What diseases cause pain
| Name of the disease | Symptoms |
| Disc herniation in the cervical spine | Causes nagging pain in the shoulder joint and neck, headaches and dizziness. A person feels a decrease in hand sensitivity. This happens due to a pinched nerve root. |
| Cervical osteochondrosis | Severe acute pain in the neck, which radiates to the arm and intensifies when turning the head. |
| Spinal canal stenosis | Causes numbness in the arms and upper body, weakness, and disruption of brain function. |
| Muscle spasm | Occurs due to overstrain of the neck muscles, when being in an uncomfortable position or during prolonged work at the computer. It occurs suddenly and causes severe pain. |
| Cervical radiculitis, discogenic pain syndrome | It occurs due to compression of the nerve root by a herniated intervertebral disc during sudden movements of the head. Accompanied by severe neck pain that does not go away for 3 or more days. Often the neck becomes immobilized. |
| Cervical spondylosis | Causes chronic, aching pain in the neck, shoulder, or arm that can last for months. The disease causes severe deformities of the vertebrae. |
| Inflammation of the tendons of the shoulder joint | Inflammation from the shoulder joint spreads to the surrounding muscles and neck muscles, restricts movement in the neck, causes periodic nagging pain and can provoke the development of cervical osteochondrosis. |
Other causes of neck pain: cervical myositis, instability of the cervical vertebrae, glenohumeral periarthritis, disc protrusion in the cervical spine, consequences of birth injuries, scoliosis, displacement of the cervical vertebrae (listhesis).
Pain in the neck and occipital part of the head. Causes and their treatment
Meanwhile, the source of headaches or back pain can be serious illnesses. The most common today is osteochondrosis, but other diseases of the cervicothoracic back can also occur.
The neck is a very sensitive and delicate part of the human body. This rather small area contains all the clusters important for human life. These include large veins and aortas, blood vessels and nerve clusters, lymph nodes, etc. It is not surprising that problems in this part of the spine lead to deterioration of well-being, decreased ability to work, and disruption of the functioning of the entire body.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis in the cervical area of the back are often similar to the symptoms of a disease such as vertebral artery syndrome. Then the sensations of aching pain in the back of the head and neck intensify, accompanied by muscle strain or increased tone, inflammatory processes, circulatory disorders, and swelling.
In the early stages of the disease, pain may appear when you are in an uncomfortable position for a long time, with prolonged tension of the neck muscles, sudden turns or tilts of the neck. Pain can also be caused by local hypothermia resulting from prolonged exposure to an air conditioner or when traveling in a vehicle with open windows, etc.
The localization of pain in the cervical spine can be either on the left side or on the right, or can be immediately felt on both sides. In this case, the intensity of pain can fluctuate from severe acute attacks to aching chronic, barely noticeable.
The root cause of pain in the cervical spine:
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, pathological damage to the ligaments or muscles of the cervical corset;
- traumatic injuries, tumors (also oncological);
- muscle spasms that occur after sudden movements or prolonged static physical activity;
- viral infections, arthritis (for example, rheumatoid);
- meningitis, retropharyngeal abscess;
- hypothermia and long-term stay in an uncomfortable position.
The root cause of pain in the back of the head:
- diseases of the cervical vertebrae;
- cervical spondylosis;
- violation of the condition of the muscles of the cervical corset, as a result of incorrect posture, hypothermia, nervous strain, stress;
- muscle spasms of physical or nervous origin;
- overstrain of physical or mental origin;
- neuralgia of the occipital nerve endings (in this case, pain can spread along the back, radiate to the upper limbs, as well as to the lower jaw, ears);
- arterial hypertension;
- muscle fatigue caused by improper physical activity;
- migraine of the cervical region (sensation of burning pain in the temporal parts of the skull, occipital part, in the superciliary arches).
Diagnosing pain at home
It is extremely difficult to diagnose at home, especially if it is not attempted by a specialist in the relevant field. There are often cases when hypertension (high blood pressure) is considered the cause of headaches, without suspecting that pain can occur due to diseases of the spine. In this case, the prescribed treatment will not bring any results or will have the opposite effect.
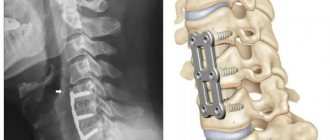
In order to establish an accurate diagnosis, and accordingly the root cause of pain in the back of the head or cervical region, various research methods are used. This includes radiography, magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography, etc. Based on the results of the images, the doctor will make the correct diagnosis and prescribe a specific treatment. Accordingly, it is simply impossible to carry out this diagnosis at home, and do not even try to self-medicate.
Treatment
The first step in treating pain in the neck and back of the head is pain relief. For these purposes, painkillers are used, sometimes in combination with anti-inflammatory or anti-edema agents. After the patient feels a little better, the process of diagnosing diseases that cause pain begins.
Having established an accurate diagnosis, the doctor prescribes a course of treatment. Moreover, for each patient it will be individual, taking into account all the structural features of the body, state of health and symptoms and stages of the disease. For different detected diseases, different therapeutic treatments will be prescribed, but the principles and methods of treatment in most cases will be similar.
After drug treatment or in parallel with it, physiotherapy, a course of special physical therapy, all types of general massages, manual therapy and osteopathy are usually prescribed. For almost all diseases, it is recommended to start swimming.
treatment of the spine, including the cervical spine, is a very long and complex process, even more complicated due to the structural features of the neck. After all, for the cervical area it is almost impossible to organize complete rest, which is necessary for treatment.
If pain syndromes accompany the patient for a long time and seriously limit his motor activity, or the disease begins to affect the functioning of internal organs and other body systems, surgical intervention is permissible.
But remember, surgery is used only in extreme cases or in severe complications. For the most part, it is possible to cure ailments that cause pain in the back of the head or neck using the conservative methods listed above. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Diagnostics
Patients who have neck pain on the side require an initial consultation with a general practitioner or traumatologist, then, according to indications, the person is referred to related specialists. A diagnostic search involves conducting modern instrumental imaging methods to determine the cause of pain and prescribing additional laboratory tests. The most informative are:
- Sonography
. Ultrasound of the cervical region is used to study the condition of internal organs, lymph nodes and endocrine glands. The study allows you to detect space-occupying formations, ulcers, and cysts. Additionally, an ultrasound of the abdominal organs is performed. - X-ray examination
. To exclude a vertebrogenic cause of neck pain on the right, an X-ray of the cervical spine is performed in frontal and lateral projections. If dislocations or traumatic injuries to the atlas are suspected, an image is taken through the mouth. - Examination of ENT organs
. Often, pain syndrome is caused by severe diseases of the respiratory tract, so pharyngoscopy and indirect laryngoscopy are necessary. If suspicious signs are detected, endoscopy of the larynx and pharynx is performed. - Neurological examination
. Pain in the neck area can be a consequence of pathological processes in the central nervous system, so superficial and deep tendon reflexes and coordination of movements must be studied. If necessary, a CT or MRI of the brain is done. - Blood chemistry
. The levels of acute phase indicators and the percentage of protein fractions are determined, which is necessary to exclude signs of the inflammatory process. Liver tests, pancreatic enzymes, and a complete blood count are assessed.
When ultrasound reveals large formations of the thyroid gland, a fine-needle biopsy of the node is required, followed by cytomorphological examination. Be sure to do a blood test for thyroid-stimulating hormones of the pituitary gland, T3 and T4, and parathyroid hormone. In some cases, duplex scanning of the neck vessels is required to assess the speed of blood flow. If it is suspected that the superior vena cava is compressed, radiography of the OGK is indicated to exclude mediastinal tumors.
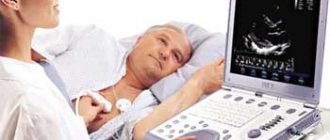
Ultrasound of neck vessels: when is it prescribed?
What diseases can ultrasound of the neck vessels help diagnose? Is it possible to undergo this study on your own initiative, without waiting for a doctor’s referral? What does the procedure itself look like? These and other questions are answered by Sabina Zaurbekovna Kadzhaeva, an ultrasound diagnostics doctor at Clinic Expert Vladikavkaz.
— Sabina Zaurbekovna, why is ultrasound of the neck vessels prescribed?
— In short, ultrasound of the neck vessels is done to assess the structural, anatomical, hemodynamic features of the brachiocephalic vessels (arteries and veins). These vessels are also called main vessels; they are responsible for the blood supply to the brain, tissues of the head and shoulder girdle.
— What does ultrasound of the neck vessels show?
— The doctor examines the lumen of the vessels, studies the condition of their walls, the nature of intraluminal formations, if any - these are plaques or blood clots that interfere with blood supply. An ultrasound will show whether the plaque is dense, with calcifications (inclusions containing calcium) - that is, old, or loose - which means it has recently formed and has a high risk of embolization. The degree of stenosis (narrowing) of the affected vessels is assessed. If this is a thrombus, then it will also be clear how much it closes the lumen of the vessel, and it is necessary to evaluate the condition of the apex of the thrombus (flotation). We can also determine hypoplasia (this is a congenital disease, an abnormally small diameter of the vessels) and aplasia - the complete absence of some vessels.
The assessment of hemodynamics refers to the speed of blood flow in each vessel and the spectrum of blood flow (graphic reflection on the screen): low speed may indicate low cardiac blood output, high blood flow speed does not exclude hypertension, stenotic lesion of the vessel or pathological tortuosity. The blood flow spectrum helps the doctor detect arrhythmia and problems associated with the thyroid gland.
Read materials on the topic:
Find and neutralize. How to protect against blood clots? Diagnosis of carotid artery stenosis using MRI. Off scale! We are looking for the causes of high blood pressure. We recognize the enemy of the heart. What is arrhythmia?
— How is an ultrasound of the neck vessels done?
— The procedure is not complicated. The patient is placed on his back, and in some cases a special cushion is placed under the shoulder blades. And then the person’s task is to simply lie still, not talk, try not to cough. This standard study lasts 15-20 minutes, but in some cases the procedure can last up to 30-40 minutes.
— What is the preparation for an ultrasound of the vessels of the neck?
— The study does not require any special preparation.
— What specialty does a doctor usually refer for an ultrasound scan of the vessels of the neck?
— In 70% of cases it is a neurologist. To make an accurate diagnosis, a cardiologist can also refer you for an ultrasound scan of the vessels of the neck; this study is carried out by patients with hypertension and heart rhythm disturbances. If we are talking, for example, about atherosclerosis, a referral can be made by a vascular surgeon, in case of diabetes mellitus - by an endocrinologist, in case of visual impairment - by an ophthalmologist. If hearing decreases or some noise appears in the ear, an ENT doctor may prescribe an ultrasound. Well, besides this, a therapist can give a referral.
You can make an appointment with specialists here. ATTENTION: the service is not available in all cities
— Can a person come for an ultrasound of the neck vessels without a referral? And if so, does it make sense - particularly if nothing is bothering you?
- In principle, anyone can come to us to find out the condition of their blood vessels, even if there are no problems or complaints. For example, I decided to do an ultrasound of the vessels of my neck in order to understand whether I have any congenital vascular changes, features with the vertebral arteries - the same hypoplasia, aplasia, congenital tortuosity. Because, sooner or later, it will make itself felt. And the more information we have about ourselves, the better: this way we can prevent or delay some of their clinical manifestations. It is especially important for smokers to undergo such a study in order to once again reconsider their attitude towards this addiction.
You can sign up for an ultrasound examination here. ATTENTION: the service is not available in all cities
Interviewed by Igor Chichinov
The editors recommend:
What will a heart ultrasound tell you? Holter (24-hour) ECG monitoring - complete instructions for the patient When is 24-hour blood pressure monitoring prescribed?
For reference
Kadzhaeva Sabina Zaurbekovna
In 2004 she graduated from the medical faculty of the North Ossetian State Medical Academy (SOGMA).
From 2004 to 2005 - internship in the specialty "Surgery".
From 2005 to 2007 - clinical residency (“Surgery”).
From 2009 to 2014 she worked as a surgeon at the SOGMA clinical hospital.
From 2014 to the present - ultrasound diagnostics doctor at the Federal State Budgetary Institution SK MMC (Beslan).
Receives at the address: Vladikavkaz, st. Barbashova 64.