Chocolate is widely known not only for its taste, but also for its beneficial effects on health. It perfectly tones the muscular and nervous system, strengthens the body's defenses. But this delicacy may not be so useful for everyone.
People with hyperlipidemia always look at any sweets with caution and caution, as they can cause deterioration in health. How do our beloved chocolate and cholesterol interact? How safe is it to consume? Let's try to figure this out.
Types and composition of chocolate
Depending on the composition and purpose, several types of product are distinguished:
- Bitter – from 60-99% cocoa;
- Black – 45-50% cocoa;
- White – 0% cocoa powder;
- Dairy – up to 30% cocoa and various fillers;
- Dietary - for diabetics (instead of sugar - substitutes);
- Porous - a type of milky;
- Glaze – for confectionery products;
- Powder – for drinks.
If the confectionery product is prepared in accordance with the classic recipe, it contains:
- 5-8% proteins;
- 38% fat;
- 5-63% carbohydrates.
Fats in chocolate products of plant origin. Animal fats increase cholesterol levels the most. From this we can conclude: there is almost no cholesterol in chocolate.
From the history of delicacies
The history of the drink made from the fruits of the cocoa tree goes back to the distant past. Scientists suggest that they began to use it more than 3,000 years ago. The homeland of the cocoa tree is Central America.
There is a legend about a gardener named Quetzalcoatl. The gods endowed this man with the gift of planting and growing wonderful gardens. It so happened that this gardener managed to grow a discreet, inconspicuous tree, the fruits of which contained seeds that were distinguished by an incomparable smell and bitter taste. The drink made from these seeds had magical properties - it lifted the mood, charged with vigor, cured diseases, and prolonged youth. That is, back in ancient times, people noticed that cocoa contains substances that are today called antioxidants. And antioxidants, as we know, prevent the aging of the body, including preventing the formation of cholesterol, which means that the answer to the question - does chocolate increase cholesterol - is negative, and this answer has been thousands of years old.
The Indian tribes that lived in this territory were the first to highly appreciate the drink made from aromatic fruits and began planting cocoa trees. Among the Mayan Indians, cocoa was considered a gift from above, and sacrifices were made and prayers were performed to the cocoa god named Ek Chuah. Cocoa seeds were in great demand for the preparation of a divine drink and served as currency.
Chocolate came to Europe after the Spanish conquistadors began conquering America. Bringing all sorts of exotic things from new lands, the Spaniards could not ignore the cocoa fruits, which were so highly valued among the Indians. From the cocoa beans presented to the Spanish king, the drink chocolatl was prepared, which was to the taste of the royal house and quickly became fashionable among the Spanish nobility. Cocoa beans in Europe have long been considered a cure for many diseases and were very expensive. Thus, there are documents indicating that for 100 cocoa beans you could buy a slave.
For a long time, chocolate was considered a man's drink, since, despite its beneficial properties, it had a very bitter taste. But adding milk to the drink made it enjoyable for children and women. Until the beginning of the 19th century, chocolate was consumed only in liquid form. In 1819, the first solid chocolate was produced, and in 1820, the world's first solid chocolate factory began operating in Europe. Since then, the production and consumption of chocolate has only grown, the recipe has been improved, various additives and ingredients have been included in chocolate to maximize the satisfaction of any tastes and preferences of sweet lovers.
Today, the consumption of chocolate and its variety is simply amazing. We perceive it as a delicacy, and recently we have begun to think about whether chocolate is healthy or harmful.
Possibilities of cocoa beans
What characteristics allow this product to be included in the rations of special forces soldiers, climbers, pilots, submariners, polar explorers, and astronauts? The unique composition of the chocolate bar is not an advertising gimmick: cocoa beans contain a special component – theobromine, which in Latin means “food of the gods”.
The substance creates conditions for the synthesis of endorphins - happiness hormones that lift your spirits.
The product also contains magnesium, which strengthens memory, helps overcome stress, improves immunity, as well as calcium to strengthen bone tissue, phosphorus, which is involved in the formation of the nervous system, fluorine to protect teeth and other microelements.
By the way, Canadian dentists claim that chocolate is an anti-caries agent and an excellent prevention of tartar. Therefore, by eating a bar of this affordable luxury, we receive a large supply of nutrients.
Not all chocolates are created equal
So, if you eat quality chocolate (containing 60-70% cocoa) rather than confectionery chocolate made with lots of sugar and hydrogenated or partially hydrogenated oils, you are really helping your health.
The darker or more natural the chocolate, the higher the amount of polyphenols it contains. For comparison, dark chocolate has about two and a half times more antioxidants than milk chocolate. Other compounds found in dark chocolate also help strengthen the heart, lower cholesterol and prevent cardiovascular disease.
Plant sterols, compounds found in vegetable oils, grains and fruits, may help lower blood cholesterol levels. Many foods are fortified with plant sterols to improve their ability to lower bad cholesterol. Chocolate is one of those products that initially contain plant sterols.
The cocoa beans from which real chocolate is derived are a natural product and therefore contain many chemicals that can interact with the human body. For example, chocolate contains caffeine, and we all know what caffeine does in the body.
Can diabetics have chocolate?
Dark chocolate is not dangerous for diabetics, since it is a dietary product: it has a low glycemic index, it does not cause a rapid rise in glucose and an equally rapid release of insulin.
By eating 50-60 g of treats per day, it is impossible to harm your figure and health. The components of such sweets increase insulin resistance, reducing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. An experiment with checking blood glucose levels when consuming different types of chocolate bars - shown in this video
How many carbohydrates does a 100 g bar contain? You can read about this on the packaging. In its bitter variety there is less than 0.1% sugar, in 70% dark there is more sugar, in milk and porous types of cocoa there is even less, and more than half of sugar: 52-57%. You can eat no more than 25 g of this delicacy per day. Is the product good for hypertensive patients?
The bitter variety of chocolate products lowers blood pressure. According to statistics, lovers of this type suffer from pathologies of the cardiovascular system less than those who do without the joy of chocolate.
Austrian researchers found that dark varieties lower blood pressure, since they contain a flavonol substance with an effect similar to medications for hypertension. It enhances the production of nitric oxide, which helps dilate arteries, and increases blood flow in the liver.
Rules for consuming chocolate if you have high cholesterol
A tasty and beloved product, which came to our attention today, must be consumed with caution, despite the breadth of its beneficial properties. Like any other substance, it has a number of contraindications . Depending on the variety:
- Dairy products contain a high number of simple carbohydrates and therefore are not recommended for those who are overweight.
- Diabetes. People with this disease need to eliminate all sugar-containing foods from their diet. Only dark chocolate is not dangerous - it is a dietary product with a low glycemic index.
- Allergic reactions.
- Due to their action as an activator on the nervous system, chocolate products are not indicated for insomnia and sleep disorders.
- During pregnancy, frequent consumption of sweet foods can lead to unnecessary excess weight, which can negatively affect the growth of the fetus and the condition of the mother of the unborn child, so during this period it is recommended to consume chocolate products in minimal quantities.
Research by experts says that chocolate with a cocoa content above 60% has beneficial anti-cholesterol properties. High-quality dark varieties not only restore physiological cholesterol levels, but also normalize the functioning and condition of many systems of our body.
Cocoa makes us smarter
An obvious advantage of dark chocolates is the ability to stimulate cerebral circulation. Oxford scientists studied the connection between brain activity and the effect of chocolate in two thousand Norwegian volunteers aged 70-75 years. Tests have confirmed that cognitive performance is higher among lovers of chocolate desserts, red wine and green tea.
New England magazine traces the connection between the level of consumption of chocolate products and the number of Nobel laureates in the country. In this regard, Switzerland is the undisputed leader.
Possible harm and contraindications
Cocoa beans are grown and harvested in the forests of the Amazon, Brazil and West Africa. Sanitation requirements in these countries differ from European standards. Cocoa is a favorite treat for cockroaches, after which chitin remains on the product - a harmful substance that requires chemical treatment.
Agents that kill bacteria and disinfect the product are quite aggressive, which can cause complex allergic reactions.
Therefore, the product must be purchased from a trusted manufacturer who purchases raw materials in the countries where they grow, and not in China, for example, where chocolate trees do not grow.
The natural composition of cocoa, in addition to numerous useful elements, also contains purine bases and caffeine, so cocoa is not recommended for consumption:
- Children under three years old, as it will cause increased excitability and nervousness in them; patients with nervous system problems;
- People suffering from gout, due to purine bases that can accumulate uric acid;
- Pregnant and lactating women due to the risk of developing allergic reactions in the child;
- People with excess body weight, since cocoa has a high calorie content.
Patients suffering from atherosclerosis and diabetes mellitus are advised to consume cocoa with caution.
Cocoa improves blood composition
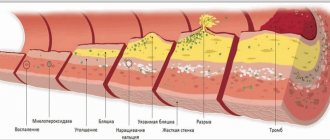
It is cocoa that contains flavonoids that cleanse the blood of clots and improve its composition, which is important for high cholesterol. Dark chocolate has a cocoa percentage above 90%, which enhances its beneficial properties. Like green tea, chocolate is a good antioxidant. Such opportunities are provided by catechin, which reduces the concentration of free radicals in the body.
American biologists have found that those who eat half a bar per day have blood vessels in good condition. The delicacy makes them elastic, does not allow plaques to linger on the walls of blood vessels, reducing the risk of developing atherosclerosis.
Let's understand the composition
Research has shown that dark chocolate may be good for your heart. It is made from cocoa beans, and they are rich in flavonoids (flavanols to be precise), which are antioxidants. Antioxidants counteract oxidation, a harmful chemical reaction that occurs in our bodies. Thus, the oxidation of “bad” cholesterol contributes to the development of cardiovascular diseases (here it should be noted that “bad” cholesterol is not so bad, it is involved in important processes for the body, but it becomes harmful precisely when oxidized).
Keep in mind that chocolate is not a low-calorie food. Frequent consumption can lead to obesity, which in itself is already a risk factor for heart disease. Therefore, some quality dark chocolate (no more than 50 grams daily) and a healthy diet and lifestyle can be good for your heart.
High-quality chocolate contains large amounts of cocoa butter, which is cholesterol-free because it is extracted from cocoa beans. Cocoa butter contains three types of fatty acids:
- palmitic – saturated fat (in small quantities);
- stearic – a saturated fat that does not affect cholesterol levels;
- Oleic is a monounsaturated fat that can protect us from many diseases, including cardiovascular disease.
Affordable anti-stress
Chocolate improves your mood. People consuming 42 g/day feel more cheerful
compared with the control group. When eating products containing cocoa, the brain synthesizes serotonin and endorphin - pleasure hormones, so we often eat stress with this delicacy.
Swiss researchers claim that eating half a dark chocolate bar will reduce the concentration of cortisol, which relieves stress, and bad protein, a companion of inflammatory processes.
Cocoa contains ingredients that protect the skin from the sun. The magazine “Nutrition” published the results of an experiment confirming that a chocolate dessert allows you to stay in the open sun 2 times longer without the risk of getting sunburn.
Useful properties of chocolate
This product contains a whole range of substances necessary for a person to function normally. It includes:
- Alkaloids (caffeine, theobromine). Activate brain function; increase concentration and performance. Promotes the production of endorphin - the hormone of good mood.
- Antioxidants (vitamin E). Strengthens the endothelium (inner lining) of blood vessels, and also improves the rheological properties of blood (reduce viscosity). Such properties prevent the deposition of atherosclerotic plaques.
- Microelements (potassium, magnesium, phosphorus). Activate brain functions, improve the functioning of the heart muscle.
- Vitamins (A, D, group B). Contains cocoa beans. Helps thin the blood. They also have an antiatherogenic effect (prevent the formation of atherosclerotic plaques on the vascular endothelium). But the effectiveness of these properties depends on the percentage of cocoa content in chocolate: bitter contains up to 75%, black – about 45%, milk – 30%.
How to eat the “food of the gods”
Is it possible to eat chocolate if you have high cholesterol?
It is possible and necessary, but taking into account the following recommendations:
- Only dark chocolate will be safe and even healthy if you use it regularly and no more than 40-50 g per day.
- Milk bars contain animal fat: with the same dosage, lipid profile results can worsen by 25% in a month! Milk chocolate, due to its composition, not only improves mood, but also increases volume, blood sugar, and activates caries. Regarding cleansing blood vessels and reducing pressure, the effect will be weak.
- The white variety of chocolates are empty calories, since there is no cocoa powder, the most valuable ingredient, and even a small piece (20 g) increases cholesterol by 1.8 mmol/l. It contains cocoa butter, sugar, milk.
- The price can also serve as a guide when choosing: the higher the percentage of cocoa in the product, the more expensive the tile.
- Before introducing your child to chocolates and candy bars, you need to discuss your intentions with your pediatrician.
Statistics say that our average compatriot eats about 5 kg of chocolate products per year. If the smell of this dessert makes you feel positive, don’t deny yourself this pleasure. The main thing is to observe the measure, and everything will be in chocolate.
A little chemistry
In the mid-1990s, when the first studies on chocolate and cholesterol were conducted, nutritionists did not recommend this product. However, it turned out that chocolate was no worse than other high-carbohydrate foods in this regard. In addition, this confectionery product, according to the latest scientific data, may even be useful.
In the mid-1990s, researchers had to figure out why foods containing saturated fat, namely stearic acid (which, as stated above, is found in chocolate) would not lead to unhealthy changes in blood cholesterol levels like other saturated fats.
First, let's find out what a saturated fatty acid is, or fat for that matter.
First of all, fat is oil and oil is fat. There is only one difference: fat remains solid at room temperature, while oil becomes liquid. They are also similar at the molecular level. Fatty acids are long chains of carbon and hydrogen atoms with a carboxylic acid at the end. The number of carbon and hydrogen atoms in a fatty acid dictates many of its properties, from its taste to how well it dissolves in water and whether it is a solid or liquid.
If all the carbon atoms are connected by single bonds (for example, in stearic and myristic acids), it is a saturated fatty acid. If the molecule has one double bond, it is a monounsaturated fat; if there are two or more double bonds, as in linoleic acid, it is a polyunsaturated fat.
In general, mono- and polyunsaturated fatty acids (or simply fats and oils) are much healthier for the body than saturated fats. The latter, as a rule, raise the level of “bad” cholesterol and sometimes reduce the level of good cholesterol. Apparently, a fatty acid with 18 carbon atoms breaks the general rule.
Stearic acid, an 18-carbon saturated fat, has been shown to lower plasma total cholesterol and "bad" cholesterol (but also good cholesterol). Using the formulas above, you can see how stearic acid contained in chocolate differs from other fatty acids.