Pain Treatment Center
Alekseeva
Oksana Alexandrovna
23 years of experience
Doctor, highest qualification category, member of the European Association of Neurologists, Russian Interregional Society for the Study of Pain (ROIB), Association of Interdisciplinary Medicine. Has experience working in hospital and outpatient services. He has seven published works on neurology.
Make an appointment
In ensuring the normal functioning of the human body, one of the key positions is occupied by the autonomic nervous system (ANS) - a complex of nervous structures responsible for maintaining a constant internal environment (homeostasis). The efforts of the ANS regulate the functioning of the circulatory and lymphatic systems, internal organs, and endocrine glands. The ANS itself is part of the nervous system (NS), but has an important feature - autonomy, that is, a person cannot control it with his own will.
Various disorders in the functioning of the ANS are called vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD). This term does not mean a separate disease itself, but a syndrome - a condition caused by diseases of certain organs and systems (mental or somatic pathologies, hormonal imbalances).
Main symptoms and signs
The manifestations of VSD are diverse; the general list includes over several dozen items, but patients experience only a few of them (usually from 5 to 20) in different combinations. An important point: with VSD, there is a combination of several symptoms that appear simultaneously, but in the complete absence of organic disorders. A separate manifestation of any of these signs is not a reason for diagnosing vegetative-vascular dystonia, since it usually indicates a specific pathology.
Doctors distinguish several forms of VSD, classifying them on the basis of identifying relatively typical sets of symptoms that resemble the course of certain pathologies of organs or systems.
Respiratory form of VSD
Respiratory vegetative-vascular dystonia is the most common. The patient complains of the inability to take a deep breath, is afraid of suffocating, gasps for air, feels soreness, tightness in the throat, heaviness or pain in the chest, and coughs frequently.
Tachycardial form
Complaints of rapid heartbeat (tachycardia), irregular heart rhythm, sensation of vascular pulsation and heat in the temples and neck. It should not be confused with a similar picture with arrhythmia, paroxysmal tachycardia.
Cardiological form
In the area of the heart, pain of a different nature is noted (long-term aching or sharp, sharp), without a clear localization. During an attack of cardiac vegetative-vascular dystonia, the patient is anxious and breathes heavily. The pain lasts longer than with cardiovascular diseases (angina pectoris, myocardial infarction), does not depend on physical activity and is not relieved by appropriate medications (validol, nitroglycerin and others).
Hypotonic form
Characterized by dizziness, darkening of the eyes, sudden perspiration on the forehead, sweating, weakness, cold palms. Blood pressure drops briefly to 90/60 or below.
Hypertensive form
During an attack, tachycardia and heart pain are observed against the background of a short-term increase in blood pressure. The main difference from real hypertension: the pressure does not exceed 150/90.
Asthenic form
Performance decreases, complaints of fatigue, weakness, inability to concentrate, and sometimes body temperature rises slightly. Tremor (shaking in the hands) is possible, especially with the slightest physical exertion or a stressful situation. Irritability for no apparent reason or due to insignificant reasons, tearfulness.
Visceral form
Manifested by symptoms from the gastrointestinal tract (functioning disorder, nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, irritable bowel syndrome).
Mixed form
It combines certain signs characteristic of all the above forms of VSD, in arbitrary combinations.
Sometimes patients experience acute manifestations of symptoms, so-called attacks of dystonia or vegetative crises. An attack of VSD is characterized by sudden, spontaneous and rapid development, regardless of the circumstances. It can happen both during physical activity or a stressful situation, and at rest or sleep; alone or in a crowded place. Patients are afraid of suffocation, fear of death from respiratory or cardiac arrest, some feel feverish, others feel cold.
Separately, it is worth mentioning pre-syncope and fainting. They can have different origins; based on trigger mechanisms, they are distinguished:
- psycho-emotional - as a result of experiences, fear, reaction to the sight of blood;
- orthostatic - due to a sudden change in position, usually when abruptly getting up from a chair or bed;
- hypotonic – due to a sharp decrease in blood pressure.
Loss of consciousness is usually short-lived, lasting 1-3 minutes, the patient quickly comes to his senses. A history of fainting may indicate more severe pathologies, such as adrenal or cardiovascular insufficiency, nephropathy, or diabetes mellitus.
With such an impressive range of complaints, patients often do not experience any pathological changes in the structure or functioning of organs and systems. They often experience fear of developing a serious pathology, attributing to themselves some kind of disease based on similar signs. So, some fear paralysis due to mild numbness of the limbs or a heart attack due to chest pain.
Do you have symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD)?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Vegetative-vascular dystonia: symptoms and treatment in adults
The term VSD is used in their practice only by doctors from CIS countries; in the West, such a disease does not exist. In this regard, some confusion arises. Some experts do not recognize the existence of vegetative-vascular dystonia in adults, while others, on the contrary, consider it a conditional nosological form. The complex of symptoms and causes of dystonia are extensive, so the examination must be comprehensive and qualified. Still, in most cases, the syndrome is not associated with any serious disease, but is a sign. To find out whether it is possible to get rid of vegetative-vascular dystonia forever, you need to know its symptoms and current treatment regimens, including folk remedies. It is these aspects of VSD in adults that we will consider in the article. Classification To date, a unified classification of VSD has not been developed. According to various authors, autonomic dysfunction differs according to a number of the following criteria: 1. Mixed type. It occurs when there is a conflict between parasympathetic and sympathetic. This looks like a struggle for leadership in the nervous system and this is also not normal. 2. Hypotonic type. If the parasympathetic nervous system significantly predominates throughout the day, the body is filled with energy, but cannot use its strength, depression, hypotension, etc. occurs. 3. Hypertensive type. If the sympathetic nervous system predominates throughout the day, a person feels palpitations, a feeling of fear, the body quickly gets tired, sleeps poorly, the parasympathetic system cannot cope, and strength is not restored. Based on the nature of the attacks that complicate the symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia, sympathoadrenal, vagoinsular and mixed crises are distinguished. Mild crises are characterized by monosymptomatic manifestations, occur with pronounced vegetative changes, and last 10-15 minutes. Crises of moderate severity have polysymptomatic manifestations, pronounced vegetative changes and last from 15 to 20 minutes. Severe crises are manifested by polysymptoms, severe vegetative disorders, hyperkinesis, convulsions, attacks lasting more than one hour and post-crisis asthenia for several days. Causes Why does VSD occur, and what is it? Vegetative-vascular dystonia is a disorder of the autonomic nervous system. The ANS is responsible for maintaining internal balance in the human body, influencing all organs and organ systems. Disturbances in the functioning of the ANS most often manifest themselves in the form of dysfunctions of blood circulation, digestion, and heat exchange. In adults, the prevalence of the syndrome is high in the age group of 20-30 years, while in women manifestations of dystonia are more common than in men. In old age, the likelihood of developing VSD decreases sharply. Among the external factors that contribute to the appearance of signs of VSD are: • severe stress, depression; • severe viral infection; • exposure to electric current; • radioactive exposure; • excessive insolation; • unfavorable environment; • alcoholism, drug addiction; • insomnia, mental fatigue; • heavy physical activity; • traumatic brain injury; • protracted bacterial disease (eg, sore throat, bronchitis). The risk group affects a fairly large number of the population: 1. Women. Oddly enough, women, by nature, are more emotional, vulnerable and receptive. Accordingly, the mental state is more easily disturbed. 2. Teenagers, pregnant women, women during menopause (sharp hormonal disruptions). 3. People whose work is closely related to travel (constant acclimatization) and a sedentary lifestyle. 4. Men and women diagnosed with cervical osteochondrosis. 5. Living in constant psycho-emotional discomfort. 6. VSD can occur in people who have suffered birth injuries, oxygen starvation, even at birth. 7. Suspicious and stressed people are also at risk. 8. People in whom the majority of family members are diagnosed with VSD (hereditary predisposition). 9. Suffering from chronic diseases. The disease manifests itself with certain symptoms, which occur in attacks or are permanent. Moreover, the presence of constant symptoms indicates congenital instability of the nervous system. General signs of VSD in adults Vegetative-vascular dystonia in adults has very different symptoms depending on the weak point in the body that reacts to the stimulus. However, most often, experts note the following signs: • hot flashes; • vascular spasms; • shallow sleep; • tremor of the hands and even legs; • fainting conditions; • strong heartbeat; • apathy and lack of strength; • severe lack of air; • frequent headaches and even migraines; • cardiac arrhythmia in all its manifestations; • internal trembling and various manifestations of fears; • joint pain, regardless of arthritis and arthrosis; • cold hands at any time, even at above-zero temperatures and heat; • neurotic deviations from overexcitability to active passivity. These are the most characteristic signs of VSD, which adults often ignore, attributing them to individual physiological characteristics. Symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia In the case of vegetative-vascular dystonia, the symptoms are very diverse, which is due to the multifaceted influence on the body of the VNS, which regulates the basic vegetative functions - breathing, blood supply, sweating, urination, digestion, etc. In this regard, several groups of vegetative symptoms are distinguished -vascular dystonia in adults due to predominant disturbances in the activity of various body systems. These disorders can manifest themselves in isolation or in combination with each other: 1. In the cardiovascular system: disturbances in heart rate (increasing or stopping), fluctuations in blood pressure, pain in the left half of the chest; 2. In the respiratory system: feeling of lack of air, suffocation, shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, rapid breathing; 3. In the digestive system: nausea and gag reflex, flatulence, belching, heartburn, constipation and diarrhea; 4. In the thermo-regulatory system: chills, coldness in the extremities, increased sweating, increased temperature due to stress; 5. In the vestibular system: dizziness, lightheadedness; 6. In the genitourinary system: frequent urination, pain and itching in the genital area; 7. In the emotional sphere: anxiety, restlessness, phobias, increased fatigue, decreased performance, constant emotional stress, low mood, tearfulness, appetite and sleep disorders. The course of vegetative-vascular dystonia can be hidden, can be permanent, or can manifest itself in paroxysms (vegetative crises). Most often, crises occur against the background of mental and physical stress, with increased emotional stress, as well as with various infectious diseases. Their duration can vary from several minutes to several hours. Attacks of exacerbation of VSD An attack of vegetative-vascular dystonia begins sharply, suddenly. A person suddenly experiences palpitations, increased blood pressure, pale skin, increased body temperature, and developed chills. During an attack, a person has a pronounced strong fear. After a crisis, a large amount of light-colored urine is released and severe weakness develops, including trembling in the legs and the inability to move normally. In the period after the crisis, a sharp decrease in blood pressure is possible. In addition, exacerbation of VSD can occur in the form of a vagoinsular crisis. It is characterized by the appearance of sudden fainting, which is preceded by short-term pre-fainting phenomena (for example, darkening in the eyes, noise in the head, severe weakness, a feeling of the unreality of what is happening). Also, during an attack, a person may experience sharp and severe pain in the abdomen, an imperative desire to empty the intestines, increased motility of the digestive tract, decreased blood pressure, bradycardia, increased sweating, as well as a feeling of heat, nausea, melancholy and severe fear. Diagnosis of VSD To understand how to treat vegetative vascular dystonia, it is necessary not only to diagnose the disease, but also to determine the cause of its development. Therefore, in order to correctly diagnose VSD, professionalism is required, as well as the coordination of the work of such specialists as a cardiologist, neurologist, and therapist. It is necessary to weed out other diagnoses that have similar symptoms. To do this, you will have to undergo certain examinations: • computer electroencephalography, • electrocardiography, • magnetic nuclear resonance, • vegetative tests. Of course, the diagnosis will be prescribed based on the results of a conversation with the patient, after familiarizing himself with his complaints. Treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia When vegetative-vascular dystonia is detected, treatment is carried out depending on the type of syndrome, and the therapeutic strategy should also take into account other existing somatic diseases. The treatment complex includes medicinal methods of controlling VSD and non-medicinal methods, which can sometimes be very effective and even replace basic drug therapy. Therefore, treatment with this syndrome should begin not with the use of medications, but with changes in diet and lifestyle. It is necessary to observe: • an adequate work and rest schedule; • balanced and healthy diet; • adequate level of physical activity; • rejection of bad habits; • elimination of occupational hazards; • avoiding stressful situations or developing stress resistance; • normalization of body mass index. The following methods also have an excellent effect on curing VSD: • water procedures; • reflexology; •massotherapy. Also, the physiotherapeutic effect will depend on the type of dysfunction of the autonomic system. • for vagotonia, electropharesis with calcium, caffeine and mesatone is prescribed. • for sympathicotonia - with papaverine and bromine, magnesium and aminophylline. If these measures, which are aimed at a general strengthening effect, do not help much, then pharmaceutical drugs are prescribed. They are selected individually for each patient, starting with minimal doses and gradually increasing to the desired concentration. Particular attention is paid to getting rid of chronic foci of infection in the body, treating endocrine and other pathologies. Drug treatment of VSD in adults Treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia is carried out mainly according to symptoms. It is impossible to say exactly what drugs will be prescribed for treatment; it depends on the characteristics of the case, they are selected only after examining the patient. First of all, antidepressants and tranquilizers are prescribed. The dosage is selected based on the severity of symptoms. In addition to them, antihypertensive drugs are prescribed or, on the contrary, caffeine to raise blood pressure. B vitamins, ginseng and beta blockers are considered mandatory. A special group in the treatment of VSD consists of nootropic drugs (such as Nootropil, Piracetam), which have the ability to improve energy processes and blood supply to the brain, increasing the brain’s resistance to oxygen starvation. These drugs activate intellectual functions and improve brain memory. However, you cannot take them on your own. Let's consider some drugs used in the treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia: 1. Persen. Has a calming and relaxing effect. 2. Novo-passit. The herbal drug has a pronounced sedative effect and helps in the fight against fears and anxiety. 3. Corvalol. Calms the body and helps normalize sleep. Also has a slight relaxing effect. 4. Valocormid. It has an antispasmodic, relaxing and cardiotonic (reducing the load on the heart) effect. Corrects the excitability of the nervous system. 5. Normatens. A drug that fights hypertension. The medicine also causes vasodilation and minimizes overall peripheral vascular resistance. Makes physiological sleep deeper. 6. Azafen. Eliminates anxiety, improves mood, eliminates sadness. 7. Vinpocetine. A medicine that improves cerebral circulation. Produces a vasodilating effect. Thus, the range of drugs used to treat VSD is quite wide. This is due to the fact that, along with treatment of the underlying disease, it is necessary to carry out effective symptomatic therapy aimed at relieving the painful manifestations of VSD. Folk treatment of vegetative vascular dystonia The use of folk methods is classified depending on the type of VSD: 1. For vegetative disorders of the hypotonic type, herbs such as ginseng, aralia, sandy immortelle, eutherococcus, eleutherococcus, Leuzea safflower, juniper, bearberry, Schisandra chinensis, lingonberry are used . They are designed to improve well-being and increase blood pressure. 2. For disorders of the hypertensive or mixed type, herbal preparations and plants that have a calming effect are widely used: mint, valerian, sage, motherwort, peony root, lemon balm, hops. These herbs, on the contrary, soothe and lower blood pressure. Vegetative vascular dystonia is primarily a disorder of the nervous system. Therefore, in most cases, treatment of VSD with folk remedies is based on taking soothing decoctions of medicinal plants with the function of normalizing blood pressure and the activity of the heart muscle. 1. Take equal quantities of calendula flowers, valerian root and rhizome, caraway fruits, motherwort, dill seeds and mix thoroughly. 1 teaspoon of the mixture per 200 ml of boiling water, let stand for two hours, filter. Use for vegetative-vascular dystonia 4-5 times, 1 tbsp. spoon a day. 2. We use 0.5 shares of juniper fruits, 0.5 shares of calamus rhizomes, 2 shares of rose hips, 2 shares of yarrow herb, 1 share of strawberry leaves, 1 share of speedwell grass, 1 share of St. John's wort herb, 1 share of chicory flowers, mix. Let's take 2 tbsp. l. collection, add 500 ml of boiling water, leave in a thermos overnight. We filter and take the infusion in 3 doses on an empty stomach. 3. Motherwort tincture. Take 40–50 drops 3–4 times a day. In terms of effectiveness, this drug surpasses even valerian tincture. It relieves pain in the heart, relieves nervous shock and palpitations. 4. You need to mix 200 ml of natural Cahors, honey and freshly squeezed juices of carrots, garlic, lemon, radish and beets. Take this medicine 15 ml (tablespoon) half an hour before breakfast, lunch and dinner. 5. Crushed valerian rhizome – 15 g, yarrow – 50 g, lemon balm – 10 g, pour 1 liter of hot water, put on low heat and boil for 20 minutes, filter. Drink a decoction for vegetative-vascular dystonia, 150 ml 3 times a day before meals. 6. 200 g of dried apricots, 25 g of walnuts, seedless raisins, figs - preferably dried, chop everything. Use 1 tbsp once a day. spoon with kefir. The course of treatment is one month, take a break for 1 week and repeat. The mixture is useful for vegetative-vascular dystonia and also has taste qualities. 7. Pour one glass of dill seed and 10 g of crushed dry valerian root into 1 liter of boiling water in a thermos, let it sit for two days, filter, then add 50 g of honey, strain. Drink 2 tbsp. spoons before meals. Healing herbs do not cause dependence or addiction; they can be taken for a long time. They have a mild healing effect on the body; in addition, it is possible to quickly determine whether they are suitable for treatment in each particular case. However, before you start taking folk remedies, you should check with your doctor for any contraindications. Physiotherapy Methods of physiotherapeutic treatment of this autonomic disorder include: • electrosleep; • electrophoresis; • inductothermy; • darsonvalization; • galvanization; • laser therapy; • magnetic therapy; • aeroionotherapy. Physiotherapy in the treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia is aimed at regulating vascular tone, normalizing metabolism and eliminating pain. The nature, systematicity and intensity of the procedures are selected by the doctor in accordance with the characteristics of the disease. Massage Massage for vegetative neurosis should be carried out in accordance with the type of disease. For the hypertensive type, massage of the collar area, legs, and abdomen is recommended. Impact techniques along with beating should be excluded. For hypotensive vegetative-vascular dystonia, acupressure and general massage are performed using elements such as stroking, rubbing, kneading, and vibration. Massage helps to normalize the functionality of the nervous system, eliminate headaches, and improve the patient’s sleep. Physical exercise Daily walks in the fresh air and moderate exercise bring relief. It is especially good to visit the pool regularly; swimming is recommended by all doctors. Skiing in the winter forest, hiking - anything that gives sufficient stress to the muscles and brings joy. The latter is especially important. Classes must be pleasure. You can engage in the development of the dance of the abdomen or Latin dance. Movement to music, live communication is a beautiful medicine for depression. Prevention of VVD: How to avoid crises these preventive measures will help to avoid crises that people suffering from people suffering from people. First of all, this applies to compliance with certain rules: 1. A rational balanced diet with the rejection of harmful food (salty, spicy, fried, flour, sweet, fast food, etc.); 2. A full -fledged night vacation (sleep should last at least 8 hours in a well -ventilated room); 3. Sports (mandatory: 10-15-minute morning gymnastics and 2-3 times a week visiting the sports section); 4. Daily 1-2 hour walks in the fresh air; 5. Harmonization of labor activity and rest; 6. Refusal of pernicious habits. Thus, vegetovascular dystonia is a disease that does not pose a threat to human life, but at the same time significantly reduces its quality. The presence of any signs of VSD is a reason for consulting a specialist. After all, only timely and correct treatment is a guarantee of improving the condition, thereby increasing the chances of getting rid of the VSD forever.
Diagnostics
To begin with, the doctor, during a conversation with the patient, collects a detailed anamnesis - finds out the complaints, their nature, frequency of occurrence, the presence of a hereditary factor (are there people in the family who suffer from confirmed VSD).
Then a general examination is carried out, attention is paid to the patient’s behavior and his emotional background.
Due to the presence of symptoms similar to those of various other diseases (arrhythmia, hypertension, pathologies of the thyroid gland, gastritis, etc.), each patient with suspected VSD must undergo a detailed therapeutic examination in a clinical setting. To confirm the diagnosis of VSD, it is necessary to absolutely exclude diseases with similar symptoms. For this purpose, laboratory tests are prescribed:
- general blood analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- liver and kidney function indicators;
- analysis of thyroid hormone levels;
- clarifying tests at the discretion of the doctor.
Next, a referral is given for instrumental examinations, of which the most frequently used are:
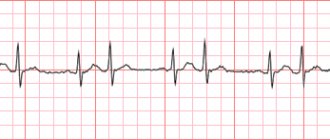
- electrocardiography (ECG);
- echocardiography;
- 24-hour Holter blood pressure monitoring;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs, kidneys, neck vessels, thyroid gland;
- chest x-ray;
- spirometry;
- bicycle ergometry.
Sometimes the doctor requires additional diagnostic methods, such as computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), electroencephalography, colonoscopy and others. Various functional tests are also carried out (psycho-emotional, orthostatic, physical exercise, pharmacological).
What is VSD
Vegetovascular dystonia (VSD), or neurocirculatory syndrome, is a functional disorder of the autonomic nervous system, in which a complex of symptoms appears that are not characteristic of a specific disease. Examination of patients with suspected VSD most often does not reveal changes in the structure of internal organs, but may show deviations in their function at the border of normal.
Autonomic dysfunction cannot be called a full-fledged disease; this diagnosis is not included in the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10). But therapists, cardiologists and neurologists continue to make this diagnosis to patients in whom the examination did not reveal any disorders, and complaints of poor health continue.
It is believed that manifestations of pathology arise due to disturbances in the coordination of the two structures of the autonomic nervous system. It consists of the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems, which differ in their effects on the body. The activator of sympathy is the hormone adrenaline, so it performs the following functions:
- increases the number of heart contractions;
- increases blood pressure;
- stimulates the release of glucose into the blood;
- dilates the arteries of the brain, lungs and heart;
- reduces saliva secretion;
- suppresses peristalsis of the digestive tract;
- dilates the bronchi and enhances gas exchange;
- enlarges pupils;
- causes spasm of the sphincters of the bladder and digestive tract.
These reactions are necessary to protect the body in a dangerous situation, to activate it to escape. The parasympathetic nervous system works in the opposite direction. It reduces blood pressure, accelerates peristalsis of the intestines and urinary organs, and constricts the pupils and bronchi. The parasympathetic activator is the substance acetylcholine. It slows down the heartbeat, reduces blood glucose levels and relaxes all the sphincters in the body.
Autonomic dystonia occurs when the sympathetic or parasympathetic system is activated spontaneously, for no apparent reason. Therefore, a person suddenly has an increased heartbeat while at rest, his blood pressure rises, and he is worried about anxiety.
But often vegetative-vascular dystonia is a precursor to serious diseases. Having arisen at a young age without treatment, after a few years it leads to the formation of arterial hypertension, heart disease, digestive tract and hormonal disorders.
Causes of occurrence and development
The etiology of VSD, as well as its symptoms, is extremely diverse. Among the main reasons, doctors name:
- pathological changes that occurred during pregnancy or childbirth (intrauterine hypoxia, infectious process, birth injuries, etc.);
- changes in hormonal levels (during puberty or during hormonal therapy);
- hereditary tendency (presence of autonomic disorders in close relatives);
- traumatic brain injuries of any severity;
- traumatic stressful situation, frequent psycho-emotional stress;
- high mental stress;
- excessive, or conversely, insufficient physical activity;
- toxic effects of certain substances;
- unbalanced, irregular nutrition;
- long-term course of chronic diseases (diabetes mellitus, hypertension, coronary heart disease, bronchial asthma, hypo- and hyperthyroidism, gastric ulcer, etc.);
- chronic lack of sleep, sleep disorder;
- sudden changes in weather conditions or prolonged stay in a place with severe climatic conditions;
- the presence of foci of infectious agents (chronic sinusitis, rhinitis, otitis, tonsillitis, etc.);
- bad habits (smoking, alcoholism, drug addiction).
There are certain risk groups, people from whom are more likely than others to develop VSD: people who are underweight or overweight, have low resistance to stress, and occupy responsible positions; girls during puberty, women during pregnancy and menopause.
Complications
The most common complication of VSD is vegetative crisis. This is a sudden attack during which a massive disruption of the autonomic nervous system occurs. Depending on the type of violation, there are three types of crises.
- Sympathoadrenal. Accompanied by a massive release of adrenaline into the blood, an increase in blood pressure, pulse and body temperature. The skin turns pale, hands and feet become cold and numb. The person experiences severe chills, unexplained anxiety, and fear of death. The condition is also often called a panic attack.
- Vagoinsular. The patient feels hot and suffocated, his face turns red, and severe sweating appears. Blood pressure decreases, pulse becomes rare. Often the condition is accompanied by frequent loose stools.
- Mixed. The crisis manifests itself with mixed symptoms.
If the symptoms of VSD are ignored for a long time and there is no treatment, the pathology can cause the development of:
- persistent arterial hypertension, poorly corrected by medications;
- cardiomyopathy;
- diabetes mellitus type 2;
- cholelithiasis or urolithiasis;
- stroke;
- myocardial infarction.
Excessive excitability of the autonomic nervous system also causes a decrease in immunity.
Treatment
Therapeutic measures consist of a set of effective methods, each of which is selected individually. Since most of the occurrences of VSD occur due to stress, it makes sense to pay attention to ways to combat them:
- normalization of sleep;
- rejection of bad habits;
- building an adequate work and rest regime, if necessary, the issue of changing jobs is considered;
- nutritious nutrition in compliance with the meal schedule;
- performing special sets of physical exercises, therapeutic exercises, yoga;
- work with a psychologist (individual or group classes, psychological trainings, consultations);
- physiotherapeutic procedures (massage, electrophoresis, contrast and therapeutic showers, etc.);
- Spa treatment.
All of the above methods are quite effective; when used, not only the disappearance of VSD symptoms is noted, but also an overall positive effect on the body as a whole.
Treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia
Treatment of VSD is always selected strictly individually. In this case, the neurologist must take into account a lot of factors and formulate the optimal tactics. Not only the type of vegetative-vascular dystonia, the severity and frequency of attacks, the patient’s age, but also the presence of concomitant diseases and their characteristics are taken into account.
When prescribing treatment for patients with VSD, neurologists pursue two goals: eliminating the symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia and influencing the cause of the development of dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system. The second task is of particular importance, since sometimes it is not possible to find the true cause of VSD. But the patient’s quality of life in the future primarily depends on this, since by eliminating the cause of VSD, the cause itself will also be eliminated. Therefore, treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia is often carried out not only by a neurologist, but also by other specialized specialists, in particular, a cardiologist.
Also, treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia involves influencing the psycho-emotional state of patients, since stress and prolonged nervous tension definitely do not improve their condition.
Thus, the treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia is always complex. It includes:
- drug therapy;
- lifestyle correction;
- psychotherapy;
- Spa treatment.
To combat the causes of VSD, manual therapy is often used. This is due to the fact that a competent effect on the spine can improve the performance of almost every organ of the human body. After all, it is in the spinal cord that the autonomic centers are located, which suffer greatly in the presence of spinal pathologies.
Therefore, the elimination of scoliosis, protrusions, herniated intervertebral discs, spondylosis and other disorders necessarily leads to a significant improvement in the condition of patients, and when treated in the early stages, a complete elimination of the causes of the development of VSD.
One of the most effective methods of manual therapy is the original Gritsenko method. With its help, you can restore the normal position of each vertebra and thereby completely normalize the functioning of the spinal cord. As a result, blood circulation also improves, back and chest pain, breathing problems, and a host of other disorders go away. An additional “bonus” is an increase in the body’s adaptive capabilities and a slowdown in the natural aging process.
When manual therapy is performed correctly, improvements are observed after the first sessions. But to consolidate the results and eliminate the causes of vegetative-vascular dystonia, you need to undergo a course of manual therapy. Moreover, sessions can be combined with work, study, business trips and other activities.
Drug therapy
Treatment of VSD involves the use of a whole range of medications, the list of which, as well as the dosage, is determined by the neurologist on an individual basis. Thus, drug therapy for vegetative-vascular dystonia may include:
- Antidepressants help eliminate excessive anxiety, increased irritability and help overcome depression, psycho-emotional stress, and apathy. Often, while taking antidepressants, there is a decrease in heart pain and muscle pain, even in cases where they previously could not be relieved by other means.
- Tranquilizers - used to reduce the risk of panic attacks, eliminate causeless fears and relieve increased anxiety.
- Sedatives - initially preference is given to herbal remedies, but if they do not have the desired effect, they are replaced with “heavy artillery”. Herbal remedies act gently; in the absence of allergies, they do not have a negative effect on the body, but have a beneficial effect on the nervous system.
- Nootropics are designed to activate blood circulation in the vessels of the brain, remove the negative effects of hypoxia (oxygen deficiency) and increase the body’s ability to resist stress.
- Adrenergic blockers are prescribed when problems with the heart are detected.
- Diuretics - used in the presence of headaches, attacks of dizziness that occur against the background of increased intracranial pressure or arterial hypertension. They help remove excess fluid from the body, but lead to a decrease in sodium levels, and some potassium levels. This can negatively affect the functioning of the heart, so diuretics are often combined with drugs that replenish the deficiency of these ions.
- Vitamin preparations containing B vitamins improve the conductivity of nerve impulses and generally have a positive effect on the state of the nervous system as a whole.
- Metabolic drugs - designed to increase control over glucose levels, have microcircular, antihypoxic properties.
Lifestyle correction
In order to improve the functioning of the autonomic nervous system, patients with VSD are recommended to reconsider their lifestyle and habits. Thus, neurologists recommend to all patients:
- Organize the correct work and rest schedule. During the workday, it is important to take breaks, leave your chair and go for a walk to improve blood flow in the body and give your head a chance to rest.
- Get enough sleep. It is recommended to sleep at least 8 hours every day.
- Walk outdoors every day. It's worth walking for about an hour. This is enough to improve the functioning of the entire body.
- Make moderate physical activity an integral part of your life. Fanatical exercise with VSD will be detrimental, but half an hour of jogging, aerobics, and swimming will be very helpful.
- Eat properly. Patients are advised to avoid foods with a high content of trans fats, which contribute to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques and also increase nervous excitability. But a strict diet for VSD is not indicated, since strict restrictions can negatively affect the psycho-emotional state of the patient, which will aggravate the course of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Since the topic of nutrition in VSD raises many questions, it requires a more detailed consideration. With such a diagnosis, the diet should be built in accordance with the following principles:
- enriching the diet with foods that are sources of potassium and magnesium and have a positive effect on the functioning of the cardiovascular system, in particular blood pressure levels;
- normalization of water-salt balance by drinking 1.5 liters of water per day, in addition to tea, juices and other drinks;
- enjoying food;
- bringing the diet as close as possible to the requirements of a healthy diet.
The nature of the diet may vary depending on the type of vegetative-vascular dystonia. So, in case of hypertensive form, it is important to exclude foods containing large amounts of “hidden” salt. For this purpose, it is recommended to refrain from eating fast food, canned food, marinades, semi-finished products, etc. Instead, patients are asked to include soups with vegetable or weak meat or fish broth in their daily menu. It is also recommended to replace traditional wheat or rye bread with products made from whole grain flour or with bran.
With hypotonic VSD, when creating a menu, you should pay special attention to vegetables and fruits that contain increased amounts of well-absorbed vitamin C and β-carotene, as well as foods that increase blood pressure. Thus, with this form of dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system, it is worth introducing into the daily diet:
- citrus fruits, bananas, bell peppers, pineapples, pomegranate;
- any nuts, buckwheat, liver, brains;
- cheeses;
- herring;
- dark chocolate, cocoa, coffee.
With hypotonic VSD, it is not prohibited to eat white bread, potatoes and even sweets.
If a patient is diagnosed with a cardiac form of the disease, he is recommended to bring foods that are a source of magnesium and potassium to his table. This will have a positive effect on the functioning of the heart muscle and reduce the risk of developing dangerous complications. Therefore, they should pay attention to:
- oatmeal, buckwheat;
- legumes;
- onions, eggplants;
- apricots, peaches, grapes, including in the form of dried fruits;
- natural juices, compotes, jelly;
- dairy products;
- chicken eggs;
- lean varieties of fish and meat.
Psychotherapy
With vegetative-vascular dystonia, it is important not to close yourself off from the problem, but to solve it. Therefore, competent psychotherapy plays a significant role in the treatment of VSD. Psychotherapy helps you understand yourself better, become calmer and more confident.
Spa treatment
An annual holiday in a sanatorium outside the period of exacerbation of vegetative-vascular dystonia has a positive effect on the physical and psycho-emotional state of people, which helps to prolong remission. But with VSD, long trips abroad will not be the best idea. It would be more correct to choose a balneological resort in the climatic zone in which he permanently lives, since a sharp change in climate can negatively affect a person’s condition and provoke a new exacerbation of VSD.
Drug therapy for VSD
Prescription of medications is resorted to in case of ineffectiveness of non-drug measures. Treatment of VSD involves the use of medications strictly as prescribed by the doctor. Only a specialist determines the necessary drugs, their dosage and frequency of administration in each specific case. Among the main groups of medications are:
- sedatives of plant origin (normalize sleep, have a mild and effective effect);
- antidepressants – reduce anxiety, relieve headaches of varying intensity and duration;
- tonic and restorative drugs (improve tone, increase resistance to stress, physical and mental stress);
- metabolic agents – improve and normalize metabolic processes in the body, in particular in the brain and nervous system;
- tranquilizers - prescribed with caution, as they have clear indications and many side effects;
- microelements and vitamins;
- drugs aimed at eliminating various specific symptoms and their causes (hypotensive, antiarrhythmic, prokinetics, antispasmodics, etc.).
The patient must understand that VSD does not belong to the category of severe pathologies. With proper treatment and strict adherence to medical recommendations, recovery is guaranteed. The right attitude towards recovery plays an important role, when a person is not afraid of the manifestations of dystonia, but strives to overcome them. This is especially true for attacks of anxiety, restlessness, and various phobias - as soon as the groundlessness of such fears is realized, they gradually disappear forever.
Therefore, it is very important not to be afraid to talk about the problem. Sometimes patients are embarrassed by this and are in a vicious circle when they cannot cope with the problem on their own, but do not dare to visit a doctor. And it’s completely in vain, because already during a conversation with a specialist it turns out that it is much easier to cope with the situation together, moreover, the prognosis is favorable.
Symptoms
The symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia are varied, since the ANS is responsible for the functioning of all organs and structures of the human body. All manifestations of the disease can be divided into several groups:
- respiratory (respiratory): rapid breathing, subjective feeling of lack of air, inability to take a deep breath, aggravated by stress;
- cardiac (cardiac): frequent or rare pulse, interruptions (feeling of freezing) in the work of the heart, pain and a feeling of squeezing in the sternum or in the left half of the chest;
- thermoregulatory: an increase in temperature not associated with any infectious disease or inflammatory process; usually goes away on its own;
- dysdynamic: a sharp increase or decrease in blood pressure, accompanied by corresponding symptoms: headache, dizziness, flashing spots before the eyes, fainting, etc.;
- psychoneurological: increased sensitivity to changes in atmospheric pressure and temperature (meteosensitivity), drowsiness during the day and insomnia at night, apathy, irritability, causeless anxiety, fatigue;
- gastrointestinal: constipation, diarrhea or their alternation, pain and heaviness in the stomach, heartburn, increased gas formation in the intestines;
- sexual: decreased sexual desire, lack of arousal, inability to achieve orgasm, impotence in men.
The disease can cause both individual symptoms and various combinations of them. This makes it much more difficult to diagnose.
Doctors treating VSD
In addition to the attending physician, a neurologist, endocrinologist, otolaryngologist, ophthalmologist, and instrumental diagnostic specialists take part in the process of diagnosing VSD. Depending on the symptoms, you may need to consult a specialist doctor - cardiologist, gastroenterologist, pulmonologist, urologist and other related specialties.
At the clinic of JSC “Medicine”, a comprehensive approach allows us to accurately establish the mechanisms of the occurrence and development of VSD, triggers, and timely identify or exclude concomitant pathologies. Doctors of the highest category with many years of experience, doctors of medical sciences, practice here. This is the key to successful treatment, but much depends on the patient himself: how timely he sought qualified medical help, how carefully he followed the doctor’s instructions for diagnosis and treatment.
Kinds
Depending on the predominant syndrome (complex of symptoms), vegetative-vascular dystonia is divided into the following types:
- hypertensive: accompanied by a short-term increase in blood pressure (within 140 mmHg), headache, rapid heartbeat;
- hypotonic: blood pressure is constantly low or decreases sporadically, which is often accompanied by severe dizziness, darkening of the eyes or fainting; patients also complain of excessive fatigue, frequent headaches and a feeling of aches throughout the body;
- cardiac: manifests itself as an increased, decreased or uneven pulse, chest pain, as well as attacks of shortness of breath, in which the patient experiences a strong feeling of lack of air;
- vagotonic: a person, first of all, complains of breathing problems: the inability to take a full breath, a feeling of tightness in the chest; the condition is accompanied by strong salivation;
- mixed: a combination of different symptoms or their alternation.
Depending on the severity, there are three types of VSD:
- mild: a person experiences symptoms rarely, they do not disrupt his lifestyle or reduce his ability to work; there are no crises;
- moderate severity: symptoms are clearly expressed and interfere with normal life activities; periodically a person may experience crises during which his ability to work decreases;
- severe: manifestations of the disease are observed almost constantly, the person cannot work normally, and is often on sick leave; vegetative crises are repeated very often.
Indications for treatment
The main indication is a clinically confirmed diagnosis of vegetative-vascular dystonia. Since VSD is a syndrome, the indications for its therapy correspond to disorders of various etiologies: vascular, psychological, neurological, cardiological and many others.
If your professional responsibilities involve high mental and emotional stress, stressful situations, overwork, or if you have a hereditary predisposition to VSD, sign up for a consultation with a specialist. Timely prevention will help avoid worsening problems, because the disease is easier to prevent than to treat.
Causes
Vegetative-vascular dystonia affects various systems and organs. Symptoms may appear already in fetal development. It has been proven that the largest number of diagnosed cases are detected between the ages of 20 and 40 years. Among the main reasons for the development of VSD are the following:
- hereditary burden;
- physiological features of the structure of the body;
- psycho-emotional or physical stress;
- hormonal instability;
- chronic somatic pathologies;
- history of traumatic brain injury.
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital quickly identify the causes of the development of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
In accordance with the identified etiological factors, a treatment program is developed. Make an appointment
Contraindications
Contraindications for the treatment of VSD are determined by the methods used. If we talk about drug therapy, then almost every drug has contraindications for use. The same can be said about physiotherapeutic procedures. That is why the course and tactics of treatment are determined by a highly qualified doctor who is able to take into account all factors.
There is one contraindication that is simultaneously applicable in all cases - self-treatment. In the case of VSD, this is especially true, since such patients are often excessively suspicious and tend to attribute severe pathologies to themselves. In an attempt to treat a non-existent disease, they can not only significantly aggravate their situation, but also cause irreparable harm to the body.
Prevention
In order to reduce the risk of developing symptoms of VSD, the following preventive recommendations must be followed:
- to live an active lifestyle;
- avoid psycho-emotional stress;
- do not abuse alcohol or caffeine-containing drinks;
- stop smoking;
- adhere to a rational and balanced diet.
These medical advice will help minimize the possibility of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
When the first signs of pathology appear, you must contact a doctor for a medical examination. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital in Moscow will perform a full course of diagnostics necessary to identify vegetative-vascular dystonia. They will prescribe treatment that will relieve the unpleasant symptoms of the disease.
You can ask questions or make an appointment with a doctor by phone.
Make an appointment
Cost of initial appointment, diagnostic examinations and treatment
As for the initial appointment, its cost in most cases is low; in fact, it is a consultation procedure. But one should not neglect its importance - an experienced doctor is able to recognize characteristic symptoms and notice even small but important manifestations of abnormalities.
The price of diagnostic procedures and laboratory tests may vary significantly in different clinical cases. For one patient, general tests and several examinations will be enough; for another, diagnosis may take longer and require additional studies and tests. This is due to both the complex nature of VSD and the individual characteristics of each patient’s body.
A similar picture is typical for treatment. Its cost is determined by many factors; sometimes the therapeutic process has to be adjusted. To roughly navigate the prices for diagnosis and treatment of VSD in Moscow, you can familiarize yourself with the corresponding table of costs for the most common diagnostic procedures.
Advantages of the clinic
The Health Energy Clinic offers each patient the highest quality medical services at an affordable price. By contacting us, you will receive:
- consultations with experienced doctors of various profiles;
- full diagnostics to identify obvious and hidden pathologies;
- a modern and effective complex treatment scheme, selected in accordance with the characteristics of your body.
Our clinic has its own day hospital, where you can undergo various therapeutic and diagnostic procedures in accordance with the doctor’s prescription. Convenient parking and location next to the metro allows you to get to us with maximum comfort.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia can be a serious problem that interferes with a full life. Do not submit to the disease, sign up for the Energy of Health clinic.
Advantages of treating VSD at the clinic of JSC "Medicine"
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is a multifactorial disorder in the body; its successful treatment requires an integrated approach and coordinated work of doctors of many specialties. Among the undeniable advantages of JSC “Medicine” (clinic of academician Roitberg), it is worth mentioning 3 key points:
- High professionalism of doctors - the staff consists of more than 300 experienced practicing doctors and diagnosticians of 67 medical specialties. Leading corresponding members of the Russian Academy of Sciences, academicians, professors, doctors and candidates of medical sciences advise here. The clinic was the first in Russia to receive accreditation according to the international standards for assessing the quality of medical care JCI. Joint Commission International, considered the highest level of accreditation worldwide.
- Ultra-modern technical base - equipped with the latest generation diagnostic and treatment equipment from the world's leading manufacturers. This allows you to create your own scientific and clinical developments in almost all medical areas. For many years, the clinic of JSC "Medicine" has served as a clinical base for the Department of Therapy and Family Medicine of the Russian National Research Medical University named after N.I. Pirogov (RNIMU) and is among the innovatively active healthcare institutions in Moscow.
- High-quality medical care - the effectiveness and safety of treatment is guaranteed by the principle of Academician N.A. Semashko, which states: “One patient - one doctor.” The attending physician is assigned to each patient and works closely with colleagues from related medical specialties. A developed diagnostic base and medical care technology built according to international standards make it possible to make a diagnosis at an unprecedented speed. In just 1 day from the moment of the initial examination and diagnostic measures, you can receive detailed results of laboratory tests, detailed diagnostic reports and doctor’s recommendations.
It is important to know: VSD is not a critically severe disorder, but can provoke one in the absence of proper medical care. In case of early access to a doctor, treatment time is significantly reduced and financial costs are reduced. Don’t delay your visit, make an appointment at a time convenient for you, and we will help you regain your health!
Treatment at the Energy of Health clinic
Doctors at the Health Energy clinic choose an integrated approach to the treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia. After a thorough diagnosis and exclusion of other pathologies, combination therapy will be prescribed, including:
- modern medications if necessary (the choice depends on the severity of symptoms);
- physiotherapy, massage and physical therapy to strengthen the body in general and the nervous system in particular;
- acupuncture, manual therapy if indicated.
We will certainly discuss your lifestyle, tell you about ways to correct it, and help you create the right diet. Regular monitoring by our doctors will help keep the disease under control.
Treatment and prognosis
In patients with vegetative-vascular dystonia, treatment is carried out under the supervision of doctors of the following specializations: therapist, neurologist, endocrinologist, psychiatrist. Certain prescriptions will depend on the predominant symptoms of VSD. Usually, taking into account the nature and etiology of the disease, complex long-term individual therapy is carried out.
Physical therapy classes
Special physical education is most useful in the treatment of VSD in both adults and children. Such exercises have a general strengthening effect and are an excellent way to train the whole body and improve performance. Designed for the treatment of VSD and thought out taking into account age and health status, physical therapy should also exclude jumping. In general, an active lifestyle can be an integral component of the prevention of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Undergoing physical therapy
Therapeutic massage, water treatments, and reflexology also have a positive effect in the treatment of VSD. The physiotherapeutic effect is selected depending on the type of disease: it can be electrophoresis with calcium or caffeine (in the case of vagotonia) or with magnesium, papaverine or bromine (for the treatment of sympathicotonia).
Use of drug treatment
If general strengthening and physiotherapeutic measures are insufficient for the effective treatment of VSD, the specialist individually selects drug therapy, which may include the following drugs:
- sedatives that reduce the activity of autonomic reactions, antidepressants, nootropics;
- beta-blockers and herbal psychostimulants that help reduce vegetative-vascular manifestations;
- Vitamin-mineral complexes usually have a beneficial general strengthening effect.
If necessary, to treat various forms of VSD, a course of therapy is also carried out aimed at eliminating chronic foci of infection, concomitant endocrine or somatic pathology. The doctor regularly monitors a patient with vegetative-vascular dystonia. Clinical examination may be prescribed (every 3-6 months), especially in the autumn-spring period.