Laryngeal stenosis in children
Conservative therapy
In case of acute stenosis, medicinal measures are of an auxiliary nature and are included in the emergency care package.
The child is administered corticosteroids in age-appropriate dosages and anticholinergic drugs. To compensate for hypoxia, after eliminating the stenosis, breathing with humidified oxygen mixtures is carried out. After stabilization of well-being, treatment is selected according to the etiopathogenetic principle. Mild forms of the disease are subject to outpatient therapy; for others, hospitalization is recommended. If symptoms of laryngitis are detected, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and antihistamines are prescribed. To eliminate viscous sputum, which clogs the lumen of the respiratory tract, mucolytics and alkaline inhalations are used (for children after 4-5 years). Antibacterial therapy is selected if necessary.
According to the cause of stenosis, antiviral, antimicrobial, and antifungal drugs can be used in the hospital. When symptoms are caused by neuromuscular disorders, muscle relaxants are indicated. In case of intense edema, adrenergic agonists are effective in the form of solutions and inhalations, which have a powerful vasoconstrictor effect. Physiotherapy includes ultraviolet irradiation and electrophoresis on the neck area.
Surgery
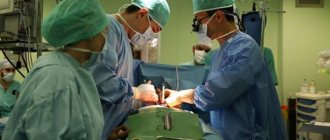
In case of acute development of severe stenosis and asphyxia, surgical intervention is performed as quickly as possible. In emergency cases, a conicotomy is indicated - a dissection of the larynx between the cartilages to ensure air flow into the respiratory tract. In children over 8 years of age, a less traumatic puncture conicotomy is performed, during which a catheter with a needle is installed.
For chronic cicatricial stenoses, surgical correction is performed routinely. Endoscopic operations are more often used: balloon dilatation, laser microsurgery, intervention using a microdebrider. In children, surgical treatment with external access is also used: laryngoplasty using an autograft, resection of the larynx, laterofixation of the vocal folds.
Rehabilitation
For successful recovery after surgical treatment, the child is prescribed a gentle regimen. Observation by an ENT doctor is carried out for 2-3 months, once every 2 weeks. Experts advise maintaining a voice mode (quiet conversation, avoiding screaming and loud laughter), eliminating hot and spicy foods so as not to irritate the mucous membranes and not provoke symptoms of suffocation.
Causes
The cause of stenosis can be not only viruses or bacteria, but also allergic reactions to home treatment: honey, raspberries, inhalations with herbs, pine buds, fir oil. Very often, children suffocate to the smell of Vietnamese balsam “Star”, flowering plants, cosmetics, perfumes, gasoline and other chemicals. Food allergens are also unsafe in this regard: citrus fruits, red vegetables and fruits, chicken eggs, sea fish, seafood, nuts, chocolate and other sweets.
Degrees of stenosis
The degree of stenosis is determined by changes occurring in the body:
- 1st degree: no serious disorders are observed, although plaques are already forming on the walls of blood vessels, shortness of breath appears during physical activity. With gastric stenosis at this stage, a sour taste in the mouth and belching appears; with spinal stenosis – fatigue increases, the back gets tired and the legs become heavier; with laryngeal stenosis – shortness of breath appears;
- 2nd degree: symptoms of any type of stenosis become more acute and already cause significant discomfort, forcing you to seek help from a doctor;
- 3rd degree: if treatment has not been prescribed so far, the patient puts his life at risk. Because at this stage, patency in the affected tissues and organs is approaching minimal.
Chronic forms of the disease progress slowly, gradually reducing the patient's quality of life. Acute forms are characterized by sudden attacks.
Diagnostics
Laryngeal stenosis in children is diagnosed by a differential method, as a result of which it is possible to identify the causes and distinguish laryngeal stenosis from laryngospasm, tracheal stenosis, and an attack of bronchial asthma. Stenosis is detected by examination and palpation against a background of severe symptoms.
To qualitatively identify the cause of stenosis, the following examinations are carried out: tomography, laryngoscopy, radiography of the larynx and the entire esophagus, ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland, bacteriological examinations of the pharynx, tracheobronchoscopy.
Treatment
Laryngeal stenosis in children develops too quickly and there is no point wasting time here. If choking is evident, a prednisone injection can be given to help the child breathe easier. You just need to know for sure that there is no other choice and judge, if possible, sensibly: if the doctors are already on the way, and hot steam and rubbing the legs help, the child is breathing, then there is no need to inject the drug.
Calling an ambulance followed by a visit to the local pediatrician is vital for recovery. Firstly, the attack may recur, but you cannot inject the drug every time. The child is in dire need of good and comprehensive treatment, a course of physiotherapy, treatment with antibiotics and elimination of swelling of the larynx.
At the time of an attack, a critical situation often occurs, then specialists have to perform surgery on the spot. A section is made in the trachea area to allow air to enter, and a special tube is inserted.
During a crisis, constant monitoring is necessary and can only be provided in a hospital setting.
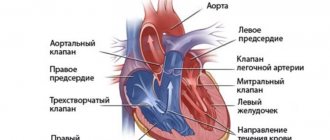
Symptoms of heart defects in newborns and children
Usually the pathology is detected by a neonatologist in the first days of a baby’s life:
- cyanosis (blue discoloration) or grayness of the skin;
- tachypnea - rapid shallow breathing;
- widening of the nostrils when inhaling;
- grunting while inhaling;
- swelling of the legs, abdomen, face;
- breathing problems when feeding.
In a less severe form, it manifests itself at a growing age:
- fatigue during exertion;
- shortness of breath, pain in the heart area when playing sports;
- swelling of the hands, ankles, feet.
The earlier the clinical manifestations appear, the more difficult the process.
Important! Note to parents
Regardless of whether a child has a heart pathology or not, it is necessary to undergo regular medical examinations.
It is especially important to make an appointment with a pediatric cardiologist before starting sports. There are disorders in which the cardiovascular system can cope with them through compensatory force. Diseases go undetected for years.
When playing sports, the load on the cardiovascular system increases many times over. Compensatory mechanisms in this mode are often insufficient, which is manifested by dizziness, loss of consciousness, and can cause a life-threatening condition for the child.
This does not mean that playing sports is strictly contraindicated. The type of sport and load must be determined by a doctor.
If a child is diagnosed with a heart defect, medical supervision when playing sports is mandatory. A medical examination by a pediatric cardiologist, pediatrician, or cardiac surgeon is required.
Symptoms
The first signs of illness in a baby may not be noticed even by the most attentive parents. This is explained by the fact that the symptoms of stenosis are very similar to the clinical manifestations of a common acute respiratory infection. The baby may have a slight increase in body temperature and a runny nose.
The next stage of development of stenosis is characterized by a strong paroxysmal cough, hoarse voice and rapid noisy breathing. Parents should also be concerned that the child’s condition is rapidly deteriorating, he becomes lethargic and irritable, which indicates the onset of hypoxia.
Kinds
Depending on the location, there are several types of stenosis:
- narrowing of the spinal canal is spinal stenosis. It develops equally in both children and adults. Spinal stenosis is divided into congenital and acquired. Based on anatomical characteristics, they are divided into lateral and central. Lateral stenosis is a narrowing of the opening between the vertebra and the radicular canal, central stenosis is a narrowing of the distance between the vertebral body and the vertebra in the area of the spinous process. Spinal stenosis can have a secondary form, when the disease develops as a concomitant deformation of articular, bone tissue and ligaments with the formation of bone growths;
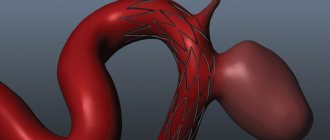
- Vascular stenosis develops due to high cholesterol levels, disorders of lipid-protein metabolism and deposition of lipoprotein particles on the walls of blood vessels. Blockage of blood vessels is accompanied by dizziness, vomiting, tinnitus, hallucinations, and general weakness of the body. The first degree of vascular stenosis, as a rule, does not have symptoms that would force you to immediately consult a doctor;
- Stenosis of the larynx (trachea) often affects children. This is a decrease in airway patency. The pathology is more often found as congenital. The main symptom is shortness of breath or suffocation;
- A stomach ulcer provokes the development of gastric stenosis. As a result of narrowing of the lumen between the gastric walls, spasms occur. Without treatment, gastric stenosis leads to an imbalance in the internal environment.