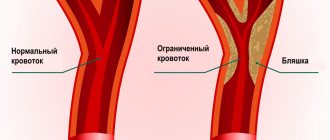
Symptoms of absolute stenosis
The signs of this serious disease will vary depending on where the critical narrowing of the spinal canal is located.
- Cervical region
Severe weakness of the arms, a feeling of partial numbness and “pins and needles” in the upper body, difficulty breathing. In some cases, a person loses sensation throughout the entire body from the neck down. Cervical absolute stenosis is the most dangerous, since there is a possibility of not only disability of the patient, but also death.
- Thoracic region
A rare pathology that manifests itself as chest pain, disorders of the genitourinary system, intestines, numbness of the arms and shoulder girdle.
- Lumbar
This is where stenosis develops most often. It is the lower back that is subject to the greatest stress in a person’s everyday life. Absolute stenosis manifests itself as severe pain – the pain radiates to the leg and buttock. So-called lumbago may be felt, walking is impossible or very difficult, and paralysis of the lower extremities develops - complete or partial. Stenosis also contributes to sexual dysfunction, spontaneous urination and defecation.
What is subclavian artery stenosis?
23.10.2019
The clinical presentation of subclavian and innominate peripheral artery (SIPA) ranges from arm claudication to cerebral hypoperfusion to distal embolization and digital ischemia. PAAD of the upper extremity may present as lower extremity claudication in patients undergoing extraanatomic axillary or femoral bypass surgery.
Survey
Physical examination is significant for weak pulses on the ipsilateral limb, systolic blood pressure difference greater than 10 mmHg. Art. compared to the contralateral limb. Sometimes the affected hand may feel cool to the touch, and in severe cases digital ischemia has also been described. Often the disease is present during the sixth or seventh decades of patients' lives if they have associated risk factors for peripheral arterial , such as smoking, diabetes mellitus , hyperlipidemia, hypertension .
Subclavian artery stenosis causes notable morbidity because it causes symptomatic ischemic problems that affect the upper extremities, brain and heart . Atherosclerosis is the most common cause. Other etiologies include:
- arteritis;
- inflammation caused by radiation;
- compression syndromes;
- fibromuscular dysplasia ;
- neurofibromatosis.
PAD of the great vessels is associated with narrowing of the arteries due to atherosclerosis . It is estimated that about 2% of the population has PAD of the subclavian artery . The prevalence in adults over 70 years of age is about 15%. Of these, almost 25% require revascularization. Most patients are asymptomatic due to the slow progression of the disease. Symptoms usually appear when there is 50% luminal narrowing of the vessel .
Prevalence
The prevalence of disease in the brachiocephalic artery in patients with PDPA is approximately 42%. About half of patients with this peripheral artery have left subclavian artery stenosis (30%). Half of patients with subclavian arterial disease have coronary artery , and a third have carotid or vertebral disease.
Risk factors
Vascular risk factors, including diabetes , hyperlipidemia, hypertension , and tobacco abuse, increase cell adhesion molecules, which promote the adherence of inflammatory cells to the arterial . This process causes remodeling of the arterial wall and lipid deposition through the tunica. the arterial lumen eventually narrows , which in turn causes calcification of the arterial .
In addition, the brachiocephalic arteries , including the innominate and subclavian arteries, can be affected by vasculitides such as Takayasu arteritis and giant cell arteritis. The disease of brachiocephalic atherosclerosis can be single-focal or multifocal. Brachiocephalic artery can present in several ways, including transient ischemic attack (TIA), upper limb ischemia or claudication, and vertebrobasilar insufficiency. Brachiocephalic artery aneurysms are uncommon and may be associated with atherosclerotic poststenotic dilatation, trauma, inflammation, or infection.
Symptoms
Upper extremity symptoms include arm lameness or muscle fatigue and finger necrosis. Neurological problems include vertebrobasilar hypoperfusion, visual , syncope, ataxia, vertigo facial sensory deficits .
In patients with internal mammary artery resulting from coronary artery bypass surgery symptoms of artery disease , including angina , caused by coronary-subclavian theft are predominant.
While diagnosis is usually based on imaging, a thorough physical examination is important. Upon examination you can show:
- unequal pressure on the hand;
- absent or significantly reduced impulses;
- neurological and cardiac complications;
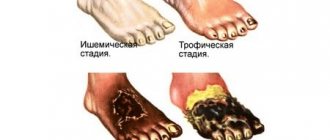
- ulcers;
- gangrenous skin changes.
Initial diagnosis of patients with subclavian arterial disease involves measuring blood pressure in both arms to assess for upper extremity discrepancies and the presence of contusions (carotid, cervical, or supraclavicular). Less common physical findings include ulcers , necrosis, splinter hemorrhages, or gangrenous skin changes.
Published in Cardiology Premium Clinic
Diagnostics
- Studying the patient's complaints - the doctor asks about the location of the pain, its manifestation, and the presence of accompanying symptoms.
- Physical examination - the patient’s posture is studied, the presence of scoliosis, palpation and percussion diagnostics are performed.
- X-ray – X-ray will show bone formations and can also evaluate narrowing of the intervertebral canal to confirm the diagnosis of relative stenosis. If a narrowing of the lumen of less than 10 mm is detected, the patient is diagnosed with absolute stenosis.
- Multislice CT scan – detects degenerative processes of bone and cartilage tissue.
- A myelogram is an x-ray with contrast that allows you to evaluate the degree of pressure on the nerve roots.
- Magnetic resonance imaging – visualizes the condition of soft tissues and the spinal cord.
When to see a doctor
At the first symptoms of spinal stenosis in the lumbar, cervical or thoracic region, you should consult a specialist. JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg), located in the center of Moscow (near Mayakovskaya metro station, Belorusskaya metro station, Novoslobodskaya metro station, Tverskaya metro station, Chekhovskaya metro station), offers the opportunity undergo professional diagnostics and effective treatment. The staff consists of highly qualified doctors. Treatment of spinal canal stenosis l4 l5 and other levels is carried out by:
- vertebrologist
- neurologist.
Specialists prescribe the optimal treatment method, taking into account the degree of development of the disease and the individual characteristics of the patient.
Treatment of absolute stenosis
If the diagnosis of absolute spinal stenosis is confirmed, the patient must undergo surgical treatment as soon as possible. Drug therapy or exercise therapy are powerless in this case, and the time lost on them does not benefit the patient.
The operation protocol may be different:
- Discectomy – the disc at the level of which the maximum narrowing of the canal has formed is completely or partially removed. If a hernia is to blame for the narrowing, only it can be removed. Next, the patient receives a disc implant.
- Laminectomy - the surgeon removes part of the vertebral arch, resulting in the release of the spinal canal. Most often, such intervention is performed if the stenosis is of traumatic origin. After eliminating the compression factor, the patient is given an implant that ensures normal motor function of the spine and protects it.
Possible complications if left untreated
Without timely and adequate treatment, absolute stenosis can have extremely serious consequences. And irreversible paralysis of the limbs is far from the only thing. Thus, due to impaired nutrition of spinal cord cells and deterioration of its oxygen supply, an ischemic stroke of the spinal cord may occur. And if the spinal canal is critically narrowed at the level of the thoracic or cervical region, death may occur due to respiratory distress or sudden cardiac arrest.
Vertebral artery syndrome (Barre-Lieu) - symptoms and treatment
For chronic neck pain, surgical and pharmacological treatment methods are used, as well as various methods of traction therapy —spinal traction with the help of special devices (blocks, belts, rings) [12].
The effectiveness of manual therapy methods - soft techniques, post-isometric relaxation, muscle stretching - is still being studied. To this end, two studies were conducted in 2015. A meta-analysis by Chinese scientists showed that manual techniques are less effective in eliminating pain than cervical spine traction [13]. However, a study by Canadian scientists found that manual therapy becomes more effective when combined with another method of active treatment for acute and chronic neck pain. Also, manual techniques cope better with chronic pain than massage, and more effectively combat acute and subacute neck pain than drug treatment. However, due to side effects from taking medications, manual therapy is preferable. In terms of effectiveness, manual techniques are similar to mobilization of the cervical spine, but mobilization as a separate intervention does not reduce pain [14].
As for the non-drug treatment method of acupuncture , a 2021 meta-analysis showed its effectiveness over sham acupuncture (acupuncture of non-acupuncture points) and inactive treatment [15].
An undoubted effective method of treating the syndrome is physical exercise . Their effectiveness in relieving acute and chronic pain is supported by a 2005 review. In this case, it is worth focusing on stretching the cervical region, shoulder girdle and chest. And the combination of exercises with mobilization and manual techniques on the cervical spine helps reduce pain in the short and long term [16].
Surgical methods include :
- puncture interbody fusion - combining and fixing several vertebrae to avoid their displacement;
- fenestration - partial removal of the arch of the intervertebral disc;
- autodermoplasty of intervertebral discs - replacement of the disc with one's own tissues.
During the operation, porous explants made of an alloy of titanium and nickel are implanted. Due to their porosity, bone tissue quickly grows in them. This makes the fixation strong and significantly reduces the patient’s period of incapacity for work and the neck being in a stationary position.
In addition to stabilizing operations of the cervical spine, other types of interventions are also performed:
- decompressive-stabilizing - removal of compression with subsequent fixation of the spine;
- decompressive-plastic (laminoplasty) - elimination of compression by enlarging the spinal canal while maintaining the integrity of the posterior elements of the vertebrae;
- decompressive operations - removal of the intervertebral disc or its arch, compressing the artery, etc. [9].
There is considerable experience in reconstruction of vertebral arteries . The following methods are used:
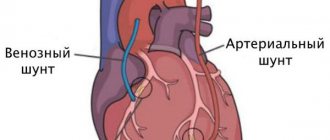
- transposition - displacement of the vertebral artery into the subclavian (common carotid);
- angioplasty - dilation of a vessel using an expanding balloon;
- Stenting is the expansion of a vessel by installing a stent.
If the first and second segments of the vertebral artery are simultaneously affected, bypass surgery is performed—creating a bypass at the level of the third segment [17].
Make an appointment with doctors at the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences
The best specialists of the department of vertebrology
They receive patients with spinal canal stenoses of varying degrees of severity and origin.
The patient is examined directly on site, and an individual treatment program is developed for him, including drug therapy and physical therapy. In difficult cases, when absolute stenosis is accurately diagnosed, surgeons at the Central Clinical Hospital in Moscow
perform spinal surgeries, returning patients to motor activity and life without pain.
make an appointment
with
a vertebrologist, rheumatologist
or other musculoskeletal specialist by phone or using the online form.
Risk factors
There is a category of people who are most susceptible to the disease absolute spinal canal stenosis at the level of the lumbar, chest and neck. This disease predominantly affects older people. This is caused by age-related changes and degenerative spinal diseases. In the age group (50 years and older), this figure is 1.8-8%.
Most often, acquired spinal canal stenosis occurs at the level of l5 s1 and l4 l5 of the last stage of spinal osteochondrosis, that is, when the bone tissue of the vertebral bodies and osteophytes actively grows.