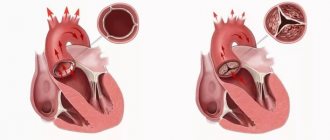
Heart cancer is a malignant tumor that affects the heart muscle and pericardium. An extremely rare disease. Even in the world's largest oncology clinics, such patients are encountered no more than once a year.
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
There are primary and secondary malignant tumors of the heart. Most often, it is secondary cancer, which is nothing more than metastases. In this case, the cancerous tumor first develops in another organ, for example, the lungs or kidney, and then is carried through the bloodstream to the heart, where an additional focus is formed.
The primary malignant tumor, which initially affects only the heart, is sarcoma. There are several types of neoplasms:
- Angiosarcoma arises from the cells lining blood vessels and accounts for up to 40% of malignant heart tumors.
- Fibrosarcoma - the substrate is connective tissue cells.
- Liposarcoma - develops from adipocytes, fat cells.
- Rhabdomyosarcoma - develops from myocytes.
- Leiomyosarcoma develops from smooth muscle cells.
- Undifferentiated sarcomas. The cells are so altered that they cannot be classified as any tissue. Such sarcomas account for 25% of cases.
Another type of malignant heart tumor is pericardial mesothelioma. It affects mainly men.
Sarcoma of the heart is even less common than its metastatic lesion. It's all about the characteristics of the heart tissue. As we know, the heart consists of special muscle cells - myocytes. They stop dividing quite early, even in childhood. And further growth of the organ occurs due to an increase in cell size. Actually, this aspect is the most important protection against cancer, because malignant tumors are characterized by excessive proliferation, i.e., uncontrolled cell division. And more often they affect actively dividing tissues, for example, epithelium.
On the one hand, the lack of regeneration creates a kind of protection against malignant tumors, and on the other hand, it leads to serious cardiac problems. For example, during myocardial infarction, a disruption in the nutrition of a muscle area occurs, and its cells die in this place. Because they do not repair themselves, scar tissue forms instead. It cannot perform the functions of myocytes, and accordingly a number of problems arise.
Kinds
Types of heart cancer are:
- Sarcoma. Among malignant tumors, the most common one usually affects patients in middle age (around 45 years). There are many types of sarcomas and their characteristics.
- Pericardial mesothelioma. A rare type of cancer, most often affects men, the age of patients varies greatly. Capable of metastasizing to the spine, brain, and nearby soft tissues.
- Primary lymphoma. An even rarer type of tumor is more often observed in patients with various types of immunodeficiencies. This type of heart cancer grows very quickly.
Other types of cancer can also affect the heart and cause heart damage. For example, melanoma, breast or lung carcinoma, kidney cancer - all of this can metastasize to the heart. Leukemia and lymphoma have similar properties. But here we are not talking about heart oncology itself, but about the fact that oncology of another localization invades this organ.
Prevention
The development of a malignant neoplasm in the heart can be prevented by following certain rules:
- do not neglect physical activity, gymnastics, keep yourself in good shape;
- carry out timely treatment of infectious diseases, preventing them from becoming chronic;
- monitor your weight;
- avoid eating carcinogenic, fatty and unhealthy foods;
- complete cessation of bad habits;
- control cholesterol and blood sugar levels;
- annual medical examination.
Symptoms
The issue of symptoms is very complex. In the first stages, the disease usually has no symptoms. And when heart cancer symptoms and signs begin to appear, they can easily be confused with signs of other diseases. Therefore, patients often seek help in late stages or even die without knowing that they had such a diagnosis (sudden death). Possible symptoms of the disease include:
- cough;
- joint pain and fever;
- blue color of fingers when pressing them;
- swelling of different parts of the body: legs, abdomen, face;
- bloating of veins;
- difficulty breathing, shortness of breath, fatigue;
- dizziness, fainting;
- rapid heartbeat, irregular heart rhythm;
- feeling of a lump in the chest, creeping pain;
- noise in ears.
Heart problems are constantly getting worse, increasing - and the patient’s well-being is deteriorating. It is by no means necessary that even if the listed signs are present, we are talking about symptoms of heart cancer - cardiologists can diagnose a completely different problem, but going to a consultation and getting a diagnosis is very important.
Symptoms and signs of heart cancer development
It can be difficult to determine the disease, because heart cancer exhibits symptoms characteristic of heart failure, stroke, and coronary artery disease. There are three groups of symptoms:
- extracardinal (arthralgia, chills, fever, weight loss, drowsiness, petechiae, shortness of breath);
- intramyocardial (arrhythmia, tachycardia);
- intracavitary (heart failure, valvular stenosis).
Shows signs of heart cancer depending on the type of tumor. Myxomas can signal the presence of a problem in the form of embolic disease and cause a distal murmur. When listening, there is a “tumor pop”, which is produced due to the prolapse of myxoma into the mitral compartment during distole. With fibroelastomes it is more difficult. This kind of heart cancer shows practically no signs - it is asymptomatic. But fibroids are dangerous due to the manifestation of arrhythmias, which can cause sudden death. If there are signs of cyanosis and respiratory distress, teratomas can be diagnosed. Malignant tumors behave more aggressively. Sarcomas cause signs of ventricular tract obstruction, mesotheliomas manifest as pericarditis and cardiac tamponade. Fever, night sweats, malaise, swelling of the legs - heart cancer often produces symptoms of this nature.
When to see a doctor
The many faces of heart cancer symptoms can be characteristic or ambiguous. Heaviness in the chest, emerging arrhythmias, unexplained pain, weight loss, prolonged cough without sputum and often elevated temperature without signs of a cold 37-37.2°C - reasons to make an appointment at the Sofia Cancer Center with an oncologist near the Mayakovskaya metro station " in Moscow. A survey of patients showed that 80% of them did not pay attention to the symptoms.
Causes and risk factors
The causes of heart cancer in men and women, as in many other cases, are not 100% identified. But there are a number of factors that increase the risk of developing the disease. These include the following:
- serious immunity disorders;
- chemical, radiation and UV effects on the body;
- genetic predisposition;
- degeneration of a benign tumor into a malignant one;
- weakening of the body against the background of various negative factors: alcohol abuse, smoking, drug use, poor quality nutrition, sedentary lifestyle, etc.
As already mentioned, cancer in the heart may not be primary - that is, it develops in the form of a subsequent lesion due to oncology in another area. In this case, it is considered secondary, and the cause of the development of oncology is considered to be the primary disease.
Causes of cancer development
There are reasons why heart cancer does not develop as actively as other types of cancer. Cardiomyocytes (structural cells of the heart muscle) practically do not divide. This explains the low incidence rate. The mechanism of the appearance of atypical cells is known: their DNA replaces the DNA of normal cells. They begin to actively divide, a primary tumor is formed, which, as it develops, penetrates into neighboring organs and tissues in the form of metastases. In the absence of active division of cardiac muscle cells, pathological DNA has practically no chance of being integrated into the gene apparatus.
One feature of cardiovascular tissue should be noted. When defects occur, the heart muscle does not recover. It is replaced by other tissues (this picture can be observed during the formation of post-infarction scars). Scientists who have studied the relationship between myocardial infarction and the risk of heart cancer have not found a direct correlation. However, according to doctors, in patients who have had a heart attack, in the first six months the risk of developing malignant tumors in the lungs and bladder increases, which can become a risk factor for heart damage. These data were presented at the 2015 American College of Cardiology (ACC) Scientific Sessions.
Risk factors
The study of the mechanisms of oncological diseases is still ongoing. Risk factors for the occurrence of this pathology include:
- Hereditary predisposition. Transmission through the gene mechanism of the tendency to form atypical cells is possible. Since heart cancer is sometimes detected even during fetal development, there is a possibility that a hereditary factor may be the main factor in the mechanism of its occurrence.
- Weakening of the immune system. Periodically, the immune system weakens, which provokes the development of a variety of diseases. Frequent infectious diseases arise due to a malfunction of the immune system, which normally blocks the appearance and development of cancer cells. The risk group includes people with weakened immune systems (for example, with AIDS or HIV).
- Harmful effects of the environment. There are factors that have a negative impact on the body. This is a bad environment, air polluted with toxic substances, water that contains waste from hazardous industries. Humans are constantly exposed to substances that cause cell mutation due to the use of chemistry in a variety of industries. Separately, it is worth mentioning man-made disasters, which have more than once led to a sharp increase in cancer incidence in disaster areas.
- Radiation. This factor is known to provoke the development of radiation sickness. Anyone who works in conditions of increased radiation is at risk.
- Unhealthy Lifestyle. This term includes several concepts at once. Poor nutrition, lack of sleep, bad habits (tobacco smoking, alcohol abuse) are recognized as risk factors for the appearance of atypical cells.
- Diseases. The development of metastases from primary tumors in the absence of treatment leads to the appearance of secondary tumors. They are formed in various organs and cause the development of metastatic heart cancer. Primary tumors in the lungs, mammary glands or skin cells (melanoma) are especially dangerous. Benign tumors in the heart sometimes degenerate into malignant ones. Endocrine diseases are considered a risk factor, since hormonal imbalances can trigger the development of cancer.
The listed carcinogenic factors are not specific. They can provoke the development of any oncology. The presence of risk factors does not always lead to the development of pathology. They only increase the risk of atypical cells appearing in the body.
Diagnostics
To diagnose heart cancer in women or men, it is necessary to carry out a set of measures and studies:
- Examination and interview at an appointment with a cardiologist.
- X-ray examination.
- Angiocardiography. The method is used to study the thoracic veins, other large vessels, and chambers of the heart.
- ECG, MRI, CT, EchoCG.
- Echoscopy with Doppler examination. It is performed in one of two ways: through the chest, like a regular ultrasound, or through the esophagus.
- Coronary angiography (one of the X-ray methods).
- Several laboratory tests: tumor markers, histological analysis, as well as a number of blood tests (ESR, leukocytes, platelets, hemoglobin, C-reactive protein).
A thorough investigation is very important, as signs of heart cancer may end up pointing to a completely different diagnosis that has a much better prognosis.
Heart tumors
Myxomas
Myxoma accounts for half of all primary cardiac tumors.
Sporadic myxomas of the heart are 2-4 times more common in women. There is a hereditary Carney complex with an autosomal dominant type of inheritance, characterized by multicentric tumors of various localizations - cardiac myxomas, pigmented skin tumors, breast fibroadenomas, ovarian cysts, nodular adrenal dysplasia, myxoid testicular tumors, pituitary adenomas, peripheral nerve schwannomas. The predominant localization of myxomas is the left atrium (about 75%). Pedunculated myxomas prolapse through the mitral valve, making it difficult for the left atrium to empty and to fill the ventricle during diastole. Macroscopically, myxomas can have a mucus-like, hard, lobulated or loose structure. Unformed friable myxomas pose the greatest danger in terms of the development of systemic embolism.
Papillary fibroelastomas
Among primary cardiac tumors, the second most common are benign papillary fibroelastomas, predominantly affecting the aortic and mitral valves. Morphologically, they are avascular papillomas with anemone-like branches extending from the central core. Most often they are pedunculated, but unlike myxomas, they do not cause valve dysfunction, but increase the likelihood of embolism.
Rhabdomyomas
Rhabdomyomas account for 20% of all benign heart tumors and are the most common neoplasm in children. Typically, rhabdomyomas are multiple, have an intramural localization in the septum or wall of the left ventricle, and affect the conduction system of the heart. The course of rhabdomyoma may be accompanied by tachycardia, arrhythmias, and heart failure. These heart tumors are often associated with tuberous sclerosis, sebaceous gland adenomas, and benign kidney tumors.
Fibroids
Connective tissue tumors of the heart also mainly occur in children. They can affect the valves and conduction system of the heart, cause mechanical obstruction, simulating valvular stenosis, the clinical picture of heart failure, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, constrictive pericarditis. Cardiac fibroids may be part of basal cell nevus syndrome (Gorlin syndrome).
Other benign heart tumors
Hemangiomas occur in 5-10% of all primary heart tumors. More often they do not cause clinical symptoms and are detected during routine examination. Less commonly, intramyocardial hemangiomas are accompanied by disturbances in atrioventricular conduction, and when they invade the atrioventricular node, they can lead to sudden death.
Cardiac lipomas can develop at any age. These are usually broad-based tumors located in the epicardium or endocardium. Lipomas are often asymptomatic; when they reach large sizes, they can cause arrhythmias, conduction disturbances, and changes in the shape of the heart, detected by x-ray.
Pheochromocytomas can have intrapericardial or myocardial localization and be accompanied by the secretion of catecholamines. Pericardial cysts on chest radiographs often mimic cardiac tumors or pericardial effusion. More often they are asymptomatic and can sometimes cause symptoms of chest compression.
Treatment
For symptoms of heart cancer and an accurate diagnosis, the following treatment options are offered:
- Radiation therapy. In this case, brachytherapy is often used - this is when a radio source is injected directly into the tumor.
- Chemotherapy is usually used to control metastases in other organs.
- Surgical intervention. It is performed extremely rarely in the treatment of heart cancer - only if the heart is affected and other organs are not yet affected.
- Maintenance therapy. The patient is prescribed medications that alleviate his condition and support the body to fight the disease.
Forecasts
This type of heart cancer has a poor prognosis in men and women. If the problem is detected early and treated effectively, survival of five years is possible. But most often the disease is found late, so the survival time is much shorter.
Two-year survival rate at different stages is possible in the following percentage:
- Stage 1 - 8.3%.
- Stage 2 - 3%.
- Stages 3 and 4 - 0.9%.
If metastases have not spread to the spinal cord and brain, even in the last stages the prognosis is more favorable - 11-14% survival rate over two years.
The situation is more complicated with sarcomas - these are aggressive types of cancer in men and women, which on average give the following survival rate:
- Angiosarcoma: 6-11 months.
- Rhabdomyosarcoma: 2 years at stages 1 and 2, less than a year at stages 3 and 4, provided the primary tumor is removed and chemotherapy is used.
- Liposarcoma: 6-8 months.
As you can see, the prognosis will depend on the characteristics of a particular heart cancer, and it can only be determined after a thorough diagnosis.
Stages of disease development
There are several stages in the development of heart cancer. Zero is the stage before the appearance of the first atypical cells; it is also called a precancerous condition. At this time, the first, not yet noticeable changes occur in the body.
Stages of heart cancer development:
- Stage I: the normal structure of DNA is disrupted. The structure of the cell changes and a period of rapid division begins. This leads to the formation of a primary tumor without clear contours measuring less than 2 cm.
- Stage II: the malignant formation acquires a clear structure, its size is from 2 to 5 cm.
- Stage III: the tumor is larger than 5 cm and begins to metastasize.
- Stage IV: the primary tumor recurs, metastases appear in distant organs.
Statistics
It is difficult to provide global statistics on this disease. But there is one interesting fact. One of the largest research centers in the world, the private Mayo Clinic in the USA, notes that per year they see no more than one patient who shows signs of heart cancer.
But such statistics should not justify a negligent attitude towards the previously listed symptoms. In addition to oncology, there are many other heart-related problems that, if left untreated, can lead to death.
Diagnosis and treatment of heart cancer in Moscow
The Institute of Nuclear Medicine (Moscow region, Khimki, Klyazma quarter) has all the necessary equipment for the diagnosis and treatment of malignant tumors of the heart. Patients are received in a modern outpatient diagnostic complex, built taking into account the latest advances in oncology and radiology.
How to make an appointment with a specialist in oncology
Experienced oncology specialists will help diagnose heart cancer, which is located at the address: Moscow, 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya lane, 10. Nearby, within walking distance, are the Mayakovskaya, Belorusskaya, Tverskaya, Chekhovskaya and Novoslobodskaya". The diagnosis of heart cancer directly with the formation of a tumor in the organ occurs in 1 case out of 100. If you suspect the disease or for the purpose of a preventive examination, make an appointment at the oncology center at the number: +. On the website you can order a call back or fill out a contact form. Take care of your health and that of those close to you!
Forecast
The three-year survival rate after removal of single benign cardiac tumors is 95%. After surgical treatment, patients are observed by a cardiologist and cardiac surgeon with mandatory annual echocardiography monitoring for timely diagnosis of tumor recurrence. When multiple tumors are present, the five-year survival rate is only 15%. For metastatic and primary cardiac tumors, the prognosis is considered unfavorable. Radiation therapy and chemotherapy have no effect on the prognosis, and surgical treatment is considered ineffective.