics doctor;
- emergency doctor;
- Family doctor;
- pediatrician.
The procedure itself is carried out by nurses in a specially equipped room.
After receiving the test results, you must make an appointment with the doctor who prescribed the ECG to receive recommendations or treatment prescriptions.
Duration of the procedure
How long the study will last depends on the type of ECG.
| Type of study | Time |
| Standard ECG | 5–10 minutes |
| ECG with stress | 10–15 minutes |
Decoding the results
The attending cardiologist interprets the results of echocardiography. You should not try to interpret the results of EchoCG yourself: there are standards for indicators, and only a doctor can discuss deviations.
In our center, patients can undergo examination and receive advice from an experienced cardiologist. The clinic is equipped with the latest equipment that provides accurate research results.
To make an appointment, just call us and tell us a convenient time. Operators will recommend the best doctor. The cardiologist will pay attention to the problem, conduct an echocardiogram and prescribe the optimal course of treatment.
Preparing for the examination
Rules for preparing for an ECG:
- On the day of the procedure, you should refrain from drinking coffee, tea and energy drinks.
- Do not eat heavy food 2 hours before the test.
- Do not take sedative medications. If you regularly take cardiac medications (antiarrhythmics, beta blockers, cardiac glycosides), be sure to inform your doctor about this.
- Smokers should stop smoking an hour before the ECG.
- Do not expose yourself to physical stress. It is advisable to arrive 10–15 minutes before the examination and relax on the couch.
- Do not use greasy cream or lotion in the chest area.
- Clothing should be comfortable so that you can quickly expose your wrists, legs and chest. You will also have to remove all metal jewelry and watches.
- Be sure to take your previous cardiograms and test results with you.
Electrocardiography: indications for the procedure
You can come for an ECG at your own request or as prescribed by a cardiologist. You can get a referral at your local clinic or at our medical center. You should seek medical help if you have the following symptoms:
- 1. Weakness that appears for no apparent reason.
- 2. Frequent headaches and fainting.
- 3. Frequent heart rate that is not associated with physical activity.
- 4. Shortness of breath that appears even with minimal activity.
- 5. Patients over 40 years of age should attend the procedure at least once a year.
For the purpose of prevention, it is also worth undergoing an ECG if there are additional risks. For example, if the patient smokes, drinks alcohol and drugs, eats irrationally, with fatty and spicy foods predominating, and has a history of infectious diseases.
Electrocardiography should also be prescribed for direct symptoms:
- 1. The doctor suspects serious diseases of the cardiovascular system, for example, heart attack, defect, inflammation. The technique is relevant for high blood pressure, arrhythmia, etc.
- 2. Increased blood sugar levels, problems with the thyroid gland, impaired metabolic processes.
- 3. Obesity, exhaustion.
- 4. Chronic diseases of the respiratory system.
General algorithm of actions when taking an ECG
How to do an ECG:
- The health worker writes down all the patient's data in a journal.
- The wrists, legs and chest are exposed.
- Electrodes are attached while lying down. Before this, the skin is degreased with alcohol, and for better contact with the sensors, a special gel is applied, or wet gauze wipes are used.
- The indicators are recorded on paper, after which the terminals are removed and the skin is wiped dry.
There is no need to be nervous or talk during the ECG. The recording technology is absolutely safe and painless. The duration of the examination is 10–15 minutes.
Breathing should be smooth and calm. It may be necessary to record inspiratory readings. In this case, the nurse will instruct you to take a deep breath and hold your breath.
ECG manipulation is carried out in the functional diagnostics room. The room should be warm and isolated from possible sources of electrical interference. It is also recommended to turn off your mobile phone.
How to take an ECG correctly
The technique for performing electrocardiography has a simple procedure and is carried out in stages:
- patient preparation;
- application of electrodes;
- recording bioelectrical activity on paper;
- deciphering the results.
It is important not to confuse the electrodes, but to check the device for serviceability before use.
A video about the ECG recording technique was filmed by the channel - OFFICIAL TNU.
Application of electrodes
To record standard and enhanced leads, three electrodes (red, yellow and green) are used, which are placed on the arms and left leg and form an Einthoven triangle. The black electrode, which is placed on the right leg, grounds the system.
You need to set them like this:
- red - right hand;
- yellow - left hand;
- green - left leg;
- black - right leg.
To record the chest leads, one or six pear-shaped electrodes are used (depending on the type of cardiograph).
How to place chest electrodes:
- lead V1 - in the IV intercostal space along the right edge of the sternum;
- lead V2 - in the IV intercostal space along the left edge of the sternum;
- lead V3 - between the second and fourth positions;
- lead V4 - in the 5th intercostal space along the left midclavicular line;
- lead V5 - at the same horizontal level as V4, along the left anterior axillary line;
- lead V6 - along the left midaxillary line at the level of V4.5.
Scheme for applying chest electrodes
Marking of tips and electrodes
For convenience, all electrodes have their own color.
The location of the four main ones is easy to remember from a traffic light or from a funny reminder “Every Woman Is Meaner Than the Devil.”
In a single-channel cardiograph, one white bulb is used to take chest leads on an ECG.
In six-channel:
- V1 - red;
- V2 - yellow;
- V3 - green;
- V4 - brown;
- V5 - black;
- V6 - blue.
Lead diagram
When recording an ECG, 12 standard leads are currently used: 6 from the limbs and 6 from the chest.
Each of the 6 leads shows one or another part of the heart.
On standard leads:
- I - anterior cardiac wall;
- II - posterior cardiac wall;
- III - their totality.
Diagram of standard limb leads
On reinforced leads:
- aVR - lateral cardiac wall on the right;
- aVL - lateral cardiac wall anterior to the left;
- aVF - posterior inferior wall of the heart.
Scheme of reinforced limb leads
On the chest leads:
- V1 and V2 - right ventricle;
- VZ - septum between the two ventricles;
- V4 - upper cardiac section;
- V5 - anterior lateral wall of the left ventricle;
- V6 - left ventricle.
Chest lead diagram
This simplifies the task of diagnosing diseases. Changes in each lead characterize the pathology in a certain area of the myocardium.
Recording a cardiogram
The procedure may differ on different cardiographs. Let's consider the ECG recording algorithm using the EK1T-03M2 device as an example.
Photo of electrocardiograph EK1T-03M2
If the device is powered from a 220V network, it must be grounded. To do this, one end of the ground wire is connected to the ground socket, and the other is connected to a water tap or an unpainted area of the central heating radiator. Devices with a battery do not require grounding.
After applying the electrodes and turning on the device, the control millivolt is recorded. This is the recording scale, it is important for further measurements and for comparing electrocardiograms recorded on different devices with each other.
Using the EK1T-03M2 device as an example, this is done like this:
- The switch should set the mV height to 10 mm, check that the lead switch is set to 1 mV.
- Turn on the belt movement at a speed of 50 mm/sec. And immediately quickly press the millivolt recording button 3-4 times, then stop the tape movement.
- Several rectangular teeth 10 mm high will be recorded on the tape; when deciphering an ECG, they are called millivolts.
Next, the standard leads are recorded sequentially:
- To do this, switch the device to lead I recording mode.
- Then turn on the tape, record 4-5 complexes and stop the tape.
- Switch the device to lead II recording mode and repeat the entire procedure.
- After recording lead III, the patient should be asked to take a deep breath, hold his breath, and in this position record lead III again.
- Then record the enhanced leads aVR, aVL and aVF.
Recording chest leads:
- To do this, set the lead switch to position V.
- The chest electrode is placed on the patient's chest at the recording point of lead V1 and the pen stabilizer is turned on.
- The sedative is turned off. Record at a speed of 50 mm/sec. 4–5 complexes.
- The pacifier is turned on and the electrode is moved to point V2.
- The entire procedure is repeated until lead V6 is recorded.
The control millivolt is recorded again, the tape is passed forward and torn off. The device is turned off.
The cardiogram indicates:
- Patient's full name;
- age;
- date and time of recording.
Features of ECG according to Slopak
In medicine, there is another way to conduct electrocardiography - ECG according to Slopak. It differs from the standard procedure. Used to diagnose posterobasal myocardial infarction.
Description of the method:
- Green - left leg.
- Black - right leg.
- The yellow electrode is placed on the fifth intercostal space on the left along the posterior axillary line (at the level of thoracic V6).
- Red is moved sequentially and used to remove the chest leads.
The marking looks like this:
- S1 - at the left edge of the sternum;
- S2 - in the middle of the distance between leads S1 and S3;
- S3 - second intercostal space on the left along the midclavicular line;
- S4 - second intercostal space on the left along the anterior axillary line.
In this case, the contact switch must remain in position I.
Why is an ECG of the heart done?
What is electrocardiography? This is a popular and effective technique that allows you to promptly identify any deviations in the functioning of the cardiovascular system. As part of the manipulation it is possible to:
- 1. Assess the frequency, the source of the heartbeat rhythm.
- 2. Determine the lack of blood flow and diagnose coronary disease.
- 3. Confirm that there is a myocardial infarction and specify its location.
- 4. Diagnose ventricular hypertrophy and assess the general condition of the organ.
Electrocardiography has been used for a long time and to this day has no competitors in terms of diagnostic potential. In combination with other studies, it allows you to get a complete picture of the state of the cardiovascular system. Due to the fact that the price of electrocardiography is low, this allows patients with suspected problems to take timely measures in order to begin treatment as quickly as possible.
How to do an ECG for women
ECGs are done for women in the same way as for men. The only peculiarity is that the girls take off their bra, since the impulse does not pass through the fabric of the bra. For the same reason, it is not advisable to wear tights or stockings.
Are there any special features during pregnancy?
There are no contraindications for ECG during pregnancy. This is the same stage of monitoring the health of the expectant mother as an ultrasound. That is why women should not refuse to perform such a study.
During pregnancy, the heart experiences increased stress. During pregnancy, an ECG is prescribed 2 times. In addition, an electrocardiogram is performed not only on the woman, but also on the fetus - this study is called CTG (cardiotocography).
During pregnancy, the following changes appear on the cardiogram:
- displacement of the electrical axis of the heart to the left;
- increased heart rate, single extrasystoles;
- negative T wave in the third and fourth leads;
- shortened PR interval;
- pathological Q wave in the third lead and aVF (right arm lead).
24-hour Holter ECG monitoring
Not in all cases it is possible to detect other problems with an organ such as the heart. After all, the procedure takes a minimum of time. To analyze the state of the cardiovascular system, daily monitoring is carried out, which involves the use of a compact device. It is installed on the human body, after which the device takes readings for 24 hours. The presence of the device does not affect the quality of life and allows you to do everything that you are used to. The study allows one to assess the state of the entire system under conditions familiar to the subject. In this case, various parameters are taken into account, arrhythmia attacks are counted, ischemia and many other factors are detected.
You can sign up for a consultation for electrocardiography using the feedback form or by making a phone call. We offer high-quality medical care that allows you to get an accurate picture of the state of the cardiovascular system. Registration is possible for any convenient day and time.
Decoding indicators
ECG is assessed according to several criteria:
- The rhythm is correct and regular. No extraordinary contractions (extrasystoles).
- Heart rate. Normally - 60–80 beats/min.
- Electrical axis - normally R exceeds S in all leads except aVR, V1 - V2, sometimes V3.
- Width of the ventricular QRS complex. Normally no more than 120 ms.
- QRST - complex.
QRST - normal complex
Brief designation of the main elements of the film:
- P wave - shows atrial contraction;
- PQ interval is the time the impulse reaches the atrioventricular node;
- QRS complex - shows ventricular excitation;
- T wave - indicates depolarization (restoration of electrical potential).
Video about ECG norms from the Mass Medika channel.