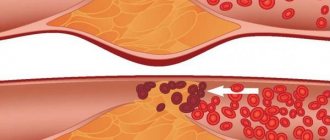
A cholesterol test is called a lipid profile. It has important diagnostic value for identifying atherosclerosis or predisposition to it. Blood is taken from the patient for testing. Using this analysis, you can assess the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases in individuals without clinical signs of pathology.
Decoding the cholesterol test is the responsibility of the attending physician. Since the lipid profile has several important indicators and a person who does not have special knowledge will not be able to objectively evaluate them. In addition, all designations in the form are given in Latin symbols.
Detailed description of the study
HDL cholesterol (high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, α-cholesterol) is the only lipid fraction that prevents the formation of atherosclerotic plaques in blood vessels (therefore, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol is also called “good” cholesterol). The antiatherogenic effect of HDL is due to their ability to transport cholesterol from vascular cells to the liver, where it is utilized and excreted from the body. Therefore, the content of this lipid fraction is very important for assessing the risk of developing atherosclerosis and its complications (coronary heart disease, strokes, etc.).
A decrease in HDL is most often observed with:
- disorders of lipid metabolism (so-called dyslipidemia);
- diabetes mellitus;
- chronic liver diseases with impairment of its functions (cirrhosis, hepatitis, liver cancer);
- kidney diseases with signs of chronic renal failure;
- general exhaustion (including cancer cachexia);
- severe acute bacterial and viral infections (short-term decrease in the indicator with its normalization after cure of the underlying disease).
Increasing HDL levels is considered an antiatherogenic factor and is therefore one of the main goals of antiatherosclerotic therapy (especially diet).
However, there are situations where an increase in HDL takes on a pathological character and indicates a severe pathology: alcoholism, primary biliary cirrhosis (the only type of cirrhosis in which HDL is high), chronic active hepatitis.
Lipid profile and total cholesterol
A lipidogram is an extended biochemical blood test, including the lipid spectrum and reflecting the content of total cholesterol, high and low density lipoproteins, as well as triglycerides. In addition, this analysis determines the ratio of these indicators. One of the main indicators of the lipid profile is total cholesterol. It reflects the total content of a substance such as sterol in the blood.
Cholesterol is a fat-like alcohol that is insoluble in water. There are 2 sources of cholesterol in the human body: exogenous, which is caused by the consumption of fatty foods, and endogenous - the body produces cholesterol on its own. With certain metabolic disorders, cholesterol formation occurs faster than usual. This leads to an increase in its level in the blood.
Total cholesterol is denoted in Latin - CHOL. According to the current recommendations of the World Health Organization, the following indicators have been adopted to assess the level of total cholesterol in the blood:
- less than 5.15 mmol/l – optimal;
- 5.15 to 6.18 mmol/l – borderline;
- more than 6.2 mmol/l – high value.
An increase in these indicators indicates not only metabolic disorders, but also the development of certain diseases. Pathology is considered to be both an increase and a decrease in these indicators.
The reason for the increase in total cholesterol, or hypercholesterolemia, is observed in the following pathologies and conditions:
- excessive dietary intake of saturated fats;
- blockage of the bile ducts;
- cardiac ischemia;
- hypothyroidism;
- diabetes;
- gout;
- liver diseases;
- family predisposition to hypercholesterolemia;
- lack of somatotropic hormone.
If during pregnancy a woman was found to have a slight increase in total cholesterol, then there is no need to worry, since this is regarded as normal. A similar result can result from donating blood while taking certain medications from the group of diuretics and androgens, as well as cyclosporine, amiodarone, and ergocalciferol.
Hypocholesterolemia, or a decrease in total cholesterol, may occur when a patient has a blood test after a long fast or while on a diet low in saturated fat. A decrease in this indicator may also indicate malabsorption syndrome, liver necrosis, hyperthyroidism, megaloblastic anemia, and rheumatism.
Total cholesterol levels reflect the risk of atherosclerotic plaque formation
Hypocholesterolemia may occur in patients with extensive burns, severe infection, or mental retardation. If there is a hereditary disorder of hemoglobin synthesis, the cholesterol level will also be reduced.
General information
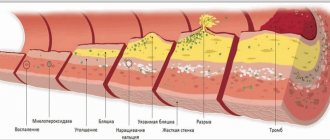
The amount of VLDL serves as an indicator of the level of harmful cholesterol and lipid metabolism. Excess cholesterol is deposited on the walls of blood vessels. First, plaque forms on them, and over time plaques form. Excess cholesterol can also have a negative effect on triglyceride transport. The test results are assessed taking into account the clinical picture and data from other studies.
Cholesterol refers to substances without which the body cannot function normally. At the same time, its excess is dangerous to health. This substance is necessary for the construction of cell membranes, the synthesis of certain hormones, and the formation of fatty acids. Lack of cholesterol leads to disruption of these processes. Cholesterol, which is necessary for the functioning of the body, is produced by the liver. This substance is also absorbed from food. An increase in its level is observed if a person constantly eats too much animal fat, as well as in the presence of a hereditary predisposition.
Decoding the results
Reference values are 0.26-1.04 mmol/l. An increase in indicators indicates a violation of lipid metabolism. The reason for this may be either a hereditary predisposition or poor nutrition (excess fat in the daily diet). If violations are detected, therapy or preventive measures are prescribed. Laboratory values are monitored at regular intervals until they return to normal. For patients with kidney pathologies and diabetes, increased levels pose a particularly high danger. A high level of VLDL in the presence of such pathologies leads to the rapid development of atherosclerosis.
It is necessary to take into account that blood is donated for research when a person is practically healthy. After an acute illness or surgery, at least 1.5 months must pass.
How to take a cholesterol test
First, the patient takes a cholesterol test. If its level does not exceed the normalized indicators, then there is no point in further tests. If the indicators do not correspond to the established parameters, then further research is prescribed to identify the lipid profile.
Such a study can also be prescribed to patients at risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, as well as when the doctor monitors the dynamics of lipid reduction using appropriate therapy.
Tests are taken early in the morning, since the patient must be on an empty stomach to perform them. Blood is drawn from a vein.
In addition to the fact that the patient cannot eat anything in the morning, a number of other requirements are imposed on him:
- You should not eat anything fatty or fried the day before.
- Under no circumstances should you drink alcohol.
- The last meal on the eve of the study should be no later than 18:00.
- Two weeks before the test, the patient is stopped taking certain medications, such as fibrates or statins.
Compliance with the necessary rules before taking the analysis cannot be ignored, as they have a huge impact on the indicators. For reliable results, all of the above instructions must be followed.
After the blood is drawn, it is tested in the laboratory using a special analyzer. A similar analysis can be carried out at home; for this purpose, there are a number of portable analyzers for which capillary blood is taken. The advantage of portable analyzers is that the patient can find out the result within five minutes.
If cholesterol levels need to be monitored from time to time, it is best to use portable devices, but a laboratory test is necessary for a complete examination.
Cholesterol designation
Usually, when diagnosing various diseases or for prevention, a biochemical blood test is taken. It allows you to determine your total cholesterol level. It is designated Chol on the form. Its norm differs in people depending on age, type of activity, in men and women. If the results exceed 5.2 mmol/l, the doctor recommends taking an extended lipid profile.
In addition to total cholesterol, it reflects several more indicators:
- high density lipoproteins - HDL;
- low-density lipoprotein LDL;
- very low density lipoproteins;
- triglycerides;
- atherogenic index.
Latin is used to denote these indicators. The first letters of the Latin name or abbreviation are used. It is difficult for people who do not know Latin to understand what certain symbols mean. Therefore, a doctor should decipher the tests.
A biochemical test is taken from a vein in the morning on an empty stomach. For the results to be reliable, you should not eat anything 12 hours before donating blood; you should give up fatty foods and alcoholic beverages for a week. Before the analysis itself, you should not smoke, you need to avoid physical activity and calm down. Blood is taken in an amount of 5 ml and sent to the laboratory for testing.
What does cholesterol consist of?
Although Chol, like all other medical terms, is denoted by Latin letters, its origin is from the Greek language, where the name was formed from two words that together give the phrase translated into Russian as solid bile. It was so named because it was first discovered in gallstones.
Its generator is our liver, which produces the main part of it; the body receives the rest through food.
Cholesterol is made up of a mixture of high-density lipoproteins (HDL) and low-density lipoproteins (LDL). If there is an imbalance between this connection, many serious diseases can develop.
The bulk of lipids are found in the brain, liver and muscles.
Cholesterol circulates through the cardiovascular system along with the blood. It is responsible for the creation of new cells; without it, the cellular structure will not have the proper density. In addition to this important function, cholesterol has another mission - it is involved in the production of the main sex hormones - testosterone, estrogen and cortisone.
It transports antioxidants to the brain, which ensures normal nutrition of brain cells and oxygen saturation. Circulating in the blood, it helps the absorption of fats. But for all the above positive functions in the body, Chol should be within the specified limits.
How does cholesterol affect your health?
This component is indispensable in the body system. When its level is normal, new cells are formed, since it is an important component in their formation, necessary and important sex hormones are produced, which are responsible not only for the human reproductive system, but are also an important factor influencing his mood and general well-being .
The brain functions normally, since it supplies it with oxygen in a timely manner and in the right quantity, the digestive organs work well, because cholesterol is involved in the process of breaking down fats.
If the level of Chol in the blood is too high, then this leads the body to a whole series of provocations of diseases, the most dangerous and having the greatest risk of death are: atherosclerosis, heart attack and stroke.
If the Chol level is reduced, this is also not good, as it can lead to the development of anemia and various disorders in lipid metabolism.
Therefore, it is important to take the necessary tests in a timely manner.
Blood chemistry. Decoding the main indicators
5. Total protein. Total protein in the blood is the total amount of all protein fractions in the blood. The normal level of total protein in the blood in adults ranges from 65 to 85 g/l.
Total protein consists of albumin, fibrinogen and four globulin fractions (alpha1, alpha2, beta and gamma globulins). The level of protein in plasma allows you to assess the condition of organs such as the liver, kidneys, pancreas, identify disturbances in carbohydrate, lipid or protein metabolism, determine micronutrient deficiency, etc.
Urea and creatinine will tell you about the function of the kidneys: 6. Urea. Creatinine. They are indicators of kidney function. A urea test is usually ordered in combination with a blood creatinine test. To assess kidney function in a range of conditions (in conjunction with a creatinine test). For the diagnosis of kidney disease and for checking the condition of patients with chronic or acute renal failure.
Generally, 2.2 - 7.3 mmol/L is considered normal urea level and any value higher or lower means that there is some abnormality in the body and it is necessary to pay attention and find out the reason for the change in urea level.
Creatinine is a chemical waste product created when muscles function. Its increase is affected by the consumption of large amounts of protein or liver pathology.
Creatinine levels may also temporarily increase with intense exercise or with the use of certain medications such as sulfamethoxazole, trimethoprim, or chemotherapy drugs (such as sports supplements). Other causes include conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure or thyroid disease.
7. Iron. It's also worth checking regularly. Iron is one of the most important microelements in the body. It is part of the hemoglobin of red blood cells and thus participates in the transfer of oxygen. The normal level of iron in the blood is one at which the body can fully function. If hemoglobin is low, this is a reason to consult a doctor and conduct the necessary research. Typical reasons for low iron levels include:
- improper diet;
- heavy blood loss;
- impaired absorption of iron;
- increased need for microelements.
8. C-reactive protein (CRP) is an informative indicator of the current inflammatory process in the body. This protein is synthesized by the liver and is one of the markers of the acute phase of inflammation.
The level of CRP in the blood may increase within several hours after the onset of an infectious disease, injury, or in the first hours after surgery. CRP quickly responds to changes in the dynamics of the disease and quickly returns to normal upon recovery.
9. Uric acid. Normally – up to 428 µmol/l. Uric acid is a waste product from the metabolism of nucleic acids and purines in the body. The latter are formed mainly in the process of natural cell death. Uric acid enters the body from meat products (liver, red meat, legumes, fish) and from liquids (beer, wine) and is formed in the body. A uric acid test is necessary to determine the cause of gout. When the content of this compound in the body exceeds the norm, its salts begin to be deposited in the joints, causing acute arthritis and the formation of nodules called tophi. In addition, this acid promotes the formation of kidney stones.
During the Middle Ages, gout was often called the “disease of kings.” This is explained by constant large meals without any measure, as well as the tendency to illness in men over forty years of age. The kidneys of those who abused food and wine could not cope with the huge concentration of uric acid. Ordinary people ate a limited diet, and could not afford so much meat and alcohol, which contain the most purines, so they got sick less often.
The material was prepared with the direct participation of N.V. Degtyareva, a doctor of laboratory diagnostics of the highest category at the Botkin Hospital.
Thank you for your assistance and information!
What to do if there are deviations from the norm
If a patient understands the indications of cholesterol levels in blood tests, they will be able to understand when treatment is needed. If deviations from normal values are small, it is enough to change your lifestyle and diet. The following measures will help normalize cholesterol levels:
- quit smoking and stop drinking alcoholic beverages;
- exclude fatty foods, sauces, fried foods, sweets, and confectionery from the diet;
- eat more vegetables and fruits;
- increase physical activity, walk, ride a bike, do gymnastics;
- Go to bed on time, avoid overtiredness.
These methods can reduce cholesterol levels by 10-15%. But if there is a serious deviation, they will not help. Therefore, it is necessary to follow the doctor’s recommendations and take prescribed medications. Statins are most often used in combination with fibrates. The doctor selects the necessary medications.
Sometimes you need to increase your cholesterol. At the same time, the amount of HDL increases, which helps prevent atherosclerosis. To do this, you also need to change your diet and lifestyle, and give up bad habits. It is recommended to consume more polyunsaturated fatty acids; they are found in vegetable oil and fatty fish. Medicines containing vitamin B3 are prescribed.
To prevent vascular disease, every adult needs to have blood tests for cholesterol every 3-5 years. In this case, it is advisable to know how it is indicated on the form. You won’t be able to fully decipher the results yourself, but you can find out whether there is a risk of cardiovascular disease. The work of many organs is associated with this substance. Therefore, any deviation from the norm indicates a serious violation of metabolic processes.