The designation GRA in a blood test refers to cells such as granulocytes. These are components of liquid connective tissue related to leukocytes. It is important to know that GRA in a blood test are cells whose presence is normal. But both an increase and a decrease in the level of granulocytes may indicate the development of a pathological process in the body. Indications for analysis, features of preparation for the study, interpretation of the obtained values and treatment are described below.
Granulocytes: concept
All leukocytes are divided into 2 large groups. The first are agranulocytes, the second are granulocytes. The latter are the ones that are grainy. Agranulocytes, accordingly, lack it.
Granulocytes have a nucleus divided into several segments. However, it is of irregular shape. The cells are formed in the bone marrow and make up up to 70% of all leukocytes. The life cycle of granulocytes ranges from 3 to 10 days. After a few days they die. They are replaced by new cells.
Granulocytes is a collective term. These cells include eosinophils, basophils and neutrophils.
Despite the fact that they are united in one group, they are responsible for performing their specific functions. Eosinophils are cells that perform cytotoxic activities. In other words, they help destroy and eliminate parasites from the body. Eosinophils are cells that can also reduce the severity of an allergic reaction. At the same time, they can become a provoking factor in its development.
The main task of basophils is to trigger an immediate allergic reaction. They are also able to attract other granulocytes to the area of the pathological focus. Basophils also increase vascular permeability, improve blood circulation and lymphatic fluid flow, and regulate the coagulation of fluid connective tissue.
Neutrophils are cells that have the ability to move freely throughout the body. They easily leave the blood vessels and move to the pathological area. These cells are also capable of destroying fungi and bacteria. With the development of the inflammatory process, neutrophils absorb pathogenic microorganisms, but at the same time they die, releasing biologically active substances. The latter, in turn, stop the inflammatory process.
Types of granulocytes in the human body and their functions
GRA (in a blood test this is an indicator of shaped white cells) have specific granules in the semi-liquid contents of the cells, which are represented by lysosomes and pyroxisomes. Granular leukocytes are the most numerous representatives of white cells of liquid connective tissue and are secreted by the organ of the hematopoietic system that carries out hematopoiesis from a single precursor cell.
Once in the hematocirculatory pathway, granular leukocytes are divided into macrophages and parietal pools. This state for granulocytes is the primary step before leaving the channel of liquid connective tissue into the organs and systems of the body, where white cells live for about 48 hours. The main feature of granular leukocytes is a reaction to normal staining during laboratory testing.
This allows granulocytes to be divided into:
- segmented neutrophils;
- eosinophilic leukocytes;
- granolocytic basophils.
| Name | Peculiarities | Functions |
| Neutrophil leukocytes |
|
|
| Segmented eosinophils |
|
|
| Granulocytic basophils | contain in large quantities:
|
|
Indications for the study
Doctors do not prescribe a GRA blood test for patients separately. This is an indicator that is displayed in the conclusion after a clinical examination of liquid connective tissue.
A general blood test is prescribed in all cases when it is necessary to diagnose a person’s health condition. With the help of the study, it is possible to identify the presence of inflammatory processes in the body in the early stages of their development. In addition, using the analysis, the doctor assesses the degree of effectiveness of the treatment and, if necessary, makes adjustments to the treatment regimen.
Preparation
The collection of biomaterial is carried out in the morning. Blood must be donated on an empty stomach. The last meal should take place 8-10 hours before donating liquid connective tissue. At the same time, it is recommended to exclude fatty, fried, smoked, spicy and salty foods from the diet the day before.
In addition, it is undesirable to subject the body to high-intensity physical activity during the day. This is due to the fact that overexertion can distort the results of a blood test (the GRA indicator is also likely to change).
Immediately before submitting the biomaterial, it is recommended to sit quietly for about 15 minutes. Psycho-emotional stress is also a factor that can distort the results.
Granulocyte test
Read the article: Increased number of white blood cells in the blood
A blood test for granulocytes is carried out in many diseases and when various pathologies are suspected. The presence of immature forms most often indicates a disease. Typically, a test for neutrophils occurs during a general blood test marked “detailed analysis,” which is taken on an empty stomach in the morning. Blood is taken from a finger. The day before, it is recommended to avoid alcoholic beverages, fatty and fried foods. At least eight hours must have passed since your last meal. It is not recommended to engage in sports or heavy physical work the day before. It is necessary to stop taking medications that may distort the results. If this is not possible, you should inform your doctor. In emergency cases, blood can be taken from a vein at any time of the day.
Modern analyzers allow you to count the number of immature granulocytes with a high degree of accuracy. Automatic calculation significantly reduces the time of analysis and delivery of the finished result.
Blood sampling algorithm
The biological material is usually capillary liquid connective tissue.
Blood sampling algorithm:
- The nurse generously soaks cotton wool in an antiseptic solution and treats the pad of the ring finger of the left or right hand with it. A disposable alcohol wipe can also be used for this purpose.
- The intended puncture site is wiped with sterile dry material.
- The nurse removes from the package a disposable needle or vacuum instrument intended for collecting capillary blood.
- The specialist quickly makes a puncture. The first few drops are wiped off with a napkin or cotton wool soaked in antiseptic. The rest are collected into instruments.
- After obtaining a sufficient amount of capillary blood, the nurse applies an alcohol pad or cotton wool to the puncture site.
It is important to keep the attached material with the antiseptic for a few more minutes. Minor pain may persist at the puncture site for several hours.
How is the analysis carried out?
To determine the number of granulocytes, it is necessary to take capillary or venous blood.
In the first case:
- a medical specialist disinfects the extreme phalanx of the ring finger of the upper limb with wine alcohol using a cotton sponge;
- wipes the injection site with a dry cloth;
- the medical assistant takes out a scarifier needle from the sterile package, which is necessary for drawing capillary blood;
- quickly pierces the skin on the finger;
- wipe the first drops of liquid connective tissue with a cotton swab dipped in ethyl alcohol;
- using medical instruments, collects the required amount of blood to determine the number of granular leukocytes;
- Apply a sponge with an antiseptic to the damaged area.
After taking blood for testing, it is necessary to hold a piece of cotton wool at the puncture site so that the blood clots and there is no hematoma.
In the second option:
- a medical laboratory assistant disinfects the skin on the elbow with an antiseptic;
- using a vacuum syringe, pierces the epidermis and venous vessel;
- selects 10 ml of liquid connective tissue;
- The puncture is pressed down with a cotton swab dipped in wine alcohol.
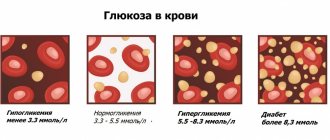
GRA in blood test: normal values
Only a doctor can correctly decipher the result of the study. This is due to the fact that based on an increase or decrease in the number of any cells, it cannot be guaranteed that there is a pathology. If the development of the disease is suspected, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive diagnosis. With the help of analysis, it is only possible to suspect the course of the pathological process.
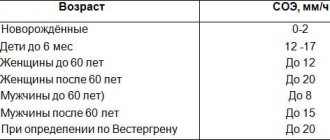
It is important to understand that granulocytes are cells that must be present in the body of every person. Normal indicators directly depend on a person’s age:
- 12 months - 31%;
- up to 10 years - 51-53%;
- 10-16 years old - 53-57%;
- 16-21 years old - 59%.
In newly born children, the granulocyte level should be 35%. In adult women and men, the normal rate is 47-72%. Some laboratories use other units of measurement. In adults, the norm of granulocytes is 1.2-6.8 x 109 (in 1 liter of blood).
It is important to remember that granulocytes are a group of cells that includes several functional units. When decoding the study, it is necessary to pay attention to their indicators.
GRA norm in blood test:
- Basophils. In children under 12 months, their level should be at least 0.4% and no more than 0.9%. In adolescents and adults, the normal rate is 0.6-1%.
- Eosinophils. The level of these cells directly depends on the degree of functioning of the adrenal glands. The norm is 120-350 (in 1 ml of blood). In the morning their level can be increased by 15%, at night (in the first half) - up to 30%.
- Neutrophils. These cells are divided into rod and segmented. The number of the former should not exceed 6%. The norm for segmented neutrophils is 40-70%.
As a rule, if granulocytes are increased or decreased, this means that a pathological process is developing in the body. However, sometimes deviations from the norm can occur for physiological reasons. In women, granulocytes are elevated before menstrual bleeding, in the third trimester of pregnancy and during the delivery process. In both sexes, deviations from the norm to a greater extent may be a consequence of overeating and high-intensity physical activity.
The presence of immature granulocytes in the blood is not a pathology. This is explained by the fact that the life cycle of granular leukocytes is only a few days. In other words, the change to young cells occurs very quickly, the number of the latter ranges from 1 to 5%.
Neutrophils
When working to eliminate pathogens, leukocytes quickly lose their potential and soon become unviable. In order to avoid this deficiency, the bone marrow produces new portions of granulocytes. These cells are immature, but they are able to perform a protective function. A general blood test allows you to determine the number of immature (young) neutrophils, and draw a conclusion about the seriousness and danger of the inflammatory process.
Types and functions
This type of granulocyte is the most numerous of the white blood cells. Their percentage is normally at least 45%, but should not exceed 75%. In blood taken from peripheral vessels (capillaries) in healthy adults and children, the presence of segmented and band-type neutrophils can be determined.
The first granulocytes are characterized by the presence of a small nucleus and a fairly large volume of cytoplasm. The nucleus contains 5–6 segments. The second type of these cells is a younger form of white blood cells. Their core resembles the shape of a horseshoe, and the normal rate for adults is not more than 6%. Normal values for newborns are significantly different - they increase to 20%, and only with age there is a tendency for these blood cells to decrease.
The main function of neutrophils is phagocytosis - searching, capturing and digesting foreign cells. The large number of grains that make up these granulocytes ensures the destruction of pathological particles, which leads to the formation of pus in the area with the inflammatory process. Therefore, the pus-like substance largely consists of tissue cells that have undergone a process of destruction. At the same time, it contains infectious agents in combination with fluid formed as a result of inflammation.
Reference! These blood cells are formed in the bone marrow in about 10 days and then enter the blood. Their life cycle does not exceed 10 hours, and the appearance of immature neutrophils in the body is indisputable evidence of the occurrence of pathological processes.
Normal white blood cell counts for a healthy adult
Reasons for deviation of neutrophils from the norm
The concentration of neutrophil blood cells may vary relative to normal levels. This is due to the specific characteristics of the diseases, and some diseases are characterized by increased values, and some by decreased ones. A pathology in which the neutrophil count is reduced is called neutropenia, that is, their level becomes less than 1.7 * 109/l.
This decrease is due to:
Ultrasound of the hepatobiliary system
- radiation sickness (including long-term chemotherapy);
- oncological diseases of the bone marrow;
- anemia (decrease in the level of red blood cells) of various types;
- infectious diseases - typhoid fever, malaria;
- excessive exhaustion of the human body;
- autoimmune pathologies;
- diseases or removal of the spleen.
In addition to the above, neutrophils decrease with viral infectious diseases - influenza, rubella, hepatitis and AIDS, as well as with long-term use of drugs that have increased toxicity. There are cases of congenital neutropenia, the so-called Kostman syndrome. The pathology is autoimmune-recessive in nature and most children die in the first years of life. This is due to the lack of functioning of cellular immunity, which makes the body vulnerable to multiple pathogens.
If the transcript of a general blood test shows a significant excess of normal neutrophil levels, then, most likely, sepsis is currently developing in the body. This pathology is often a consequence of infectious diseases and is considered a very life-threatening complication. With sepsis, such a large number of pathogenic microbes are formed in the body that the body itself is not able to cope.
Only timely administration of antibacterial therapy can save a person from this disease and its negative consequences.
Also, this type of granulocytes can be increased during the formation of tumors. Then immature neutrophils appear in the blood in large numbers. But at the same time, neutrophilia - an increase in the concentration of neutrophils in the peripheral blood does not mean one hundred percent presence of cancer. Sometimes certain medications or exposure to animal poisons can increase the level of neutrophil granulocytes.
An excess of the norm of these blood cells is often observed during heart attacks, rheumatoid arthritis, gangrene and skin diseases. It should be noted that there are quite a lot of diseases characterized by an increase in the concentration of neutrophil GRA in human blood. Therefore, to establish the correct diagnosis, decoding must be carried out by an experienced specialist who can compare all the indicators being studied and draw a conclusion based on an objective look at the examination results.
Deviations from the norm to a greater extent
If granulocytes are elevated, this means that an inflammatory process is developing in the body (in the absence of physiological reasons).
The number of granular leukocytes increases against the background of:
- Course of acute infectious diseases.
- Allergic reaction.
- Neoplasms of a malignant nature.
- Intoxication process (caused, among other things, by uncontrolled use of medications).
- Worm infestation.
- Diseases characterized by necrotic manifestations.
An increase in GRA in a child’s blood test is often a consequence of vaccination.
An increase in the neutrophil count occurs for the following reasons:
- Acute hemorrhages.
- Taking certain medications.
- Acute bacterial infections.
- Intoxication of the body.
- Myeloproliferative diseases.
Reasons for the increase in the number of eosinophils:
- Pathologies of the endocrine system.
- Cardiovascular disorders.
- Systemic connective tissue diseases.
- Pathologies of a dermatological nature.
- Allergic reactions.
- Presence of tumors.
- Helminthic infestations.
- Impaired functioning of the immune system.
Reasons for increased basophil levels:
- Allergic reactions.
- Hodgkin's syndrome.
- Blood diseases.
- Ulcerative colitis.
- Hemolytic anemia.
- Inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Taking certain medications.
When deciphering GRA in a blood test, the doctor always evaluates the number of other leukocytes, as well as lymphocytes and red blood cells. Only with the help of an integrated approach can one suspect the presence of a particular disease.
Structure, norms and purpose of basophils
Basophilic granulocytes are a type of small white blood cell with a large nucleus and a small amount of cytoplasmic fluid. The number of nuclear segments of these bodies is even less than in neutrophils and eosinophils. When entering the blood of peripheral vessels, the circulation of basophils does not exceed 4 hours. Then, if there is an inflammatory process of allergic origin in the body, they move into the tissues.
Basophils actively participate in anaphylactic reactions, to some extent slowing down the function of lymphocytes. In pathological foci they release mediators aimed at the inflammatory process. The life cycle of basophilic granulocytes is about 12 days. Moreover, their norm in women, men and even children has approximately the same value, and is no more than 0.5 * 109/l of the total number of leukocytes in the blood.
A decrease in the basophil count to less than 0.1*109/l indicates the presence of an acute form of infectious pathology, for example, pneumonia, or indicates severe stress conditions. This may also be a signal of thyroid problems. This symptom can be caused by taking hormonal drugs that have an anti-inflammatory effect. And as a rule, low basophils are characteristic of pregnant women and women during the ovulation period.
Reference! It is important to note that a significant decrease in the concentration of basophilic granulocytes is quite rare. Most often, this indicates severe inhibition of the hematopoietic system.
Deviations from the norm to a lesser extent
If GRA in a blood test is low, this may also indicate the development of a pathological process in the body. If the granulocyte count is less than normal, it is necessary to evaluate the level of subtype indicators.
When eosinophils decrease, it is customary to talk about such a phenomenon as eosinopenia. If these granulocytes are low, this means that a pathological process is developing in the body. Main reasons for deviation:
- Acute bacterial infection.
- Sepsis.
- Physical overexertion.
- Burn disease.
- Anemia.
- Taking glucocorticoids.
- Prolonged stay in a state of stress.
- Various types of injuries.
- Anemia.
- Eosinopenia as a consequence of surgery.
A decrease in the level of these cells in children, as a rule, indicates the presence of disorders in the hematopoietic system.
When the basophil count decreases, it is customary to talk about basopenia. This condition is diagnosed extremely rarely. In most cases, it indicates disturbances in the functioning of the hematopoietic system. In addition, basopenia can develop against the background of an infectious process, pneumonia, hyperthyroidism, Graves' disease, Cushing's syndrome. Physiological reasons for deviations from the norm are pregnancy and the period of ovulation.
A decrease in the level of neutrophils (neutropenia) may indicate the presence of the following pathologies:
- Radiation damage.
- Anemia.
- Neoplasms localized in the bone marrow.
- Diabetes.
- Typhoid fever.
- Malaria.
- Toxic goiter.
- Tularemia.
- Brucellosis.
- Flu.
- Hepatitis.
- Rubella.
- AIDS.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus.
- Collagenoses.
- Cachexia.
- Alcoholism.
- Hypersplenism.
- Intoxication of the body due to long-term use of tranquilizers, immunomodulators and antibiotics.
In children, a decrease in the level of neutrophils is observed in the presence of a congenital pathology - Kostman's syndrome. The disease is characterized by a loss of the ability to produce a sufficient amount of these cells.
Neutropenia is an extremely dangerous condition. Against this background, there is a significant weakening of cellular immunity, as a result of which multiple inflammatory processes are launched in the body. The prognosis in this case is unfavorable, as there is a high risk of death.
Analysis transcript
GRA in a blood test is an important diagnostic indicator. White formed elements of liquid connective tissue perform a protective function in the human body. Laboratory testing makes it possible to assess the patient’s general condition and the functioning of the immune system.
Different types of polymorphonuclear cells are responsible for specific functions in the human body.
Calculating the leukocyte formula allows the specialist doctor to see the full picture of the disease process and determine the diagnosis in order to prescribe adequate treatment in the future. From the results of scientific research, quantitative changes in leukocytes are of two types.
An increase in the number of young neutrophils, accompanied by the appearance of young granulocytes in the liquid connective tissue:
- infections with serous purulent inflammation;
- acute complex pathological process;
- release of blood beyond the vascular bed;
- loss of consciousness with fading reflexes;
- a shift in the body’s acid-base balance towards increased acidity;
- muscular fatigue;
- excessive formation of connective tissue in the bone marrow with loss of hematopoietic elements and increased extramarrow blood formation;
- acute myeloid leukemia;
- damage to the body by secondary malignant foci;
Predominance of mature neutrophils over young ones:
- malignant anemia caused by impaired hematopoiesis due to a lack of vitamin B12 in the body;
- pathologies of the hepatobiliary system;
- insufficiency of the paired bean-shaped organ that produces urine.
The interpretation of the GRA analysis is carried out by the doctor ordering the study. If there are changes in the leukocyte formula, only a medical specialist can determine the pathological process.
The following indicators and deviations are typical for a general clinical blood test:
| Indicator name | Norm in % | Promotion | Demotion |
| Eosinophilic leukocytes | from 1-5% |
|
|
| Segmented neutrophils | 41-71% |
|
|
| Granulocytic basophilic leukocytes | 0-0,5% |
|
Treatment
If granulocytes are increased or decreased, the doctor prescribes a comprehensive examination to the patient, which includes both laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods. Based on the research results, a treatment regimen for the root cause that caused the pathological deviation of the indicators from the norm is drawn up.
If a decrease or increase in the level of granulocytes is caused by physiological processes, it is recommended to undergo a course of treatment with nettle infusion. It should be consumed immediately before meals, 100 ml three times a day. The course of treatment is 7 days.
In addition, to normalize indicators, it is necessary to follow the principles of a healthy lifestyle: adjust your diet, spend more time in the fresh air, regularly expose the body to moderate physical activity, and organize proper sleep.
Cost of analysis
Biomaterial can be submitted for general clinical examination in both public and private medical institutions. In the first case, the blood test is performed free of charge, but only if the patient has an insurance policy.
In private clinics, the cost of analysis is on average 350 rubles. Additionally, you need to pay for the collection of biomaterial. Usually the cost of this service does not exceed 150 rubles.
Analysis results are ready on the same day.
Where to get tested
To determine the number of polymorphonuclear cells, a medical specialist prescribes a medical test. Most often, a test for the number of granulocytes is performed using the leukocyte formula, which is the percentage of white cells in the liquid connective tissue and refers to a constant value.
This type of laboratory examination can be done in any private clinic by collecting liquid connective tissue from the venous bed.
The cost of the analysis will vary from 125 rubles. up to 160 rub. depending on the level of qualifications of medical personnel and the status of the institution.
General practitioners also prescribe a clinical blood test to determine the amount of GRA. A basic study can be done in any multidisciplinary specialized treatment and preventive institution for the provision of outpatient medical care. In this case, a laboratory technician takes capillary blood from the ring finger, and the procedure is free.