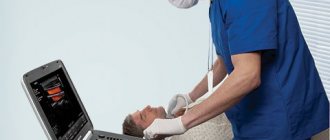
Fetal echocardiography is a modern method for studying the heart. It is carried out using a special ultrasound diagnostic device, which is equipped with special cardiac programs. Using this method, it is possible to timely detect anatomical changes in the heart, as well as the functional state of large vessels and the pericardium: increased wall thickness or dilatation of the ventricles, as well as the atria, ventricular contractility, the presence of blood clots or fluid in the pericardium, or the formation of tumors.
The peculiarity of an echocardiogram is that this method allows you to examine the internal state of the heart using sound waves. This study is carried out using a multifunctional special device called a transducer. It is installed on different areas of the pregnant woman's abdominal cavity and allows you to examine the heart and valves of the fetus from different positions.
The fetal echocardiography method is absolutely harmless. It has virtually no contraindications, so it can be performed on pregnant women more than once. The reflected signal of ultrasonic waves is transmitted to a computer system and displayed on the monitor in the form of bright dots, which then merge into a common image of the object under study.
Fetal echocardiography is an absolutely safe method that cannot harm either the mother or her unborn child. New generation devices from well-known manufacturers, such as the iE33 ultrasound machine, allow you to examine in detail unborn children in a variety of conditions and at the same time obtain the most accurate results. Ultrasound diagnostics gives doctors the opportunity to identify heart defects early enough in pregnancy and make an accurate diagnosis even before the baby is born. Thanks to it, sick children have a better chance of living a full life, since heart surgery is often performed on babies immediately after birth.
Preparing for fetal echocardiography
The bulk of heart diseases are defects, namely anatomical disorders of the structure of the heart, which subsequently lead to hemodynamic disturbances even in the prenatal period or immediately after the birth of the child. It is the method of fetal echocardiography that makes it possible to identify heart defects during pregnancy, as well as such rare diseases as cardiomyopathies, which are accompanied by enlargement of the cavities of the heart. In addition, this diagnosis allows doctors to detect heart tumors in the prenatal period and promptly decide on treatment tactics.
Fetal echocardiography today is carried out using modern and multifunctional ultrasound equipment if there is any suspicion that the child may have cardiac pathology. Indications for the use of this method may include factors such as the presence of congenital heart disease in parents, the birth of previous children with congenital heart disease, suspicion of the development of chromosomal abnormalities, various embryonic abnormalities detected by ultrasound, thyrotoxicosis, diabetes mellitus or chronic infections found in future mother. Fetal echocardiography is also performed if a woman took antibiotics or psychotropic drugs in early pregnancy, or if the mother suffered from rubella during pregnancy. Indications for this diagnostic method may include intrauterine growth retardation, detection of cardiac changes during a screening ultrasound examination of the fetus, deviation from the norm of indicators that were obtained when assessing a section through 3 vessels. The study is also prescribed when the thickness of the fetal cervical fold, identified during ultrasound screening in the first trimester, is more than 2.5 mm or when the normal rhythm of the fetal heart is disrupted.
The optimal period for fetal echocardiography is between 18 and 24 weeks of pregnancy, but the study can also be performed at any other time. This diagnostic method does not require special preparation on the part of the pregnant woman. The procedure takes from 30 to 45 minutes. In the early stages, the study can be carried out using a transvaginal sensor, followed by repeating the study to clarify the results obtained.
Child
At the age of one month, all children need to have their heart examined by ultrasound (ECHO-CG) of the child’s heart. The child, provided that everything is normal and there are no pathologies, should undergo the next examination at the age of one year. Parents need to be aware of alarming symptoms, for example, a murmur in the baby’s heart. The heart of a newborn is relatively large and makes up 0.8% of body weight, while in an adult it is only 0.4%. With age, the child's heart weight increases; by 8 months the weight doubles, by three years it triples, and by six years the weight increases 11 times. This is why it is so important to observe children in different years of their lives.
Contraindications for the study
Fetal echocardiography is not a study that can harm the health of a pregnant woman or her child, therefore there are no contraindications to its conduct today. Carrying out a normal diagnosis can only be hampered by deformation of the abdominal cavity or serious changes in the skin of an allergic or inflammatory nature that are present in the area of the study.
In modern medicine, fetal echocardiography is divided into several types. It can be two-dimensional, which allows you to study the anatomy of the main structures of the heart. The condition of the leaflets, walls and valves of the heart can be examined using M-mode echocardiography, and Doppler echocardiography allows you to study and correctly assess the hemodynamics and rhythm of the heart.
The described technique allows you to study in detail the speed and direction of blood flow, and also gives doctors the opportunity to assess the degree of narrowing of the heart vessels and determine the volume of blood that leaves and returns to the heart. To carry out echocardiography as accurately as possible, new generation ultrasound machines are used, which are absolutely harmless to the health of the expectant mother and her baby.
If a serious pathology is discovered in a child during echocardiography, then a repeat examination is prescribed after one to two weeks to exclude a possible medical error. Sometimes, after the study, the expectant mother is referred for a more detailed consultation with a cardiologist, pediatric surgeon and neonatologist.
Some heart pathologies detected in the fetus may disappear on their own even before birth, so repeated examinations sometimes do not reveal deviations from the norm. The quality of the images obtained during the study can be influenced by factors such as the location of the fetus in the womb and the weight of the mother, since it is much more difficult for obese women with a large fat layer to make a diagnosis.
Advantages of cardiac ultrasound (ECHOCG) in Mother and Child.
The group is a leading scientific and practical medical institution in the Russian Federation in the field of cardiology. Doctors of the clinics annually undergo training in the best European and domestic cardiology centers with an impeccable reputation. Specialists of the Centers are in contact with the Union of Pediatricians of Russia. In this regard, examination, treatment and observation in any of them has a number of undeniable advantages:
- the clinics are equipped with the most modern diagnostic equipment, including ultrasound equipment, which allows us to obtain the optimal data necessary for an accurate diagnosis in the shortest possible time;
- all departments of diagnostic and treatment complexes have one of the best laboratory services in the Russian Federation;
- qualified, highly professional medical staff are friendly and always guard the interests of patients;
- the centers have created the most comfortable environment for receiving visitors in compliance with the rules of the medical and protective regime;
- An ultrasound of the heart is performed in 20 minutes, the results are deciphered immediately after the procedure, and the doctor’s conclusions are handed over to you;
- if a pathology is detected, there is the possibility of immediate or delayed hospitalization in a hospital hospital with adequate therapy, including surgery or referral to a consultative appointment with a specialized specialist;
- if necessary, a consultation of clinic doctors can be organized with the involvement of colleagues from abroad and Russian cardiology centers.
Norm and interpretation of results
Fetal echocardiography is a non-invasive diagnostic method that is highly informative. An echocardiogram can only be interpreted by a cardiologist, since independent study of the indicators cannot clarify the full picture of the study.
Any echocardiogram conclusion contains a number of mandatory indicators, the values of which reflect the structure and functions of the heart chambers. In the conclusion, the parameters of the right and left ventricles, atria, interventricular septum, and the condition of the heart valves and pericardium must be indicated. With the help of special medical aids, certain standards have been established, deviations from which may indicate the appearance of various heart pathologies.
The following indicators must be recorded in the protocol after this examination:
- value of left ventricular myocardial mass;
- value of left ventricular myocardium;
- end systolic size;
- short axis;
- long axis;
- end-diastolic volume of the left ventricle;
- aorta;
- right atrium;
- left atrium;
- myocardial thickness of the interventricular septum systological;
- myocardial movement;
- myocardial thickness of the interventricular septum diastological;
- miltral valve;
- aortic valve;
- ejection fraction;
- wall thickness in diastole;
- pulmonary artery;
- stroke volume;
- diastolic wall thickness;
- diastolic size.
The main indicators that determine the normal development and functioning of the heart muscle are data indicating the functioning of the ventricles, as well as the development of the septum between them. Decoding the data after the study may indicate a manifestation of heart failure or stenosis. Failure develops when the heart valve leaflets, which prevent the reverse flow of blood, fail to cope with their functions, because of this, blood is directed into an adjacent chamber, and the heart becomes less efficient. With stenosis, there is a decrease in the diameter of the valve opening, as a result of which blood pumping worsens.
Interpretation of cardiac echocardiography necessarily includes data on myocardial contractility, as well as the pumping function of the left ventricle in dynamics, the presence of scars, aneurysms, tumors, blood clots, as well as their size and impact on the contractility of the walls. In addition, based on the study, the doctor has the opportunity to reliably assess the condition and functional characteristics of the heart valves, as well as the degree of hypertrophy of their walls. This technique allows you to examine blood flow through valves and large vessels, as well as detect the presence and existing degree of reverse blood flow through the valves.
The essence of the diagnostic procedure
Four-chamber view
There are three types of four-chamber views: apical, basal and lateral. The most informative view is the apical or basal four-chamber. The lateral four-chamber view is the best view for visualizing the interventricular and interatrial septa.
Parameters that are studied using a four-chamber view.
- Number of cameras. Usually four cameras are visible.
- Comparison of camera sizes. Usually both atria are the same size. The ventricles should also be the same size, with no signs of thickening of the walls.
- Assessment of morphological features - there is a band of echogenic retardant in the right ventricle. The foramen ovale flap is opened into the left atrium.
- The core of the heart consists of the membranous portion of the interventricular septum, the septum primum of the atrial septum, and the septa of the mitral and tricuspid valves.
- Assessment of the position of the tricuspid and mitral valves. Incorrect placement of the valves may indicate atrioventricular septal defects.
- Examination of the interventricular septum from apex to base for any defects.
- Assessment of the condition of two atrioventricular valves - mitral and tricuspid. The opening and closing of these valves must be assessed in real time.
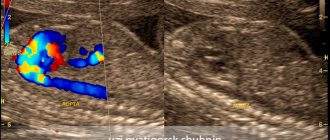
- Study of flow through the atrioventricular valves using color Doppler. The direction of flow is from the atria to the ventricles. Same for both valves. No smoothing should be visible.
- Examination of the area behind the heart. Between the left atrium and the spine, only one vessel should be visible - the descending aorta.
Churn views
View of three vessels . The three vessels visible at this sensor position are:
- pulmonary artery in longitudinal section, viewed from the front and left;
- aorta in cross section, central view;
- superior vena cava (SVC) in cross section as viewed from the right.
Right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT). Color and pulsed Doppler evaluation of RVOT is performed to identify distortions on the pulmonary valve. Peak pulmonary artery systolic velocity can be obtained using pulsed Doppler.
Left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT). It confirms the continuity of the aortic septum and the correct movement of the aortic valve.
Aortic arch . With color Doppler, the direction of flow can be seen from the ascending aorta to the arch and then to the descending aorta.
Ductal arch. The ductal arch begins anteriorly behind the sternum. On the color Doppler image, there is a smoothing area in the arc; this corresponds to the region of the ductus arteriosus.
Venoatrial connections. Of the four pulmonary veins, only two or three can be visualized. On color Doppler, flow is directed toward the left atrium.
Ultrasound techniques for diagnosing the fetal heart
At the very beginning of the formation of the embryo, its heartbeat is determined using a conventional ultrasound examination. With the normal development of pregnancy, using a transvaginal sensor, the heartbeat of the embryo can be heard as early as the fifth or sixth week of pregnancy. The heart rate of the embryo varies depending on the duration of pregnancy. So in the sixth to eighth week this figure is 130 beats per minute. Then, in the ninth to tenth week, this figure is 170-190 beats per minute, and from the eleventh week until the moment of birth it is 140-160 beats per minute. The ongoing changes in heart rate are directly related to the development, as well as the formation of the functions of the autonomic nervous system.
It is the heart rate that is the most important indicator of the normal development of the embryo; if these parameters change, it is necessary to carry out treatment that is aimed at eliminating the cause of the development of abnormalities. It should also be noted that the absence of heartbeats in an embryo longer than 8 mm indicates a non-developing pregnancy.
In the second and third trimesters of pregnancy, the location of the heart in the chest is examined, and the frequency and nature of heart contractions is determined. With a lack of oxygen, the heart rate can increase to 160 beats per minute, and with a sharp deterioration in the condition of the fetus, this figure can decrease. Ultrasound examination of the fetal heart allows timely detection of approximately 75% of existing defects. If during the described study any changes are detected, then the pregnant woman is prescribed a more informational and accurate diagnosis - fetal echocardiography.
How long does it take to do it?
The condition of the fetal heart can be assessed at any time during pregnancy after an ultrasound scan.
In the first trimester (11–14 weeks), cardiac findings may be poorly detected, but the presence of pulsatile ductus venosus or tricuspid regurgitation can be a very strong marker of cardiac and chromosomal abnormalities.
The fetal heart can be assessed in the third trimester, but there are many limitations due to oligoamniosis and shadowing from the fetal spine, ribs, and extremities.
The best time to evaluate fetal heart health is between 18 and 22 weeks of pregnancy.
A technique that saves lives
Fetal echocardiography is a complex research method that uses various operating modes of an ultrasound scanner. The purpose of fetal echocardiography is the early detection of various pathologies of cardiac development. The accuracy of the study directly depends on the duration of pregnancy, the amount of amniotic fluid, the obesity of the pregnant woman, the experience of doctors and the class of ultrasound machine used.
During the examination, a receiving device pre-lubricated with gel is installed on the pregnant woman’s stomach. It uses ultrasound to display the movements of the fetal heart. Such manipulations allow the doctor to quickly assess the main indicators of heart function. The entire study takes no more than 15-20 minutes. As the fetus develops in the mother's womb, its cardiovascular system also changes, which is why it is so important to regularly monitor possible pathological changes. Fetal echocardiography allows you to obtain a lot of useful data indicating the state of health of the child, without causing any harm to him.
Indications
The uniqueness of functional diagnostics (Echo CG) lies in the absence of contraindications and age restrictions. There are devices that allow intrauterine examination. The manipulation can be done repeatedly. Identified pathology is the reason for an annual examination. Indications for studying the functioning of a child’s heart are:
- deviations in x-rays, electrocardiogram;
- murmurs of unknown etiology;
- shortness of breath (including traumatic, rheumatic pulmonological nature);
- acrocyanosis (bluish coloration of fingers, nasolabial triangle, lips);
- malnutrition, lack of appetite;
- fatigue, headaches, increased sweating;
- fainting;
- pain in the chest area;
- arrhythmias;
- unstable blood pressure;
- swelling of the legs;
- postoperative period;
- severe flu, sore throat, oncology, anti-inflammatory treatment;
- developmental delay.