We offer you a comprehensive examination of the heart and cardiovascular system. If a disease is detected, we will offer you the help of a therapist, cardiologist, etc. In addition to conducting the study, our specialist will interpret the ECG, ABPM results, etc.
- Methods for studying the cardiac vascular system
- Search for the cause of the disturbance in the functioning of the cardiovascular system
Watch our video about diagnostics of the heart, blood vessels and the function of external respiration
. The heart performs the main pumping function in our body, its task is to ensure adequate supply of blood to the tissues, and with it oxygen and nutrients. With heart diseases (coronary artery disease, atherosclerosis, carditis, etc.), not only the heart itself suffers, but also other organs, including the brain.
In our clinic, research of the cardiovascular system takes place in two directions:
- Study of the structure and function of the heart muscle;
- Vascular examination;
- Search for the cause of the disturbance in the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
Diagnostics in cardiology
Diagnosis of heart disease begins with questioning the patient and examination. The result is a preliminary diagnosis and a plan for further management of the patient. Using laboratory and instrumental methods of further examination, the cardiologist can assess the severity of the disease and decide on further tactics for managing the patient. When a doctor examines a patient, he pays attention to skin color, the presence or absence of shortness of breath, swelling, etc. Quite often, in patients with heart disease and the development of cardiac failure, one can see “blueness” of the lips, tip of the nose, fingers, especially under the nails. And the cardiologist calls this “cyanosis” acrocyanosis (peripheral cyanosis). There are also patients whose skin everywhere on all parts of the body has a “bluish” color - this often happens with very severe heart lesions, heart defects, diseases of the lungs, and body. A cardiologist calls this “cyanosis” central cyanosis. When examining a patient, the cardiologist also pays attention to the pulsation in large vessels, thanks to which a lot of information can be obtained about the state of the cardiovascular system.
ECHO-cardiography (ECHO-CG)
If, during an examination, the patient has elevated blood pressure numbers, expansion of the boundaries of the heart, murmurs when listening to the heart, pathological changes are detected on the ECG, and also if changes in the size and shape of the heart are visible on the chest x-ray, its atypical location, or modified aorta and pulmonary artery, the doctor prescribes an ultrasound examination of the heart: transthoracic echocardiography.
ECHO-cardiography (ECHO-CG, cardiac ultrasound) is an ultrasound method for studying the structure and function of the heart. The method is based on capturing ultrasonic signals reflected from the structures of the heart by a sensor and converting them into an image on the monitor screen. When performing ECHO-CG, the doctor evaluates:
- the size of the heart and its chambers, as well as the pressure in them,
- condition of the atria and ventricles (heart chambers) and heart valves,
- the thickness of the walls of the heart, their structure and integrity,
- contractile function of the myocardium (work of the heart muscle),
- features of blood movement inside the heart through the valves
- condition of the outer lining of the heart - the pericardium
- condition of the pulmonary artery and aorta, pressure in them.
ECHO-CG is the main method for diagnosing acute and chronic heart diseases: defects, inflammatory diseases of the heart valve apparatus and its membranes (endocarditis, pericarditis). This study also evaluates and clarifies the degree of myocardial hypertrophy, the presence of dysfunction of the heart muscle when it is damaged (infarction, myocarditis), and the presence of blood clots in the cavities of the heart. A cardiologist or therapist, correlating the data obtained from ECHO-CG with the clinical picture, decides on the tactics for further management of the patient.
Electrocardiography
Quite often, a patient comes to a cardiologist with previously taken ECGs. This is not surprising, because the ECG shows the cardiologist the state of the atria, ventricle, and how the heart feels at the moment, whether it receives enough blood, whether there are rhythm disturbances. All this can be read from the ECG, but information from the ECG is information here and now at some fraction of a second, but also if we talk about previously occurring disasters, such as myocardial infarction, then the ECG can tell. To have even more detailed information (this is often to understand what the blood supply to the heart is like when the patient moves, sleeps, laughs, cries. This method is called Hm-ECG (this is an ECG during the day). Such a study can give a cardiologist a lot of information, because that this method monitors the patient’s condition for 24 hours and the likelihood of detecting changes can be much greater, since there is a lot of time involved in monitoring the condition of the heart. Thanks to ECHO-CG, it is possible to uniquely and safely determine the condition of the heart and large vessels for the patient. This method allows you to assess the condition of the heart valves, see how the walls contract, how actively and in what volume blood is ejected from the heart, see with the help of a Doppler study the direction and what intensity the blood moves through the parts of the heart.
Methods for studying the cardiac vascular system
- ECG, Holter-ECG, ECG with stress - determination of the electrical potentials of the heart to clarify the causes of pain in the heart, sensations of “interruptions” in the work of the heart, fainting, tachycardia and other paroxysmal conditions.
- Echo-CG - this method allows you to assess in real time the condition of heart tissue, the contractility of the heart muscle, and the functioning of the heart valves.
- Daily blood pressure monitoring, blood pressure testing under stress – If problems arise with a decrease or increase in blood pressure, the examination of the patient usually begins with a study of daily blood pressure. Daily monitoring provides much more information than a single measurement.
- Coronary radiography – used to diagnose coronary heart disease by visualizing the coronary arteries on coronary radiographs
- Self-monitoring of blood pressure and pulse rate - in many cases, we recommend regularly measuring your pulse and blood pressure to determine the effectiveness of your treatment.
- Polysomnography. Sleep study. Diagnosis of sleep problems - if heart problems occur during sleep, for example, stopping breathing during sleep (sleep apnea), nighttime episodes of palpitations, increased blood pressure associated with snoring, we recommend polysomnography.
- biochemical blood test (lipid profile
- coagulogram
- consultation with a therapist or cardiologist.
Electrocardiography: ECG, Holter-ECG, ECG with stress
Electrocardiography. ECG is the main and mandatory method for studying the heart and its functional state. An ECG helps to determine the cause of pain, shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, to obtain an explanation for the sensations of “interruptions” in the work of the heart, the cause of edema, and to identify hidden heart rhythm disturbances.
A typical routine ECG is performed in the supine position for a few minutes. Sensors are attached to the patient’s chest, arms and legs, from which signals are sent to the recording device, and the doctor describes them. A cardiogram taken within a few minutes does not reflect a complete picture of the condition of the heart and is not a diagnosis . If we are talking about paroxysmal conditions, it is more advisable to carry out daily Holter ECG monitoring.
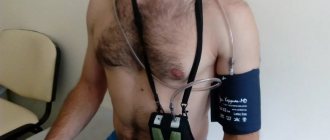
Holter -ECG (Holter monitoring). A method of continuous recording of heart function throughout the day, which makes it possible to identify short-term changes in the rhythm and blood supply of the heart that occur during the day, including at night, thereby identifying hidden and short-term heart problems. The results of Holter monitoring show the heart’s reaction to all events that occurred during the day, including physical activity, stress, sleep, food intake, etc.
How is Holter monitoring performed? ECG recording is carried out using a special portable recorder, the size of a mobile phone, and sensors on the chest, which the patient carries with him under his clothes. After installing the recorder, we recommend that you lead your normal lifestyle with hourly display in the diary of emotional and physical stress received during the day.
ECG with stress. Basically, performing an ECG with stress is required to determine a person’s suitability for various kinds of extreme stress, for example, for pilots, athletes, and before conscription into the army. Carrying out an ECG with stress allows us to identify hidden cardiovascular insufficiency and the threshold of physical activity that the patient can tolerate without harm to his health. Stress ECG is more often performed in young patients.
How is a stress ECG performed? An exercise ECG is performed using a bicycle ergometer (an exercise bike) or a treadmill (a moving treadmill). The doctor installs special sensors on the patient’s body and, in a mode of increasing physical activity, a continuous ECG recording is performed, which makes it possible to determine the threshold of physical activity that does not cause disturbances in cardiac activity.
We recommend that you take with you to the clinic the results of previously conducted ECG studies, which may be useful for more accurately determining the dynamics of pathological processes in the heart muscle.
Main indications for ECG, Holter-ECG, ECG with stress:
- Pain in the heart area
- Cardiac ischemia
- Shortness of breath of unknown origin
- Cardiopalmus
- Feeling of interruptions in the heart
- Edema of unspecified nature
- Increased or decreased blood pressure
- Preventive examination
Echocardiography / Echo-CG / Ultrasound of the heart
Echocardiography or Echo-CG, cardiac ultrasound is a method of ultrasound diagnostics of the functional and anatomical state of the heart muscle and the valvular apparatus of the heart. Ultrasound of the heart is relatively simple to perform, does not have a harmful effect on the patient, and is highly informative. As a rule, we perform echocardiography to diagnose coronary heart disease, when examining for heart pain, heart failure, heart defects and inflammatory diseases (carditis).
How is Echo-CG performed: Ultrasound of the heart is performed using an ultrasound machine equipped with a cardiac sensor and an appropriate program with the patient lying on the couch. Ultrasound freely penetrates the intercostal spaces and, reflected from the heart and moving blood, returns to the sensor. The doctor, using a sensor, receives an ultrasound signal that displays the anatomical state of the tissues of the heart muscle and valve apparatus, then, using a set of programs, processes the resulting image and calculates the parameters of the heart.
We recommend that you take with you to the clinic the results of previous echocardiography studies, which may be useful for comparison with the new echocardiography data obtained. This way you can judge the effectiveness of the treatment and the improvement/deterioration of the heart condition.
Main indications for Echo-CG:
- Pain in the heart area
- Fainting during exercise
- Cardiac ischemia
- Anatomical malformations of the heart
- Heart valve insufficiency or stenosis
- Impaired cardiac hemodynamics
- Inflammatory processes in the heart - carditis
- Swelling of the legs
- Resolving the issue of indications for surgical treatment
24-hour blood pressure monitoring, blood pressure testing under stress
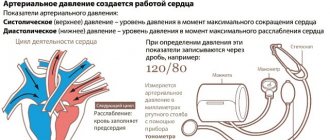
Daily blood pressure (BP) monitoring reflects its true values during the day during your normal lifestyle. These data cannot be obtained with a single blood pressure measurement. In some cases, it is advisable to simultaneously monitor an ECG (electrocardiogram) and blood pressure.
Daily monitoring of blood pressure with high blood pressure allows for early diagnosis of arterial hypertension, its connection with emotional and physical stress, and optimization of the time of taking medications. This method allows you to identify patients with nocturnal hypertension, when the increase in blood pressure is invisible and therefore dangerous, as well as for assessing blood pressure during nocturnal angina and respiratory failure.
Daily monitoring of blood pressure with low blood pressure allows you to find the cause of fainting and semi-fainting states, attacks of weakness.
How is daily blood pressure monitoring performed? The patient is given a cuff on his left arm, which is then placed on the arm for 24 hours, and a small compressor with a recorder, which pumps air into the cuff at a certain frequency and measures blood pressure. It is important to lead an ordinary lifestyle with an hourly display in the diary of the emotional and physical stress received during the day.
Study of blood pressure under load. The study of blood pressure under load makes it possible to assess the direction and severity of shifts in basic hemodynamic parameters under the influence of different types of physical activity, as well as the speed of their recovery.
How is blood pressure tested under stress? The patient's blood pressure is measured at rest and its value is compared after exercise on a bicycle ergometer or physical exercise. When carrying out 24-hour blood pressure monitoring, you can conduct test stair climbs (to be agreed with your doctor). We recommend that you take with you to the clinic the results of previous blood pressure tests, which may be useful for the early diagnosis of arterial hypertension and optimize the timing of taking medications.
Main indications for daily blood pressure monitoring:
- Unstable blood pressure readings
- Frequent headaches of unspecified nature
- Swelling in the legs
- To clarify the degree of arterial hypertension and individual rhythms of blood pressure fluctuations during ducks
- To select adequate therapy for hypertension
- To control the treatment
- Fainting
The main indications for performing a blood pressure test under load:
- Prolonged stress conditions
- Unstable blood pressure readings
- Feeling worse during physical activity
- Examination before stress loads (pilots, athletes, military personnel)
Coronary angiography – diagnosis of coronary heart disease
Coronary angiography is a contrast X-ray examination of the vessels of the heart, performed on an outpatient basis without hospitalization. Coronary angiography allows you to determine the nature, location, extent and degree of narrowing of the coronary vessels of the heart. This study is performed to determine the feasibility of surgical treatment of coronary heart disease.
How coronary angiography is performed: Under local or general anesthesia, the doctor installs a special catheter through the femoral artery or through the artery of the forearm, which is passed through the bloodstream through the upper part of the aorta into the vessels that supply the heart. A radiopaque substance is injected through the catheter, which is carried through the bloodstream through the coronary arteries that supply the heart muscle. Using a special device, an angiograph, areas of obstruction in the patency of the bloodstream are recorded. Upon completion of the study, the doctor makes a conclusion on the choice of treatment method.
Preparation for coronary angiography: Before performing coronary angiography, it is necessary to take a general blood test, determine the blood group and Rh factor, and test the blood for hepatitis and HIV infection. The issue of the need for coronary angiography is decided after consultation with a cardiologist.
Main indications for coronary angiography:
- Coronary heart disease with risk of developing myocardial infarction
- Heart failure
- Unstable angina not amenable to drug correction
- Left ventricular dysfunction accompanied by arterial hypotension or pulmonary edema
- Establishing the degree of risk of complications during planning heart surgery for valve replacement and correction of congenital heart defects
Self-monitoring of blood pressure and pulse rate
The easiest way to monitor heart function and blood pressure is to take self-measurements and record the data in a diary. We recommend regular blood pressure and pulse measurements for 10 days: this period is usually sufficient to obtain a statistically reliable result. Such control, among other things, makes it possible to assess the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment.
How to independently monitor blood pressure and pulse rate: We recommend performing the measurement procedure while sitting on a chair with a backrest, placing your hands on the table at chest or stomach level. Measurements are taken in the morning immediately after waking up from sleep and in the evening before going to bed in a quiet environment. It is not recommended to walk up the stairs, drink hot drinks, eat heavily or take a shower before measuring blood pressure and pulse. It is allowed to carry out the measurement procedure at intervals of 15–20 minutes after these moments. All results of measurements of pulse number and pressure are recorded on a tablet with which after 5 - 10 days you need to come to the doctor or send it by e-mail.
Exercise tests
There is another very interesting method for identifying the degree of decrease in blood circulation (this is the so-called myocardial ischemia) these are tests with physical activity: veloergometry (the patient with the ECG electrodes connected is on a bicycle and pedals). The state of the heart and blood vessels is assessed in response to physical activity. A similar method is the treadmill test (only the patient is on a treadmill). Thus, we see that thanks to the combination of all examination methods, it is possible to collect a detailed picture about this disease. Thus, the cardiologist has a clear picture of the disease and is already moving along the precisely planned path of treatment for this disease.
Expert electrocardiographers
Professional cardiographic systems designed specifically for cardiology clinics and departments. Manufactured using the latest technical advances, electrocardiographs are distinguished by their modern ergonomic design, functionality and ease of use. The high-resolution touch screen displays all 12 leads. The quality of electrocardiogram printing will satisfy even the most demanding cardiologist.
24-hour Holter ECG monitoring
Depending on the nature of the pathological process, the clinical picture at the current time may not provide clear criteria for establishing a clinical diagnosis. In this case, the doctor prescribes diagnostic studies carried out over a wider time range, during the patient’s daily activities, allowing not only to monitor the activity of the cardiovascular system, but also to identify those trigger factors that lead to pathological changes. This group of studies used in outpatient practice includes 24-hour Holter ECG monitoring (Holter CMECG) and 24-hour blood pressure monitoring (ABPM).
The 24-hour ECG monitoring system consists of an ECG recorder (which the patient usually wears on his belt in the provided case) and a system of electrodes (wires) attached to the patient's body. At the end of the study, the doctor transfers the ECG data into a computer program, and after performing digital analysis, interprets the results and draws up a medical report.
Indications for daily ECG monitoring are:
- suspicion of cardiac arrhythmia and conduction disturbances;
- suspicion of coronary heart disease;
- assessment of the correct operation of the artificial pacemaker (pacemaker);
- history of fainting, attacks of dizziness and sudden weakness.
To conduct the study, it is important to properly prepare the skin for the placement of electrodes: the hair at the places where the wires are connected is shaved off, and the skin is degreased. It is advisable for the patient to wear loose, comfortable clothing during the examination. Water procedures (bathing, showering) are excluded for the duration of the SMEKG.
During the study, the patient leads a normal lifestyle (works, plays sports, walks), recording all complaints that arise during the monitoring process in a special diary. In addition, the diary indicates possible medication intake and changes in types of physical activity.
Description of ECG
The ECG graph analyzes:
- An isoelectric line is a horizontal line recorded during a period when no excitation of activity is noted in the heart). It is the starting point for the changes listed below;
- teeth - deviations from the isoelectric line (the upper tooth is called positive, the lower - negative); The teeth in the figure are: P, Q, R, S, T, U
- a segment is an isoelectric line between teeth; the figure shows the segment ST and PQ
- intervals are fragments of the ECG graph that include ……… and the adjacent tooth; The figure shows the QT and PQ
In the ECG display we see (from left to right):
- P wave - characterizes depolarization of the atrial muscle
- segment PQ – reflects the time of depolarization through the atrioventricular node
- PQ interval - reflects the time of depolarization from the sinoatrial node to the atrioventricular node
- QRS complex – corresponds to depolarization of the ventricular myocardium
- QT interval - reflects the time of the action potential of the ventricular myocardium (depolarization + repolarization)
- ST segment – reflects the period of ventricular repolarization
- T wave - corresponds to ventricular repolarization
- U wave - not observed in practice